Content for TS 23.558 Word version: 19.2.0
0…
5…
6…
6.2a…
6.2b…
6.3…
6.4…
7…
8…
8.3…
8.3.3…
8.3.3.3…
8.4…
8.4.3…
8.4.4…
8.5…
8.6…
8.6.3…
8.6.4…
8.6.6…
8.7…
8.8…
8.8.2.5…
8.8.2A…
8.8.3…
8.8.4…
8.8.5…
8.9…
8.14…
8.14.3…
8.15…
8.17…
8.17.3…
8.17.4…
8.18…
8.19…
8.20…
9…
A…
A.4…
A.5…
B…
E…
6.4 Service-based interfaces
6.5 Reference Points
6.5.1 General
6.5.2 EDGE-1
6.5.3 EDGE-2
6.5.4 EDGE-3
6.5.5 EDGE-4
6.5.6 EDGE-5
6.5.7 EDGE-6
6.5.8 EDGE-7
6.5.9 EDGE-8
6.5.10 EDGE-9
6.5.11 NM-UU
6.5.12 NM-S
6.5.13 NM-C
6.5.14 ECI-1
6.5.15 ECI-2
6.5.16 ECI-3
6.5.17 ECI-4
6.5.18 CLOUD-1
6.5.19 CLOUD-2
6.5.20 CLOUD-3
6.5.21 CLOUD-4
6.5.22 EDGE-10
6.6 Cardinality rules
6.6.1 General
6.6.2 Functional Entity Cardinality
6.6.3 Reference Point Cardinality
6.7 Capability exposure for enabling edge applications
...
...
6.4 Service-based interfaces p. 39
The architecture for enabling edge applications contains the following service-based interfaces:
Eecs:
Service-based interface exhibited by ECS.
Eees:
Service-based interface exhibited by EES.
6.5 Reference Points p. 39
6.5.1 General p. 39
This clause describes the reference points of the architecture for enabling edge applications.
6.5.2 EDGE-1 p. 39
EDGE-1 reference point enables interactions between the EES and the EEC. It supports:
- registration and de-registration of the EEC to the EES;
- retrieval and provisioning of EAS configuration information;
- discovery of EASs available in the EDN; and
- service continuity procedures (e.g. ACR initiation).
6.5.3 EDGE-2 p. 39
EDGE-2 reference point enables interactions between the EES and the 3GPP Core Network functions and APIs for retrieval of network capability information. It supports:
6.5.4 EDGE-3 p. 39
EDGE-3 reference point enables interactions between the EES and the EASs. It supports:
- registration of EASs with availability information (e.g. time constraints, location constraints);
- de-registration of EASs from the EES;
- discovery of T-EAS information to support ACT;
- providing access to network capability information (e.g. location information);
- requesting the setup of a data session between AC and EAS with a specific QoS and receiving QoS related information; and
- service continuity procedures (e.g. ACR status).
6.5.5 EDGE-4 p. 40
EDGE-4 reference point enables interactions between the ECS and the EEC. It supports:
- provisioning of Edge configuration information to the EEC.
6.5.6 EDGE-5 p. 40
EDGE-5 reference point enables interactions between AC(s) and the EEC. It supports:
- registration, registration update and de-registration of AC to the EEC;
- EAS discovery by the AC;
- ACR triggering by the AC;
- EEC services subscription; and
- UE ID request.
6.5.7 EDGE-6 p. 40
EDGE-6 reference point enables interactions between the ECS and the EES. It supports:
- registration of EES information to the ECS;
- de-registration of EES information from the ECS;
- retrieval of the T-EES information from the ECS; and
- subscription and notification for service continuity related events.
6.5.8 EDGE-7 p. 40
EDGE-7 reference point enables interactions between the EAS and the 3GPP Core Network functions and APIs for retrieval of network capability information. It supports:
6.5.9 EDGE-8 p. 40
EDGE-8 reference point enables interactions between the ECS and the 3GPP Core Network functions and APIs for retrieval of network capability information. It supports:
6.5.10 EDGE-9 p. 41
EDGE-9 reference point enables interactions between two EESs. EDGE-9 reference point may be provided between EES within different EDN (Figure 6.5.10-1) and within the same EDN (Figure 6.5.10-2).
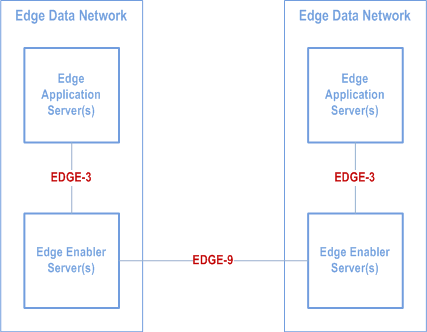
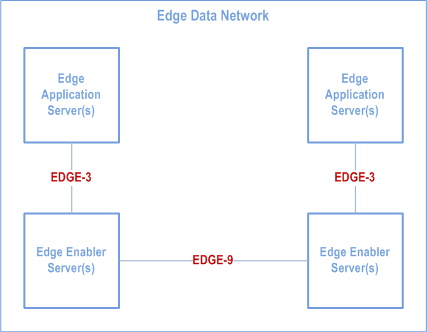
EDGE-9 supports:
- discovery of T-EAS information to support ACR;
- EEC context relocation procedures; and
- transparent transfer of the application context during EELManagedACR.
6.5.11 NM-UU |R18| p. 41
NM-UU reference point is as specified in TS 23.434.
6.5.12 NM-S |R18| p. 41
NM-S reference point is as specified in TS 23.434, where EES or ECS acts VAL server.
6.5.13 NM-C |R18| p. 42
NM-C reference point is as specified in TS 23.434, where EEC acts as VAL client.
6.5.14 ECI-1 |R18| p. 42
ECI-1 enables interaction between CAS and EES. ECI-1 supports:
- notifying the CAS about selection of an EES to provide edge enabler services;
- discovery of T-EAS to support ACT from CAS to T-EAS; and
- selected T-EAS declaration where CAS acts as S-EAS.
- ACR status update between EES and CAS as specified in clause 8.8.2A.6; and
- T-EAS discovery procedure initiated by CAS as specified in clause 8.8.2A.6.
6.5.15 ECI-2 |R18| p. 42
ECI-2 enables interaction between CAS and ECS.
6.5.16 ECI-3 |R18| p. 42
ECI-3 enables interaction between CES and ECS.
ECI-3 supports:
- T-EES retrieval procedure.
6.5.17 ECI-4 |R18| p. 42
ECI-4 enables interaction between CES and EES.
ECI-4 supports:
- EEC context relocation procedure; and
- ACR parameter information procedure.
6.5.18 CLOUD-1 |R18| p. 42
CLOUD-1 enables interaction between CAS and CES.
CLOUD-1 supports:
- providing access to network capability information (e.g. location information);
- requesting the setup of a data session between AC and CAS with a specific QoS and receiving QoS related information; and
- service continuity procedures (e.g. ACR status).
6.5.19 CLOUD-2 |R18| p. 42
CLOUD-2 enables interaction between CES and CES.
6.5.20 CLOUD-3 |R18| p. 43
CLOUD-3 enables interaction between CAS and the 3GPP core network.
6.5.21 CLOUD-4 |R18| p. 43
CLOUD-4 enables interaction between CES and the 3GPP core network.
6.5.22 EDGE-10 |R18| p. 43
EDGE-10 reference point enables interactions between the ECS and another ECS. It supports:
- service provisioning information retrieval.
- registration and de-registration of the ECS to the ECS acting as edge repository; and
- retrieval or discovery of information about other ECS(s) of the federation.
6.6 Cardinality rules p. 43
6.6.1 General p. 43
The cardinality rules are applied to the architecture specified in clause 6.2. The cardinality rules are classified as functional entity cardinality and reference point cardinality. The functional entity cardinality specifies the multiplicity of the functional entity that can exist as per the architecture. The reference point cardinality specifies the multiplicity of source and target functional entities that can exist in a relationship defined by the reference point in the architecture.
6.6.2 Functional Entity Cardinality p. 43
6.6.2.1 General p. 43
6.6.2.2 AC p. 43
The following cardinality rules apply for ACs:
- one or more ACs may be located in a UE.
6.6.2.3 EEC p. 43
The following cardinality rules apply for EECs:
- One or more EEC(s) may be located in a UE.
6.6.2.4 ECS p. 43
The following cardinality rules apply for ECSs:
- One or more ECS(s) may be deployed to support one EDN;
- One ECS may be deployed to support one or more EDN(s);
- One or more ECS(s) may be deployed by a PLMN operator; and
- One or more ECS(s) may be deployed by an ECSP.
- One ECS-ER may be deployed by a PLMN operator; and
- One ECS-ER may be deployed by an ECSP.
6.6.2.5 EES p. 44
The following cardinality rules apply for EES:
- One or more EES(s) may be located in an EDN; and
- One or more EES(s) may be located in an EDN per ECSP.
6.6.2.6 EAS p. 44
The following cardinality rules apply for EASs:
- One or more EAS(s) may be located in an EDN.
6.6.2.7 CES |R18| p. 44
The following cardinality rules apply for CES:
- One CES may be located in a cloud DN per ECSP.
6.6.2.8 CAS |R18| p. 44
The following cardinality rules apply for CASs:
- One or more CAS(s) may be located in a cloud DN.
6.6.3 Reference Point Cardinality p. 44
6.6.3.1 General p. 44
Void.
6.6.3.2 EDGE-1 (Between EEC and EES) p. 44
The following cardinality rules apply for EDGE-1:
- One EEC may communicate with one or more EES(s) for one or more AC concurrently; and
- One EES may communicate with one or more EEC(s) concurrently.
6.6.3.3 EDGE-3 (Between EAS and EES) p. 44
The following cardinality rules apply for EDGE-3:
- One EAS may communicate with only one EES within the same EDN; and
- One EES may communicate with one or more EAS(s) concurrently.
6.6.3.4 EDGE-4 (Between EEC and ECS) p. 44
The following cardinality rules apply for EDGE-4:
- One EEC may communicate with one or more ECS(s) concurrently; and
- One ECS may communicate with one or more EEC(s) concurrently.
6.6.3.5 EDGE-5 (Between AC and EEC) p. 45
The following cardinality rules apply for EDGE-5:
- One AC may communicate with only one EEC; and
- One EEC may communicate with one or more AC(s) concurrently.
6.6.3.6 EDGE-6 (Between EES and ECS) p. 45
The following cardinality rules apply for EDGE-6:
- One EES may communicate with one or more ECS(s) concurrently; and
- One ECS may communicate with one or more EES(s) concurrently.
6.6.3.7 EDGE-9 (Between EES and EES) p. 45
The following cardinality rules apply for EDGE-9:
- One EES may communicate with one or more EES(s) concurrently.
6.6.3.8 EDGE-10 (Between ECS and ECS) |R18| p. 45
Following cardinality rules apply for EDGE-10:
- One ECS may communicate with one or more ECS(s) concurrently.
6.6.3.9 ECI-1 (Between CAS and EES) |R18| p. 45
The following cardinality rules apply for ECI-1:
- One CAS may communicate with one or more EES(s) concurrently; and
- One EES may communicate with one or more CAS(s) concurrently.
6.6.3.10 ECI-2 (Between CAS and ECS) |R18| p. 45
The following cardinality rules apply for ECI-2:
- One CAS may communicate with one or more ECS(s) concurrently; and
- One ECS may communicate with one or more CAS(s) concurrently.
6.6.3.11 ECI-3 (Between CES and ECS) |R18| p. 45
The following cardinality rules apply for ECI-3:
- One CES may communicate with one or more ECS(s) concurrently; and
- One ECS may communicate with one or more CES(s) concurrently.
6.6.3.12 ECI-4 (Between CES and EES) |R18| p. 45
The following cardinality rules apply for ECI-4:
- One CES may communicate with one or more EES(s) concurrently; and
- One EES may communicate with one or more CES(s) concurrently.
6.6.3.13 CLOUD-1 (Between CAS and CES) |R18| p. 46
The following cardinality rules apply for CLOUD-1:
- One CAS may communicate with only one CES within the same cloud DN; and
- One CES may communicate with one or more CAS(s) concurrently.
6.6.3.14 CLOUD-2 (Between CES and CES) |R18| p. 46
The following cardinality rules apply for CLOUD-2:
- One CES may communicate with one or more CES(s) concurrently.
6.7 Capability exposure for enabling edge applications p. 46
6.7.1 General p. 46
The Figure 6.7.1-1 shows the capability exposure for enabling edge applications.
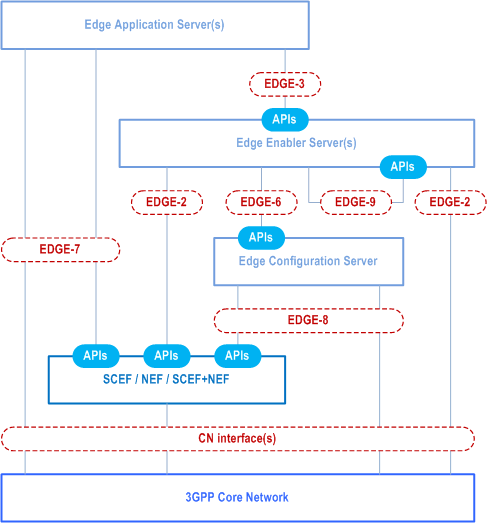
Capability exposure includes the 3GPP core network (i.e. 5GC, EPC), ECS and the EES capability exposure, to fulfil the needs of the edge service operations. The capability exposure functionality is utilized by the functional entities (i.e. EES, EAS and ECS) depicted in the architecture for enabling the edge applications.
6.7.2 APIs provided by the Edge Enabler Layer p. 46
Table 6.7.2-1 summarizes the APIs exposed by the ECS.
| API Name | Known Consumers | References |
|---|---|---|
| Eecs_ | EEC | 8.3 |
| Eecs_ | EES | 8.4.4 |
| Eecs_ | EES, CES | 8.8.3.3 |
| Eecs_ | ECS | 8.17.2.2 |
| Eecs_ | ECS | 8.17.2.3 |
| Eecs_ | ECS | 8.17.2.4 |
| Eecs_ | EES | 8.20.2 |
| Eecs_ | EES | 8.8.3.11 |
Table 6.7.2-2 summarizes the APIs exposed by the EES.
| API Name | Known Consumers | References |
|---|---|---|
| Eees_ | EEC | 8.4.2 |
| Eees_ | EAS | 8.4.3 |
| Eees_ | EEC | 8.5 |
| Eees_ | EAS | 8.6.2 |
| Eees_ | EAS, EES, CAS | 8.6.3 |
| Eees_ | EAS | 8.6.4 |
| Eees_ | EEC, EAS | 8.6.5 |
| Eees_ | EAS | 8.6.6 |
| Eees_ | EAS | 8.6.7 |
| Eees_ | EAS, EES, CAS | 8.8.3.2 |
| Eees_ | EEC, EAS, EES | 8.8.3.4 |
| Eees_ | EEC | 8.8.3.5 |
| Eees_ | EES, EAS | 8.8.3.6 |
| Eees_ | EAS, CAS, EES | 8.8.3.7 |
| Eees_ | EAS, CAS, EES | 8.8.3.8 |
| Eees_ | EES, CES | 8.8.3.9 |
| Eees_ | EES | 8.9.4.2 |
| Eees_ | EES | 8.9.4.3 |
| Eees_ | EEC, EES | 8.15 |
| Eees_ | EES | 8.19 |
Table 6.7.2-3 summarizes the APIs exposed by the CAS.
| API Name | Known Consumers | References |
|---|---|---|
| Ecas_ | EES | 8.8.3.10 |
Table 6.7.2-4 summarizes the APIs exposed the EEC.
| API Name | Known Consumers | References |
|---|---|---|
| Eeec_ | AC | 8.14.4.2 |
| Eeec_ | AC | 8.14.4.3 |
| Eeec_ | AC | 8.14.4.4 |
| Eeec_ | AC | 8.14.4.5 |
| Eeec_ | AC | 8.14.4.6 |
Table 6.7.2-5 summarizes the EES APIs re-used by the CES.
| API Name | Known Consumers | References |
|---|---|---|
| Eees_ | CAS | 8.4.3 |
| Eees_ | CAS | 8.6.2 |
| Eees_ | CAS | 8.6.3 |
| Eees_ | CAS | 8.6.4 |
| Eees_ | CAS | 8.6.5 |
| Eees_ | CAS | 8.6.6 |
| Eees_ | CAS | 8.6.7 |
| Eees_ | EES | 8.8.3.2 |
| Eees_ | CAS | 8.8.3.4 |
| Eees_ | EEC | 8.8.3.5 |
| Eees_ | CAS | 8.8.3.7 |
| Eees_ | CAS | 8.8.3.8 |
| Eees_ | EES | 8.8.3.9 |
| Eees_ | EES | 8.9.4.3 |