TS 33.501
Security Architecture and Procedures for 5G System
V18.6.0 (PDF)
2024/06 … p.
V17.14.0
2024/06 … p.
V16.18.0
2024/03 262 p.
V15.18.0
2024/03 196 p.
- Rapporteur:
- Dr. Zugenmaier, Alf
NTT DOCOMO INC.
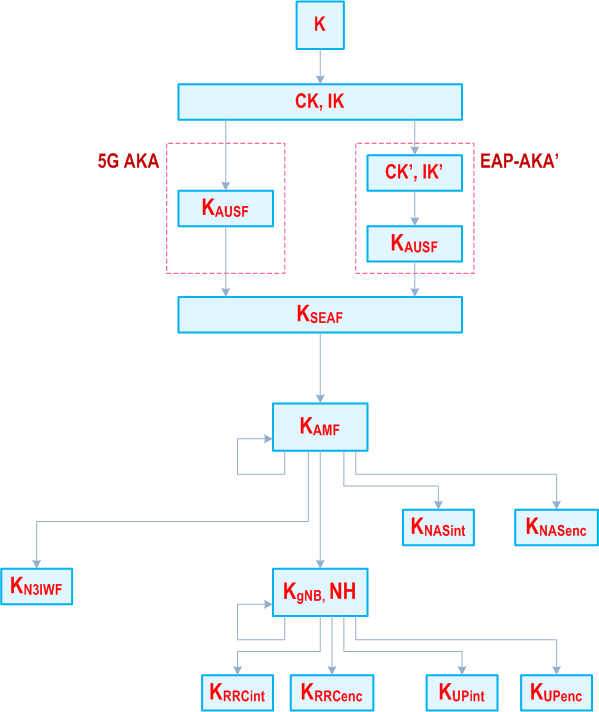
essential Table of Contents for TS 33.501 Word version: 18.6.0
each title, in the "available" or "not available yet" area, links to the equivalent title in the CONTENT
editorial Errors in TS 33.501 Word version: 18.5.0
bad references are displayed in this form, followed by the correction
bad references for which a correction was not found are displayed in this form
bad references for which a correction was not found are displayed in this form
- Missing clauses in the Table of Contents
-
6.16.2 Connection Resume in CM-IDLE with Suspend to a new ng-eNB 8.5.3 Initial Attach Procedure 13.3.5 Authentication between SEPP and SCP X.2 Authorization of NF Service Consumers for data access via DCCF
X.3 Authorization of NF Service Consumers for data access via DCCF when notification sent via MFAF
X.4 Security protection of data via Messaging Framework
X.5 Protection of data transferred between AF and NWDAF
X.6 Protection of UE data in transit between NFs