Content for TS 33.501 Word version: 19.0.0
1…
4…
5…
5.3…
5.9…
5.10…
6…
6.1.3…
6.1.4…
6.2…
6.2.2…
6.3…
6.4…
6.5…
6.6…
6.7…
6.8…
6.9…
6.10…
6.11
6.12…
6.13
6.14…
6.15…
6.16…
7…
7A…
7A.2.3…
7B…
8…
9…
10…
11…
12…
13…
13.2.2…
13.2.4…
13.3…
13.4…
14…
15…
16…
A…
B…
C…
D…
E…
F…
G…
I…
I.9…
J…
K…
M…
N…
O…
P…
R
S…
T…
U…
V…
W…
X…
Y…
Z…
X Security aspects of enablers for Network Automation (eNA) for the 5G system (5GS)
X.1 General
X.2 Authorization of NF Service Consumers for data access via DCCF
X.3 Authorization of NF Service Consumers for data access via DCCF when notification sent via MFAF
X.4 Security protection of data via Messaging Framework
X.5 Protection of data transferred between AF and NWDAF
X.6 Protection of UE data in transit between NFs
X.7 User consent requirements
X.8 Protection of data and analytics exchange in roaming case
X.8.1 General
X.8.2 Procedure for protection of analytics exchange in roaming case
X.8.2.1 Policies configured locally in Roaming entry NWDAF producer
X.8.2.2 Policies configured as extended claims in access token
X.9 Authorization of selection of participant NWDAF instances in the Federated Learning group
X.10 Security for AI/ML model storage and sharing
...
...
X (Normative) Security aspects of enablers for Network Automation (eNA) for the 5G system (5GS) |R17| p. 302
X.1 General p. 302
This Annex provides security requirements and procedures for the Network Automation features.
The feature for enablers for Network Automation by 5GS is described in 3GPP TS23.501[2] and 3GPP TS23.288 [105].
X.2 Authorization of NF Service Consumers for data access via DCCF p. 302
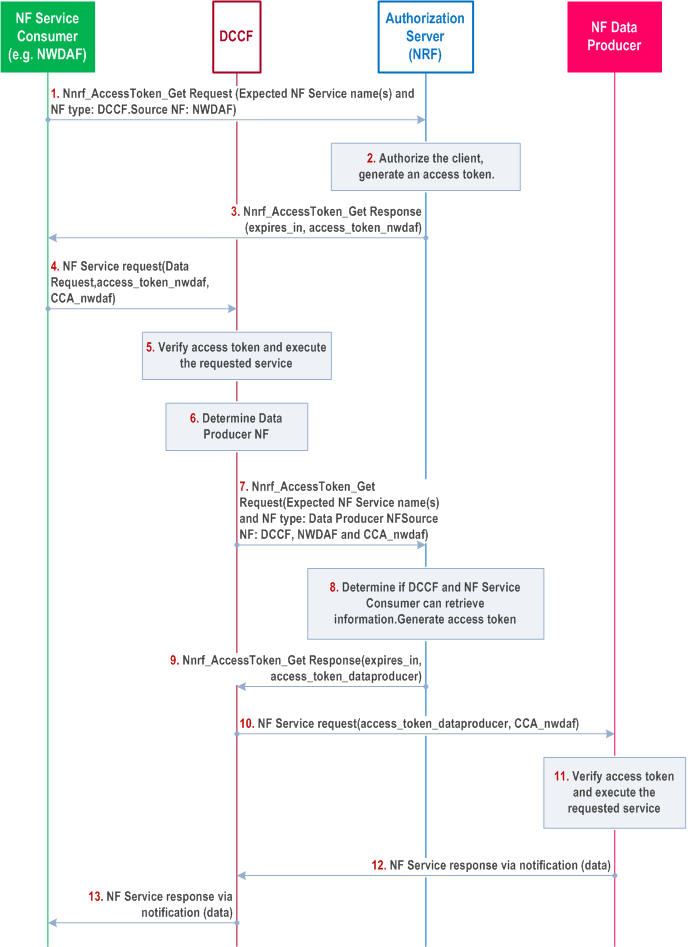
The detailed procedure for NF Service Consumer to receive data from Service Producers via DCCF is depicted in Figure X.2-1:
Step 1-3.
NF Service Consumer shall send a request to the NRF to receive an access token to request services of DCCF, to be used for data collection request. NRF after verifying shall generate access token and sends it to the NF Service Consumer.
Step 4.
The NF Service Consumer initiates a NF service request to the DCCF which includes the access_token_nwdaf. The NF Service Consumer shall also generate a Client Credentials Assertion (CCA) token (CCA_NWDAF) as described in the clause 13.3.8 and includes it in the request message in order to authenticate itself towards the NF Service Producers.
Step 5.
The DCCF shall verify if the access_token_nwdaf is valid and executes the service. If the NRF does not support authorization of the source NF (e.g. NWDAF) for data access via the DCCF (e.g. if the NRF is Rel-16), the DCCF authorizes the data access of the NF Service Consumer.
Step 6.
The DCCF determines the NF Service Producer(s) from where the data is to be collected (as specified in clause 6.2.6.3.2 in TS 23.288).
Step 7.
The DCCF sends a Nnrf_AccessToken_Get request to NRF including the information to identify the target NF (NF Service Producer), the source NF (NF Service Consumer e.g. NWDAF), the NF Instance ID of DCCF and the CCA_NWDAF provided by the NF Service Consumer. The nfInstanceId IE attribute in the access token request (Nnrf_AccessToken_Get ) indicates the NF instance ID of the DCCF as intermediate NF Service Consumer, whereas the sourceNfInstanceId IE attribute indicates the source NF instance ID (NF Service Consumer e.g., NWDAF).
Step 8.
The NRF shall check whether the DCCF and the NF Service Consumer (e.g. NWDAF) are allowed to access the service provided by the identified NF Service Producers, and the DCCF as the proxy is allowed to request the service from the identified NF Service Producers on behalf the NF Service Consumer. NRF authenticates both DCCF and NWDAF based on one of the SBA methods described in clause 13.3.1.2.
Step 9.
The NRF after successful verification then generates and provides an access token to the DCCF as described in the clause 13.4.1.1.2, with NF Instance ID of the DCCF (subject), and an additional access token claim containing the identity ofthe source NF Service Consumer, in order to authorize both DCCF and NF Service Consumer (e.g.. NWDAF) to consume the services of NF Service Producer.
Step 10.
In the case the NRF is from Rel-16 or earlier, the NRF generates an OAuth2.0 access token with "subject" claim mapped to the intermediate NF Service Consumer, i.e., in this case DCCF, and no additional claim for the source NF Service Consumer (e.g., NWDAF) identity is added.
Step 11.
The NF Service Producer(s) authenticates the NF Service Consumer and ensures that the source NF Service Consumer identity is included as an access token additional claim. The NF Service Producer authenticates and authorizes the DCCF following clauses 13.3.2 and 13.4.1. After authentication and authorization is successful, the NF Service Producer(s) executes the service.
Step 12.
The NF Service Producer(s) shall provide requested data to the DCCF.
Step 13.
The DCCF forwards the received data to the NF Service Consumer(s).
X.3 Authorization of NF Service Consumers for data access via DCCF when notification sent via MFAF p. 304
The detailed procedure for NF Service Consumer to receive data from Service Producers via DCCF when notification is sent via MFAF is depicted in Figure X.3-1:
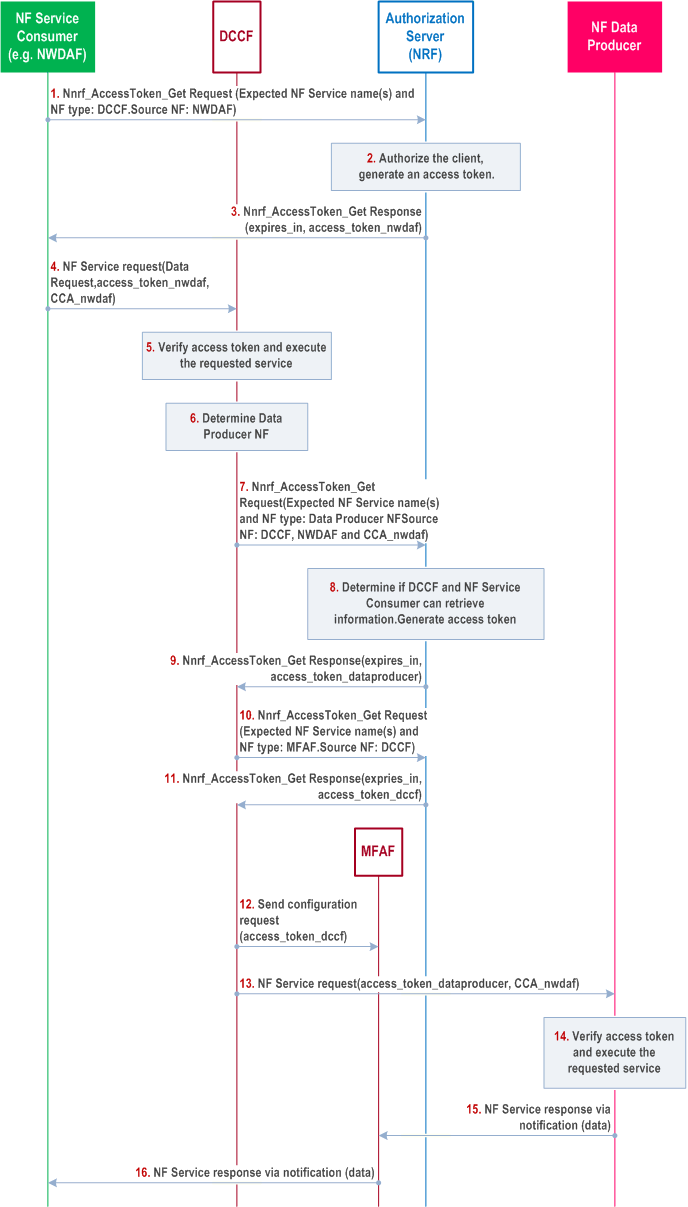
Steps 1-9 are same as Steps 1 - 9 of Annex X.2.
Step 10-11.
Steps 13 - 14 are same as Steps 10 - 11 of Annex X.2
The DCCF sends an access token request to the NRF to request service from MFAF. NRF after verifying sends access_token_dccf to DCCF to consume the services of MFAF.
Step 12.
DCCF shall then send the Nmfaf_3daDataManagement_Configure request to MFAF (as specified in the Clause 6.2.6.3.2 in TS 23.288) along with the access_token_dccf.
X.4 Security protection of data via Messaging Framework p. 306
The transfer of the data between the data source and data consumer via the messaging framework shall be confidentiality, integrity, and replay protected.
Confidentiality protection, integrity protection, and replay-protection shall be supported on the new interfaces between 3GPP entities and MFAF by reusing the existing security mechanism defined for SBA in Clause 13.
X.5 Protection of data transferred between AF and NWDAF p. 306
As specified in TS 23.288, the NWDAF may interact with an AF to collect data from UE Application(s) as an input for analytics generation. The AF can be in the MNO domain or an AF external to MNO domain. To enhance the 5GS to support collection and utilisation of UE related data for providing the inputs to generate analytics information (to be consumed by other NFs), the communication between AF and NWDAF needs to be secured.
The NWDAF interacts with the 5GC NFs and the AF using Service-based Interfaces. The existing 5G security mechanism can be reused for the transfer of UE data over the SBA interface between AF and NWDAF. When the AF is located in the operator's network, the NWDAF uses Service-Based Interface as depicted in clause 13 to communicate with the AF directly. When the AF is located outside the operator's network, the NEF is used to exchange the messages between the AF and the NWDAF. The security aspects of NEF is specified in clause 12.
X.6 Protection of UE data in transit between NFs p. 306
According to clause 13.1.0, all network functions shall support mutually authenticated TLS and HTTPS. TLS shall be used for transport protection within a PLMN unless network security is provided by other means. Thus, communication between NFs is integrity, confidentiality and replay protected.
NFs shall obtain an access token from NRF for requesting analytics from an analytics function or providing analytics data to the analytics function.
X.7 User consent requirements p. 307
The user consent requirements for enablers of network automation shall comply with Annex V of the present document and TS 23.288.
For scenarios where local regulations permit, for example vPLMN and hPLMN subject to the same regulatory requirements, the NWDAF shall be deemed to be the enforcement point and shall be subject to the requirement specified in Annex V.
X.8 Protection of data and analytics exchange in roaming case |R18| p. 308
X.8.1 General p. 308
The protection of data and analytics exchange in roaming case including authorization and anonymization of data/analytics:
- Authorization at data and analytics level is enforced by the roaming entry NWDAF producer. The parameters used by NWDAF service consumer to request/subscribe to the services provided by NWDAF producer are defined in clause 6.1.5 of TS 23.288. Accordingly, the operator authorization policies can be configured locally in the NWDAF producer. Also, when the NWDAF in one PLMN requests an access token from the NRF in the peer PLMN, the access token request and the access token claims may contain the Analytics ID.
- The roaming entry NWDAF producer is responsible to control the amount of exposed data/analytics and to abstract or hide internal network aspects in the exposed data/analytics. The corresponding mechanisms used to restrict the data/analytics and/or anonymization are subject to the implementation.
X.8.2 Procedure for protection of analytics exchange in roaming case p. 308
X.8.2.1 Policies configured locally in Roaming entry NWDAF producer p. 308
Pre-requisites:
- Roaming entry NWDAF producer, i.e. NWDAFp shall be pre-configured with a list of allowed analytics per PLMN.
- If token-based authorization is used, NWDAFc shall have acquired an access token from the PLMN2 to consume the services exposed in Nwdaf_RoamingAnalytics_Subscribe/Request APIs.
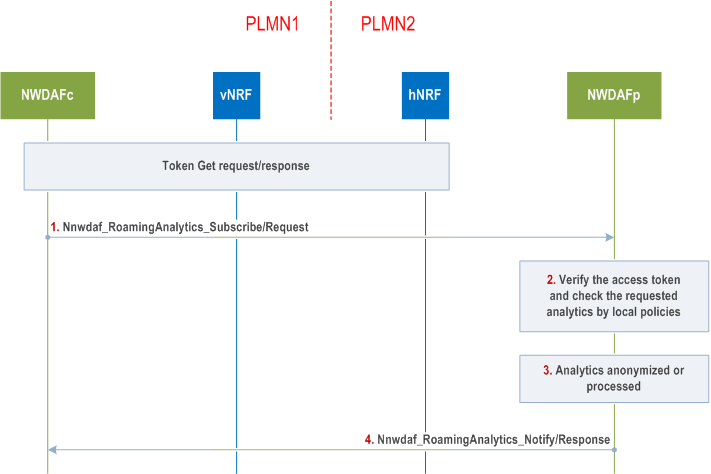
Step 1.
NWDAFc sends Nnwdaf_RoamingAnalytics_Subscribe /Request message to NWDAFp to request analytics.
Step 2.
The roaming entry NWDAFp shall verify the service request, including verifying token and the visited PLMN ID and determine whether the requested analytics are allowed to be exposed to NWDAFc in PLMN1 by pre-configured policies.
Step 3.
The roaming entry NWDAFp shall apply the security policies per consumer (PLMN) to the requested analytics and decide on their anonymization, restriction or desensitization based on operator's policy.
Step 4.
NWDAFp returns the requested and processed analytics to NWDAFc.
X.8.2.2 Policies configured as extended claims in access token p. 309
Pre-requisite:
- The producer NRF has the NF profile of the NF Service Producer including the list of allowed Analytics ID(s) per PLMN. According to clause 5.2.1 of TS 29.510, the NF profile can be configured in the NRF by other means such as O&M.
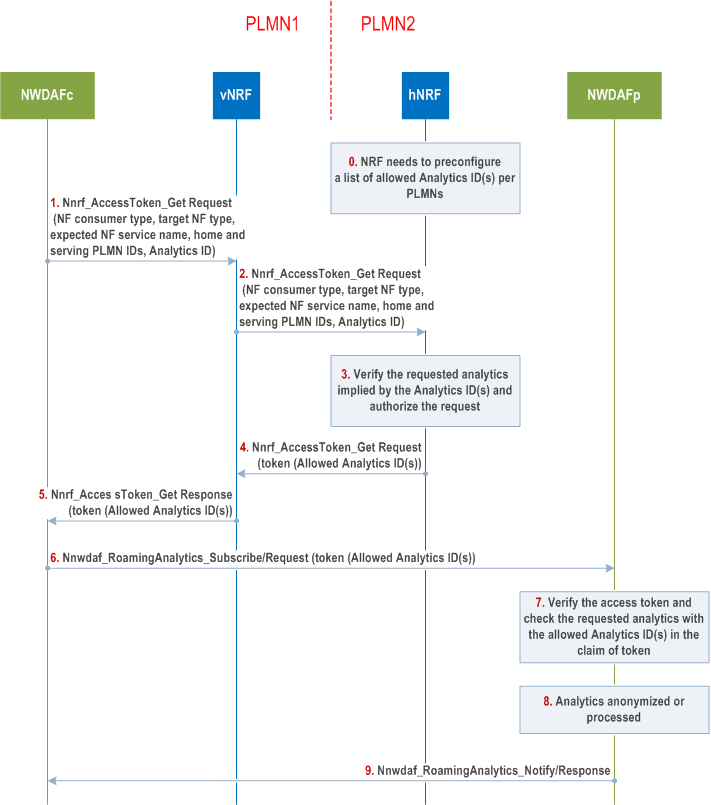
Step 1.
NWDAFc sends an access token get request to the consumer NRF as specified in clause 13.4.1. The access token request may contain the Analytics ID.
Step 2.
vNRF forwards the token request message to hNRF as specified in clause 13.4.1.
Step 3.
The home network hNRF shall verify the access token get request as specified 13.4.1, and determine whether the requested analytics implied by the Analytics ID(s) can be obtained by the visited PLMN according to the allowed Analytics ID(s) of the visited PLMN.
Step 4.
If the verification success, hNRF issues the token as specified in clause 13.4.1. The allowed Analytics ID(s) of the visited PLMN may be included in the token.
Step 5.
The vNRF forwards the Token_Get Response to NWDAFc as specified in clause 13.4.1.
Step 6.
If the requested analytics is within the claim of token, the NWDAFc sends Nnwdaf_RoamingAnalytics_Subscribe /Request with the issued token to NWDAFp.
Step 7.
The roaming entry NWDAFp verifies the service request, including verifying token as specified in clause 13.4.1, and whether the requested analytics is within the allowed Analytics ID(s) in the token.
Step 8.
The roaming entry NWDAFp shall apply the security policies per consumer (PLMN) to the requested analytics and decide on their anonymization, restriction or desensitization based on operator's policy.
Step 9.
The Roaming entry NWDAFp returns the requested and processed analytics to the NWDAFc.
X.9 Authorization of selection of participant NWDAF instances in the Federated Learning group |R18| p. 310
The authorization for selecting participant NWDAF instances in the Federated Learning (FL) group uses token-based authorization as specified in clause 13.4.1, with the following additions.
Figure X.9-1 depicts the authorization mechanism for NWDAF containing MTLF acting as FL Server to initiate the Federated Learning process on the NWDAF containing MTLF(s) acting as FL Client(s). The authorization is based upon the FL capability type (FL server and/or FL client) and Vendor ID provided by the NWDAF containing MTLF acting as FL server during registration, and the Analytics ID and Interoperability Indicator per Analytics ID provided by the NWDAF containing MTLF acting as FL client during registration.
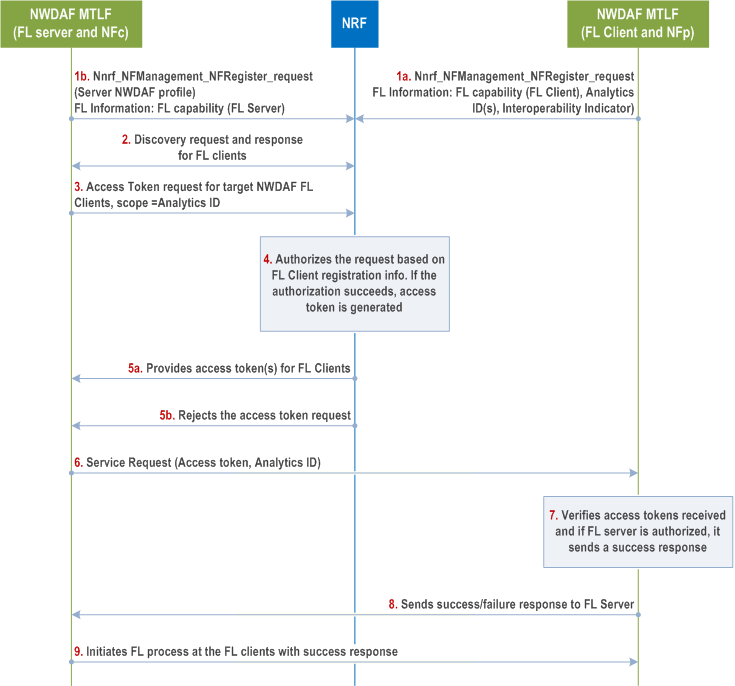
Step 1a.
Authorization of the NWDAF containing MTLF acting as FL client and receiving global model information from NWDAF containing MTLF acting as FL server is implicit, since it can join a Federated Learning group only when selected by the NWDAF containing MTLF acting as FL server.
The NWDAF containing MTLF acting as FL client registers to the NRF with its FL related information, including Vendor ID, supported FL capability (FL client), Analytics ID(s) and Interoperability Indicator per Analytics ID as described in clause 5.2 of TS 23.288.
Step 1b.
The NWDAF containing MTLF acting as FL server registers to the NRF with its Vendor ID, FL capability (FL Server).
Step 2.
The NWDAF containing MTLF acting as FL server (NF Service Consumer) sends a discovery request to NRF and receives the available NWDAFs containing MTLF acting as FL client(s) (NF Service Producer) as a response, as specified in clause 6.2C.2.1 of TS 23.288.
Step 3.
The NWDAF containing MTLF acting as FL server (NF Service Consumer) sends an access token request to the NRF as specified in clause 13.4.1. The access token request may contain the Analytics ID for the requested Federated Learning process.
Step 4.
The NRF authorizes the NWDAF containing MTLF acting as FL server (NF Consumer) based upon the information received in Step 1b, and after verifying that the Server NWDAF's Vendor ID is included in the Interoperability Indicator for the requested Analytics ID provided in Step 1a. If the authorization succeeds, NRF generates the access token(s) as specified in clause 13.4.1. The access token claims may include the Analytics ID for the request Federated Learning process.
Step 5a, 5b.
The NRF sends the access token to the NWDAF containing MTLF acting as FL Server, or rejects the request in case of failed authorization, as described in clause 13.4.1.
Step 6.
The NWDAF containing MTLF acting as FL server sends the service request to the NWDAF(s) containing MTLF acting as FL client with the access token received in Step 5a. along with the Analytics ID information for which the FL process is to be performed, as described in TS 23.288.
Step 7, 8.
The NWDAF containing MTLF acting as FL client (NF Service Producer) verifies the received access token as specified in clause 13.4.1. In case of successful access token verification, the NWDAF containing MTLF acting as FL client sends a success response to the NWDAF containing MTLF acting as FL server, as described in TS 23.288.
Step 9.
After a successful response from the NWDAF(s) containing MTLF acting as FL client, the NWDAF containing MTLF acting as FL server initiates the Federated Learning process as described in TS 23.288.
X.10 Security for AI/ML model storage and sharing |R18| p. 312
The detailed procedure for secured and authorized AI/ML model sharing between different vendors is depicted in Figure X.10-1:
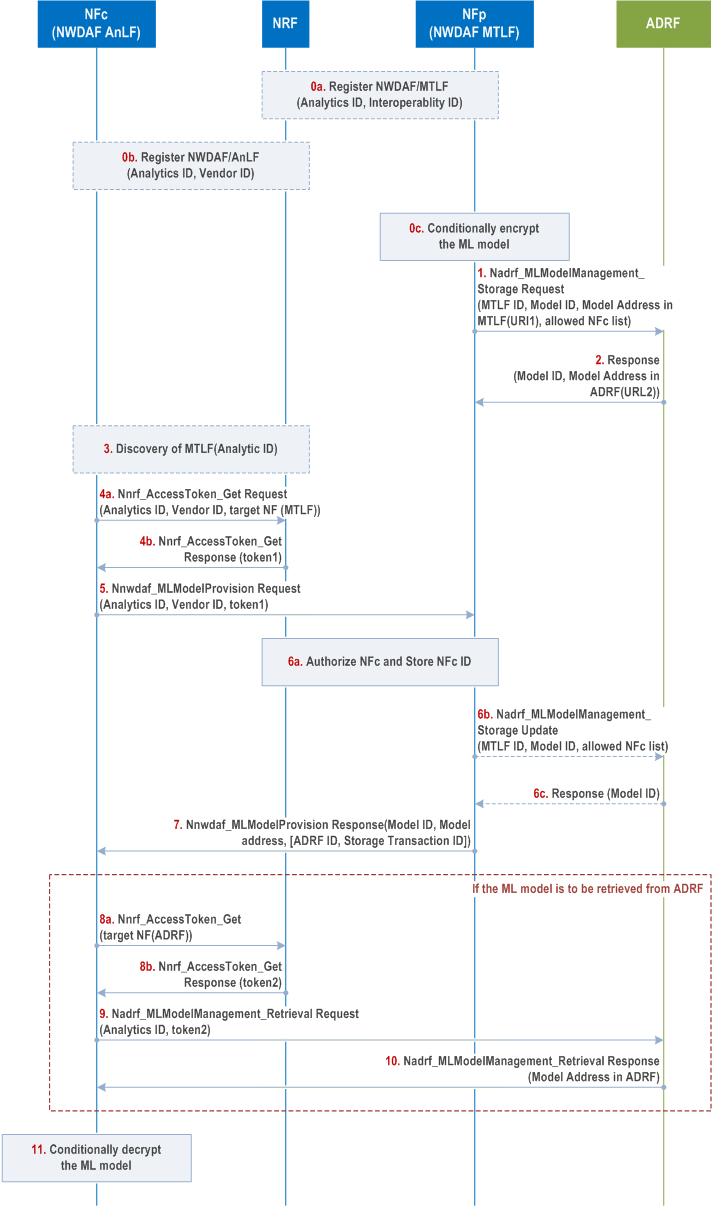
Step 0a.
NF Service producer i.e. NWDAF containing MTLF registers its NF profile in the NRF with ML Model Interoperability indicator per Analytics ID as described in clause 5.2 of TS 23.288. The ML Model Interoperability indicator is a list of NWDAF providers (vendors) that are allowed to retrieve ML models from this NWDAF containing MTLF.
Step 0b.
NF Service consumer e.g., NWDAF registers at the NRF including its Vendor ID, if the NF Service consumer is MTLF, the NWDAF containing MTLF also registers its Interoperability indicator per Analytics ID.
Step 0c.
The model is stored in encrypted format unless both the AI/ML model producer (NWDAF MTLF) and storage platform (ADRF) are part of the same system and belong to the same vendor and operator security domain.
Storage of the model in encrypted format can be required by the trust model established to store and share AI/ML models. The trust model between AI/ML NF producer (NWDAF MTLF), storage platform (ADRF) and NF consumer (e.g., AnLF) is to be determined during the implementation phase among operator and the providers of the different platforms (MTLF, AnLF, ADRF). How the model is encrypted is vendor specific. Key distribution is not specified in this document.
Step 1.
If NWDAF containing MTLF determines to store ML model in ADRF, NWDAF containing MTLF triggers the Nadrf_MLModelManagement_StorageRequest as described in TS 23.288, optionally including an allowed NFc list. The absence of allowed NFc list indicates that only the MTLF which stored the model is allowed to retrieve the model.
Step 2.
ADRF sends the response to NWDAF containing MTLF as described in TS 23.288.
Step 3.
NF Service consumer e.g., NWDAF performs Nnrf_NFDiscovery_Request operation with the requested Analytics ID to select a suitable NF Service Producer e.g., NWDAF containing MTLF.
In case of the NF service consumer (e.g. NWDAF containing MTLF) request ML models on behalf of another ML model consumer (e.g., NWDAF containing AnLF), before step 3 the ML model consumer (e.g., NWDAF containing AnLF) obtains a token for the analytics ID from NRF same as step 4 which authorizes the ML model consumer to use model retrieval service provided by the NF service consumer and sends the model retrieval service request to the NF service consumer with the Analytics ID, the obtained token, the Vendor ID and the CCA of the ML model consumer.
Step 4a.
NF Service consumer e.g., NWDAF requests an access token from the NRF using the Nnrf_AccessToken_Get request operation. The token request message contains, besides the parameters described in clause 13.4.1.1.2, the Vendor ID of the NF Service consumer and the Analytics ID. If the NF Service consumer is NWDAF containing MTLF, it also includes its Interoperability indicator per Analytics ID in the request.
In case of NF service consumer request ML models on behalf of another ML model consumer (e.g., NWDAF containing AnLF), the token request message shall also contain the NF instance ID and Vendor ID of the ML model consumer. The NF Service Consumer also includes the CCA of the ML model consumer that it has received in the service request from the ML model consumer.
Step 4b.
NRF checks whether the NF Service consumer is authorized to access the requested service in NWDAF containing MTLF. The NRF verifies that the NF Consumer's Vendor ID is included in the NF Service Producer's interoperability indicator for the Analytics ID. If NF Service consumer is a NWDAF containing MTLF, the NRF also verifies that NF Service consumer's Interoperability indicator is subset of the NF Service Producer's interoperability indicator for the Analytics ID. If the authorization is successful, the NRF grants the token (token1) including the Analytics ID as specified in the clause 13.4.1.
In case of NF Service Consumer request ML models on behalf of another ML model consumer, the NRF also verifies that the Vendor ID of ML model consumer is included in the NF Service Producer's interoperability indicator for the Analytics ID and grants the token(token1) also including the NF Instance ID of ML model consumer in the sourceNfinstanceId IE attribute. The NRF also authenticates the ML model consumer based on one of the SBA methods described in clause 13.3.1.2.
Step 5.
NF Service Consumer performs Nnwdaf_MLModelProvision (Analytics ID, Vendor ID and token1) service operation at the NWDAF containing MTLF to retrieve ML models for the Analytics ID.
In case of NF Service Consumer request ML models on behalf of another ML model Consumer, the Nnwdaf_MLModelProvision service operation shall also contain the NF instance ID and Vendor ID of the ML model consumer and the CCA of the ML model consumer.
Step 6a.
The NF Service Producer authenticates the NF Service Consumer and verifies the access token as specified in the clause 13.4.1.1.2 and ensures that the Analytics ID is included in the access token. If verification is successful, NWDAF containing MTLF determines the ML model to be shared for the requested Analytics ID and stored the NF instance ID of NF Service Consumer as part of allowed NF instance list for the ML model.
If the NF Service Consumer request ML models on behalf of the ML model Consumer, the NF Service Producer also authenticates the ML model consumer following clauses 13.3.2 and 13.4.1, and ensures that the ML model consumer is authorized according to the sourceNfinstanceId IE attribute of the access token provided by the NF Service Consumer. The NF Service Producer stores also the NF instance ID of Model Consumer as part of allowed NF instance list for the ML model.
Step 6b.
If the determined ML model is stored in ADRF, and if the NF Service Consumer is not yet in the allowed NFc list stored at the ADRF, the NWDAF containing MTLF triggers the update of Nadrf_MLModelManagement_StorageRequest at the ADRF, with NF ID of NWDAF containing MTLF and Model ID, adding the NF Service Consumer to the allowed NFc list. The ADRF verifies that the requesting NWDAF containing MTLF is same as the one that stored the model. Then, ADRF stores the allowed NF instance list for the ML model referenced by the Model ID.
Step 6c.
ADRF sends the response to NWDAF containing MTLF which contains Model ID.
Step 7.
NWDAF containing MTLF sends Nnwdaf_MLModelProvision Notify to the NF Service Consumer with Model ID, the address of the determined ML model, which can be either the one stored in NWDAF containing MTLF or in ADRF,or ADRF(set) ID. If the address of the determined ML model is provided, steps 8a to 10 are skipped.
If the ADRF(set) ID is provided, the following steps are applied:
Step 8a.
NF Service Consumer requests an access token from the NRF to be authorized to retrieve the model stored in ADRF as specified in clause 13.4.1.
Step 8b.
NRF verifies that the NF Service consumer e.g., NWDAF is authorized to access the service provided by the ADRF. If verification is successful, NRF grants the token (token2), based on the information provided in ADRF's NF profile.
Step 9.
NF Service consumer e.g., NWDAF requests to retrieve the target model by sending Nadrf_MLModelManagement_Retrieval Request as described in clause 10.3.4 of TS 23.288, including token2.
Step 10.
ADRF authenticates the NF Service Consumer and verifies the access token (token2) as specified in the clause 13.4.1.1.2. ADRF verifies also the NF Service Consumer's NF ID is included in the allowed NF instance list for the ML model and/or is same as the NF ID of the MTLF that stored the model. If verification is successful, ADRF sends Nadrf_MLModelManagement_Retrieval Response to the NF Service Consumer, which contains the address of the stored model in ADRF.
Step 11.
NF Service Consumer retrieves the ML model from NWDAF containing MTLF or ADRF based on the ML model file address and decrypts the model per the vendor's implementation.