Content for TS 23.280 Word version: 19.2.0
1…
5…
5.2.8…
6
7…
7.3.2
7.4…
7.4.3…
7.5…
8…
9…
9.2.2…
9.2.2.2…
9.3…
10…
10.1.2…
10.1.3…
10.1.4.3…
10.1.4.5…
10.1.5…
10.1.6…
10.2…
10.2.3…
10.2.4.2…
10.2.4.3…
10.2.5…
10.2.7…
10.3…
10.6…
10.7…
10.7.3…
10.7.3.4…
10.7.3.7…
10.7.3.7.3
10.7.3.8…
10.7.3.10…
10.8…
10.8.4…
10.8.5…
10.9…
10.9.3…
10.9.3.5…
10.9.3.8…
10.9.3.9…
10.9.3.9.3…
10.9.3.9.4…
10.9.3.10…
10.9.3.10.4…
10.9.3.10.6…
10.10…
10.10.1.2.3…
10.10.2…
10.10.3…
10.10.3.3…
10.10.3.4…
10.11…
10.11.5…
10.12…
10.13…
10.13.3…
10.13.7…
10.13.10…
10.14…
10.15…
10.15.3…
10.15.3.3…
10.15.3.4…
10.16…
10.17…
10.17.3…
10.17.5…
11…
11.3…
11.5…
11.5.2…
11.5.3…
11.5.3.3.2A…
11.5.4…
A…
B…
C…
10.7.3.4 Use of MBMS bearer for application level control signalling
10.7.3.5 MBMS bearer announcement over MBMS bearer
10.7.3.6 MBMS bearer quality detection
...
...
10.7.3.4 Use of MBMS bearer for application level control signalling p. 140
10.7.3.4.1 Description p. 140
The MC service server may use an MBMS bearer for application level control signalling, according to this subclause. An MBMS bearer for application level control signalling is typically used for the purposes beyond the benefit for using MBMS for resource efficiency, e.g. for improved MC service performance (KPIs), handling of high load scenarios.
The MBMS bearer for application level control signalling may be used to transmit the following messages:
- Transmission control (e.g. call setup and floor control)
- MBMS bearer announcement for media bearers
- Group application paging
- Group dynamic data (e.g. status of the group)
- Group state (e.g. emergency alerts)
10.7.3.4.2 Procedure p. 140
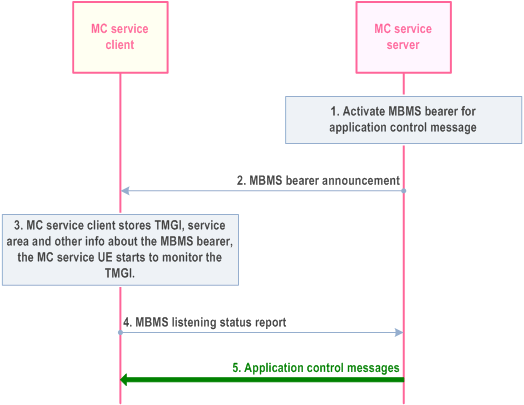
The procedure in Figure 10.7.3.4.2-1 shows only one of the receiving MC service clients using an MBMS bearer.
Step 1.
The MC service server determines to activate MBMS bearer for application level control signalling, The activation of the MBMS bearer is done on the MB2-C reference point and according to TS 23.468.
Step 2.
The MC service server passes the MBMS bearer info for the service description associated MBMS bearer to the MC service client. The MC service client obtains the TMGI, identifying the MBMS bearer, from the service description.
Step 3.
The MC service client stores the information associated with the TMGI. The MC service client uses the TMGI and other MBMS bearer related information to activate the monitoring of the MBMS bearer by the MC service UE.
Step 4.
The MC service client that enters or is in the service area of the announced TMGI indicates to the MC service server that the MC service client is able to receive application level control messages over the MBMS bearer. The MC service client may also indicate at which MBMS reception quality level it has received the MC service media on the MBMS bearer. Hence, the MC service server may decide to use the MBMS bearer for MC application control messages.
Step 5.
The MC service server transmit MC application control messages
10.7.3.5 MBMS bearer announcement over MBMS bearer p. 141
10.7.3.5.1 Description p. 141
The MBMS announcement may be done on either a unicast bearer or a MBMS bearer. Using a unicast bearer for MBMS bearer announcement provides an interactive way of doing announcement. The MC service server will send the MBMS bearer announcement message to the MC service client regardless if there is an MBMS bearer active or the MC service client can receive the data on the MBMS bearer with sufficient quality. The benefit of the existing procedure is that it gives a secure way to inform the MC service client about the MBMS bearer and how to retrieve the data on the MBMS bearer.
When there is more than one MBMS bearer active in the same service area for MC service, there are not the same reasons to use unicast bearer for additional MBMS bearer announcement. Instead a MBMS bearer for application level control signalling can be used to announce additional MBMS bearers.
The MBMS bearer announcement messages are sent on an MBMS bearer used for application control messages. This bearer will have a different QoS setting compared to an MBMS bearer used for media, since application signalling messages are more sensitive to packet loss.
10.7.3.5.2 Procedure p. 141
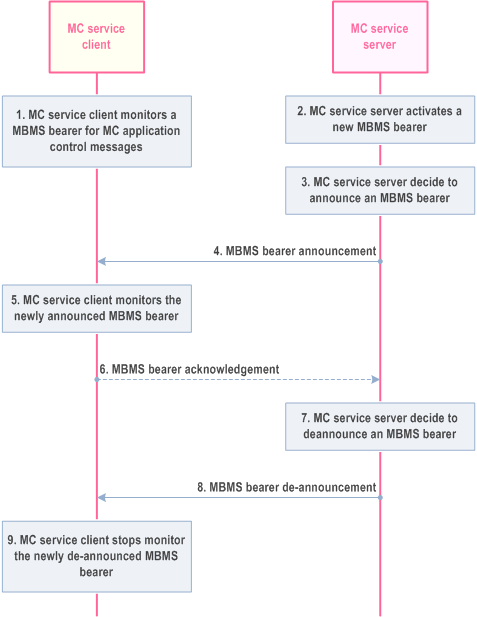
The procedure defined below enables the MC service to announcement a new MBMS bearer.
Pre-conditions:
- An MBMS bearer used for MC service application control messages must have been pre-established and announced to the MC service client.
- Additional MBMS bearer information may have already been announced to the client.
Step 1.
The same procedure can also be used to modify existing MBMS bearer announcement information. Example of such modification could be addition of UDP ports or modification of codec in the SDP.
The MC service client monitors an MBMS bearer that is used for MC service application signalling messages, such as bearer announcement messages.
Step 2.
The MC service server activates a new MBMS bearer.
Step 3.
The MC service server announce the MBMS bearer to the MC service client. The bearer may have just been activated or may have already been running for some time. The step may be repeated as needed.
Step 4.
The MC service server sends a MBMS bearer announcement on the MBMS bearer used for MC application control messages. The MBMS bearer announcement contains the identity of the MBMS bearer (i.e. the TMGI) and may optionally include additional information about the newly announced bearer. Required and optional MBMS bearer announcement details may have already been provided. In this case the MBMS bearer identity could be used as a key for such MBMS bearer details.
Step 5.
The MC service clients start to monitor the newly announced MBMS bearer.
Step 6.
If requested by the MC service server, the MC service client sends an acknowledgement of the MBMS bearer to the MC service server.
Step 7.
The MC service server de-announce the MBMS bearer.
Step 8.
The MC service server sends a MBMS bearer de-announcement message that contains the identity of the MBMS bearer.
Step 9.
The MC service client stops monitoring the de-announced MBMS bearer.
10.7.3.6 MBMS bearer quality detection p. 143
10.7.3.6.1 Description p. 143
The MC service client and MC service server use this procedure to report and take action on the MBMS bearer quality. An MC service client monitors an MBMS bearer to receive MC service media. Based on the received quality (e.g. radio level quality, transport level quality), the MC service client needs to inform the MC service server that the MC service client is able to receive the MC service media on the MBMS bearer with sufficient quality or not able to receive the MC service media on the MBMS bearer with sufficient quality. Furthermore, based on the received quality, the MC service client may notify the MC service server at which MBMS reception quality level it has received the MC service media on the MBMS bearer.
The issue can be more complex since the MC service client needs to estimate the quality of the bearer even in the scenario when there are no data currently transmitted on the MBMS bearer (e.g. between MCPTT group call). The reason for this is that an MC service client that has entered an area with significantly degraded MBMS quality, might not even notice that an MC service communication is ongoing, meanwhile the MC server still assumes that the MC service client can receive the media being broadcasted.
To estimate the MBMS bearer quality, for example as an equivalent BLER (Block Error Rate), when no data is sent is implementation specific. This estimation can be dependent on for example the modulation and coding scheme (MCS) and measurements from the reference signals from the eNB(s). Other metrics (e.g. RTP packet loss) may be used to estimate the MBMS bearer quality.
10.7.3.6.2 Procedure p. 143
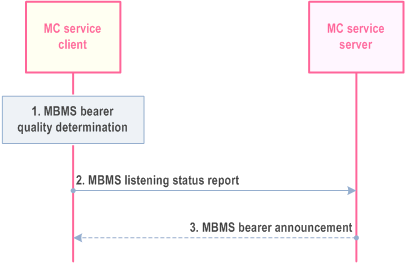
The MC service client shall indicate the ability of the MC service client to receive the MBMS bearer.
Pre-conditions:
- There is an MBMS bearer activated and the MBMS bearer information is announced to the MC service client
- The MC service client is located in the MBMS broadcasting area
- The MC service UE monitors SIB-13 (or SIB-20) and (SC-)MCCH to receive the modulation and coding scheme
- The MC service UE monitors the cell specific reference signal and when MBSFN transmission is used, the MBSFN specific reference signals
Step 1.
The MC service client determines that the MBMS bearer quality shall be reported to the MC service server. The MC service client may determine the MBMS bearer quality by using the BLER of the received data. When no data is received, the quality estimation can consider the reference signals and the modulation and coding scheme (MCS). The UE may also use predictive methods to estimate the expected MBMS bearer quality (e.g. speed and direction) to proactively inform the MBMS service server of an expected loss of the MBMS bearer quality. The MC service client may also map the determined MBMS bearer quality to a MBMS reception quality level. The MBMS reception quality level indicates at which specific MBMS bearer quality level the MC service media has been received. Based on the MBMS reception quality level, the MC service server may efficiently decide to switch to another bearer or to take measures to prepare such a switch.
Step 2.
If the MBMS bearer quality reaches a certain threshold, the MC service client sends an MBMS listening status report. The threshold is used to define the MBMS listening status, which indicates if the MBMS bearer quality has been acceptable or not to receive a specific MC service media. If the MBMS bearer quality is mapped to a different MBMS reception quality level, the MC service client may send an MBMS listening status report including the MBMS reception quality level.
Step 3.
The MC service server may send additional proposal for measurements e.g. information about neighbouring MBMS bearers. This message may be an MBMS bearer announcement message.