Content for TS 23.288 Word version: 18.6.0
1…
4…
5…
5A…
6…
6.1.3
6.1.4…
6.1.4.4…
6.1.5…
6.1A…
6.1B…
6.1B.2.3…
6.1C
6.2…
6.2.3…
6.2.6…
6.2.6.2
6.2.6.3…
6.2.6.3.3
6.2.6.3.4
6.2.6.3.5
6.2.6.3.6…
6.2.7…
6.2.8…
6.2.9…
6.2.13…
6.2A…
6.2B…
6.2B.3
6.2B.4…
6.2C…
6.2D…
6.2E…
6.2F…
6.3…
6.4…
6.5…
6.6…
6.7…
6.7.3…
6.7.4…
6.7.5…
6.8…
6.9…
6.10…
6.11…
6.12…
6.13…
6.14…
6.16…
6.17…
6.18…
6.19…
6.20…
6.21…
7…
7.4…
7.7…
7.9…
8…
9…
10…
4 Reference Architecture for Data Analytics
4.1 General
4.2 Non-roaming architecture
4.2.0 General
4.2.1 Analytics Data Repository Function
4.3 Roaming architecture
...
...
4 Reference Architecture for Data Analytics p. 13
4.1 General p. 13
The NWDAF (Network Data Analytics Function) is part of the architecture specified in TS 23.501 and uses the mechanisms and interfaces specified for 5GC in TS 23.501 and OAM services (see clause 6.2.3.1).
The NWDAF may support the following functionalities:
- Data collection based on subscription to events provided by AMF, SMF, UPF, PCF, UDM, NSACF, AF (directly or via NEF) and OAM;
- Analytics and Data collection using the DCCF (Data Collection Coordination Function);
- Retrieval of information from data repositories (e.g. from UDR via UDM for subscriber-related information or optinally via NEF(PFDF) for PFD information);
- Data collection of location information using LCS (finer granularity location information determined by LMF);
- Storage and retrieval of information from ADRF (Analytics Data Repository Function);
- Analytics and Data collection from MFAF (Messaging Framework Adaptor Function);
- Retrieval of information about NFs (e.g. from NRF for NF-related information);
- On demand provision of analytics to consumers, as specified in clause 6.
- Provision of bulked data related to Analytics ID(s).
- Provision of Accuracy information about Analytics ID(s).
- Provision or retrieval of ML Model Accuracy Information or ML Model accuracy degradation about a ML Model.
4.2 Non-roaming architecture p. 14
4.2.0 General |R17| p. 14
As depicted in Figure 4.2.0-1, the 5G System architecture allows NWDAF to collect data from any 5GC NF. The NWDAF belongs to the same PLMN as the 5GC NF that provides the data.

The Nnf interface is defined for the NWDAF to request subscription to data delivery for a particular context, to cancel subscription to data delivery and to request a specific report of data for a particular context.
The 5G System architecture allows NWDAF to retrieve the management data from OAM by invoking OAM services.
The 5G System architecture allows NWDAF to collect data from any 5GC NF or OAM using a DCCF with associated Ndccf services as specified in clause 8.2.
The 5G System architecture allows NWDAF and DCCF to collect data from an NWDAF with associated Nnwdaf_DataManagement services as specified in clause 7.4. The 5G system architecture allows MFAF to fetch data from an NWDAF with associated Nnwdaf_DataManagement service as specified in clause 7.4.
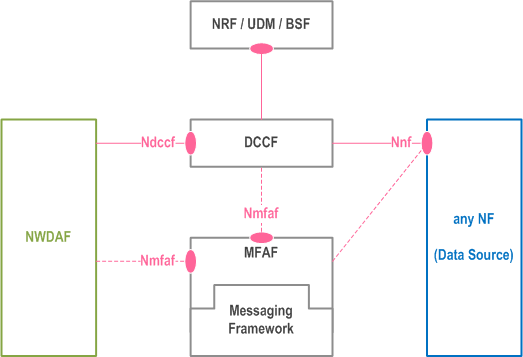
As depicted in Figure 4.2.0-1a, the Ndccf interface is defined for the NWDAF to support subscription request(s) for data delivery from a DCCF, to cancel subscription to data delivery and to request a specific report of data. If the data is not already being collected, the DCCF requests the data from the Data Source using Nnf services. The DCCF may collect the data and deliver it to the NWDAF or the DCCF may rely on a messaging framework to collect data from the NF and deliver it to the NWDAF.
As depicted in Figure 4.2.0-2, the 5G System architecture allows any 5GC NF to request network analytics information from NWDAF containing Analytics logical function (AnLF). The NWDAF belongs to the same PLMN as the 5GC NF that consumes the analytics information.

The Nnwdaf interface is defined for 5GC NFs, to request subscription to network analytics delivery for a particular context, to cancel subscription to network analytics delivery and to request a specific report of network analytics for a particular context.
The 5G System architecture allows any NF to obtain Analytics from an NWDAF using a DCCF function with associated Ndccf services, as specified in clause 8.2.
The 5G System architecture allows NWDAF and DCCF to request historical analytics from an NWDAF with associated Nnwdaf_AnalyticsSubscription services as specified in clause 7.2. The 5G system architecture allows MFAF to fetch historical analytics from an NWDAF with associated Nnwdaf_AnalyticsSubscription service as specified in clause 7.2.
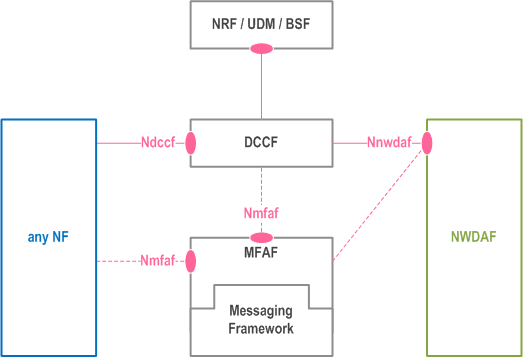
As depicted in Figure 4.2.0-2a, the Ndccf interface is defined for any NF to support subscription request(s) to network analytics, to cancel subscription for network analytics and to request a specific report of network analytics. If the analytics is not already being collected, the DCCF requests the analytics from the NWDAF using Nnwdaf services. The DCCF may collect the analytics and deliver it to the NF, or the DCCF may rely on a messaging framework to collect analytics and deliver it to the NF.
As depicted in Figure 4.2.0-3, the 5G System architecture allows NWDAF containing Analytics logical function (AnLF) to use trained ML Model provisioning services from another NWDAF containing Model Training logical function (MTLF).

The Nnwdaf interface is used by an NWDAF containing AnLF to request and subscribe to trained ML Model provisioning services.
4.2.1 Analytics Data Repository Function |R17| p. 16
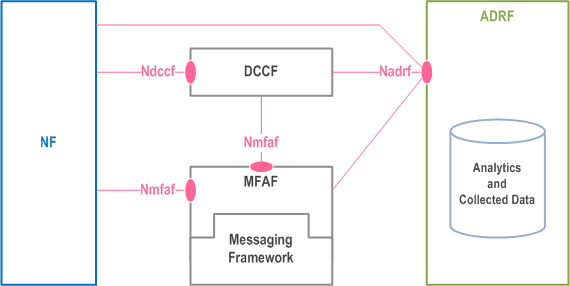
As depicted in Figure 4.2.1-1, the 5G System architecture allows ADRF to store and retrieve the collected data and analytics. The following options are supported:
- ADRF exposes the Nadrf service for storage and retrieval of data by other 5GC NFs (e.g. NWDAF) which access the data using Nadrf services.
-
Based on the NF request or configuration on the DCCF, the DCCF may determine the ADRF and interact directly or indirectly with the ADRF to request or store data. The interaction can be:
-
Direct: the DCCF requests to store data in the ADRF via an Nadrf service, or via an Ndccf_
DataManagement_ (e.g. when ADRF requested data collection notification via DCCF). In addition, the DCCF retrieves data from the ADRF via an Nadrf service.Notify -
Indirect: the DCCF requests that the Messaging Framework to store data in the ADRF i.e. via an Nadrf service or via an Nmfaf_
3daDataManagement_ . The Messaging Framework may contain one or more Adaptors that translate between 3GPP defined protocols.Configure - A Consumer NF may specify in requests to a DCCF that data provided by a Data Source needs to be stored in the ADRF.
-
Direct: the DCCF requests to store data in the ADRF via an Nadrf service, or via an Ndccf_
-
The ADRF stores data received in an Nadrf_
DataManagement_ sent directly from an NF, or data received in an Ndccf_StorageRequest DataManagement_ / Nmfaf_Notify 3caDataManagement_ or Nnwdaf_Notify DataManagement_ from the DCCF, MFAF or from the NWDAF.Notify - The ADRF checks if the Data Consumer is authorized to access ADRF services and provides the requested data using the procedures specified in clause 7.1.4 of TS 23.501.
4.3 Roaming architecture p. 17
Based on operator's policy and local regulations (e.g. privacy), data or analytics may be exchanged between PLMNs (i.e. HPLMN and VPLMN). In a PLMN, an NWDAF is used as exchange point to exchange analytics and to collect input data for analytics with other PLMNs. The NWDAF with roaming exchange capability is called Roaming Exchange NWDAF (RE-NWDAF).
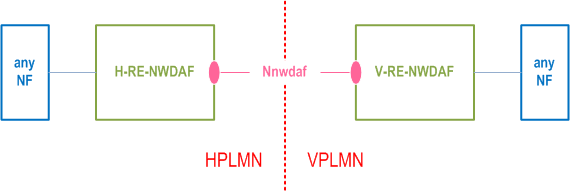
Using the architecture shown in Figure 4.3-1:
- For outbound roaming users, the NF consumer in the HPLMN can retrieve analytics from the VPLMN via the H-RE-NWDAF in HPLMN and V-RE-NWDAF in VPLMN.
- For outbound roaming users, the H-RE-NWDAF in HPLMN can collect data from the VPLMN via V-RE-NWDAF in VPLMN.
- For inbound roaming users, the NF consumer in the VPLMN can retrieve analytics from the HPLMN via V-RE-NWDAF in VPLMN and H-RE-NWDAF in HPLMN.
- For inbound roaming users, the V-RE-NWDAF can collect data from the HPLMN via the H-RE-NWDAF.