Content for TS 23.288 Word version: 18.6.0
1…
4…
5…
5A…
6…
6.1.3
6.1.4…
6.1.4.4…
6.1.5…
6.1A…
6.1B…
6.1B.2.3…
6.1C
6.2…
6.2.3…
6.2.6…
6.2.6.2
6.2.6.3…
6.2.6.3.3
6.2.6.3.4
6.2.6.3.5
6.2.6.3.6…
6.2.7…
6.2.8…
6.2.9…
6.2.13…
6.2A…
6.2B…
6.2B.3
6.2B.4…
6.2C…
6.2D…
6.2E…
6.2F…
6.3…
6.4…
6.5…
6.6…
6.7…
6.7.3…
6.7.4…
6.7.5…
6.8…
6.9…
6.10…
6.11…
6.12…
6.13…
6.14…
6.16…
6.17…
6.18…
6.19…
6.20…
6.21…
7…
7.4…
7.7…
7.9…
8…
9…
10…
5A Data Collection Coordination and Delivery Functional Description
5A.1 General
5A.2 Data Collection Coordination
5A.3 Data Delivery
5A.3.0 General
5A.3.1 Data Delivery via the DCCF or NWDAF
5A.3.2 Data Delivery via a Messaging Framework
5A.4 Data Formatting and Processing
5A.5 Historical Data Handling
5B Analytics Data Repository Functional Description
5B.1 General
5C Analytics/ML Model Accuracy Monitoring Functional Description
5C.1 General
...
...
5A Data Collection Coordination and Delivery Functional Description |R17| p. 22
5A.1 General p. 22
Data Collection Coordination and Delivery coordinates the collection and distribution of data requested by NF consumers. It prevents data sources from having to handle multiple subscriptions for the same data and send multiple notifications containing the same information due to uncoordinated requests from data consumers.
Data Collection Coordination and Delivery is supported by a DCCF via Ndccf_DataManagement service or by an NWDAF via Nnwdaf_DataManagement service. Unless otherwise stated, capabilities specified in clause 5A for a DCCF are also applicable to an NWDAF.
In this Release of the specification Data Collection Coordination and Delivery is applicable to:
- NWDAFs that request data from a Data Source (e.g. for use in computing analytics).
- NF consumers that request analytics from an NWDAF Data Source.
- NF consumers that request data from an ADRF Data Source.
- ADRFs that receive data from an NF Data Source.
5A.2 Data Collection Coordination p. 22
Data Collection Coordination is supported by a DCCF or an NWDAF. The Data Consumer may use an NRF to perform NF discovery and selection to find a DCCF that can coordinate data collection (DCCF discovery principles are defined in clause 6.3.19 of TS 23.501). Data Consumers send requests for data to the DCCF rather than directly to the NF Data Source. Whether the data consumers directly contact the NF Data Source or goes via the DCCF is based on configuration of the data consumers. For the Data Consumer and each notification endpoint in a data request, the Data Consumer may specify Formatting and Processing Instructions that determine how the data is to be provided. Upon receiving a request from a Data Consumer, the selected DCCF determines the NF instance that can be a Data Source if the Data Source is not indicated in the Data Consumer's request. The DCCF may also select an ADRF if the data is to be stored in an ADRF and an ADRF endpoint is not indicated in the Data Consumer's request. To retrieve data for a specific UE, the NRF, UDM or BSF can provide the DCCF with the identity of the Data Source using the services indicated in Table 5A.2-1.
Table 5A.2-1: NF Services consumed by DCCF or NWDAF to determine which NF instances are serving a UE
| Type of NF instance (serving the UE) to determine | NF to be contacted by DCCF | Service | Reference in TS 23.502 |
|---|---|---|---|
| UDM | NRF | Nnrf_ | 5.2.7.3 |
| AMF | UDM | Nudm_ | 5.2.3.2 |
| SMF | UDM | Nudm_ | 5.2.3.2 |
| BSF | NRF | Nnrf_ | 5.2.7.3 |
| PCF | BSF | Nbsf_ | 5.2.13.2 |
| NEF | NRF | Nnrf_ | 5.2.7.3 |
| NWDAF | NRF
UDM | Nnrf_ Nudm_ |
5.2.7.3
5.2.3.2 |
| GMLC | NRF | Nnrf_ | 5.2.7.3 |
| NSACF | NRF | Nnrf_ | 5.2.7.3 |
|
NOTE 1:
Discovery can be based on a group ID. The group ID for a UE ID can be obtained using the Nudr_
NOTE 2:
Discovery of the GMLC serving a UE is described in clause 5.1a of TS 23.273 and can also be based on DNS. A GMLC is supposed to be able to serve any UE in the PLMN; the GMLC will in turn discover an AMF serving the UE via the UDM as described in clause 6.1 of TS 23.273.
|
|||
The DCCF keeps track of the data actively being collected from the Data Sources it is coordinating. It may do so by maintaining a record of the active prior requests it sends to each Data Source. If a NWDAF subscribes for data directly with a Data Source, or a Data Source has stored data in an ADRF, the NWDAF or ADRF may register the data collection profile with the DCCF. The data collection profile may include the following parameters:
-
"Service Operation" identifies the service used to collect the data or analytics from a Data Source (e.g. Namf_
EventExposure_ or Nnwdaf_Subscribe AnalyticsSubscription_ );Subscribe - "Analytics/Data Specification" is the "Service Operation" specific parameters that identify the collected data (i.e. Analytics ID(s) / Event ID (s), Target of Analytics Reporting or Target of Event Reporting, Analytics Filter or Event Filter, etc.);
- NWDAF ID or ADRF ID specifies the ADRF or NWDAF which registers data collection profile.
5A.3 Data Delivery p. 24
5A.3.0 General p. 24
Data is provided to Consumers or notification endpoints according to the Delivery Option configured on the DCCF or NWDAF. Delivery Options are:
- Delivery via DCCF or NWDAF: Consumers or Notification Endpoints receive the data from the DCCF or NWDAF.
- Delivery via Messaging Framework: Consumers or Notification Endpoints receive the data from the Messaging Framework via the services offered by the MFAF.
5A.3.1 Data Delivery via the DCCF or NWDAF p. 24
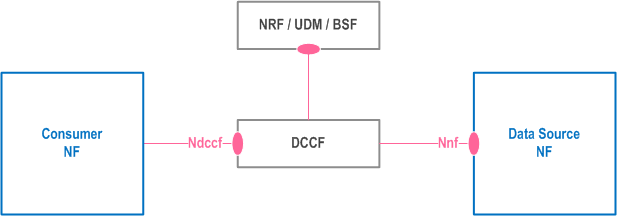
Data Delivery via DCCF is shown in Figure 5A.3.1-1. Each Event Notification received from a Data Source NF is sent to the DCCF which propagates it to all Data Consumers / Notification Endpoints specified by the Data Consumers or determined by the DCCF. Each Data Consumer may specify in its request to the DCCF multiple notification endpoints, which may include the requesting Data Consumer, an ADRF or other NFs. The DCCF may also select an ADRF or other notification endpoint based on configuration. The DCCF supports formatting and processing for each Consumer / notification endpoint so notifications comply with the data requests received from each Consumer NF.
Upon the DCCF determining the status of data collection for a data request (see clause 5A.2):
DataManagement service.
The same functionality as described above applies for Data Delivery and bulked data collection via NWDAF with Nnwdaf services replacing corresponding Ndccf services.
- If the requested data is not already being collected from a Data Source, the DCCF sends a new subscription/request towards the Data Source with the notification target specified as the DCCF.
- If the requested data is partially covered by existing subscriptions with the Data Source, the DCCF sends to the existing Data Source a request to modify the subscription and/or creates new subscription(s) to new Data Source for the newly requested data which cannot be provided by the current Data Source.
- If the requested data is already being collected from the Data Source, the DCCF determines that no subscriptions to the Data Source need to be created or modified.
5A.3.2 Data Delivery via a Messaging Framework p. 25
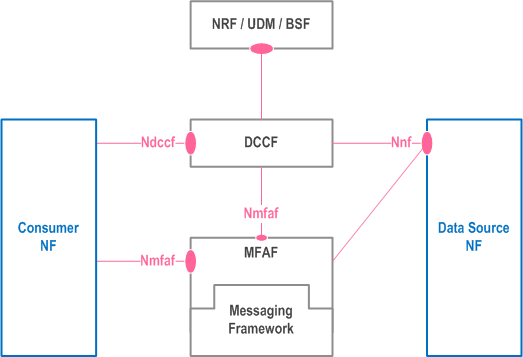
Data Delivery via a Messaging Framework is shown in Figure 5A.3.2-1. The Messaging Framework formats and processes data received from the Data Source NF and sends notifications to all Data Consumers and Notification Endpoints specified by Data Consumers or determined by the DCCF. Each Data Consumer may specify in its request to the DCCF multiple notification endpoints, which may include the requesting Data Consumer, an ADRF or other NFs. The DCCF may also select an ADRF or other notification endpoint based on configuration. While the Messaging Framework is not standardized by 3GPP, a Messaging Framework Adaptor NF (MFAF) offers 3GPP defined services that allow the 5GS to interact with the Messaging Framework. Internally, the Messaging Framework may for example support the pub-sub pattern, where received data are published to the Messaging Framework and requests from 3GPP Consumers result in Messaging Framework specific subscriptions. Alternatively, the Messaging Framework may support other protocols outside of the scope of 3GPP.
The Messaging Framework Adaptor NF offers services that enable the 5GS to interact with the Messaging Framework:
3caDataManagement service have the same content as those sent via a Ndccf_DataManagement service for Data Delivery via the DCCF.
The same functionality as described above applies for Data Delivery and bulk data collection via NWDAF with Nnwdaf services replacing corresponding Ndccf services.
-
3GPP Consumer Adaptor (3CA) Data Management Service: Nmfaf_
3caDataManagement Service delivers data to each Data Consumer or notification endpoint after formatting and processing of data received by the Messaging Framework. -
3GPP DCCF Adaptor (3DA) Data Management Service: The consumer (e.g. DCCF) may configure MFAF using Nmfaf_
3daDataManagement service to enable the MFAF to convey data or analytics received from data source NF to notification endpoints. The configuration may include data formatting and processing instruction and notification endpoints.
- If the requested data is not currently being collected from a Data Source, the DCCF sends a new subscription/request towards the Data Source with the notification target specified as the Messaging Framework.
- If the requested data is partially covered by existing subscriptions with the Data Source, the DCCF sends a request to the Data Source to modify one or more subscriptions to accommodate both the previous requests for data and the new request for data and/or creates new subscription(s) to new Data Source for the newly requested data which cannot be provided by the current Data Source.
- If the requested data is already being collected from the Data Source, the DCCF determines that no subscriptions to the Data Source need to be created or modified.
-
The DCCF uses the Nmfaf_
3daData Management service to convey information so:- the Messaging Framework can recognize data that are received from a Data Source.
- the MFAF can obtain data received by the Messaging Framework, process and format the data according to processing and formatting instructions for each Consumer / notification endpoint and send notifications or responses to the Data Consumers.
5A.4 Data Formatting and Processing p. 26
Formatting and/or Processing instructions may be provided in requests by Data Consumers via the Ndccf_DataManagement service and Nnwdaf_DataManagement service. As an alternative to providing individual events, formatting can be used to aggregate notifications and processing can be used to extract and send summary information from multiple notifications. Data Formatting and Processing are applicable to notifications due to events as they occur at data sources (runtime data or analytics) and historical data as described in clause 5A.5.
When using the Messaging Framework, the DCCF sends the formatting and/or processing instructions to the Messaging Framework via the Nmfaf_3daData_Management Service so the MFAF may format and/or process the data before sending notifications to the Data Consumers / notification endpoints. When using Data Delivery via the DCCF, the DCCF performs formatting and/or processing before sending notifications.
Formatting determines when a notification is sent to the Consumer. Formatting Instructions may indicate:
- Notification Event clubbing: Buffering and sending of several notifications in one message. The consumer may specify a minimum and/or maximum number of notifications to be clubbed.
- Notification Time Window (example: notifications are buffered and sent between 2 and 3 AM).
- Cross event reference-based notification: When a subscribing NF is subscribing to multiple events (e.g. event X and event Y) the notification for an Event-X is buffered and reported only when the Event-Y occurs.
-
Consumer triggered Notification: Notifications containing data or analytics are buffered until the consumer requests delivery using Nnwdaf_
DataManagement , Ndccf_DataManagement or Nmfaf_3caDataManagement Service. The consumer requests Consumer triggered notification by setting a "fetch flag" in its subscription request to the DCCF or NWDAF. When the requested data or analytics is available for retrieval, the DCCF, NWDAF or MFAF sends a notification containing fetch instructions to the consumer. The consumer must then fetch the data or analytics before an expiry time as provided in the fetch instructions. - Exact time-based Notification: Notifications are sent to the Consumer at an exact time, irrespective of whether the event occurs (example: every 30 min). Exact time-based notifications may be periodic.
- Increasing time window based notification: Notifications are sent to the Consumer at an increasing periodicity (example: the first notification is sent immediately, subsequent received notifications are sent after 5 min, then after 10 min, then after 15 min, etc.).
- Event;
- Processing Interval;
-
List of Event Parameter Name(s) and for each Event Parameter Name, one Event Parameter Values and sets of the following attributes as indicated in the processing instructions:
- Event Spacing: Average and variance of the time interval separating two consecutive occurrences of the same event and parameter value, or periodicity for periodic reporting;
- Event Duration: Average and variance of the Time for which the parameter value applies;
- Number of countable occurrences for the parameter (e.g. Mobility Registration Update);
- Average, variance, most frequent value, least frequent value and skew of the parameter (e.g.: number of UEs in an AoI);
- Maximum and minimum parameter values (e.g. number of UEs in an AoI).
| Event | Event parameter name | Parameter values | Attributes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Location Report | TAI | TAI-7 |
|
| Number of UEs in a Region | Region | AMF-3 |
|
| UE Reachability (status change) | CM State | Connected |
|
| PDU Session Establishment | DNN | Internet |
|
| PDU Session Establishment | PDU Session Type | Ethernet |
|
5A.5 Historical Data Handling p. 28
ADRF or NWDAF as a Data Source:
- When the DCCF receives a request for data that includes a period in the past and ADRF is deployed, the DCCF may obtain data from ADRF as the Data Source. The DCCF may also obtain historical data from an NWDAF. The data obtained from the ADRF or NWDAF is delivered to Consumers / Notification Endpoints according to a configured Delivery Option. The DCCF may determine that requested data may be available in an ADRF or NWDAF based on ADRF identification from the consumer, the data collection profile previously registered by the ADRF or NWDAF or by querying the ADRF or NWDAF.
- An ADRF or NWDAF may be a Consumer NF that initiates requests to the DCCF for data, the ADRF or NWDAF may be specified as a notification endpoint by another Consumer NF that wants to have data it requests archived, or the DCCF may be configured to archive certain data in a ADRF (e.g. all data from an AMF instance).
- If the ADRF or NWDAF instance is not specified in a request for data by a Consumer NF, the DCCF may select the ADRF or NWDAF instance based on provisioned information or information received from the NRF.
- Data is delivered to the ADRF or NWDAF according to a configured Delivery Option (via DCCF or Messaging Framework).
5B Analytics Data Repository Functional Description |R17| p. 29
5B.1 General p. 29
The ADRF offers services that enable a consumer to store, retrieve and delete data and analytics. The analytics are produced by the NWDAF as described in clause 6.1 and data are collected as described in clause 6.2. Multiple instances of ADRF may be deployed in a network, NF consumer selects a target ADRF instance using ADRF discovery mechanism defined in clause 6.3.20 of TS 23.501.
Data may be stored in the ADRF by:
ContextManagement service specified in clause 8.3.2. The registration may subsequently be used by the DCCF to obtain data from the ADRF as described in clause 6.2.6.3.6.
The ADRF offers services that enable a consumer to store, delete and retrieve ML Models. The ML Models are trained by NWDAF containing MTLF as described in clause 5.1.
ML Model(s) may be retrieved from the ADRF by:
-
a consumer sending the ADRF an Nadrf_
DataManagement_ containing the data or analytics to be stored. The ADRF response provides a result indication.StorageRequest -
a consumer sending the ADRF an Nadrf_
DataManagement_ requesting that the ADRF subscribes to receive data or analytics for storage. The ADRF then subscribes to the NWDAF or DCCF for data or analytics, providing ADRF Notification Address (+Notification Correlation ID). Analytics or Data are subsequently provided as notifications using DCCF, NWDAF or MFAF services (Ndccf_StorageSubscriptionRequest DataManagement Nnwdaf_DataManagement or Nmfaf_3caDataManagement service).
-
a consumer sending an Nadrf_
DataManagement_ request to the ADRF to retrieve data or analytics for a Storage Transaction Identifier or a Fetch Instructions received from the ADRF in an Nadrf_RetrievalRequest DataManagement_ . The ADRF determines the availability of the data or analytics in its repository and sends in the response to the consumer either the data or analytics.RetrievalNotify -
a consumer sending an Nadrf_
DataManagement_ request to the ADRF to retrieve data or analytics for a specified data or analytics collection time window. If the time window includes the future and the ADRF has subscribed to receive the data or analytics, subsequent notifications received by the ADRF are sent by the ADRF to the notification endpoint. The ADRF determines the availability of the data or analytics and sends a success/failure indication in the response to the consumer. The ADRF then sends one or more notifications using an Nadrf_RetrievalSubscribe DataManagement_ to the Notification Address (+Notification Correlation ID) specified by the consumer. The notification(s) either provide the data or analytics or provide instructions to the endpoint to fetch the data or analytics using an Nadrf_RetrievalNotify DataManagement_ .RetrievalRequest
-
a consumer sending an Nadrf_
DataManagement_ request. The ADRF response provides a result indication.Delete
-
a consumer sending the ADRF an Nadrf_
MLModelManagement_ as described in clause 10.3.4, containing one or more tuples of unique ML Model identifier stored in ADRF or Storage Transaction Identifier. The ADRF response provides one or more tuples of unique ML Model identifiers and ML Model file address of ML Model file stored in ADRF.RetrievalRequest
-
a consumer sending the ADRF an Nadrf_
MLModelManagement_ as described in clause 10.3.2, containing the ML Model or ML Model address to be stored. The ADRF response provides a result indication.StorageRequest
-
a consumer sending an Nadrf_
MLModelManagement_ request as described in clause 10.3.3. The ADRF response provides a result indication.Delete
- a lifetime indicating how long the data or analytics should be stored; and/or
- that a notification alerting the consumer be sent prior to data deletion from the ADRF.
5C Analytics/ML Model Accuracy Monitoring Functional Description |R18| p. 30
5C.1 General p. 30
A NWDAF may have the accuracy checking capability for Analytics and/or ML Models. The NWDAF may provide the accuracy information to consumers when requested or use it for its internal processes.
Input data is collected from Data Producer NF(s) when there is a request for inference/prediction per analytics ID in NWDAF for a specific time period in future. Ground truth data are collected from those Data Producer NF corresponding to the requested analytic ID at the time to which the prediction refers.
The ground truth data is the actual measured data observed at the time which the prediction refers to.
Analytics/ML Model Accuracy Monitoring is to be achieved by comparing the predictions using the current trained ML Model and its corresponding ground truth data i.e. the corresponding true observed events.
Analytics/ML Model Accuracy Information is to represent general performance measurements for analytics and ML Model respectively, which are composed of the number of correct predictions out of all predictions and the corresponding number of samples.
The NWDAF (containing AnLF/MTLF) with accuracy checking capability decides to initiate Analytics Accuracy Monitoring based on:
- A request from an analytics accuracy consumer. The analytics accuracy consumer may be an NWDAF containing AnLF, NWDAF containing MTLF or an analytics consumer NF.
- Analytics Feedback Information which may be provided by an Analytics Consumer NF.
- Comparing predictions and its corresponding ground truth data, which are collected corresponding to the requested analytic ID at the time which the prediction refers to.
- Comparing changes in internal configuration for the analytics ID generation (e.g. change of data collection parameters, change in data distribution from a Data Source).
- Previous existent records of Analytics Accuracy Information.
- Accuracy Feedback Information provided by an NF consumer.
- Determining analytics accuracy by comparing analytics accuracy using multiple ML Models that serve the same Analytics ID.
- comparing/evaluating the data: including input data, analytics output and the ground truth data either collected from various data source NFs, DCCF, AnLF, ADRF or configured by OAM;
- or AnLF providing notifications of the Analytics Accuracy Information; or
- AnLF providing Analytics Feedback Information of the analytics generated by the ML Model.