Content for TS 23.280 Word version: 19.2.0
1…
5…
5.2.8…
6
7…
7.3.2
7.4…
7.4.3…
7.5…
8…
9…
9.2.2…
9.2.2.2…
9.3…
10…
10.1.2…
10.1.3…
10.1.4.3…
10.1.4.5…
10.1.5…
10.1.6…
10.2…
10.2.3…
10.2.4.2…
10.2.4.3…
10.2.5…
10.2.7…
10.3…
10.6…
10.7…
10.7.3…
10.7.3.4…
10.7.3.7…
10.7.3.7.3
10.7.3.8…
10.7.3.10…
10.8…
10.8.4…
10.8.5…
10.9…
10.9.3…
10.9.3.5…
10.9.3.8…
10.9.3.9…
10.9.3.9.3…
10.9.3.9.4…
10.9.3.10…
10.9.3.10.4…
10.9.3.10.6…
10.10…
10.10.1.2.3…
10.10.2…
10.10.3…
10.10.3.3…
10.10.3.4…
10.11…
10.11.5…
10.12…
10.13…
10.13.3…
10.13.7…
10.13.10…
10.14…
10.15…
10.15.3…
10.15.3.3…
10.15.3.4…
10.16…
10.17…
10.17.3…
10.17.5…
11…
11.3…
11.5…
11.5.2…
11.5.3…
11.5.3.3.2A…
11.5.4…
A…
B…
C…
6 Involved business relationships p. 31
Based on the information in subclause 5.2.1 and subclause 5.2.2, Figure 6-1 shows the business relationships that exist and that are needed to support a single MC service user.
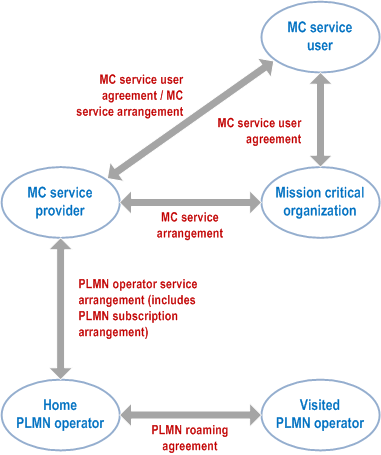
The MC service user belongs to a single mission critical organization based on a MC service user agreement between the MC service user and the mission critical organization. The MC service user can have MC service user agreement and MC service arrangement directly with a single MC service provider.
The mission critical organization and the MC service provider can be part of the same organization, in which case the business relationship between the two is internal to a single organization. The mission critical organization can have MC service arrangements with several MC service providers. In this case, a MC service user of a mission critical organization is always served by only one MC service provider. The MC service provider can have MC service arrangements with several mission critical organizations. The MC service provider can have MC service user agreements and MC service arrangements with several MC service users.
The MC service provider and the home PLMN operator can be part of the same organization, in which case the business relationship between the two is internal to a single organization.
The home PLMN operator can have PLMN operator service arrangements with multiple MC service providers and the MC service provider can have PLMN operator service arrangements with multiple home PLMN operators. As part of the PLMN operator service arrangement between the MC service provider and the home PLMN operator, PLMN subscription arrangements can be provided which allows the MC service UEs to register with home PLMN operator network.
The home PLMN operator can have PLMN roaming agreements with multiple visited PLMN operators and the visited PLMN operator can have PLMN roaming agreements with multiple home PLMN operators.
Where mutual aid operates between MC service providers, Figure 6-2 shows the required additional relationship. An MC service user can only affiliate to groups of the partner MC service provider:
- if such a service provider agreement exists; or
- subject to authorisation for a specific group membership from the partner MC service provider.

The primary and partner MC service providers do not need to be served by the same home SIP core operator in order to support mutual communication and mutual aid when interconnection between the SIP cores is available.
An example of the usage of these business relationships is elaborated for two users, one resident on its primary MC service provider and one providing mutual aid within the same group:
User A is a user on MC service provider X in group M. The relationships are as follows:
- user A has user configuration established with MC service provider X and forms part of group M;
- user A uses a PLMN subscription arrangement with PLMN operator R provided by MC service provider X; and
- MC service provider X has a PLMN operator service arrangement with PLMN operator R.
- user B has user configuration established with MC service provider Y and forms part of its own set of groups relating to MC service provider Y;
- user B uses a PLMN subscription arrangement with PLMN operator S provided by MC service provider Y;
- MC service provider Y has a PLMN operator service arrangement with PLMN operator S;
- MC service provider Y has a service provider agreement with MC service provider X that allows user B to participate within group M; and
- PLMN operator S has a PLMN roaming agreement with PLMN operator R allowing user B to roam to PLMN operator R.