Content for TS 23.228 Word version: 19.0.0
1…
3…
4…
4.2.4…
4.3…
4.4…
4.13…
4.16…
5…
5.2…
5.3…
5.4…
5.4.7…
5.4.8…
5.4a…
5.5…
5.5.3…
5.6…
5.6.3…
5.7…
5.7.3…
5.7.5…
5.7.8…
5.8…
5.10…
5.11…
5.11.3…
5.11.3.3
5.11.3.4
5.11.4…
5.11.5…
5.11.5.3…
5.11.6…
5.12…
5.16…
5.16.2…
5.19…
5.20…
A…
E…
E.2.2…
G…
G.5…
H
I…
J…
K…
L…
M…
M.3…
N…
P…
Q…
Q.2.5…
R…
S…
T…
U…
U.2…
V…
W…
X…
Y…
Z…
AA…
AA.3…
AB…
AC…
AC.7…
AC.7.2…
AC.7.2.2
AC.7.2.3…
AC.7.4…
AC.9…
AC.10…
G Reference Architecture and procedures when the NAT is invoked between the UE and the IMS domain
G.1 General
G.2 Reference models
G.2.1 IMS-ALG and IMS Access Gateway model
G.2.2 ICE and Outbound reference model
G.3 Network elements for employing the IMS-ALG and IMS Access Gateway
G.3.1 Required functions of the P-CSCF
G.3.2 Required functions of the IMS Access Gateway
G.3.3 Iq reference point
G.4 Procedures for employing the IMS-ALG and IMS Access Gateway
G.4.1 General
G.4.2 NAT detection in P-CSCF
G.4.3 Session establishment procedure
G.4.4 Session release procedure
G.4.5 Session modification
G.4.6 Media forwarding in the IMS Access Gateway
...
...
G (Normative) Reference Architecture and procedures when the NAT is invoked between the UE and the IMS domain |R7| p. 231
G.1 General p. 231
This clause specifies concepts of IMS service provisioning for the following scenarios:
- When a device or devices that perform address and/or port translation are located between the UE and the P-CSCF performing translation both of signalling and media packets.
- When IP address and/or port translation is needed between the IP-CAN and the IMS domain (e.g. different IP versions) on the media path only. This scenario covers the case when a device or devices that perform address and/or port translation are located on the media path only.
G.1.1 General requirements p. 231
The following list contains requirements that a NAT Traversal solution should satisfy:
- Support multiple UEs (on one or more devices) behind a single NAT;
- Support both inbound and outbound requests to and from UEs through one or more NAT device(s);
- Support the traversal of NATs between the UE and the IMS CN;
- Support uni-directional and bi-directional media flows;
- Minimize additional session setup delay.
G.2 Reference models p. 231
This clause describes various reference models which can be used for NAT traversal.
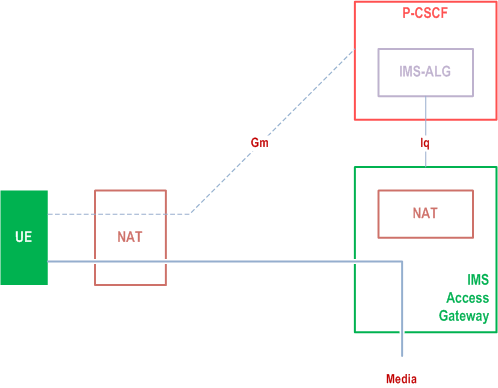
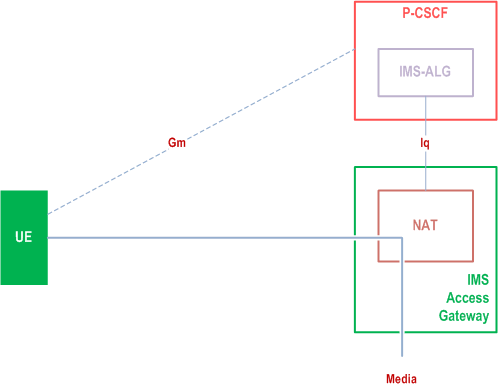
G.2.1 IMS-ALG and IMS Access Gateway model p. 232
Figure G.1 presents the general reference model for IMS access when both the signalling and media traverses NAT devices. Figure G.2 presents the general reference model when IP address translation is needed between the IP-CAN and the IMS domain. The IMS network architecture is the same for both cases. The NAT integrated with the IMS Access Gateway is under operator control in this reference model.
G.2.2 ICE and Outbound reference model p. 232
Figure G.2a presents the general reference model for IMS access when both the signalling and media traverses NAT devices. Functional elements with dashed lines represent optional functionality. The transport of the Gm signalling is also subject to the policy enforcement.
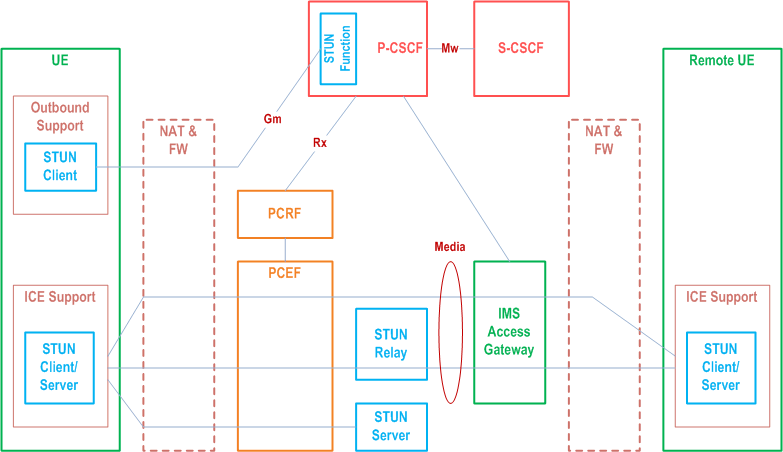
The STUN Function shown within the P-CSCF is a limited STUN Server for supporting STUN keep-alive messages as described in clause G.5.3.2.
For deployments where the IMS Access gateway (or other media manipulating functional entities, such as a MRFP, are used (see clause G.2.1), such functional entities shall be placed on the network side of the STUN server and STUN relay server (i.e. not between the UE and the STUN server or STUN relay server) as shown in Figure G.2a. Otherwise they will prevent STUN messages from reaching the STUN Relay/Server outside of a session.
G.3 Network elements for employing the IMS-ALG and IMS Access Gateway p. 233
G.3.1 Required functions of the P-CSCF p. 233
When supporting IMS communication for a UE residing behind a NAT or when IP address translation is needed between the IP-CAN and the IMS domain on the media path only, the P-CSCF may include the IMS-ALG function that is defined in Annex I of this specification. The following functions shall be performed in the P-CSCF:
- The P-CSCF shall be able to recognize that the UE is behind a NAT device or IP address translation is needed between the IP-CAN and the IMS domain on the media path only.
- The IMS-ALG function in the P-CSCF shall control the IMS Access Gateway, e.g. request transport addresses (IP addresses and port numbers) from the IMS Access Gateway, and shall perform the necessary changes of the SDP parameters.
- The IMS-ALG function in the P-CSCF shall perform the necessary changes of headers in SIP messages.
- The IMS-ALG function in the P-CSCF shall be able to support scenarios where IMS CN domain and IP-CAN use the same IP version and where they use different IP versions.
- The IMS-ALG function in the P-CSCF shall be able to request opening and closing of gates on the IMS Access Gateway.
- The IMS-ALG function in the P-CSCF may configure the IMS Access Gateway to police the remote source address/port of the associated media flow(s).
- The IMS-ALG function in the P-CSCF may configure the IMS Access Gateway to police the bandwidth/data rate of the associated media flow(s) (see TS 23.333).
- The IMS-ALG may configure the IMS Access Gateway to set the differentiated service code point for egress packets to an explicit value or alternately to allow the differentiated service code point of the ingress packet to be copied into the corresponding egress packet. An IMS Access Gateway can also support differentiated service code point marking based on local configuration.
- The IMS-ALG may request an IMS Access Gateway to detect and report inactive media flows.
G.3.2 Required functions of the IMS Access Gateway p. 233
The required functions of the IMS Access Gateway for NAT translation are the following:
- It allocates and releases transport addresses according to the requests coming from the IMS-ALG function of the P-CSCF.
- It ensures proper forwarding of media packets coming from or going to the UE.
- It shall support the scenarios where IMS CN domain and IP-CAN use the same IP version and where they use different IP versions.
- It shall support opening and closing of gates, under control of the IMS-ALG.
- It shall support policing of the remote source address/port and bandwidth/data rate of media flows, as configured by the IMS-ALG.
- It shall support the setting of the differentiated service code point for egress packets as configured by the IMS-ALG or else based on local configuration.
- It may support detection and reporting of inactive media flows.
- It shall support remote NAT traversal.
G.3.3 Iq reference point p. 234
The Iq reference point is between the P-CSCF and the IMS Access Gateway. It conveys the information necessary for the IMS-ALG to activate the procedures defined in clause G.3.2. Those procedures are further detailed in TS 23.334.
G.4 Procedures for employing the IMS-ALG and IMS Access Gateway p. 234
G.4.1 General p. 234
The procedures described in this clause are applied in addition to the procedures of the P-CSCF described in the other clauses of this specification.
G.4.2 NAT detection in P-CSCF p. 234
When supporting the IMS-ALG function, the P-CSCF, based on information received in a SIP request message (e.g. a REGISTER request), shall detect if there is NAT between the UE and itself and shall make a decision if IMS-ALG function shall be invoked for the session of subscriber. In addition to when a NAT is detected between the UE and the P-CSCF, the IMS-ALG function may be invoked for other reasons (e.g. UEs using IP address from a Private IP address range).
G.4.3 Session establishment procedure p. 234
This procedure is applied when P-CSCF invokes the IMS-ALG function for a session. This can happen at terminating side if the called party is behind a NAT or at the originating side if the session initiator is behind a NAT. Both cases are handled in the P-CSCF and the IMS Access Gateway as described in this clause.
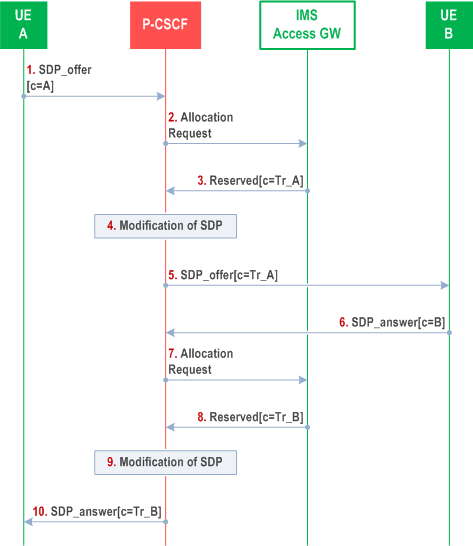
Step 1.
The P-CSCF receives a SIP message with an SDP offer from UE_A and decides to invoke the IMS-ALG function for this session. The session can either an originating or a terminating session. The SDP offer contains the transport address(es) of UE_A where the media flow(s) should be sent.
Step 2.
The P-CSCF requests a transport address for each media flow from the IMS Access Gateway. Each request contains sufficient information to determine the side of the IMS access gateway that the transport request is being requested for. (e.g. local or remote side with respect to UE_A).
Step 3.
The IMS Access Gateway reserves one of its transport addresses for the given side of the media flow and this transport address is sent back to the P-CSCF. The IMS Access Gateway shall keep the reserved temporary transport address (binding) until the session is released.
Step 4.
The P-CSCF changes the original transport address(es) of the SDP offer to the transport address(es) received from the IMS Access Gateway.
Step 5.
The P-CSCF forwards the SIP message with the modified SDP offer according to the normal routing procedures.
Step 6.
UE_B sends back a SIP message with an SDP answer, which is forwarded to the P-CSCF according to the normal SIP message routing procedures.
Step 7.
The P-CSCF requests a transport address for each media flow in the routing domain of its own IMS network from the IMS Access Gateway. The request contains sufficient information to correlate to the transport address request performed in step 2.
Step 8.
The IMS Access Gateway reserves one of its transport addresses for the given side of the media flow and this transport address is sent back to the P-CSCF.
Step 9.
The P-CSCF changes the original transport address(es) of the SDP answer to the transport address(es) received from the IMS Access Gateway.
Step 10.
The P-CSCF forwards the SIP message with the modified SDP answer according to the normal SIP message routing procedures.
G.4.4 Session release procedure p. 236
This procedure is applied when a session has to be released, for which the IMS-ALG function is invoked.
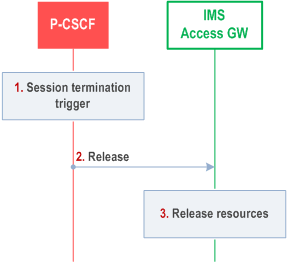
Step 1.
The P-CSCF receives a trigger to release a session, for which the IMS-ALG function is invoked.
Step 2.
The P-CSCF sends an indication to the IMS Access Gateway for each media flow of the session that the resources allocated during the session establishment procedures are to be released.
Step 3.
The IMS Access Gateway releases its resources allocated for the given media flows.
G.4.5 Session modification p. 236
A session modification can cause the creation, and/or modification, and/or release of media flows.
When a new media flow is created the procedure used during session establishment shall be applied.
When an existing media flow is released the procedure for session termination shall be applied for the particular media flow.
When an existing media flow is modified, this may lead to a modification of the media flow directly, or to the establishment of a new media flow and release of the existing one.
G.4.6 Media forwarding in the IMS Access Gateway p. 236
This clause presents the media forwarding performed by the IMS Access Gateway. The behaviour presented in this clause is valid in both directions.
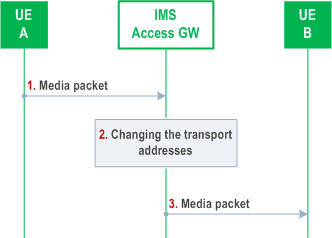
Step 1.
UE_A sends a media packet to the transport address of the IMS Access Gateway that was received during the session establishment/modification.
Step 2.
After receiving the media packet the IMS Access Gateway recognizes the media flow based on the transport address where the packet arrived at. The IMS Access Gateway changes the source transport address to its own transport address that was given to the UE_B as the destination transport address during session establishment/modification and the destination transport address to the transport address of UE_B.
The IMS Access Gateway can learn the transport addresses where the inbound (i.e. towards the UE) media packets shall be forwarded to in two ways, depending on whether there is a NAT device in the path or not. In absence of a NAT device in the path, it is the P-CSCF that signals the destination transport address for the inbound media flows. In presence of NAT device in the path, it is the IMS Access Gateway that may, upon being informed that there is a NAT in the network, determine the destination transport address of the inbound media flow based on previously received media packets in the opposite direction.
Beyond the changes of transport addresses the IMS Access Gateway shall perform the other necessary changes in the IP header as it is specified in the NAT related IETF specifications, RFC 2766 and RFC 2663.
Step 3.
The IMS Access Gateway routes the media packet towards UE_B.