Content for TS 23.288 Word version: 18.6.0
1…
4…
5…
5A…
6…
6.1.3
6.1.4…
6.1.4.4…
6.1.5…
6.1A…
6.1B…
6.1B.2.3…
6.1C
6.2…
6.2.3…
6.2.6…
6.2.6.2
6.2.6.3…
6.2.6.3.3
6.2.6.3.4
6.2.6.3.5
6.2.6.3.6…
6.2.7…
6.2.8…
6.2.9…
6.2.13…
6.2A…
6.2B…
6.2B.3
6.2B.4…
6.2C…
6.2D…
6.2E…
6.2F…
6.3…
6.4…
6.5…
6.6…
6.7…
6.7.3…
6.7.4…
6.7.5…
6.8…
6.9…
6.10…
6.11…
6.12…
6.13…
6.14…
6.16…
6.17…
6.18…
6.19…
6.20…
6.21…
7…
7.4…
7.7…
7.9…
8…
9…
10…
6.4 Observed Service Experience related network data analytics
6.4.1 General
6.4.2 Input Data
6.4.3 Output Analytics
6.4.4 Procedures to request Service Experience for an Application
6.4.5 Procedures to request Service Experience for a Network Slice
6.4.6 Procedures to request Service Experience for a UE
...
...
6.4 Observed Service Experience related network data analytics p. 162
6.4.1 General p. 162
This clause specifies how NWDAF can provide Observed Service Experience (i.e. average of observed Service MoS and/or variance of observed Service MoS indicating service MOS distribution for services such as audio-visual streaming as well as services that are not audio-visual streaming such as V2X and Web Browsing services) analytics, in the form of statistics or predictions, to a service consumer.
The Observed Service Experience analytics may provide one or more of the following outputs:
- Service Experience for a Network Slice: Service Experience for a UE or group of UEs or any UE in a Network Slice;
- Service Experience for an Application: Service Experience for a UE or group of UEs or any UE in an Application or a set of Applications;
- Service Experience for an Edge Application over a UP path: Service experience for a UE or a group UEs or any UE in an Application or a set of Applications over a specific UP path (UPF, DNAI and EC server);
- Service Experience for an Application over a RAT Type or Frequency or both: Service experience for a UE or group of UEs in an Application or a set of Applications over a RAT Type or over a Frequency or both as defined in Table 6.4.1-1.
- Service Experience for an Application transferring data over a PDU Session: Service experience for a UE or group of UEs or any UE in an Application or a set of Applications transferring data over a PDU Session with PDU Session parameters i.e. S-NSSAI, DNN, PDU Session Type , SSC mode and optionally an Access Type or with combination of PDU Session parameters such as a list of the tuple (PDU Session Type, SSC mode) optionally per Access Type.
- Analytics ID = "Service Experience";
- Target of Analytics Reporting as defined in clause 6.1.3;
- Analytics Filter Information as defined in Table 6.4.1-1 and optionally a list of analytics subsets that are requested (see clause 6.4.3);
- optionally, maximum number of objects and maximum number of SUPIs;
- optionally, preferred level of accuracy of the analytics;
- optionally, preferred level of accuracy per analytics subset;
- optionally, preferred order of results for the list of Application Service Experiences and/or Slice instance service experiences: "ascending" or "descending";
- optionally, preferred granularity of location information: TA level or cell level or "longitude and latitude level";
- Analytics target period that indicates the time window for which the statistics or predictions are requested;
- in a subscription, the Notification Correlation Id and the Notification Target Address; and
- optionally, Reporting Thresholds, which apply only for subscriptions and indicate conditions on the Service Experience to be reached in order to be notified by the NWDAF (see Table 6.4.3-1 and Table 6.4.3-2).
| Information | Description | Mandatory | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application | Network Slice | Edge Applications over a UP path | Application over RAT Type and frequency | Application transfering data over a PDU Session | ||
| Application ID (0...max) | The identification of the application(s) for which the analytics information is subscribed or requested. | Y | N | Y | Y | Y |
| S-NSSAI
(NOTE 3) | When requesting Service Experience for a Network Slice: identifies the Network Slice for which analytics information is subscribed or requested. When requesting Service Experience for an Application: identifies the S-NSSAI used to access the application together with the DNN listed below. | N | Y | N | N | C |
| NSI ID(s) | Identifies the Network Slice instance(s) for which analytics information is subscribed or requested. | N | N | N | N | N |
| Area of Interest
(NOTE 6) | Identifies the Area (i.e. set of TAIs), as defined in TS 23.501 for which the analytics information is subscribed or requested. | N | N | N | N | N |
| DNN
(NOTE 3) | When requesting Service Experience for an Application, this is the DNN to access the application. | N | N | N | N | C |
| DNAI
(NOTE 1) | Identifier of a user plane access to one or more DN(s) where applications are deployed as defined in TS 23.501. | N | N | Y | N | N |
| RAT Type
(NOTE 2) | Identifies the RAT type. | N | N | N | Y | N |
| Frequency
(NOTE 2) | Identifies the Frequency value(s) (e.g. high, low). | N | N | N | Y | N |
| Application Server Addresses (NOTE 1) | List of IP addresses/FQDNs of the Application Servers the Target of Analytics Reporting has a communication session for which Service Experience Analytic information is requested. | N | N | Y | N | N |
| UPF anchor ID (NOTE 1) (NOTE 4) | Identifies the UPF where a UE has an associated PDU session | N | N | N | N | N |
| PDU Session type (NOTE 3) | Identifies the type of the associated PDU Session | N | N | N | N | C |
| SSC Mode (NOTE 3) | Identifies the SSC Mode selected for the associated PDU Session | N | N | N | N | C |
| Access Type (NOTE 3) | Identifies the Access type of the associated PDU Session | N | N | N | N | C |
| Mapped NSSAI (NOTE 5) | Identifies the mapped NSSAI in the HPLMN. May be used in VPLMN for analytics exposure in roaming case (see clause 6.1.5). | N | N | Y | N | N |
| PLMN ID | Identifies the target PLMN (i.e. PLMN from which the analytics are requested, for analytics exposure in roaming case (see clause 6.1.5). | N | N | Y | N | N |
|
NOTE 1:
These parameters can be provided when a consumer requires analytics for an edge application over a UP path.
NOTE 2:
A service consumer can provide either a RAT Type or a Frequency or a specific combination of RAT Type and Frequency. A service consumer can also provide multiple instances of RAT Type or multiple instances of Frequency or multiple combinations of RAT type and Frequency. A service consumer can also provide "any" RAT type indication "any" Frequency value indication or "any" indication for all the RAT type and Frequency value the NWDAF has received for the application.
NOTE 3:
One or more of these parameters can be provided by the consumer when requesting analytics for an application running over a PDU Session(s).
NOTE 4:
UPF ID is only needed when the target of NWDAF analytics on Service Experience is a specific UPF.
NOTE 5:
The terms "HPLMN" and "VPLMN" here refer to a roaming case in which at least one UE served by the NWDAF analytics consumer is involved.
NOTE 6:
If the request is for fine granularity location information (i.e. with a finer granularity than cell), the AOI may be described as shown in clause 5.5 of TS 23.273.
|
||||||
The NWDAF shall notify the result of the analytics to the consumer as specified in clause 6.4.3.
NWDAF collects the network data from AF (directly or via NEF) and from other 5GC NF(s) in order to calculate and provide statistics and predictions on the observed service experience to a consumer NF or to OAM. When the AF provides Service Experience Information and the Target of Analytics Reporting is one or more UE ID(s), the AF may also provide a Service Experience Contribution Weight with each UE's Service Experience value. The Service Experience Contribution Weight is determined by the AF and indicates the relative importance of each UE's Service Experience. The NWDAF may use the Service Experience Contribution Weight(s) to calculate and provide statistics, confidence values and predictions on the observed service experience to a consumer NF or to OAM.
Based on the Analytics Filter information in Table 6.4.1-1 and the Target of Analytics Reporting provided by the service consumer in the analytics subscription or request, NWDAF determines whether service experience analytics should be delivered for:
- Application(s);
- Network Slice;
- both Application(s) and Network Slice;
- Edge Applications over a UP path;
- Application(s) over RAT Type(s) and/or Frequency value(s);
- Application(s) running over a PDU Session using the following PDU Session parameters or combination of them, i.e. S-NSSAI, DNN, PDU Session type, SSC Mode and optionally per Access Type.
6.4.2 Input Data p. 167
The service data and performance data collected from the AF (including the service data collected from the UE through the AF), the network data from other 5GC NFs and the network data from OAM and MDAS/MDAF for observed service experience are defined in Table 6.4.2-1, Table 6.4.2-1a, Table 6.4.2-2, Table 6.4.2-3, Table 6.4.2-4 and Table 6.4.2-5 respectively.
| Information | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Application ID | AF | To identify the service and support analytics per type of service (the desired level of service) |
| IP filter information | AF | Identify a service flow of the UE for the application |
| Locations of Application | AF/NEF | Locations of application represented by a list of DNAIs. The NEF may map the AF-Service-Identifier information to a list of DNAI when the DNAI(s) being used by the application are statically defined. |
| Service Experience | AF | Refers to the QoE per service flow as established in the SLA and during on boarding. It can be either e.g. MOS or video MOS as specified in ITU-T P.1203.3 [11] or a customized MOS for any kind of service including those not related to video or voice. |
| UE ID | AF | The list of Service Experience Contribution Weights that are associated with each of the provided UE IDs. |
| Service Experience Contribution Weight | AF | The list of Service Experience Contribution Weights that are associated with each of the provided UE IDs. |
| QoE metrics | UE (via AF) | QoE metrics observed at the UE(s). QoE metrics and measurement as described in TS 26.114, TS 26.247, TS 26.118, TS 26.346, TS 26.512 or ASP specific QoE metrics in TS 26.512, as agreed in the SLA with the MNO, may be used. |
| Timestamp | AF | A time stamp associated to the Service Experience provided by the AF, mandatory if the Service Experience is provided by the ASP. |
| Application Server Instance | AF | The IP address or FQDN of the Application Server that the UE had a communication session when the measurement was made. |
NWDAF subscribes to the service data from AF in the Table 6.4.2-1 either directly for trusted AFs by invoking Naf_EventExposure_Subscribe service (Event ID = Service Experience information, Event Filter information = Area of Interest, Application ID) as defined in TS 23.502, or indirectly for untrusted AFs via NEF by invoking Nnef_EventExposure_Subscribe service (Event ID = Service Experience information, Event Filter information = Area of Interest, Application ID) where NEF translates the Area of Interest into geographic zone identifier(s). For the information whose source is UE (via AF), the AF collects data from the UE as defined in clause 6.2.8.
| Information | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|
| UE identifier | AF | IP address of the UE at the time the measurements was made. |
| UE location | AF | The location of the UE when the performance measurement was made. |
| Application ID | AF | To identify the service and support analytics per type of service (the desired level of service). |
| IP filter information | AF | Identify a service flow of the UE for the application. |
| Locations of Application | AF/NEF | Locations of application represented by a list of DNAIs. The NEF may map the AF-Service-Identifier information to a list of DNAIs when the DNAIs being used by the application are statically defined. |
| Application Server Instance address | AF/NEF | The IP address/FQDN of the Application Server that the UE had a communication session when the measurement was made. |
| Performance Data | AF | The performance associated with the communication session of the UE with an Application Server that includes: Average Packet Delay, Average Loss Rate and Throughput. |
| Timestamp | AF | A time stamp associated to the Performance Data provided by the AF. |
NWDAF subscribes to the performance data from AF in the Table 6.4.2-1a either directly for trusted AFs by invoking Naf_EventExposure_Subscribe service (Event ID = Performance Data, Event Filter information = Area of Interest, Application ID) as defined in TS 23.502, or indirectly for untrusted AFs via NEF by invoking Nnef_EventExposure_Subscribe service (Event ID = Performance Data, Event Filter information = Area of Interest, Application ID) where NEF translates the Area of Interest into geographic zone identifier(s).
| Information | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Timestamp | 5GC NF | A time stamp associated with the collected information. |
| Location | AMF | The UE location information, e.g. cell ID or TAI. |
| Finer granularity location (1...max) | GMLC | UE positions. |
| ....>UE location | GAD shape or location coordinates (see TS 23.032). | |
| ....>Timestamp | A time stamp when the location was measured. | |
| ....>LCS QoS | The accuracy of the measurement. | |
| UE ID | AMF | List of SUPIs. If UE IDs are not provided as Target of Analytics Reporting for slice service experience, AMF returns the UE IDs matching the AMF event filters. |
| DNN | SMF | DNN for the PDU Session which contains the QoS flow. |
| S-NSSAI | SMF | S-NSSAI for the PDU Session which contains the QoS flow. |
| Application ID | SMF | Used by NWDAF to identify the application service provider and application for the QoS flow. |
| DNAI | SMF | Identifies the access to DN to which the PDN session connects. |
| PDU Session type | SMF | Type of the PDU Session. |
| SSC Mode | SMF | SSC Mode selected for the PDU Session. |
| Access Type | SMF | List of Access Types used for the PDU Session. |
| IP filter information | SMF | Provided by the SMF, which is used by NWDAF to identify the service data flow for policy control and/or differentiated charging for the QoS flow. |
| QFI | SMF | QoS Flow Identifier. |
| QoS flow Bit Rate | UPF | The observed bit rate for UL direction; and The observed bit rate for DL direction. |
| QoS flow Packet Delay | UPF | The observed Packet delay for UL direction; and The observed Packet delay for the DL direction. |
| Packet transmission | UPF | The observed number of packet transmission. |
| Packet retransmission | UPF or AF | The observed number of packet retransmission. |
NWDAF subscribes to the network data from 5GC NF(s) in the Table 6.4.2-2 by invoking Nnf_EventExposure_Subscribe service operation with the following Event IDs as input parameters:
-
AMF Source: Namf_
EventExposure_ (Event IDs = Location Changes, Area of Interest).Subscribe -
SMF Source: Nsmf_
EventExposure_ (Event ID = QFI allocation).Subscribe
| Information | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Timestamp | OAM | A time stamp associated with the collected information. |
| Reference Signal Received Power | OAM
(see NOTE 1) | The per UE measurement of the received power level in a network cell, including SS-RSRP, CSI-RSRP as specified in clause 5.5 of TS 38.331 and E-UTRA RSRP as specified in clause 5.5.5 of TS 36.331. |
| Reference Signal Received Quality | OAM
(see NOTE 1) | The per UE measurement of the received quality in a network cell, including SS-RSRQ, CSI-RSRQ as specified in clause 5.5 of TS 38.331 and E-UTRA RSRQ as specified in clause 5.5.5 of TS 36.331. |
| Signal-to-noise and interference ratio | OAM
(see NOTE 1) | The per UE measurement of the received signal to noise and interference ratio in a network cell, including SS-SINR, CSI-SINR, E-UTRA RS-SINR, as specified in clause 5.1 of TS 38.215. |
| RAN Throughput for DL and UL | OAM
(see NOTE 1) | The per UE measurement of the throughput for DL and UL as specified in clauses 5.2.1.1 and 5.4.1.1 of TS 37.320. |
| RAN Packet delay for DL and UL | OAM
(see NOTE 1) | The per UE measurement of the packet delay for DL and UL, including per QCI per UE packet delay as specified in clause 5.2.1.1 of TS 37.320 and per DRB per UE packet delay as specified in clause 5.4.1.1 of TS 37.320. |
| RAN Packet loss rate for DL and UL | OAM
(see NOTE 1) | The per UE measurement of the packet loss rate for DL and UL, including the per QCI per UE packet loss rate as specified in clause 5.2.1.1 of TS 37.320 and the per DRB per UE packet loss rate as specified in clause 5.4.1.1 of TS 37.320. |
| The mapping information between cell ID and frequency | OAM | The mapping information between cell ID and frequency (NOTE 2). |
| Cell Energy Saving State | OAM | List of the cells which are within the area of interest and are in energy saving state, as specified in clauses 3.1 and 6.2 of TS 28.310. |
|
NOTE 1:
Per UE measurement for a specific UE from OAM (via MDT), is as captured in clause 6.2.3.1.
NOTE 2:
The MDT measurement report provides the cell identity and carrier frequency information for UE's serving cell and neighbour cell(s). The NWDAF can get the mapping information between cell ID and frequency using OAM service as described in clause 6.2.3.
|
||
| Information | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Timestamp | 5GC NF | A time stamp associated with the collected information. |
| Location | AMF | The UE location information, e.g. cell ID or TAI. |
| Finer granularity location | GMLC | UE positions. |
| UE ID | AMF | List of SUPIs. |
| RAT Type | SMF | The RAT type the UE camps on. |
The Event Filters for the service data collection from SMF, AMF and AF are defined in TS 23.502.
The timestamps are provided by each NF to allow correlation of QoS and traffic KPIs. The clock reference is able to know the accuracy of the time and correlate the time series of the data retrieved from each NF.
The NWDAF collects the following MDAF analysis result listed in Table 6.4.2-5, as defined in clauses 8.4.2.1.3 and 8.4.4.1.3 of TS 28.104.
Table 6.4.2-5: Data collection from MDAS/MDAF of service experience and energy saving state analysis
| Information | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ServiceExperienceIssueType | MDAF | Indication of the service experience issue type. The allowed value is one of the enumerated values: RAN issue, CN issue, both. |
| AffectedObjects | MDAF | The managed object instances where the service experience is applicable, e.g. SubNetwork Instance, NetworkSlice Instance, S-NSSAI. |
| ServiceExperienceStatistics | MDAF | The statistics of the level of service experience for a service in a certain time period, e.g. there are five levels which are represented by 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 where level 1 represents the users are enduring bad experience while level 5 represents the users' requirements are perfectly satisfied. |
| ServiceExperiencePredictions | MDAF | The predictions of the level of service experience for a service in a certain time period. |
| StatisticsOfCellsEsState | MDAF | The statistic result of current energy saving state of the cells at a certain time. |
6.4.3 Output Analytics p. 170
The NWDAF services as defined in the clause 7.2 and clause 7.3 are used to expose the analytics.
- Service Experience statistics information is defined in Table 6.4.3-1.
- Service Experience predictions information is defined in Table 6.4.3-2.
| Information | Description |
|---|---|
| Slice instance service experiences (0..max) | List of observed service experience information for each Network Slice instance. |
| > S-NSSAI | Identifies the Network Slice |
| > NSI ID (NOTE 2) | Identifies the Network Slice instance within the Network Slice. |
| > Network Slice instance service experience | Service experience across Applications on a Network Slice instance over the Analytics target period (average, variance). |
| > SUPI list (0..SUPImax) (NOTE 3) | List of SUPI(s) for which the slice instance service experience applies. |
| > Ratio (NOTE 3) | Estimated percentage of UEs with similar service experience (in the group, or among all UEs). |
| > Spatial validity (NOTE 6) | Area where the Network Slice service experience analytics applies. |
| > Validity period | Validity period for the Network Slice service experience analytics as defined in clause 6.1.3. |
| Application service experiences (0..max) | List of observed service experience information for each Application. |
| > S-NSSAI | Identifies the Network Slice used to access the Application. |
| > Application ID | Identification of the Application. |
| > Service Experience Type | Type of Service Experience analytics, e.g. on voice, video, other. |
| > UE location (NOTE 1, NOTE 5) | Indicating the UE location information (e.g. TAI list, gNB ID, or location coordinates, etc) when the UE service is delivered. |
| > UPF Info (NOTE 4) | Indicating UPF serving the UE. |
| > DNAI | Indicating which DNAI the UE service uses/camps on. |
| > DNN | DNN for the PDU Session which contains the QoS flow. |
| > Application Server Instance Address | Identifies the Application Server Instance (IP address of the Application Server) or FQDN of Application Server. |
| > Service Experience | Service Experience over the Analytics target period (average, variance). |
| > SUPI list (0..SUPImax) (NOTE 3) | List of SUPI(s) with the same application service experience. |
| > Ratio (NOTE 3) | Estimated percentage of UEs with similar service experience (in the group, or among all UEs). |
| > Spatial validity (NOTE 6) | Area where the Application service experience analytics applies. |
| > Validity period | Validity period for the Application service experience analytics as defined in clause 6.1.3. |
| > RAT Type
(NOTE 7) | Indicating the list of RAT type(s) for which the application service experience analytics applies. |
| > Frequency
(NOTE 7) | Indicating the list of carrier frequency value(s) of UE's serving cell(s) where the application service experience analytics applies. |
| > SSC Mode | SSC Mode selected for the PDU Session used to associate with the application. |
| > PDU Session Type | Type of PDU Session used to associate with the application. |
| > Access Type | List of Access Type(s) used for the PDU Session for the application. |
|
NOTE 1:
This information element is an Analytics subset that can be used in "list of analytics subsets that are requested" and "Preferred level of accuracy per analytics subset".
NOTE 2:
The NSI ID is an optional parameter. If not provided the Slice instance service experience indicates the service experience for the S-NSSAI.
NOTE 3:
The SUPI list and Ratio in the service experience information for an application can be omitted, if the corresponding parameter(s) is/are provided and are assigned with the same value(s) in the service experience information for the slice instance which the application belongs to. Otherwise, the SUPI list and Ratio are mandatory to be provided for an application service experience.
NOTE 4:
If the consumer NF is an AF, the "UPF info" shall not be included.
NOTE 5:
When possible and applicable to the access type, UE location is provided according to the preferred granularity of location information. UE location shall only be included if the Consumer analytics request is for single UE or a list of UEs. Inclusion of UE location requires user consent.
NOTE 6:
The Spatial validity is present in the output parameters if the consumer provided the Area of Interest as defined in Table 6.4.1-1.
NOTE 7:
When "any" value has been provided in the request (e.g. "any" RAT type, "any" frequency, or "any" for all the RAT type and frequency indication), the NWDAF provides an instance of the Application service experience per combination of RAT Type(s) and/or Frequency value(s) having the same Service Experience.
|
|
| Information | Description |
|---|---|
| Slice instance service experiences (0..max) | List of observed service experience information for each Network Slice instance. |
| > S-NSSAI | Identifies the Network Slice |
| > NSI ID (NOTE 2) | Identifies the Network Slice instance within the Network Slice. |
| > Network Slice instance service experience | Service experience across Applications on a Network Slice instance over the Analytics target period (average, variance). |
| > SUPI list (0..SUPImax) (NOTE 3) | List of SUPI(s) for which the slice instance service experience applies. |
| > Ratio (NOTE 3) | Estimated percentage of UEs with similar service experience (in the group, or among all UEs). |
| > Spatial validity (NOTE 6) | Area where the Network Slice service experience analytics applies. |
| > Validity period | Validity period for the Network Slice service experience analytics as defined in clause 6.1.3. |
| > Confidence | Confidence of this prediction. |
| Application service experiences (0..max) | List of predicted service experience information for each Application. |
| > S-NSSAI | Identifies the Network Slice used to access the Application. |
| > Application ID | Identification of the Application. |
| > Service Experience Type | Type of Service Experience analytics, e.g. on voice, video, other. |
| > UE location (NOTE 1, NOTE 5) | Indicating the UE location information (e.g. TAI list, gNB ID, or location coordinates, etc.) when the UE service is delivered. |
| > UPF Info (NOTE 4) | Indicating UPF serving the UE. |
| > DNAI | Indicating which DNAI the UE service uses/camps on. |
| > DNN | DNN for the PDU Session which contains the QoS flow. |
| > Application Server Instance Address | Identifies the Application Server Instance (IP address of the Application Server) or FQDN of Application Server. |
| > Service Experience | Service Experience over the Analytics target period (average, variance). |
| > SUPI list (0..SUPImax) (NOTE 3) | List of SUPI(s) with the same application service experience. |
| > Ratio (NOTE 3) | Estimated percentage of UEs with similar service experience (in the group, or among all UEs). |
| > Spatial validity (NOTE 6) | Area where the Application service experience analytics applies. |
| > Validity period | Validity period for the Application service experience analytics as defined in clause 6.1.3. |
| > Confidence | Confidence of this prediction. |
| > RAT Type
(NOTE 7) | Indicating the list of RAT type(s) for which the application service experience analytics applies. |
| > Frequency
(NOTE 7) | Indicating the list of carrier frequency value(s) of UE's serving cell(s) where the application service experience analytics applies. |
| > SSC Mode | SSC Mode selected for the PDU Session used to associate with the application. |
| > PDU Session Type | Type of PDU Session used to associate with the application. |
| > Access Type | List of Access Type(s) used for the PDU Session for the application. |
|
NOTE 1:
This information element is an Analytics subset that can be used in "list of analytics subsets that are requested" and "Preferred level of accuracy per analytics subset".
NOTE 2:
The NSI ID is an optional parameter. If not provided the Slice instance service experience indicates the service experience for the S-NSSAI.
NOTE 3:
The SUPI list and Ratio in the service experience information for an application can be omitted, if the corresponding parameter(s) is/are provided and are assigned with the same value(s) in the service experience information for the slice instance which the application belongs to. Otherwise, the SUPI list and Ratio are mandatory to be provided for an application service experience.
NOTE 4:
If the consumer NF is an AF, the "UPF info" shall not be included.
NOTE 5:
When possible and applicable to the access type, UE location is provided according to the preferred granularity of location information. UE location shall only be included if the Consumer analytics request is for single UE or a list of UEs. Inclusion of UE location requires user consent.
NOTE 6:
The Spatial validity is present in the output parameters if the consumer provided the Area of Interest as defined in Table 6.4.1-1.
NOTE 7:
When "any" value has been provided in the request (e.g. "any" RAT type, "any" frequency, or "any" for all the RAT type and frequency indication), the NWDAF provides an instance of the Application service experience per combination of RAT Type(s) and/or Frequency value(s) having the same Service Experience.
|
|
The number of Service Experiences and SUPIs are limited respectively by the maximum number of objects and the Maximum number of SUPIs provided as part of Analytics Reporting Information by the NWDAF Service Consumer.
6.4.4 Procedures to request Service Experience for an Application p. 173
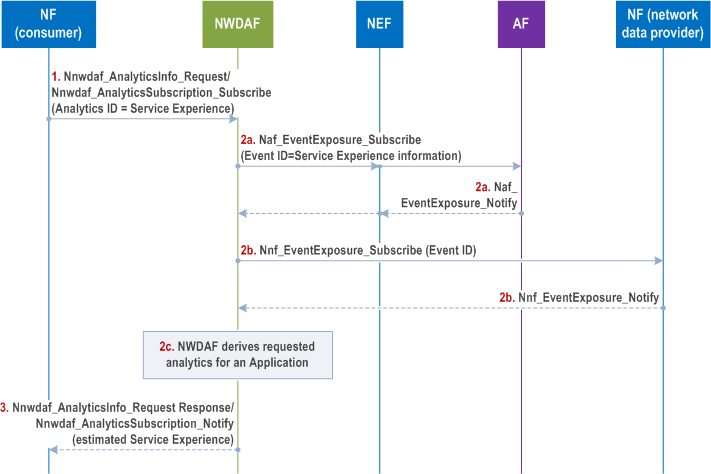
This procedure allows the consumer to request Analytics ID "Service Experience" for a particular Application. The consumer includes both the Application ID for which the Service Experience is requested and indicates that the Target of Analytics Reporting is "any UE". If the Target for Analytics Reporting is either a SUPI or an Internal-Group-Id the procedure in clause 6.4.6 applies. At the same time, for an Application ID, a set of initial QoS parameter combinations per service experience window (e.g. one is for 3<Service MOS<4 and another is for 4<Service MOS<5) is defined in PCF (e.g. by configuration of operator policies) that may be updated based on the Service Experience reported by NWDAF.
Step 1.
If the consumer NF is a PCF and it determines that the application SLA is not satisfied, it may take into account the Observed Service Experience and the operator policies including SLA and required Service Experience (which can be a range of values) to determine new QoS parameters to be applied for the service, as defined in clause 6.1.1.3 and clause 6.2.1.2 of TS 23.503.
If the consumer NF is an AF (e.g. MEC or other Application Server), it may use the Observed Service Experience related network data analytics to determine whether the user experience can be satisfied. If not, the AF may determine to adjust service parameters, e.g. for a video service this may be bit rate, frame rate, codec format, compression parameter, screen size, etc. to better match the network conditions and achieve better user experience.
If the consumer NF is SMF, PCF or AF/Application Server, it may take into account the Observed Service Experience analytics per UP path (i.e. UPF and/or DNAI and/or AS instance address as defined in Table 6.4.3-1) to perform the following procedures:
Consumer NF sends an Analytics request/subscribe (Analytics ID = Service Experience, Target of Analytics Reporting = any UE, Analytics Filter Information that may include one or more of the following as defined in Table 6.4.1-1 (Application ID, S-NSSAI, DNN, Application Server Address(es), Area of Interest, RAT type(s), Frequency value(s)), Analytics Reporting Information=Analytics target period) to NWDAF by invoking a Nnwdaf_AnalyticsInfo_Request or a Nnwdaf_AnalyticsSubscription_Subscribe .
Step 2a.
NWDAF subscribes the service data from AF in the Table 6.4.2-1 by invoking Nnef_EventExposure_Subscribe or Naf_EventExposure_Subscribe service (Event ID = Service Experience information, Application ID, Event Filter information, Target of Event Reporting = Any UE) as defined in TS 23.502.
Step 2b.
NWDAF subscribes the network data from 5GC NF(s) in the Table 6.4.2-2 by invoking Nnf_EventExposure_Subscribe service operation.
Step 2c.
With these data, the NWDAF estimates the Service experience for the application.
Step 3.
The NWDAF provides the data analytics, i.e. the observed Service Experience (which can be a range of values) to the consumer NF by means of either Nnwdaf_AnalyticsInfo_Request response or Nnwdaf_AnalyticsSubscription_Notify , depending on the service used in step 1, indicating how well the used QoS Parameters satisfy the Service MoS agreed between the MNO and the end user or between the MNO and the external ASP.
- The consumer SMF determines to (re)selects UP paths, including UPF and DNAI, as described in clause 4.3.5 of TS 23.502. In addition, the SMF may (re)configure traffic steering, updating the UPF regarding the target DNAI with new traffic steering rules.
- The consumer AF/Application Server determines to adjust service parameters, e.g. service parameters of video for adjustment may be bit rate, frame rate, codec format, compression parameter, screen size, etc. or service parameters for the AI/ML operations described in clause 6.40 of TS 22.261. In addition, the AF/ Application Server may provide an updated list of DNAI(s) for SMF to perform relocation when appropriate.
- The consumer PCF may provide an updated list of DNAI(s) for SMF to perform relocation upon AF request.
6.4.5 Procedures to request Service Experience for a Network Slice p. 175
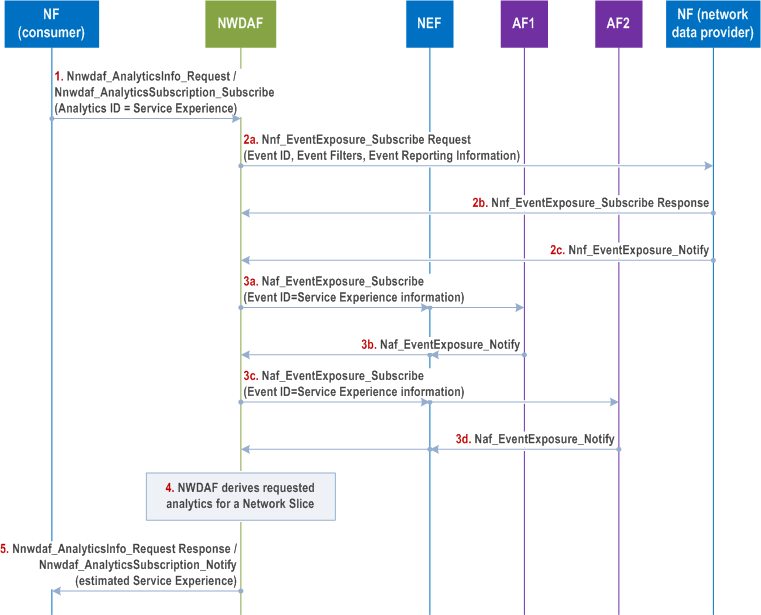
This procedure is similar to the procedure in clause 6.4.4, with the following differences. The consumer needs to request the Analytics ID "Service Experience" for a Target for Analytics Reporting as defined in clause 6.1.3 on a Network Slice, identified by an S-NSSAI. If multiple Network Slice instances of the same Network Slice are deployed, associated NSI ID(s) may be used in addition to S-NSSAI. If 'any UE' is the Target of Analytics Reporting, NWDAF may subscribe to UE mobility event notifications of AMF as described in clause 5.3.4.4 of TS 23.501 using event ID "UE moving in or out of Area of Interest" and Event Filters as described in Table 5.2.2.3.1-1 of TS 23.502 if it is needed to retrieve the list of SUPIs (and GPSIs if available) in the area of interest. The event exposure service request may also include the immediate reporting flag as Event Reporting Information as described in Table 4.15.1-1 of TS 23.502.
In addition, service experience data may need to be collected from multiple Applications. If each Application is hosted in different AFs, NWDAF subscribes the service data in the Table 6.4.2-1 from the different AFs by invoking Nnef_EventExposure_Subscribe or Naf_EventExposure_Subscribe services for each Application (Event ID = Service Experience information, Event Filter information, Application ID) as defined in TS 23.502. Figure 6.4.5-1 shows an example procedure with two AFs. If one AF provides the service experience data of multiple Applications, the set of Application IDs is provided by NWDAF to the AF with the Naf_EventExposure_Subscribe service operation, as defined TS 23.502.
The Observed Service Experience for a Network Slice when consumed by OAM could be used as described in Annex H of TS 28.550.
6.4.6 Procedures to request Service Experience for a UE |R17| p. 175
Figure 6.4.6-1 depicts procedure for NWDAF providing Service Experience for an application for a UE or a group of UEs.
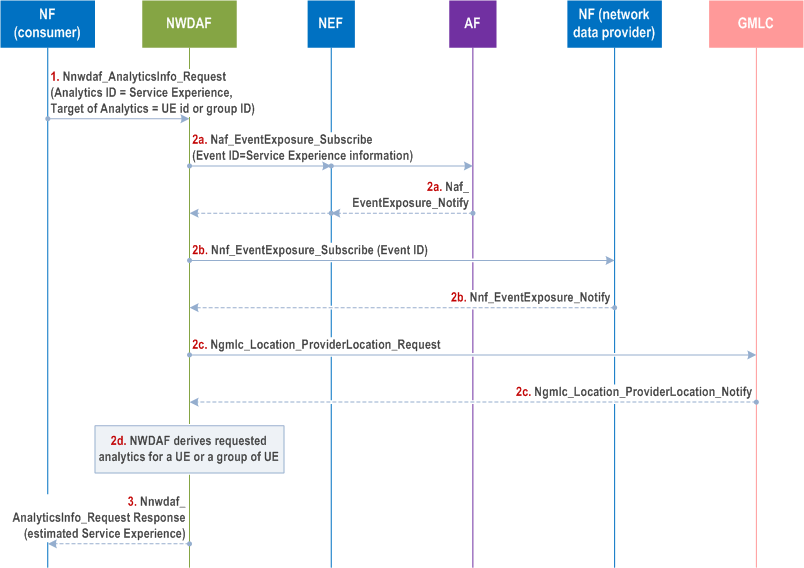
The procedure in clause 6.4.4 applies with the following additions. The consumer needs to request the Analytics ID "Service Experience" for a UE identified by a SUPI or a group of UEs identified by a list of Internal Group-Ids. The consumer includes both the Application ID for which their Service Experience is requested and the Target of Analytics Reporting. Analytic Filter Information can be set according to clause 6.4.1. The NWDAF may collect UE location information from the GLMC if the consumer requested fine granularity location information according to clause 6.4.2.1. When NEF is the NF service consumer, the NEF translates a GPSI into a SUPI or an External-Group-Id into an Internal-Group-Id then includes it in the Target of Analytics Reporting.