Content for TS 23.228 Word version: 18.6.0
1…
3…
4…
4.2.4…
4.3…
4.4…
4.13…
4.16…
5…
5.2…
5.3…
5.4…
5.4.7…
5.4.8…
5.4a…
5.5…
5.5.3…
5.6…
5.6.3…
5.7…
5.7.3…
5.7.5…
5.7.8…
5.8…
5.10…
5.11…
5.11.3…
5.11.3.3
5.11.3.4
5.11.4…
5.11.5…
5.11.5.3…
5.11.6…
5.12…
5.16…
5.16.2…
5.19…
5.20…
A…
E…
E.2.2…
G…
G.5…
H
I…
J…
K…
L…
M…
M.3…
N…
P…
Q…
Q.2.5…
R…
S…
T…
U…
U.2…
V…
W…
X…
Y…
Z…
AA…
AA.3…
AB…
AC…
AC.7…
AC.7.2…
AC.7.2.2
AC.7.2.3…
AC.7.4…
AC.9…
E IP-Connectivity Access Network specific concepts when using GPRS and/or EPS to access IMS
E.0 General
E.1 Mobility related concepts
E.1.0 General
E.1.1 Procedures for P-CSCF discovery
E.1.1.0 General
E.1.1.1 GPRS/EPS procedure for P-CSCF discovery
E.1.2 Support for Enhanced Coverage for data centric UEs
E.2 QoS related concepts
E.2.1 Application Level Signalling for IMS
E.2.1.0 General
E.2.1.1 QoS Requirements for Application Level Signalling
E.2.1.2 Requirements for IM CN subsystem signalling flag
E.2.1.3 Application Level Signalling support for IMS services
E.2.1a PDP context/EPS Bearer procedures for IMS
E.2.1a.1 Establishing PDP Context/EPS bearer for IM CN Subsystem Related Signalling
E.2.1a.2 Deletion of PDP Context/EPS bearer used to transport IMS SIP signalling
...
...
E (Normative) IP-Connectivity Access Network specific concepts when using GPRS and/or EPS to access IMS |R6| p. 217
E.0 General p. 217
This clause describes the main IP-Connectivity Access Network specific concepts that are used for the provisioning of IMS services over GPRS and EPS system using GERAN and/or UTRAN radio access and/or E-UTRAN (using EPC only).
When using GPRS-access, the IP-Connectivity Access Network bearers are provided by PDP Context(s).
When using EPS the SGSN is responsible for mapping PDP Context(s) to EPS bearers, i.e. the UE (using GERAN/UTRAN) is using PDP Context(s) whereas EPS bearers are used from the SGSN towards the S-GW/P-GW. However, throughout this annex PDP context(s) are used when referring to an IP-CAN bearer for GPRS networks and when a UE is connected to EPS via GERAN/UTRAN access.
When GGSN/P-GW is shown, it represents either a GGSN or a P-GW for a specific UE connection towards a PDN.
E.1 Mobility related concepts p. 217
E.1.0 General p. 217
The Mobility related procedures for GPRS and EPS are described in TS 23.060 and TS 23.401 respectively and the IP address management principles are described in TS 23.221. As specified by the GPRS/EPS procedures, the UE shall acquire the necessary IP address(es) as part of the PDP Context activation procedures for GERAN/UTRAN access and Attach (or PDN connectivity)/EPS bearer activation procedure(s) for E-UTRAN.
If the UE changes its IP address due to changes triggered by the GPRS/EPS procedures or according to TS 23.221, then the UE shall re- register in the IMS.
If the UE acquires an additional IP address, then the UE may perform an IMS registration using this additional IP address as the contact address. If IMS registration is performed, this IMS registration may co-exist with the previous IMS registration from this UE and the UE shall be notified that this IMS registration results in multiple simultaneous registrations.
When a routeing area update or tracking area update is not performed due to the Idle mode Signalling Reduction feature being active (see TS 23.401 for more information), then the UE shall also not perform an IMS re registration because of such routeing area and tracking area change.
Similarly, the UE shall not perform an IMS re registration because the UE has moved between GERAN and UTRAN cells that share the same RAI.
When the PLMN changes, and the attempt to perform an inter-PLMN routeing area update or tracking area update is unsuccessful, then the UE should attempt to re-attach to the network using GPRS/EPS procedures and register for IMS services. Typically this will involve a different GGSN/P-GW.
In Dual Connectivity with EPC case, the UE shall use the access network information based on the primary cell of the Master RAN node that is serving the UE for network location information when the UE interacts with IMS, regardless whether the IMS traffic is routed via the Master RAN node or the Secondary RAN node or both.
E.1.1 Procedures for P-CSCF discovery p. 218
E.1.1.0 General p. 218
This clause describes the P-CSCF discovery procedures applicable for GERAN/UTRAN access. All the procedures described in clause 5.1.1 apply with the following additions:
P-CSCF discovery shall take place after GPRS/EPS attach and after or as part of a successful activation of a PDP context (in the case of GERAN/UTRAN access) and EPS bearer (in the case of E-UTRAN access) for IMS signalling using the following mechanisms:
- For GERAN/UTRAN access: Transfer a Proxy-CSCF address within the PDP Context Activation signalling to the UE, as described in clause E.1.1.1. The UE shall request the P-CSCF address(es) when activating the PDP context. The GGSN/P-GW shall send the P-CSCF address(es) to the UE when accepting the PDP context activation. Both the P-CSCF address(es) request and the P-CSCF address(es) shall be sent transparently through the SGSN/S-GW for GERAN/UTRAN.
- For E-UTRAN access: Transfer a P-CSCF address within the EPS Attach or PDN Connectivity Procedures to the UE, as described in clause E.1.1.1. The UE shall request the P-CSCF address(es) in the EPS Attach or PDN Connectivity request. The P-GW shall send the P-CSCF address(es) to the UE when accepting the EPS Default bearer activation. Both the P-CSCF address(es) request and the P-CSCF address(es) shall be sent transparently through the intermediate network entities (e.g. MME/S-GW).
E.1.1.1 GPRS/EPS procedure for P-CSCF discovery p. 218
This alternative shall be used for UE(s) not supporting DHCP. This may also be used for UE(s) supporting DHCP.
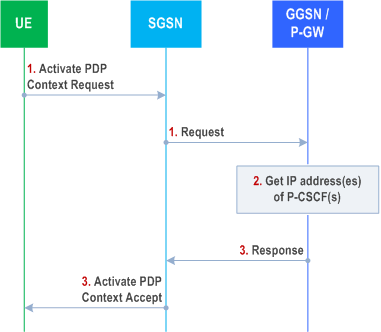
Step 1.
After reception of the IP address of a P-CSCF the UE may initiate communication towards the IM CN Subsystem.
E-UTRAN access only:
The procedure for E-UTRAN access applies to both Initial E-UTRAN Attach and PDN Connectivity Request.
The UE requests establishment of a PDP context according to clause 4.2.6 (QoS requirements for IM CN subsystem signalling). The UE indicates that it requests a P-CSCF IP address(es). The indication is forwarded transparently by the SGSN to the GGSN in the Create PDP Context Request or to the S-GW/P-GW in the Create Default Bearer Request.
Step 2.
The GGSN/P-GW gets the IP address(es) of the P-CSCF(s). The mechanism to do this is a matter of internal configuration and is an implementation choice.
Step 3.
If requested by the UE, the GGSN/P-GW includes the IP address(es) of the P-CSCF(s) in the Create PDP Context Response or in the Create Default bearer response. The P-CSCF address(es) is forwarded transparently by the SGSN to the UE.
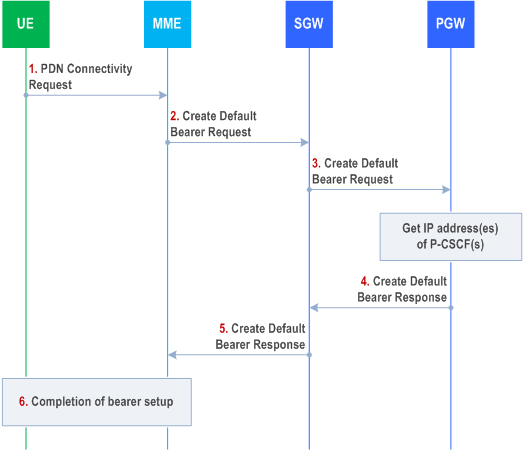
Step 1.
After reception of the IP address of a P-CSCF the UE may initiate communication towards the IM CN Subsystem.
During Initial Attach/PDN Connection Request, the UE indicates that it requests a P-CSCF IP address(es).
Step 2.
The MME sends a Create Default Bearer Request to the S-GW.
Step 3.
The S-GW forwards the request to the P-GW and the P-GW gets the IP address(es) of the P-CSCF(s). The mechanism to do this is a matter of internal configuration and is an implementation choice.
Step 4.
If requested by the UE, the P-GW includes the IP address(es) of the P-CSCF(s) in the Create Default Bearer Response.
Step 5.
The S-GW forwards the response to the MME
Step 6.
Completion of procedures, as described in TS 23.401.
E.1.2 Support for Enhanced Coverage for data centric UEs |R14| p. 219
Support for Enhanced Coverage (CE) for data centric UE is specified in TS 23.401.
If the UE's usage setting is set to "data centric" as defined in TS 23.221 and it is operating in CE mode B then IMS PS voice/video services are not to be used in this IP-CAN.
If the UE's usage setting is set to "data centric" and it is operating in CE mode B, then the UE shall reject any SIP invite for IMS PS voice/video services as per the existing IMS procedures. In addition, the UE may deregister from IMS PS voice/video services.
When the UE determines that the radio conditions are suitable for IMS PS voice/video services (e.g. UE is in normal coverage or in CE mode A) then UE may (re-)register for IMS PS voice/video services.
E.2 QoS related concepts p. 220
E.2.1 Application Level Signalling for IMS p. 220
E.2.1.0 General p. 220
When the UE uses GERAN/UTRAN-access for IMS services, it shall be able to establish a dedicated signalling PDP-Context for IM CN Subsystem related signalling or utilize a general-purpose PDP context for IM Subsystem signalling traffic.
When the UE uses E-UTRAN access for IMS services, it shall be able to request establishment of a default or dedicated EPS bearer for IM CN Subsystem related signalling.
E.2.1.1 QoS Requirements for Application Level Signalling p. 220
It shall be possible to request prioritised handling over the GERAN/UTRAN radio for IM CN Subsystem related signalling by including the Signalling Indication in the QoS IE of the PDP Context to be used for this traffic as described in clause E.2.1a.1.
It shall be possible to request prioritised handling over the E-UTRAN radio for IM CN Subsystem related signalling by including the appropriate QCI value for signalling traffic as specified in clause 6.1.7 of TS 23.203, Standardized QCI Characteristics, Table 6.1.7.
E.2.1.2 Requirements for IM CN subsystem signalling flag p. 220
The IM CN Subsystem Signalling flag is used to indicate the dedicated signalling PDP context for IMS signalling. If the network operator does not support a dedicated signalling PDP context or the UE does not include the IM CN Subsystem Signalling flag, the network will consider the PDP context as a general purpose PDP context.
The IM CN Subsystem Signalling flag is used to indicate EPS bearer dedicated for IMS signalling. If the network operator does not support a dedicated signalling EPS bearer or the UE does not include the IM CN Subsystem Signalling flag, the network will consider the EPS bearer as a default or dedicated bearer according to TS 23.401.
A PDP context/EPS bearer dedicated for IM CN Subsystem signalling provides dedicated IP-Connectivity Access Network bearers for IM CN subsystem signalling traffic, hence architectural requirements described in clause 4.2.6 for the usage of dedicated bearer resources shall be applied. The UE is not trusted to implement these restrictions, therefore the restrictions are enforced in the GGSN/P-GW by the operator of the GGSN/P-GW.
If the PDP context request/EPS bearer is initiated by the IP-CAN, then the GGSN/P-GW may provide a set of UL filters for the PDP context/EPS bearer used for IM CN Subsystem Signalling. The UL filters provide the UE with the rules and restrictions applied by the GGSN/P-GW for the dedicated IM CN Subsystem signalling IP-CAN bearer. The GGSN/P-GW may in addition provide the IM CN subsystem signalling flag to explicitly indicate to the UE the intention of using the PDP context/EPS bearer for IM CN Subsystem related signalling.
Policy and Charging Control functionality can be used to provide additional charging capabilities for dedicated signalling PDP context/EPS bearer dedicated to be used for IMS signalling (as well as for a general-purpose PDP context) as described in clause 4.2.6.
Whether the network is configured to support IM CN signalling flag or Policy and Charging Control functionality or both, is dependent on the operator configuration policy.
The requirements described above also apply in the case of E-UTRAN access and for GERAN/UTRAN access using EPS supporting dedicated bearer for IM CN Subsystem Signalling traffic and where appropriate filters are configured in the P-GW and PCRF as applicable.
E.2.1.3 Application Level Signalling support for IMS services p. 221
In order to receive different level of support for application level signalling in a PDP context/EPS bearer, the UE may choose one of the following options:
-
Include both the IM CN Subsystem Signalling Flag in the PCO IE and the Signalling Indication in the QoS. This indicates to the network (radio & core) the requirement of using the PDP context/EPS bearer for application level signalling after it has been negotiated with the networks, to provide prioritised handling over the radio interface (as described in clause E.2.1.1), with rules and restrictions applied in the network (as described in clause E.2.1.2).
- For GERAN/UTRAN access the UE includes the IM CN Subsystem Signalling Flag in the PCO IE and the Signalling Indication in the QoS IE in the PDP context activation or the Secondary PDP context activation procedure.
- For E-UTRAN access the UE includes both the IM CN Signalling Flag in the PCO IE and the appropriate QCI value for signalling traffic in the UE Requested Bearer resource Modification procedure.
- Include the IM CN Subsystem Signalling Flag in the PCO IE in the PDP context activation or the Secondary PDP context activation procedure for GERAN/UTRAN access and for E-UTRAN access in the Attach, PDN Connectivity request or the UE requested bearer resource modification procedure. This indicates to the GPRS/EPS network the requirement of using PDP context/EPS bearer for application level signalling with restricted handling as described in clause E.2.1.2, after it has been negotiated with the networks.
- Utilize a general purpose PDP Context/default EPS bearer with a negotiated QoS profile (this includes the possibility of having the Signalling Indication in the QoS IE for GERAN/UTRAN and the QCI for E-UTRAN.
E.2.1a PDP context/EPS Bearer procedures for IMS p. 221
E.2.1a.1 Establishing PDP Context/EPS bearer for IM CN Subsystem Related Signalling p. 221
It shall be possible for the UE to convey to the network the intention of using the PDP context/EPS bearer for IM Subsystem related signalling. For this purpose it uses the mechanism described in this clause and Application Level Signalling in clause E.2.1.1, clause E.2.1.2 and clause E.2.1.3.
When the bearer establishment is controlled or a bearer establishment is requested (in the case of EPS) by the UE, in order to establish a PDP context/EPS bearer for IM CN Subsystem related signalling, the UE shall be able to include the IM CN subsystem signalling flag in the PDP context activation/UE Requested Bearer Resource Modification procedure. This indicates to the network the intention of using the PDP context/EPS bearer for IM CN Subsystem related signalling.
For GERAN/UTRAN access:
To establish a PDP context for IM CN Subsystem related signalling with prioritised handling over the radio interface, the UE shall be able to set the Signalling Indication in the QoS IE in the PDP context activation procedure and the Secondary PDP context activation procedure. The Signalling indication in the QoS IE indicates to the radio and core networks the requirement for enhanced handling over the radio interface, once it has been negotiated with the networks.
A request for a general purpose PDP context having the "signalling indication" within the QoS IE may be accepted or downgraded according to operator policy configured at the GGSN using the usual QoS negotiation mechanisms described in TS 23.060. It shall not be possible to modify a general purpose PDP context into a dedicated PDP context for IM CN Subsystem related signalling and vice versa.
For E-UTRAN access:
The (default or dedicated) EPS bearer for IMS signalling may be established from network side at Attach/UE Requested PDN connectivity Request time, in which case the appropriate QCI for signalling traffic and the packet filters will provide the necessary QoS and any restrictions applicable on packets sent over this EPS bearer.
A request for an EPS bearer having the appropriate QCI for signalling traffic according to TS 23.203, may be either accepted or rejected according to operator policy configured at the P-GW i.e. there is no QoS negotiation mechanism used in EPS.
In order to establish a Dedicated EPS bearer for IM CN Subsystem related signalling, the UE shall be able to request the appropriate QCI for signalling traffic as specified in TS 23.203 in the UE Requested Bearer Resource Modification procedure. This indicates to the radio and core network the requirement for enhanced handling over the radio interface, once it has been accepted by the network. It shall not be possible to modify an existing EPS bearer in order to convert it to be dedicated for IM CN Subsystem related signalling and vice versa.
For all 3GPP accesses:
The IM CN Signalling Flag in the PCO IE is used to reference rules and restrictions on the PDP context/EPS bearer used for application level signalling, as described in clause 4.2.6. Based on operator policy the "Signalling Indication" in the QoS IE or the appropriate QCI for signalling traffic may be allowed only if the "IM CN Subsystem Signalling" flag is present in the PCO IE.
The IM CN subsystem signalling flag and the Signalling Indication in the QoS IE or the appropriate QCI for signalling traffic may be used independently of each other.
E.2.1a.2 Deletion of PDP Context/EPS bearer used to transport IMS SIP signalling p. 222
If the GPRS subsystem deletes the PDP Context used to transport IMS SIP signalling, then according to clause 5.10.3.0 the UE or GGSN shall initiate a procedure to re-establish (or modify where possible) a PDP Context for IMS signalling transport. If there are any IMS related PDP contexts active, the re-establishment of the PDP context to transport IMS signalling shall be performed by using the Secondary PDP Context Activation Procedure (or the Network Requested Secondary PDP Context Activation Procedure if initiated by the GGSN) as defined in TS 23.060.
If the EPC system deletes the Dedicated EPS bearer used to transport IMS SIP signalling, then according to clause 5.10.3.0 the UE or PDN Gateway shall initiate a procedure to re-establish (or modify where possible) an EPS bearer for IMS signalling transport. If there are any IMS related EPS bearers active, the re-establishment of the EPS bearer to transport IMS signalling shall be performed by the UE using the UE Requested Bearer Resource Modification procedure or the PDN Gateway using the Dedicated bearer activation procedure as defined in TS 23.401.
The failure in re-establishing the ability to communicate towards the UE results also in the P-CSCF/PCRF being informed that the IMS SIP signalling transport to the UE is no longer possible which shall lead to a network initiated session release (initiated by the P-CSCF) as described in clause 5.10.3.1 if any IMS related session is still ongoing for that UE. Additionally, the P-CSCF shall reject subsequent incoming session requests towards the remote endpoint indicating that the user is not reachable, until either:
- the registration timer expires in P-CSCF and the user is de-registered from IMS;
- a new Register message from the UE is received providing an indication to the P-CSCF that the PDP Context/EPS bearer used for IMS SIP Signalling transport for that user has become available again and session requests can be handled again.