Content for TS 33.501 Word version: 18.6.0
1…
4…
5…
5.3…
5.9…
5.10…
6…
6.1.3…
6.1.4…
6.2…
6.2.2…
6.3…
6.4…
6.5…
6.6…
6.7…
6.8…
6.9…
6.10…
6.11
6.12…
6.13
6.14…
6.15…
6.16…
7…
7A…
7A.2.3…
7B…
8…
9…
10…
11…
12…
13…
13.2.2…
13.2.4…
13.3…
13.4…
14…
15…
16…
A…
B…
C…
D…
E…
F…
G…
I…
I.9…
J…
K…
M…
N…
O…
P…
R
S…
T…
U…
V…
W…
X…
Y…
Z…
C Protection schemes for concealing the subscription permanent identifier
C.1 Introduction
C.2 Null-scheme
C.3 Elliptic Curve Integrated Encryption Scheme (ECIES)
C.3.1 General
C.3.2 Processing on UE side
C.3.3 Processing on home network side
C.3.4 ECIES profiles
C.3.4.0 General
C.3.4.1 Profile A
C.3.4.2 Profile B
C.4 Implementers' test data
C.4.1 General
C.4.2 Null-scheme
C.4.2.1 IMSI-based SUPI
C.4.2.2 Network specific identifier-based SUPI
C.4.3 ECIES Profile A
C.4.3.1 IMSI-based SUPI
C.4.3.2 Network specific identifier-based SUPI
C.4.4 ECIES Profile B
C.4.4.1 IMSI-based SUPI
C.4.4.2 Network specific identifier-based SUPI
...
...
C (Normative) Protection schemes for concealing the subscription permanent identifier p. 236
C.1 Introduction p. 236
The present Annex specifies the protection schemes for concealing the subscription permanent identifier. Each protection scheme is identified by a Protection Scheme Identifier. The Protection Scheme Identifiers are as follows:
null-scheme
The values 0x3 - 0xB are reserved for future standardized protection schemes. The values 0xC - 0xF are reserved for proprietary protection schemes specified by the home operator.
Care should be taken when using unique schemes for small groups of users, as this may impact the effectiveness of the privacy scheme for these users.
The size of the Scheme Output of the protection schemes is as follows:
0x0;
Profile <A>
0x1;
Profile <B>
0x2.
null-scheme
The maximum size of a Scheme Output for proprietary protection schemes shall be total of 3000 octets plus size of input .
The UE shall not send, and the network may reject SUCIs larger than the maximum size of scheme-output.
size of input, i.e., size of username used in case of NAI format or MSIN in case of IMSI;
Profile <A>
total of 256-bit public key, 64-bit MAC, plus size of input;
Profile <B>
total of 264-bit public key, 64-bit MAC, plus size of input.
C.2 Null-scheme p. 236
The null-scheme shall be implemented such that it returns the same output as the input, which applies to both encryption and decryption.
When using the null-scheme, the SUCI does not conceal the SUPI and therefore the newly generated SUCIs do not need to be fresh.
C.3 Elliptic Curve Integrated Encryption Scheme (ECIES) p. 237
C.3.1 General p. 237
The use of ECIES for concealment of the SUPI shall adhere to the SECG specifications [29] and [30]. Processing on UE side and home network side are described in high level in clauses C.3.2 and C.3.3.
When the SUPI is of type IMSI, the subscription identifier part of the IMSI (i.e., MSIN) that is used to construct the scheme-input shall be coded as hexadecimal digits using packed BCD coding where the order of digits within an octet is same as the order of MSIN digits specified in Figure 9.11.3.4.3a of TS 24.501. If the MSIN is composed of an odd number of digits, then the bits 5 to 8 of final octet shall be coded as "1111".
When the SUPI is of type network specific identifier, the subscription identifier part of the SUPI that is used to construct the scheme-input shall follow the encoding rules specified in Annex B.2.1.2 of TS 33.220.
C.3.2 Processing on UE side p. 237
The ECIES scheme shall be implemented such that for computing a fresh SUCI, the UE shall use the provisioned public key of the home network and freshly generated ECC (elliptic curve cryptography) ephemeral public/private key pair according to the ECIES parameters provisioned by home network. The processing on UE side shall be done according to the encryption operation defined in [29], with the following changes to Section 3.8 and step 5 and 6 of Section 5.1.3.
- generate keying data K of length enckeylen + icblen + mackeylen.
- Parse the leftmost enckeylen octets of K as an encryption key EK, the middle icblen octets of K as an ICB, and the rightmost mackeylen octets of K as a MAC key MK.
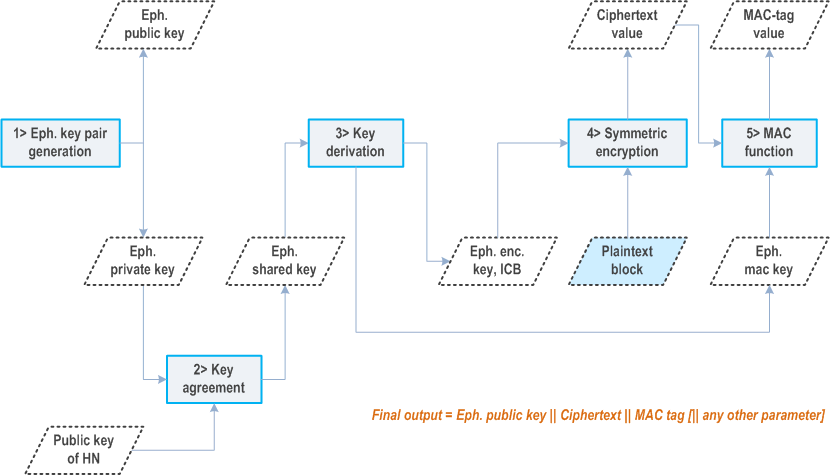
C.3.3 Processing on home network side p. 238
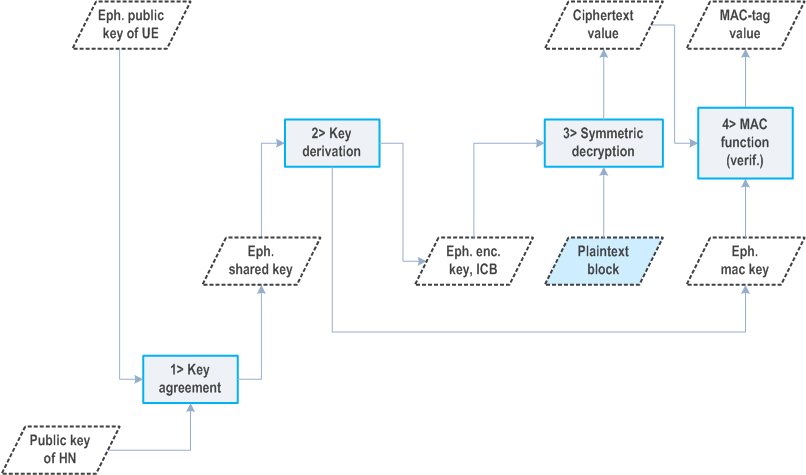
The ECIES scheme shall be implemented such that for deconcealing a SUCI, the home network shall use the received ECC ephemeral public key of the UE and the private key of the home network. The processing on home network side shall be done according to the decryption operation defined in [29], with the following changes to Section 3.8 and step 6 and 7 of Section 5.1.4.
- generate keying data K of length enckeylen + icblen + mackeylen.
- Parse the leftmost enckeylen octets of K as an encryption key EK, the middle icblen octets of K as an ICB, and the rightmost mackeylen octets of K as a MAC key MK.
C.3.4 ECIES profiles p. 238
C.3.4.0 General p. 238
Unless otherwise stated, the ECIES profiles follow the terminology and processing specified in SECG version 2 [29] and [30]. The profiles shall use "named curves" over prime fields.
For generating successive counter blocks from the initial counter block (ICB) in CTR mode, the profiles shall use the standard incrementing function in section B.1 of NIST Special Publication 800-38A [16] with m = 32 bits. The ICB corresponds to T1 in section 6.5 of [16].
The value of the MAC tag in ECIES, shall be the L most significant octets of the output generated by the HMAC function, where L equals to the maclen.
Profile A shall use its own standardized processing for key generation (Section 6 of RFC 7748) and shared secret calculation (Section 5 of RFC 7748). The Diffie-Hellman primitive X25519 (Section 5 of RFC 7748) takes two random octet strings as input, decodes them as scalar and coordinate, performs multiplication, and encodes the result as an octet string. The shared secret output octet string from X25519 shall be used as the input Z in the ECIES KDF (section 3.6.1 of [29]). As the point compression is not applied for profile A, the prefix rule for compression type defined in section 5.1.3 of [29] shall not be used in profile A, i.e., there shall be no prefix for the ephemeral public key of Profile A.
Profile B shall use point compression to save overhead and shall use the Elliptic Curve Cofactor Diffie-Hellman Primitive (section 3.3.2 of [29]) to enable future addition of profiles with cofactor h ≠ 1. For curves with cofactor h = 1 the two primitives (section 3.3.1 and 3.3.2 of [29]) are equal.
The profiles shall not use backwards compatibility mode (therefore are not compatible with version 1 of SECG).
C.3.4.1 Profile A p. 239
The ME and SIDF shall implement this profile. The ECIES parameters for this profile shall be the following:
EC domain parameters
Curve25519 [46]
EC Diffie-Hellman primitive
X25519 [46]
point compression
N/A
KDF
ANSI-X9.63-KDF [29]
Hash
SHA-256
SharedInfo1
(the ephemeral public key octet string - see [29] section 5.1.3)
MAC
HMAC-SHA-256
mackeylen
32 octets (256 bits)
maclen
8 octets (64 bits)
SharedInfo2
the empty string
ENC
AES-128 in CTR mode
enckeylen
16 octets (128 bits)
icblen
16 octets (128 bits)
backwards compatibility mode
false
C.3.4.2 Profile B p. 239
The ME and SIDF shall implement this profile. The ECIES parameters for this profile shall be the following:
EC domain parameters
secp256r1 [30]
EC Diffie-Hellman primitive
Elliptic Curve Cofactor Diffie-Hellman Primitive [29]
point compression
true
KDF
ANSI-X9.63-KDF [29]
Hash
SHA-256
SharedInfo1
(the ephemeral public key octet string - see [29] section 5.1.3)
MAC
HMAC-SHA-256
mackeylen
32 octets (256 bits)
maclen
8 octets (64 bits)
SharedInfo2
the empty string
ENC
AES-128 in CTR mode
enckeylen
16 octets (128 bits)
icblen
16 octets (128 bits)
backwards compatibility mode
false
C.4 Implementers' test data p. 240
C.4.1 General p. 240
The test data sets presented here are for encryption based on ECIES at UE with protection schemes defined in this clause.
C.4.2 Null-scheme p. 240
C.4.2.1 IMSI-based SUPI |R16| p. 240
The following test data set corresponds to ECIES-based encryption in the UE for IMSI-based SUPI and null-scheme.
IMSI consists of MCC|MNC: '274012' and MSIN: '001002086'
ECIES Scheme Input
Scheme Input: '00012080F6'
ECIES Scheme Output
Scheme Output: '00012080F6'
C.4.2.2 Network specific identifier-based SUPI |R16| p. 240
The following test data set corresponds to ECIES-based encryption in the UE for network specific identifier-based SUPI and null-scheme.
SUPI is: verylongusername1@3gpp.com
ECIES Scheme Input
Scheme Input: '766572796C6F6E67757365726E616D6531'
ECIES Scheme Output
Scheme Output: useridverylongusername1
C.4.3 ECIES Profile A p. 240
C.4.3.1 IMSI-based SUPI |R16| p. 240
The following test data set corresponds to SUCI computation in the UE for IMSI-based SUPI and ECIES Profile A.
IMSI consists of MCC|MNC: '274012' and MSIN: '001002086'
ECIES test data
The ECIES Scheme Output is computed in the UE as defined in Figure C.3.2-1 of clause C.3.2 with the following data
Home Network Private Key:
'c53c22208b61860b06c62e5406a7b330c2b577aa5558981510d128247d38bd1d'
Home Network Public Key:
'5a8d38864820197c3394b92613b20b91633cbd897119273bf8e4a6f4eec0a650'
Eph. Private Key:
'c80949f13ebe61af4ebdbd293ea4f942696b9e815d7e8f0096bbf6ed7de62256'
Eph. Public Key:
'b2e92f836055a255837debf850b528997ce0201cb82adfe4be1f587d07d8457d'
Eph. Shared Key:
'028ddf890ec83cdf163947ce45f6ec1a0e3070ea5fe57e2b1f05139f3e82422a'
Eph. Enc. Key:
'2ba342cabd2b3b1e5e4e890da11b65f6'
ICB:
'e2622cb0cdd08204e721c8ea9b95a7c6'
Plaintext block:
'00012080f6' Cipher-text vaue:
'cb02352410' Eph. mac key:
'd9846966fb7cf5fcf11266c5957dea60b83fff2b7c940690a4bfe57b1eb52bd2'
MAC-tag value:
'cddd9e730ef3fa87' Scheme Output:
'b2e92f836055a255837debf850b528997ce0201cb82adfe4be1f587d07d8457dcb02352410cddd9e 730ef3fa87'
'c53c22208b61860b06c6
'5a8d38864820197c3394
'c80949f13ebe61af4ebd
'b2e92f836055a255837d
'028ddf890ec83cdf1639
'2ba342cabd2b3b1e5e4e
'e2622cb0cdd08204e721
'00012080f6' Cipher-text vaue:
'cb02352410' Eph. mac key:
'd9846966fb7cf5fcf112
'cddd9e730ef3fa87' Scheme Output:
'b2e92f836055a255837d
C.4.3.2 Network specific identifier-based SUPI |R16| p. 241
The following test data set corresponds to SUCI computation in the UE for network specific identifier-based SUPI and ECIES Profile A.
SUPI is: verylongusername1@3gpp.com
ECIES test data
The ECIES Scheme Output is computed in the UE as defined in Figure C.3.2-1 of clause C.3.2 with the following data
Home Network Private Key:
'C53C22208B61860B06C62E5406A7B330C2B577AA5558981510D128247D38BD1D'
Home Network Public Key:
'5A8D38864820197C3394B92613B20B91633CBD897119273BF8e4A6f4EEC0A650'
Eph. Private Key:
'BE9EFF3E9F22A4B42A3D236E7A6C500B3F2E7E0C7449988BA800D664BF4FCD97'
Eph. Public Key:
'977D8B2FDAA7B64AA700D04227D5B440630EA4EC50F9082273A26BB678C92222'
Eph. Shared Key:
'511C1DF473BB88317F923501F8BA944FD3B667D25699DCB552DBCEF60BBDC56D'
Eph. Enc. Key:
'FE77B87D87F40428EDD71BCA69D79059'
Plaintext block:
'766572796C6F6E67757365726E616D6531'
Cipher-text value:
'8E358A1582ADB15322C10E515141D2039A'
Eph. mac key:
'D87B69F4FE8CD6B211264EA5E69F682F151A82252684CDB15A047E6EF0595028'
MAC-tag value:
'12E1D7783A97F1AC' Scheme Output:
ecckey977D8B2FDAA7B64AA700D04227D5B440630EA4EC50F9082273A26BB678C92222.cip8E358A1582ADB15322C10E515141D2039A.mac12E1D7783A97F1AC
'C53C22208B61860B06C6
'5A8D38864820197C3394
'BE9EFF3E9F22A4B42A3D
'977D8B2FDAA7B64AA700
'511C1DF473BB88317F92
'FE77B87D87F40428EDD7
'766572796C6F6E677573
'8E358A1582ADB15322C1
'D87B69F4FE8CD6B21126
'12E1D7783A97F1AC' Scheme Output:
ecckey977D8B2FDAA7B64
C.4.4 ECIES Profile B p. 242
C.4.4.1 IMSI-based SUPI |R16| p. 242
The following test data set corresponds to ECIES-based encryption in the UE for IMSI-based SUPI and ECIES Profile B.
IMSI consists of MCC|MNC: '274012' and MSIN: '001002086'
ECIES test data
The Scheme Output is computed in the UE as defined in Figure C.3.2-1 of clause C.3.2 with following data:
Home Network Public Key:
uncompressed:
'0472DA71976234CE833A6907425867B82E074D44EF907DFB4B3E21C1C2256EBCD15A7DED52FCBB097A4ED250E036C7B9C8C7004C4EEDC4F068CD7BF8D3F900E3B4',
if compressed:
'0272DA71976234CE833A6907425867B82E074D44EF907DFB4B3E21C1C2256EBCD1'
Home Network Private Key (Not available in the UE, provided here only for test purposes):
'F1AB1074477EBCC7F554EA1C5FC368B1616730155E0041AC447D6301975FECDA'
Eph. Public Key:
If compressed:
'039AAB8376597021E855679A9778EA0B67396E68C66DF32C0F41E9ACCA2DA9B9D1'
uncompressed:
'049AAB8376597021E855679A9778EA0B67396E68C66DF32C0F41E9ACCA2DA9B9D1D1F44EA1C87AA7478B954537BDE79951E748A43294A4F4CF86EAFF1789C9C81F'
If point compression applied (scheme output for Profile B always applies point compression for Eph. public key as specified in clause C.3.4.2 above)
Eph. Private Key:
'99798858A1DC6A2C68637149A4B1DBFD1FDFF5ADDD62A2142F06699ED7602529' Eph. Shared Key:
'6C7E6518980025B982FBB2FF746E3C2E85A196D252099A7AD23EA7B4C0959CAE'
Eph. Enc. Key:
'8A65C3AED80295C12BD55087E965702A'
ICB:
'EF285B4061C3BAEE858AB6EC68487DAE'
Scheme-input corresponding to the plaintext-block:
'00012080F6' Cipher-text vaue:
'46A33FC271' Eph. mac key:
'A5EBAC0BC48D9CF7AE5CE39CD840AC6C761AEC04078FAB954D634F923E901C64'
MAC-tag value:
'6AC7DAE96AA30A4D' Scheme Output:
'039AAB8376597021E855679A9778EA0B67396E68C66DF32C0F41E9ACCA2DA9B9D146A33FC2716AC7DAE96AA30A4D'
uncompressed:
'0472DA71976234CE833A
'0272DA71976234CE833A
'F1AB1074477EBCC7F554
If compressed:
'039AAB8376597021E855
'049AAB8376597021E855
'99798858A1DC6A2C68637149A4B1DBFD1FDFF5ADDD62A2142F06699ED7602529' Eph. Shared Key:
'6C7E6518980025B982FB
'8A65C3AED80295C12BD5
'EF285B4061C3BAEE858A
'00012080F6' Cipher-text vaue:
'46A33FC271' Eph. mac key:
'A5EBAC0BC48D9CF7AE5C
'6AC7DAE96AA30A4D' Scheme Output:
'039AAB8376597021E855
C.4.4.2 Network specific identifier-based SUPI |R16| p. 243
The following test data set corresponds to ECIES-based encryption in the UE for network specific identifier-based SUPI and ECIES Profile B.
SUPI is: verylongusername1@3gpp.com
ECIES test data
The Scheme Output is computed in the UE as defined in Figure C.3.2-1 of clause C.3.2 with following data:
Home Network Public Key:
uncompressed:
0472DA71976234CE833A6907425867B82E074D44EF907DFB4B3E21C1C2256EBCD15A7DED52FCBB097A4ED250E036C7B9C8C7004C4EEDC4F068CD7BF8D3F900E3B4',
if compressed:
'0272DA71976234CE833A6907425867B82E074D44EF907DFB4B3E21C1C2256EBCD1'
Home Network Private Key (Not available in the UE, provided here only for test purposes):
'F1AB1074477EBCC7F554EA1C5FC368B1616730155E0041AC447D6301975FECDA'
Eph. Public Key(scheme output for Profile B always applies point compression for Eph. public key as specified in clause C.3.4.2 above):
compressed:
'03759BB22C563D9F4A6B3C1419E543FC2F39D6823F02A9D71162B39399218B244B'
Eph. Private Key:
'90A5898BD29FFA3F261E00E980067C70A2B1B992A21F5B4FEF6D4DF69FE804AD'
Eph. Shared Key:
'BC3529ED79541CF8C007CE9806330F4A5FF15064D7CF4B16943EF8F007597872'
Eph. Enc. Key:
'84F9A78995D39E6968047547ECC12C4F'
Scheme-input corresponding to the plaintext-block:
'766572796C6F6E67757365726E616D6531'
Cipher-text vaue:
'BE22D8B9F856A52ED381CD7EAF4CF2D525'
Eph. mac key:
'39D5517E965F8E1252B61345ED45226C5F1A8C69F03D6C91437591F0B8E48FA0'
MAC-tag value:
'3CDDC61A0A7882EB' Scheme Output:
ecckey03759BB22C563D9F4A6B3C1419E543FC2F39D6823F02A9D71162B39399218B244B.cipBE22D8B9F856A52ED381CD7EAF4CF2D525.mac3CDDC61A0A7882EB
0472DA71976234CE833A
'0272DA71976234CE833A
'F1AB1074477EBCC7F554
compressed:
'03759BB22C563D9F4A6B
'90A5898BD29FFA3F261E
'BC3529ED79541CF8C007
'84F9A78995D39E696804
'766572796C6F6E677573
'BE22D8B9F856A52ED381
'39D5517E965F8E1252B6
'3CDDC61A0A7882EB' Scheme Output:
ecckey03759BB22C563D