Content for TS 23.228 Word version: 18.6.0
1…
3…
4…
4.2.4…
4.3…
4.4…
4.13…
4.16…
5…
5.2…
5.3…
5.4…
5.4.7…
5.4.8…
5.4a…
5.5…
5.5.3…
5.6…
5.6.3…
5.7…
5.7.3…
5.7.5…
5.7.8…
5.8…
5.10…
5.11…
5.11.3…
5.11.3.3
5.11.3.4
5.11.4…
5.11.5…
5.11.5.3…
5.11.6…
5.12…
5.16…
5.16.2…
5.19…
5.20…
A…
E…
E.2.2…
G…
G.5…
H
I…
J…
K…
L…
M…
M.3…
N…
P…
Q…
Q.2.5…
R…
S…
T…
U…
U.2…
V…
W…
X…
Y…
Z…
AA…
AA.3…
AB…
AC…
AC.7…
AC.7.2…
AC.7.2.2
AC.7.2.3…
AC.7.4…
AC.9…
W Support of IMS Services for roaming users in deployments without IMS-level roaming interfaces
W.1 General
W.2 Architecture
W.2.1 EPS
W.2.2 5GS
W.4 Procedures related to PLMN ID change
W.4.1 Subscription to changes of PLMN ID at IMS Initial Registration
W.4.2 UE is not active in an IMS voice session
W.4.3 UE is active in an IMS voice session
...
...
W (Normative) Support of IMS Services for roaming users in deployments without IMS-level roaming interfaces |R14| p. 323
W.1 General p. 323
This clause describes the functions that are used to support IMS services for roaming users in deployments without IMS-level roaming interfaces. This Annex is applicable to UEs connected to EPS and 5GS. In this roaming model the mobility anchor (i.e. PGW or UPF) is located in the home PLMN and therefore UE IMS signalling and user plane traffic are routed to home PLMN. It is assumed that confidentiality protection is not used in HPLMN and VPLMN for IMS media plane traffic.
For the LBO roaming model where P-CSCF is in VPLMN, see Annex M.
W.2 Architecture p. 323
W.2.1 EPS |R18| p. 323
The architecture to support IMS services for roaming users, including Voice over IMS, in deployments without IMS-level roaming interfaces is shown in Figure W.2-1
The following architecture requirements apply:
- P-CSCF (at HPLMN) identifies the serving network (VPLMN) where the UE is located using the procedure defined in clause W.3.
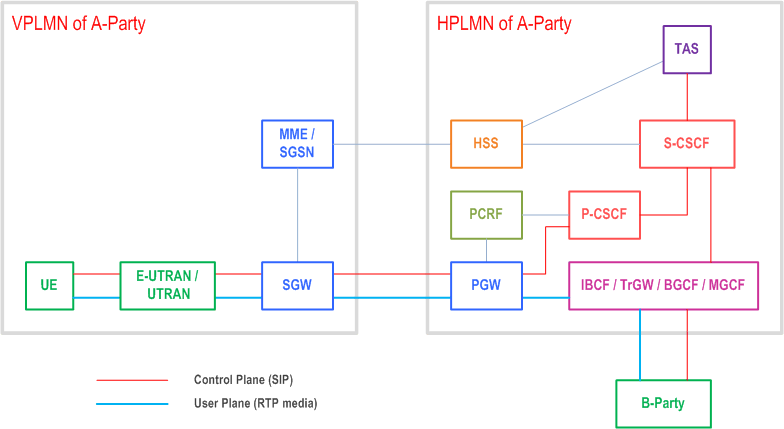
The corresponding architecture for 5GS is defined in clause Y.9.2.
W.2.2 5GS |R18| p. 323
See clause Y.9.2.
W.3 Void
W.4 Procedures related to PLMN ID change |R18| p. 324
W.4.1 Subscription to changes of PLMN ID at IMS Initial Registration p. 324
In deployments without IMS-level roaming interfaces, the home network determines the serving PLMN of the UE using procedure defined in TS 23.203, TS 23.503 or TS 29.214, where the P-CSCF requests the PCRF/PCF to report the PLMN identifier where the UE is currently located. The received PLMN ID information is then forwarded in the SIP REGISTER request.
This procedure shall be applied by the P-CSCF at initial UE IMS registration.
The below procedure relates to EPS, the corresponding procedure for 5GS is defined in Annex Y.
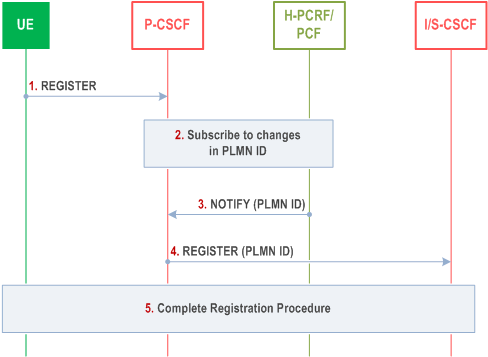
Step 1.
The UE sends a SIP REGISTER request to the P-CSCF.
Step 2.
If this is the initial IMS registration then the P-CSCF subscribes to the PCRF/PCF to be notified of the PLMN ID where the UE is currently attached. The subscription to PLMN changes is active as long as the UE is IMS registered.
Step 3.
The PCRF/PCF forwards the PLMN ID to the P-CSCF. The P-CSCF stores the PLMN ID.
Step 4.
The P-CSCF includes the received PLMN ID in the SIP REGISTER request before forwarding the request to the I-CSCF.
Step 5.
Normal IMS registration procedure is then completed.
W.4.2 UE is not active in an IMS voice session p. 324
The following procedure shall be applied by IMS at reception of PLMN change when the UE is not active in an IMS voice call, and when the PDN connection/PDU session is kept at PLMN change.
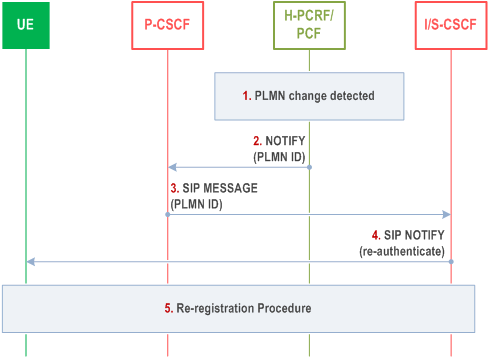
Step 1.
EPC/5GC detects PLMN change.
Step 2.
H-PCRF/PCF notifies P-CSCF that PLMN change has occurred and indicates the new PLMN ID.
Step 3.
P-CSCF sends SIP MESSAGE with new PLMN ID to S-CSCF.
Step 4.
Based on regulatory requirements (see NOTE 2), S-CSCF sends SIP NOTIFY with re-authentication request to the UE.
Step 5.
UE initiates re-registration procedure. During the re-registration procedure, the P-CSCF may update the SIP signalling encryption depending on roaming agreements, e.g. moving from HPLMN to VPLMN can result in turning off IMS encryption while retaining integrity protection of IMS signalling.
W.4.3 UE is active in an IMS voice session p. 325
The following procedure shall be applied by IMS at reception of PLMN change when the UE is active in an IMS voice call, and when the PDN connection/PDU session is kept at PLMN change.
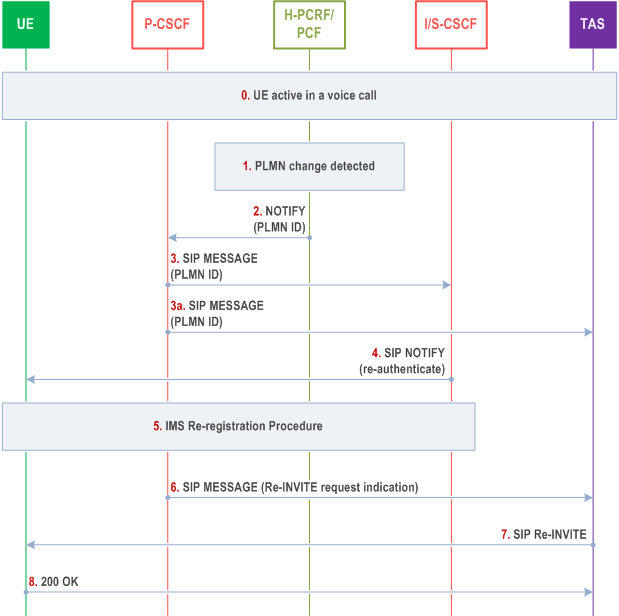
Step 0.
UE is active in an IMS voice call.
Step 1.
EPC/5GC detects PLMN change.
Step 2.
H-PCRF/PCF notifies the P-CSCF that PLMN change has occurred and indicates the new PLMN ID.
Step 3.
P-CSCF sends SIP MESSAGE with the new PLMN ID to the S-CSCF.
Step 3a.
P-CSCF sends SIP MESSAGE with new PLMN ID to the TAS so that the TAS may update any charging records with the new PLMN ID.
Step 4.
Based on regulatory requirements (see NOTE 1), S-CSCF sends SIP NOTIFY with re-authentication request to the UE.
Step 5.
UE initiates re-registration procedure. During the re-registration procedure, the P-CSCF may update the SIP signalling encryption depending on roaming agreements, e.g. moving from HPLMN to VPLMN can result in turning off IMS encryption while retaining integrity protection of IMS signalling.
Step 6.
Once the re-registration procedure is completed and based on regulatory requirements (see NOTE), the P-CSCF may send a SIP MESSAGE to the TAS indicating that TAS should send a re-INVITE request to the UE.
Step 7.
TAS sends SIP Re-INVITE to UE including, subject to the privacy settings associated with the original call, call related information (e.g. calling and called party information, indication whether UE was calling party or called party in the call, redirecting party information (if present), media endpoints and used codecs). Codec endpoints are translated in the P-CSCF if needed. The UE should not reveal this information to the user.
Step 8.
UE sends SIP 200 OK to TAS.