Content for TS 23.280 Word version: 19.2.0
1…
5…
5.2.8…
6
7…
7.3.2
7.4…
7.4.3…
7.5…
8…
9…
9.2.2…
9.2.2.2…
9.3…
10…
10.1.2…
10.1.3…
10.1.4.3…
10.1.4.5…
10.1.5…
10.1.6…
10.2…
10.2.3…
10.2.4.2…
10.2.4.3…
10.2.5…
10.2.7…
10.3…
10.6…
10.7…
10.7.3…
10.7.3.4…
10.7.3.7…
10.7.3.7.3
10.7.3.8…
10.7.3.10…
10.8…
10.8.4…
10.8.5…
10.9…
10.9.3…
10.9.3.5…
10.9.3.8…
10.9.3.9…
10.9.3.9.3…
10.9.3.9.4…
10.9.3.10…
10.9.3.10.4…
10.9.3.10.6…
10.10…
10.10.1.2.3…
10.10.2…
10.10.3…
10.10.3.3…
10.10.3.4…
10.11…
10.11.5…
10.12…
10.13…
10.13.3…
10.13.7…
10.13.10…
10.14…
10.15…
10.15.3…
10.15.3.3…
10.15.3.4…
10.16…
10.17…
10.17.3…
10.17.5…
11…
11.3…
11.5…
11.5.2…
11.5.3…
11.5.3.3.2A…
11.5.4…
A…
B…
C…
10 Procedures and information flows
10.1 MC service configuration
10.1.1 General
10.1.1.1 MC service configuration on primary MC system
10.1.1.2 MC service configuration for migration to partner MC system
...
...
10 Procedures and information flows p. 67
10.1 MC service configuration p. 67
10.1.1 General p. 67
10.1.1.1 MC service configuration on primary MC system |R15| p. 67
Depicted in Figure 10.1.1.1-1 is a MC service configuration time sequence of the data related to specific MC service, representing the general lifecycle of MC service UE using an MC service.
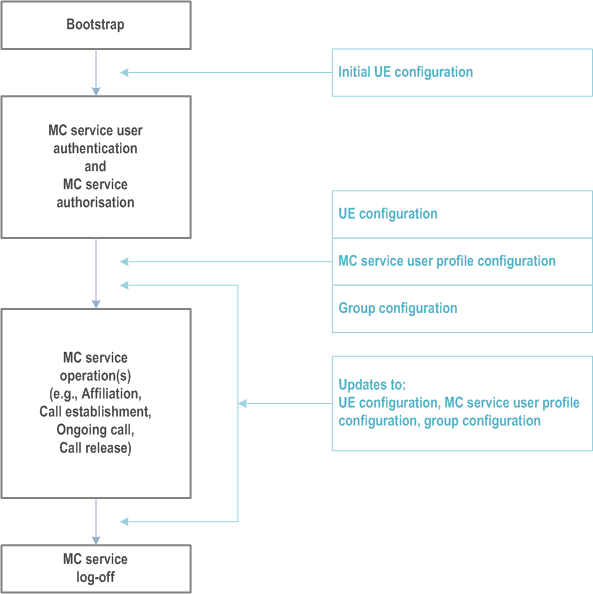
The MC service UE is provided with initial UE configuration via a bootstrap procedure that provides the MC service UE's clients (e.g. MC service client, group management client, configuration management client, identity management client, key management client, functional alias management client) with critical information needed to connect to the MC system. This includes PDN connection information corresponding to the configured MC services on the MC service UE (see "EPS bearer considerations" in the TS 23.379) and on-network server identity information for all application plane servers with which the MC service UE needs to interact. See Annex A.6 for more information.
The MC service UE is provided with UE configuration, MC service user profile configuration and group configuration via online configuration. While the MC service UE is using the MC service it may receive online configuration updates. If the MC service user profile configuration contains multiple MC service user profiles for an authenticated MC service user, then the MC service client and MC service server set the active MC service user profile to the configured pre-selected MC service user profile after MC service authorization (which can be updated by the MC service user using the procedure specified in subclause 10.1.4.6). The active MC service user profile can be changed by the MC service user to a different MC service user profile during MC service service (see MC service TSs).
The MC service is configured with the service configuration (not shown in the Figure 10.1.1.1-1) which the MC service enforces during the entire phase of MC service UE using the MC service.
10.1.1.2 MC service configuration for migration to partner MC system |R15| p. 69
Figure 10.1.1.2-1 depicts a general MC service configuration time sequence of the data related to MC service, representing the general lifecycle of MC service UE which obtains MC service when migrated to a partner MC system. The MC service user can only receive MC service from one MC system at a time.
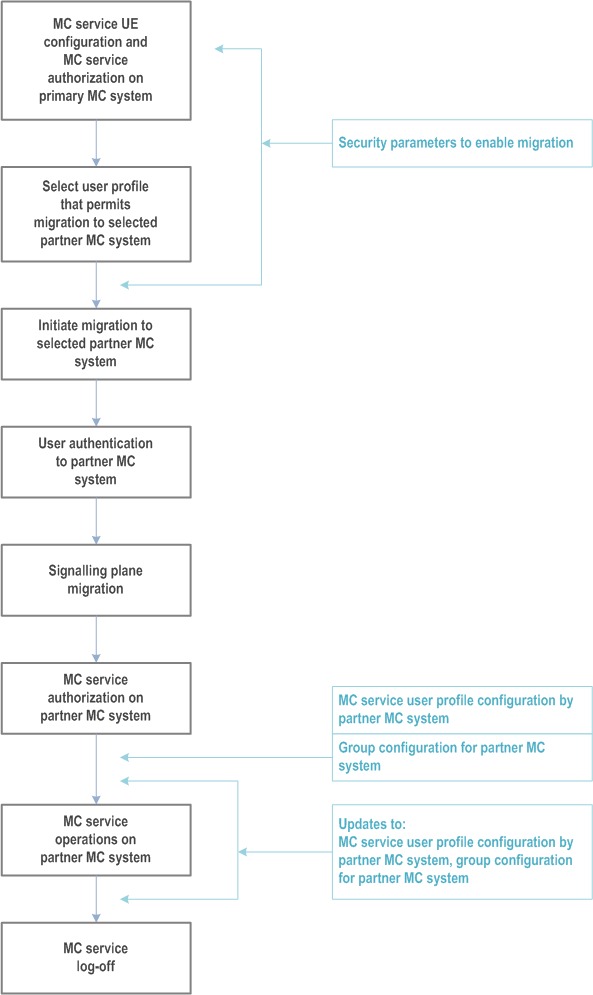
The MC service user and MC service UE first follow the MC service UE configuration and MC service user authorization steps described in subclause 10.1.1.1 to obtain one or more MC service user profiles from the primary MC system. Each user profile received from the primary MC system contains a list of partner MC systems to which migration is permitted using that user profile, together with the access information needed to communicate with the application plane servers of the partner MC system. See Annex A.3 for more information. The MC service user also obtains the necessary security parameters needed to authenticate and become service authorized on the partner MC system; the process for this is specified in TS 33.180. At this point, the MC UE is configured sufficiently for the partner system so that the MC service user is capable of utilizing "limited services" as described in TS 33.180.
To initiate migration, the desired partner system from those listed in the chosen user profile is selected, and the access information provided in the user profile is used to initiate communication with the partner MC system.
The MC service user performs user authentication to the partner MC system as specified in TS 33.180.
The user profile or profiles for that MC service user which are to be used for service when migrated to the partner MC system are then downloaded to the configuration management client in the MC service UE by the partner MC system, and these downloaded profile or profiles are used by the MC service user during the ensuing period of MC service on the partner MC system.
Group configuration for the MC service groups listed in the user profile are then obtained by the group management client in the MC service UE. After these configuration steps, the MC service user obtains service authorization on the partner MC system.
Once service authorized, further configuration changes may be provided by the partner MC system during the period of operational MC service, in accordance with subclause 10.1.1.1. The partner MC system enforces the use of the user profiles and group configuration that have been provided by the configuration process described in this subclause.