Content for TS 23.228 Word version: 18.6.0
1…
3…
4…
4.2.4…
4.3…
4.4…
4.13…
4.16…
5…
5.2…
5.3…
5.4…
5.4.7…
5.4.8…
5.4a…
5.5…
5.5.3…
5.6…
5.6.3…
5.7…
5.7.3…
5.7.5…
5.7.8…
5.8…
5.10…
5.11…
5.11.3…
5.11.3.3
5.11.3.4
5.11.4…
5.11.5…
5.11.5.3…
5.11.6…
5.12…
5.16…
5.16.2…
5.19…
5.20…
A…
E…
E.2.2…
G…
G.5…
H
I…
J…
K…
L…
M…
M.3…
N…
P…
Q…
Q.2.5…
R…
S…
T…
U…
U.2…
V…
W…
X…
Y…
Z…
AA…
AA.3…
AB…
AC…
AC.7…
AC.7.2…
AC.7.2.2
AC.7.2.3…
AC.7.4…
AC.9…
H Example HSS deployment |R7| p. 246
This clause describes possible deployment scenarios for the HSS when it operates as an IMS only database.
The following depicts the HSS functionality as described in TS 23.002 repeated here for clarity; note that the functional description in TS 23.002 shall always be considered as the most updated version, if it is different than the version shown here. 3GPP HSS contains functions also known as HLR and AuC, which are needed for 3GPP GPRS and CS domain access authentication and authorization and overall subscription handling as well as service data management.
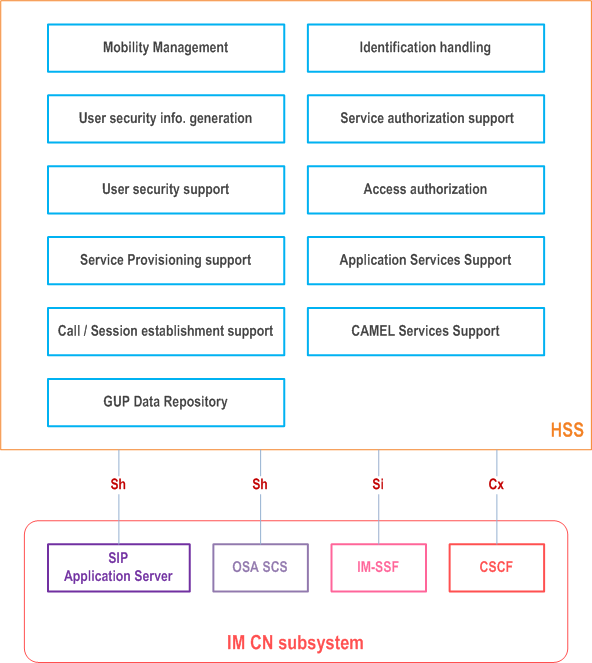
In cases where the HSS would operate as an IMS only entity, the functions and interfaces specific to IMS operations would be applicable. These include support of functionalities such as identification handling, service provisioning support, call/session establishment support, application services support, IMS access authentication and authorization provided by the interfaces Cx, Sh and Si (if applicable to interwork with CAMEL) and any additional subscription and configuration handling for IMS users. This type of configuration of the HSS would be used for access to the IMS as defined by, for example, TISPAN NGN.