Content for TS 23.228 Word version: 18.6.0
1…
3…
4…
4.2.4…
4.3…
4.4…
4.13…
4.16…
5…
5.2…
5.3…
5.4…
5.4.7…
5.4.8…
5.4a…
5.5…
5.5.3…
5.6…
5.6.3…
5.7…
5.7.3…
5.7.5…
5.7.8…
5.8…
5.10…
5.11…
5.11.3…
5.11.3.3
5.11.3.4
5.11.4…
5.11.5…
5.11.5.3…
5.11.6…
5.12…
5.16…
5.16.2…
5.19…
5.20…
A…
E…
E.2.2…
G…
G.5…
H
I…
J…
K…
L…
M…
M.3…
N…
P…
Q…
Q.2.5…
R…
S…
T…
U…
U.2…
V…
W…
X…
Y…
Z…
AA…
AA.3…
AB…
AC…
AC.7…
AC.7.2…
AC.7.2.2
AC.7.2.3…
AC.7.4…
AC.9…
5.7.5 (AS-T#1) PSI based Application Server termination - direct
5.7.6 (AS-T#2) PSI based Application Server termination - indirect
5.7.7 (AS-T#3) PSI based Application Server termination - DNS routing
...
...
5.7.5 (AS-T#1) PSI based Application Server termination - direct |R6| p. 139
This clause depicts a routing example for incoming session where the session request is routed directly to the AS hosting the PSI.
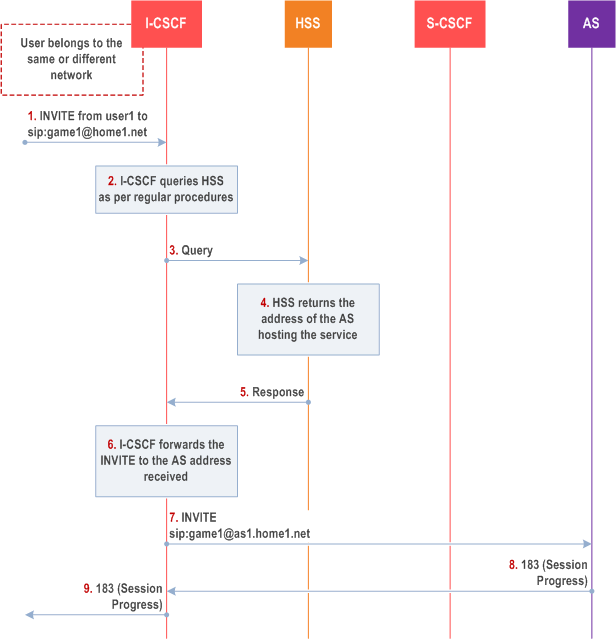
Step 1.
I-CSCF receives a request destined to the PSI.
Step 2-3.
I-CSCF queries the HSS in order to determine the next hop in the routing path for the PSI.
Step 4.
HSS determines the routing information, i.e. the address of the AS hosting the PSI.
Step 5.
HSS returns the AS address to the I-CSCF.
Step 6-7.
I-CSCF forwards the request to the address received from the query.
Step 8-9.
Session setup continues as per existing procedures.
5.7.6 (AS-T#2) PSI based Application Server termination - indirect |R6| p. 139
This clause depicts an example routing scenario where the basic IMS routing via S-CSCF is used to route the session.
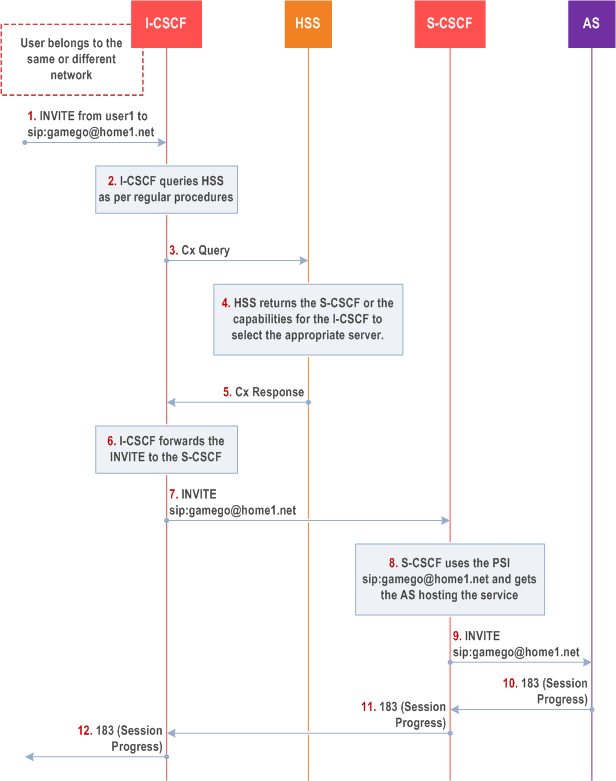
Step 1.
I-CSCF receives a request destined to the PSI.
Step 2-3.
I-CSCF queries HSS in order to determine the next hop in the routing path for the PSI.
Step 4.
HSS determines the routing information, which is the S-CSCF defined for the "PSI user".
Step 5.
HSS returns the S-CSCF address/capabilities to the I-CSCF.
Step 6-7.
I-CSCF, as per existing procedures, forwards the request towards the entity (i.e. S-CSCF) received from the query, or the I-CSCF selects a new S-CSCF if required.
Step 8.
S-CSCF evaluates the filter criteria and gets the AS address where to forward the request.
Step 9.
The request is then routed towards the AS identified by the filter criteria.
Step 10-12.
Session setup continues as per existing procedures.
5.7.7 (AS-T#3) PSI based Application Server termination - DNS routing |R6| p. 140
This clause shows an example of DNS based routing of an incoming session from an external network. The routing from the external network leads to the entry point of the IMS subsystem hosting the subdomain of the PSI.
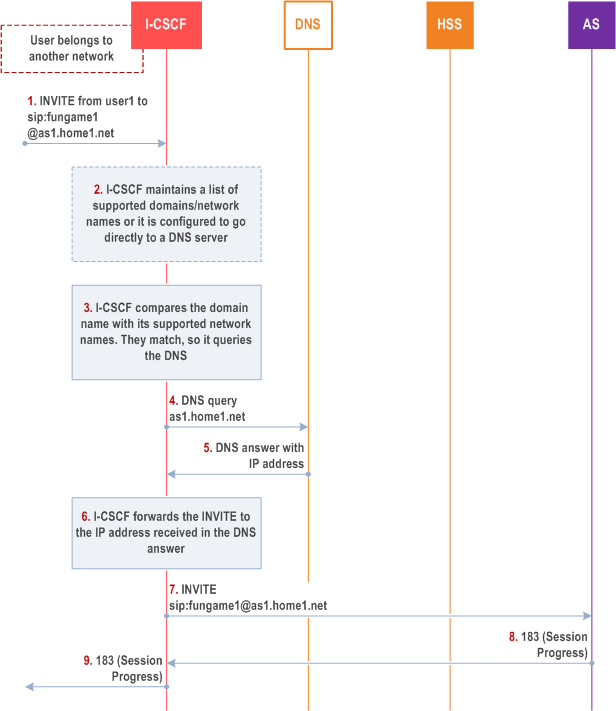
Step 1.
I-CSCF receives a request that is destined to the PSI.
Step 2.
I-CSCF has been configured with the list of supported domains/network names, or it may have been configured to directly query a local DNS server.
Step 3.
In this case the I-CSCF checks the list and finds a match.
Step 4.
I-CSCF sends DNS query to find the route.
Step 5.
DNS server returns the IP address of the AS hosting the PSI.
Step 6-7.
I-CSCF forwards the request towards the IP address received from the query.
Step 8-9.
Session setup continues as per existing procedures.