Content for TS 23.558 Word version: 19.2.0
0…
5…
6…
6.2a…
6.2b…
6.3…
6.4…
7…
8…
8.3…
8.3.3…
8.3.3.3…
8.4…
8.4.3…
8.4.4…
8.5…
8.6…
8.6.3…
8.6.4…
8.6.6…
8.7…
8.8…
8.8.2.5…
8.8.2A…
8.8.3…
8.8.4…
8.8.5…
8.9…
8.14…
8.14.3…
8.15…
8.17…
8.17.3…
8.17.4…
8.18…
8.19…
8.20…
9…
A…
A.4…
A.5…
B…
E…
8.5 EAS discovery
8.5.1 General
8.5.2 Procedures
8.5.2.1 General
8.5.2.2 Request-response model
8.5.2.3 Subscribe-notify model
8.5.3 Information flows
8.5.3.1 General
8.5.3.2 EAS discovery request
8.5.3.3 EAS discovery response
8.5.3.4 EAS discovery subscription request
8.5.3.5 EAS discovery subscription response
8.5.3.6 EAS discovery notification
8.5.3.7 EAS discovery subscription update request
8.5.3.8 EAS discovery subscription update response
8.5.3.9 EAS discovery unsubscribe request
8.5.3.10 EAS discovery unsubscribe response
8.5.4 APIs
8.5.4.1 General
8.5.4.2 Eees_EASDiscovery_Request operation
8.5.4.3 Eees_EASDiscovery_Subscribe operation
8.5.4.4 Eees_EASDiscovery_Notify operation
8.5.4.5 Eees_EASDiscovery_UpdateSubscription operation
8.5.4.6 Eees_EASDiscovery_Unsubscribe operation
...
...
8.5 EAS discovery p. 95
8.5.1 General p. 95
Discovery procedures enable entities in an edge deployment to obtain information about EAS and their available services, based on specified criteria of interest.
EAS discovery enables the EEC to obtain information about available EASs of interest (e.g. instantiated EASs registered with the EES and instantiable EASs that may be created when needed). The discovery of the EASs is based on matching EAS discovery filters provided in the request.
When multiple EASs are discovered for a specific AC, the EEC may select one or more EASs to enable AC communication with one of the selected EASs. The selection algorithm is outside the scope of this specification. Once the EAS is selected, the EEC may subscribe for the ACR event notifications at the EES of the selected EAS, as described in clause 8.8.3.5.2. The EDN configuration information received from ECS may be used for establishing a connection to EAS(s).
EAS discovery may be initiated by the EEC when a certain trigger condition at the UE is met. Some examples are as follows:
- AC related updates available at the EEC (e.g. due to AC installation/re-installation/activation), AC requesting application server access;
- Lifetime received via EAS discovery response specified in clause 8.5.3 is expired; or
- EEC detects the need of application context relocation as in clause 8.8.
8.5.2 Procedures p. 96
8.5.2.1 General p. 96
Following procedures are supported for EAS discovery:
- Request-response procedure;
-
Subscribe-notify procedures for EAS discovery and EAS dynamic information subscription, comprising:
- Subscription procedure;
- Subscription update procedure; and
- Unsubscribe procedure;
8.5.2.2 Request-response model p. 96
Pre-conditions:
- The EEC has received information (e.g. URI, IP address) related to the EES;
- The EEC has received appropriate security credentials authorizing it to communicate with the EES as specified in clause 8.11; and
- The EES is configured with ECSP's policy for EAS discovery.
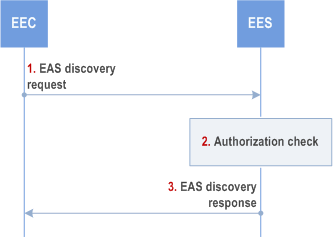
Step 1.
Step 2.
Step 3.
Upon receiving the EAS discovery response, if the EEC selects an EAS which is instantiated (i.e., an EAS profile was provided), the EEC uses the endpoint information for routing of the outgoing application data traffic to EAS(s), as needed, and may provide necessary notifications to the AC(s). The EEC may use the border or overlap between EAS Geographical Service Areas for service continuity purposes. The EEC may cache the EAS information (e.g. EAS endpoint) for subsequent use and avoid the need to repeat step 1. If the Lifetime IE is included in the response, the EEC may cache the EAS information only for the duration specified by the Lifetime IE.
Upon receiving the EAS discovery response, if the EEC selects an EAS which is instantiable but not yet instantiated (i.e. an EAS profile is not provided), the EEC sends the EAS information provisioning request indicating the selected EASID as in clause 8.15.
If the EAS discovery request fails, the EEC may resend the EAS discovery request, taking into account the received failure cause. If the failure cause indicated that EEC registration is required, the EEC shall perform an EEC registration before resending the EAS discovery request.
The EEC sends an EAS discovery request to the EES. The EAS discovery request includes the requestor identifier [EECID] along with the security credentials and may include EAS discovery filters, EEC service continuity support, and may also include UE location to retrieve information about particular EAS(s) or a category of EASs, e.g. gaming applications, or Edge Applications Server(s) available in certain service areas, e.g. available on a UE's predicted or expected route. The request may include an EAS selection request indicator.
Step 2.
Upon receiving the request from the EEC, the EES checks if the EEC is authorized to discover the requested EAS(s). The authorization check may apply to an individual EAS, a category of EASs or to the EDN, i.e. to all the EASs. If UE's location information is not already available, the EES obtains the UE location by utilizing the capabilities of the 3GPP core network as specified in clause 8.10.3. If EAS discovery filters are provided by the EEC, but it does not contain Application group profile, the EES identifies the EAS(s) based on the provided EAS discovery filters and the UE location.
When the bundle EAS information is provided, then;
When EAS discovery filters are not provided, then:
- If bundle EAS information includes EAS bundle identifier, the EES identifies all or part of the EAS(s) associated with the same EAS bundle identifier.
- If bundle EAS information includes a list of EASIDs, the EES identifies the EASs which are all or part of the EAS bundle.
- if available, the EES identifies the EAS(s) based on the UE-specific service information at the EES and the UE location;
- EES identifies the EAS(s) by applying the ECSP policy (e.g. based only on the UE location);
- not available, then based on the policy if EES needs to select the common EAS, the EES identifies an EAS for the Application Group ID based on the provided EAS discovery filters such as KPIs, UE-specific service information or the ECSP policy. Furthermore, the EES stores the common EAS information and related Application Group ID.
-
available at the EES, then the EES provides information of that EAS as result for EAS discovery.
Furthermore, if the E2E response time is received:
- when the UE in the overlapping area between the EDNs of common EAS and EAS registered to this EES (e.g. UE can connect either common EAS or EAS registered to this EES), the EES identifies either common EAS or EAS registered to this EES for the UE based on the common EAS KPI as specified in Table 8.2.5-1 and EDN information, registered EAS KPI as specified in Table 8.2.5-1 and EDN information, and inter-EAS communication performance of these EASs.
- When the UE is not in the overlapping area between the EDNs of common EAS and EAS registered to this EES (e.g. UE is not in the common EAS service area), then the EES identifies candidate EAS(s) for the group from its registered EASs and checks if the candidate EAS(s) can satisfy the E2E response time considering the response time of the candidate EAS(s), the response time of available common EASs in other EDNs and the inter-EAS communication latency. If the E2E response time cannot be satisfied, the EES will respond the EEC in step 3 indicating such a rejection reason; otherwise, the EES selects a candidate EAS and interacts with the ECS-ER to store it as common EAS as described in clause 8.20.2.3.
- If the UE is in the overlapping area between the EDNs of common EAS and EAS registered to this EES (e.g. UE can connect either common EAS or EAS registered to this EES), the EES identifies either common EAS or EAS registered to this EES for the UE based on the common EAS KPI as specified in table 8.2.5 and EDN information, registered EAS KPI as specified in table 8.2.5 and EDN information, and inter-EAS communication performance of these EASs.
- otherwise, the EES checks with the ECS-ER about all available common EASs and their corresponding EDNs by using procedure defined in clause 8.20.2.2. If no common EAS is available for the group, EES identifies one EAS for the group and interacts with the ECS-ER to store the common EAS information as described in clause 8.20.2.3. If current EDN already has available common EAS, the EES selects such common EAS considering the required E2E response time. If there are available common EASs in other EDNs, the EES identifies candidate EAS(s) for the group from its registered EASs and checks if the candidate EAS(s) can satisfy the E2E response time considering the response time of the candidate EAS(s), the response time of available common EASs in other EDNs and the inter-EAS communication latency. If the E2E response time cannot be satisfied, the EES will respond the EEC in step 3 indicating such a rejection reason; otherwise, the EES selects a candidate EAS and interacts with the ECS-ER to store it as common EAS as described in clause 8.20.2.3.
Step 3.
If the processing of the request was successful, the EES sends an EAS discovery response to the EEC, which includes information about the discovered EASs and Instantiable EAS Information. For discovered EASs, this includes endpoint information. Depending on the EAS discovery filters received in the EAS discovery request, the response may include additional information regarding matched capabilities, e.g. service permissions levels, KPIs, AC locations(s) that the EASs can support, ACR scenarios supported by the EAS, etc. The EAS discovery response may contain a list of EASs and Instantiable EAS Information. This list may be based on EAS discovery filters containing a Geographical or Topological Service Area, e.g. a route, included in the EAS discovery request by the EEC. When the discovered EAS is for a certain application group, then the Application Group ID is also included in the response message. If the discovered EAS is registered to another EES, then the EES endpoint of the EES where the discovered EAS is registered is also included in the response message.
When the EES accepts the request and determines to trigger the EAS instantiation, then the response may indicate that the EAS instantiation is in progress so that the detailed EAS profile information will be available later. When EEC receives the EAS instantiation in progress indication, the EEC may send EAS discovery subscription request message if not subscribed yet or send EAS discovery request message later to the EES for obtaining updated EAS information.
If the EES is unable to determine the EAS information using the inputs in the EAS discovery request, UE-specific service information at the EES or the ECSP policy, the EES shall reject the EAS discovery request and respond with an appropriate failure cause.
If the EEC is not registered with the EES, and ECSP policy requires the EEC to perform EEC registration prior to EAS discovery, the EES shall include an appropriate failure cause in the EAS discovery response indicating that EEC registration is required.
If the UE location and predicted/expected UE locations, provided in the EAS discovery request, are outside the Geographical or Topological Service Area of an EAS, then the EES shall not include that EAS in the discovery response. The discovery response may include EAS(s) that cannot serve the UE at its current location if a predicted/expected UE location was provided in the EAS discovery request.
8.5.2.3 Subscribe-notify model p. 99
8.5.2.3.1 General p. 99
Clause 8.5.2.3.2 and clause 8.5.2.3.3 together illustrate the EAS discovery procedure based on Subscribe/ Notify model.
Clause 8.5.2.3.4 illustrates the EAS discovery update procedure.
Clause 8.5.2.3.5 illustrates the EAS discovery unsubscribe procedure.
8.5.2.3.2 Subscribe p. 100
Figure 8.5.2.3.2-1 illustrates the EAS discovery subscription procedure between the EEC and the EES. This subscription enables EES to inform EEC of various EAS discovery related events of interest to EEC (e.g. EAS discovery notification and EAS dynamic information).
Pre-conditions:
- The EEC has received information (e.g. URI, IP address) related to the EES;
- The EEC has received appropriate security credentials authorizing it to communicate with the EES as specified in clause 8.11;
- The EES is configured with ECSP's policy for EAS discovery; and
- The EEC has optionally acquired a Notification Target Address to be used in its subscriptions to notifications.
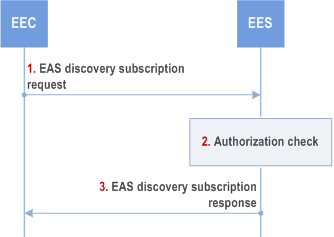
Step 1.
The EEC sends an EAS discovery subscription request to the EES. The EAS discovery subscription request includes the EECID along with the security credentials, Event ID, and may include EAS discovery filters and EAS dynamic information filters to subscribe to information about particular EAS(s) or a category of EASs (e.g. gaming applications) or dynamic information about EAS(s).
If the application triggering is supported and required by the EEC, the EEC may include the EEC Triggering request information element instead of the Notification Target Address in the request message.
Step 2.
Upon receiving the request from the EEC, the EES checks if the EEC is authorized to subscribe for information of the requested EAS(s). The authorization check may apply to an individual EAS, a category of EASs or to the EDN, i.e. to all the EASs. The EES may utilize the capabilities (e.g. UE location) of the 3GPP core network as specified in clause 8.10.3. If the request is authorized, the EES creates and stores the subscription for EAS discovery.
Step 3.
If the processing of the request was successful, the EES sends an EAS discovery subscription response to the EEC, which includes the subscription identifier and may include the expiration time, indicating when the subscription will automatically expire. To maintain the subscription, the EEC shall send an EAS discovery subscription update request prior to the expiration time. If an EAS discovery subscription update request is not received prior to the expiration time, the EES shall treat the EEC as implicitly unsubscribed.
In the case of subscription to an EAS availability change event, if there is no instantiated EAS that matches the requested EAS discovery filters and such EAS is instantiable based on the information about instantiable EASs, the request is treated as successful. If the EEC indicates EAS Instantiation Triggering in the EAS discovery subscription request and the EAS instantiation is not in progress for the requested EASID, the EES may trigger dynamic instantiation of the EAS as specified in the clause 8.12; if the EEC indicates EAS Instantiation Triggering Suppress in the EAS discovery subscription request, the EES determines not triggering the ECSP management system to instantiate the EAS and Instantiable EAS Information (e.g. instantiated, instantiable but not be instantiated yet) is provided; otherwise, the EES does not trigger the EAS instantiation nor returns the Instantiable EAS Information.
In the case of subscription to an EAS dynamic information change event, if the EES is unable to determine the instantiated EAS information using the inputs in the EAS discovery subscription request, UE-specific service information at the EES or the ECSP policy, the EES shall reject the EAS discovery subscription request and respond with an appropriate failure cause.
If the EEC is not registered with the EES, and ECSP policy requires the EEC to perform EEC registration prior to EAS discovery, the EES shall include an appropriate failure cause in the EAS discovery response indicating that EEC registration is required.
If the EAS discovery subscription request fails, the EEC may resend the EAS discovery subscription request again, taking into account the received failure cause. If the failure cause indicated that EEC registration is required, the EEC shall perform an EEC registration before resending the EAS discovery subscription request.
8.5.2.3.3 Notify p. 101
Figure 8.5.2.3.3-1 illustrates the EAS discovery notification procedure between the EEC and the EES.
Pre-conditions:
- The EEC has subscribed with the EES for the EAS discovery information as specified in clause 8.5.2.3.2.
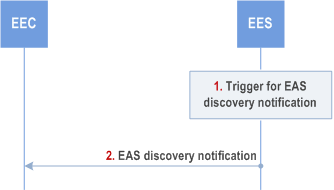
Step 1.
Step 2.
Upon receiving the EAS discovery notification, if the EEC selects an EAS which is instantiated (i.e., an EAS profile was provided), the EEC uses the endpoint information for routing of the outgoing application data traffic to EAS(s), as needed, and may provide necessary notifications to the AC(s). The EEC may use the border or overlap between EAS Geographical Service Areas for service continuity purposes. The EEC may cache the EAS information (e.g. EAS endpoint) for subsequent use. If the Lifetime IE is included in the notification, the EEC may cache the EAS information only for the duration specified by the Lifetime IE.
Upon receiving the EAS discovery notification, if the EEC selects an EAS which is instantiable but not yet instantiated (i.e. an EAS profile is not provided), the EEC may send the EAS information provisioning request indicating the selected EASID as in clause 8.15.
An event occurs at the EES that satisfies trigger conditions for notifying (e.g. to provide EAS discovery information or EAS dynamic information) a subscribed EEC. If UE's location information is not already available, the EES obtains the UE location by utilizing the capabilities of the 3GPP core network as specified in clause 8.10.3. If EAS discovery filters were provided by the EEC during subscription creation, the EES identifies the EAS(s) based on the provided EAS discovery filters and the UE location.
For EAS dynamic information change event, the EES, based on local policy, may use received EAS endpoints from EEC or all registered EAS endpoints to get edge load analytics information from ADAES services (e.g. as specified in clause 8.8 of TS 23.436) to monitor EAS service status like EAS status and EAS schedule.
When the bundle EAS information is provided, then;
- If EAS bundle identifier was provided, the EES identifies all or part of the EAS(s) associated with the same EAS bundle identifier.
- If a list of EASIDs is provided, the EES identifies the EASs which are all or part of the EAS bundle.
- if available, the EES identifies the EAS(s) based on the UE-specific service information at the EES and the UE location;
- EES identifies the EAS(s) by applying the ECSP policy (e.g. based only on the UE location);
Step 2.
The EES sends an EAS discovery notification to the EEC with the EAS information determined in step 1, which includes information about the discovered EASs and Instantiable EAS Information. For discovered EASs, this includes endpoint information. Depending on the event type and EAS discovery filters received in the EAS discovery subscription request, the notification may include additional information regarding matched capabilities, e.g. service permissions levels, KPIs, AC locations(s) that the EASs can support, ACR scenarios supported by the EAS, etc. The EAS discovery notification may contain a list of EASs and Instantiable EAS Information. This list may be based on EAS discovery filters containing a Geographical or Topological Service Area, e.g. a route, included in the EAS discovery subscription request by the EEC. When the discovered EAS is for a certain application group, then the Application Group ID is also included in the notification message. If the discovered EAS is registered to another EES, then the EES endpoint of the EES where the discovered EAS is registered is also included in the notification message.
8.5.2.3.4 Subscription update p. 103
Figure 8.5.2.3.4-1 illustrates the EAS discovery subscription update procedure between the EEC and the EES.
Pre-conditions:
- The EEC has subscribed with the EES for the EAS discovery information as specified in clause 8.5.2.3.2
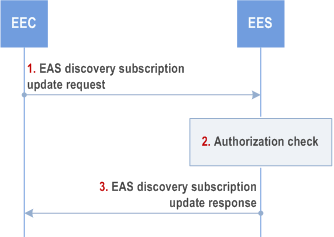
Step 1.
The EEC sends an EAS discovery subscription update request to the EES. The EAS discovery subscription update request includes the security credentials and the subscription identifier. It may also include EAS discovery filters, EAS dynamic information filters and/or proposed expiration time for the updated subscription.
Step 2.
Upon receiving the request from the EEC, the EES checks if the EEC is authorized to update the subscription information. The EES may utilize the capabilities (e.g. UE location) of the 3GPP core network as specified in clause 8.10.3. If the request is authorized, the EES updates the stored subscription for EAS discovery.
Step 3.
The EES sends an EAS discovery subscription update response to the EEC, which may include the expiration time, indicating when the updated subscription will automatically expire. To maintain the subscription, the EEC shall send an EAS discovery subscription update request prior to the expiration time. If an EAS discovery subscription update request is not received prior to the expiration time, the EES shall treat the EEC as implicitly unsubscribed.
8.5.2.3.5 Unsubscribe p. 103
Figure 8.5.2.3.5-1 illustrates the EAS discovery unsubscribe procedure between the EEC and the EES.
Pre-conditions:
- The EEC has subscribed with the EES for notification (e.g. EAS discovery information and EAS dynamic information) as specified in clause 8.5.2.3.2
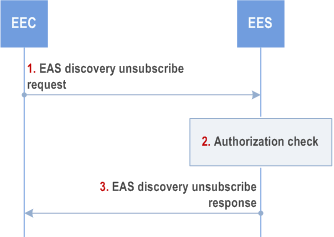
Step 1.
The EEC sends an EAS discovery unsubscribe request to the EES. The EAS discovery unsubscribe request includes the security credentials of the EEC along with the subscription identifier.
Step 2.
Upon receiving the request, the EES performs an authorization check to verify whether the EEC has authorization to perform the operation. If authorized, the EES cancels the subscription for provisioning as requested in step 1.
Step 3.
The EES responds with an EAS discovery unsubscribe response.
8.5.3 Information flows p. 104
8.5.3.1 General p. 104
The following information flows are specified for EAS discovery:
- EAS discovery request and response;
- EAS discovery subscription, notification, subscription update and unsubscribe; and
- EAS dynamic information subscription, notification, subscription update and unsubscribe.
8.5.3.2 EAS discovery request p. 104
Table 8.5.3.2-1 describes information elements for the EAS discovery request. Table 8.5.3.2-2 provides further detail about the EAS Discovery Filter information element.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Requestor identifier | M | The ID of the requestor (e.g. EECID) |
| UE Identifier | O | The identifier of the UE (i.e., GPSI). |
| Security credentials | M | Security credentials resulting from a successful authorization for the edge computing service. |
| EAS discovery filters | O | Set of characteristics to determine required EASs, as detailed in Table 8.5.3.2-2. |
| UE location | O | The location information of the UE. The UE location is described in clause 7.3.2. |
| List of UE IDs | O | List of UE IDs in an Application Group, applicable for S-EAS or S-EES triggered EAS discovery request. |
| Serving MNO information (NOTE 2) | O | The serving MNO information (e.g. MNO name, PLMN ID) which is serving the subscriber. |
| Target DNAI (NOTE) | O | Target DNAI information which can be associated with potential T-EAS(s) |
| EEC Service Continuity Support | O | Indicates if the EEC supports service continuity or not. The IE also indicates which ACR scenarios are supported by the EEC or, if this message is sent by the EEC to discover a T-EAS, which ACR scenario(s) are intended to be used for the ACR. |
| EES Service Continuity Support (NOTE 1) | O | The IE indicates if the S-EES supports service continuity or not. The IE also indicates which ACR scenarios are supported by the S-EES or, if the EAS discovery is used for an S-EES executed ACR according to clause 8.8.2.5, which ACR scenario is to be used for the ACR. |
| EAS Service Continuity Support (NOTE 1) | O | The IE indicates if the S-EAS supports service continuity or not. The IE also indicates which ACR scenarios are supported by the S-EAS or, if the EAS discovery is used for an S-EAS decided ACR according to clause 8.8.2.4, which ACR scenario is to be used for the ACR. |
| EAS Instantiation Triggering Suppress | O | Indicates to the EES that EAS instantiation triggering should not be performed for the current request, and Instantiable EAS Information (e.g. instantiated, instantiable but not be instantiated yet) is to be provided in response. |
| EAS selection request indicator | O | Indicates the request for EAS selection support from the EES (e.g., for constrained device). |
| Indication of service continuity planning | O | Indicates that this EAS discovery request is triggered for service continuity planning. |
| Prediction expiration time | O | The estimated time the UE may reach the Predicted/Expected UE location or EAS service area at the latest. This IE is used by EES as analytics input to get edge load analytics information from ADAES service as described in clause 8.8 of TS 23.436. |
|
NOTE 1:
This IE shall not be included when the request originates from the EEC.
NOTE 2:
This IE shall be included if edge node sharing is used.
|
||
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| List of AC characteristics (NOTE 1) | O | Describes the ACs for which a matching EAS is needed. |
| > AC profile (NOTE 2) | M | AC profile containing parameters used to determine matching EAS. AC profiles are further described in Table 8.2.2-1. |
| > Application group profile | O | Application group profile associated with the AC Profile, as defined in Table 8.2.11-1. |
| List of EAS characteristics (NOTE 1, NOTE 3) | O | Describes the characteristic of required EASs. |
| > EASID | O | Identifier of the required EAS. |
| > Application Group ID | O | Application group identifier as defined in clause 7.2.11. |
| > EAS content synchronization support | O | Indicates if the EAS content synchronization support is required or not. |
| > Bundle ID (NOTE 5) | O | A list of EASIDs or a bundle ID as described in clause 7.2.10. |
| > List of EASIDs (NOTE 5) | O | A list of EASIDs specific to a particular EAS bundle. |
| > Bundle type (NOTE 4) | O | Type of the EAS bundle as described in clause 7.2.10. |
| > EAS bundle requirements (NOTE 4) | O | Requirements associated with the EAS bundle as described in clause 8.2.10. |
| > EAS provider identifier | O | Identifier of the required EAS provider |
| > EAS type | O | The category or type of required EAS (e.g. V2X, UAV, application enabler) |
| > EAS schedule | O | Required availability schedule of the EAS (e.g. time windows) |
| > EAS Geographical Service Area | O | Location(s) (e.g. geographical area, route) where the EAS service should be available. |
| > EAS Topological Service Area | O | Topological area (e.g. cell ID, TAI) for which the EAS service should be available. See possible formats in Table 8.2.7-1. |
| > Service continuity support | O | Indicates if the service continuity support is required or not. |
| > Service permission level | O | Required level of service permissions e.g. trial, gold-class |
| > Service feature(s) | O | Required service features e.g. single vs. multi-player gaming service |
|
NOTE 1:
Either "List of AC characteristics" or "List of EAS characteristics" shall be present.
NOTE 2:
"Preferred ECSP list" IE shall not be present.
NOTE 3:
The "List of EAS characteristics" IE must include at least one optional IE, if used as an EAS discovery filter.
NOTE 4:
When EAS discovery request is sent by the EEC, this IE shall not be included.
NOTE 5:
"Bundle ID" and "List of EASIDs" shall not both be present.
|
||
8.5.3.3 EAS discovery response p. 106
Table 8.5.3.3-1 describes information elements for the EAS discovery response from the EES to the EEC.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Successful response | O | Indicates that the EAS discovery request was successful. |
| > Discovered EAS list (NOTE 1, NOTE 3) | O | List of discovered EAS(s). Each element includes the information described below. |
| >> EAS profile | M | Profile of the EAS. Each element is described in clause 8.2.4 |
| >> Application Group ID list (NOTE 4) | O | List of Application Group IDs associated with EAS. |
| >> EES Endpoint | O | The endpoint address (e.g. URI, IP address) of the EES. |
| >> Lifetime | O | Time interval or duration during which the information elements in the EAS profile is valid and supposed to be cached in the EEC (e.g. time-to-live value for an EAS Endpoint) |
| > Analytics information | O | Analytics data for each discovered application server. |
| >> Statistical data | O | Indicates the statistical analytics data (e.g. number of times the client received expected performance from the EAS). |
| >> Predictive data | O | Indicates predictive analytics data for EAS service status (e.g. EAS schedule, EAS status) change. |
| > Instantiable EAS Information (NOTE 1) | O | The EAS instantiation status per EASID (e.g. instantiated, instantiable but not instantiated yet, instantiation in progress). |
| >> Instantiation criteria (NOTE 2) | O | The criteria upon which EAS can be instantiated (e.g. based on specific date and time). |
| Failure response | O | Indicates that the EAS discovery request failed. |
| > Cause | O | Indicates the cause of EAS discovery request failure. |
|
NOTE 1:
At least one of the IEs must be included in the Successful response.
NOTE 2:
"Instantiation criteria" IE shall be present only when the value of "Instantiable EAS information" IE is "instantiable but not be instantiated yet".
NOTE 3:
If EAS discovery is used for ENS scenario, discovered EAS list contains only those EASs which are allowed to be used by the subscribers of the serving MNO.
NOTE 4:
"Application Group ID list" IE shall be present when "Application Group profile" is included for "AC profile" in EAS discovery request as specified in clause 8.5.3.2.
|
||
8.5.3.4 EAS discovery subscription request p. 107
Table 8.5.3.4-1 describes the information elements for EAS discovery subscription request from the EEC to the EES.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| EECID | M | Unique identifier of the EEC. |
| UE Identifier | O | The identifier of the UE (i.e., GPSI). |
| Event ID | M | Event ID:
|
| Security credentials | M | Security credentials resulting from a successful authorization for the edge computing service. |
| Notification Target Address (NOTE 1) | O | The Notification target address (e.g. URL) where the notifications destined for the EEC should be sent to. |
| EAS discovery filters | O | Set of characteristics to determine matching EASs (as detailed in Table 8.5.3.2-2). Applicable for "EAS availability change" event |
| EAS dynamic information filters | O | List of dynamic information changes (as detailed in Table 8.5.3.4-2) about EAS, the EEC is interested in. Applicable for "EAS dynamic information change" event |
| EEC Service Continuity Support | O | Indicates if the EEC supports service continuity or not. The IE also indicates which ACR scenarios are supported by the EEC. |
| Proposed expiration time | O | Proposed expiration time for the subscription |
| EAS Instantiation Triggering Indication (NOTE 2) | O | Indicates to the EES that EAS instantiation triggering may be performed for the current request if needed. |
| EAS Instantiation Triggering Suppress (NOTE 2) | O | Indicates to the EES that EAS instantiation triggering should not be performed for the current request, and Instantiable EAS Information (e.g. instantiated, instantiable but not be instantiated yet) is to be provided in the notification. |
| EEC Triggering request (NOTE 1) | O | Indicates that EEC Triggering is requested. |
| Port ID for EEC Triggering (NOTE 3) | O | Port ID used for the EEC Triggering. |
|
NOTE 1:
One of them may be included in the request message.
NOTE 2:
One of them may be included in the request message.
NOTE 3:
This IE may be provided if the EEC Triggering request is included in the EAS discovery subscription request.
|
||
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| List of dynamic information filters | M | List of EAS dynamic information required by the EEC per EAS. |
| > EASID | M | Identifier of the EAS. |
| > ACIDs | O | Flag to notify change in list of ACIDs served by the EAS. |
| > EAS Description | O | Flag to notify change in description of the EAS. |
| > EAS Endpoint | O | Flag to notify change in EAS endpoint. It may also include one or more EAS endpoints to be monitored by the EES. If no EAS endpoint is provided, all EASs registered in the EES will be monitored. |
| > EAS Features | O | Flag to notify any change in features provided by the EAS. |
| > EAS Schedule | O | Flag to notify change in availability schedule of the EAS (e.g. time windows). |
| > EAS Service Area | O | Flag to notify change in geographical service area that the EAS serves. |
| > EAS Service KPIs | O | Flag to notify change in characteristics of the EAS. |
| > EAS Status | O | Flag to notify change in the status of the EAS (e.g. enabled, disabled, etc.). |
| > Service continuity support | O | Flag to notify change in EAS support for service continuity. |
8.5.3.5 EAS discovery subscription response p. 109
Table 8.5.3.5-1 describes the information elements for EAS discovery subscription response from the EES to the EEC.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Successful response | O | Indicates that the subscription request was successful. |
| > Subscription ID | M | Subscription identifier corresponding to the subscription. |
| > Expiration time | O | Indicates the expiration time of the subscription. To maintain an active subscription, a subscription update is required before the expiration time. |
| Failure response | O | Indicates that the subscription request failed. |
| > Cause | O | Indicates the cause of subscription request failure |
8.5.3.6 EAS discovery notification p. 109
Table 8.5.3.6-1 describes the information elements for EAS discovery notification from the EES to the EEC.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Subscription ID | M | Subscription identifier corresponding to the subscription stored in the EES for the request. |
| Event ID | M | Either EAS availability change or EAS dynamic information change. |
| EAS list | O | List of discovered EAS profiles. Each element includes the information described below. |
| > EAS profile | M | Profile of the EAS. Each element is described in clause 8.2.4 |
| > Application Group ID list (NOTE 3) | O | List of Application Group IDs associated with EAS. |
| > EES Endpoint | O | The endpoint address (e.g. URI, IP address) of the common EES. |
| > Lifetime | O | Time interval or duration during which the information elements in the EAS profile is valid and supposed to be cached in the EEC (e.g. time-to-live value for an EAS Endpoint) |
| > Analytics information | O | Analytics information for EAS. |
| >> Statistical data | O | Indicates the statistical analytics data (e.g. number of times the client received expected performance from the EAS). Applicable for "EAS availability change" event. |
| >> Predictive data | O | Indicates predictive analytics data for EAS service status (e.g. EAS schedule, EAS status) change. Applicable for "EAS dynamic information change" event. |
| Instantiable EAS information (NOTE 1) | O | The EAS instantiation status per EASID (e.g. instantiated, instantiable but not be instantiated yet). |
| > Instantiation criteria (NOTE 2) | O | The criteria upon which EAS can be instantiated (e.g. based on specific date and time). |
|
NOTE 1:
"Instantiable EAS information" can be provided to EEC, if the "EAS Instantiation Triggering Suppress" is provided in EAS discovery subscription request.
NOTE 2:
"Instantiation criteria" IE shall be present only when the value of "Instantiable EAS information" IE is "instantiable but not be instantiated yet".
NOTE 3:
"Application Group ID list" IE shall be present when "Application Group profile" is included for "AC profile" in EAS discovery subscription request as specified in clause 8.5.3.4.
|
||
8.5.3.7 EAS discovery subscription update request p. 110
Table 8.5.3.7-1 describes the information elements for EAS discovery subscription update request from the EEC to the EES.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Subscription ID | M | Subscription identifier corresponding to the subscription to be updated |
| Security credentials | M | Security credentials resulting from a successful authorization for the edge computing service. |
| Proposed expiration time | O | Proposed expiration time for the subscription |
| EAS discovery filters | O | Set of characteristics to determine required EASs, as detailed in Table 8.5.3.2-2. |
| EAS dynamic information filters | O | List of dynamic information about EAS, the EEC is interested in, as detailed in Table 8.5.3.4-2. |
| EEC Service Continuity Support | O | Indicates if the EEC supports service continuity or not. The IE also indicates which ACR scenarios are supported by the EEC. |
8.5.3.8 EAS discovery subscription update response p. 111
Table 8.5.3.8-1 describes the information elements for EAS discovery subscription update response from the EES to the EEC.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Successful response | O | Indicates that the subscription update request was successful. |
| > Expiration time | O | Indicates the expiration time of the updated subscription. To maintain an active subscription, a subscription update is required before the expiration time. |
| Failure response | O | Indicates that the subscription update request failed. |
| > Cause | O | Indicates the cause of subscription update request failure |
8.5.3.9 EAS discovery unsubscribe request p. 111
Table 8.5.3.9-1 describes the information elements for EAS discovery unsubscribe request from the EEC to the EES.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Subscription ID | M | Subscription identifier corresponding to the subscription to be unsubscribed |
| Security credentials | M | Security credentials of the EEC |
8.5.3.10 EAS discovery unsubscribe response p. 111
Table 8.5.3.10-1 describes the information elements for EAS discovery unsubscribe response from the EES to the EEC.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Successful response | O | Indicates that the unsubscribe request was successful. |
| Failure response | O | Indicates that the unsubscribe request failed. |
| > Cause | O | Indicates the cause of unsubscribe request failure |
8.5.4 APIs p. 111
8.5.4.1 General p. 111
Table 8.5.4.1-1 illustrates the API for EAS discovery.
| API Name | API Operations | Operation Semantics | Consumer(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eees_ | Request | Request/ Response | EEC |
| Subscribe | Subscribe/ Notify | EEC | |
| Notify | |||
| UpdateSubscription | |||
| Unsubscribe |
8.5.4.2 Eees_EASDiscovery_Request operation p. 112
API operation name:
Eees_EASDiscovery_Request
Description:
The consumer requests for one time EAS discovery information.
Inputs:
See clause 8.5.3.2.
Outputs:
See clause 8.5.3.3.
See clause 8.5.2.2 for details of usage of this operation.
8.5.4.3 Eees_EASDiscovery_Subscribe operation p. 112
API operation name:
Eees_EASDiscovery_Subscribe
Description:
The consumer subscribes for EAS discovery information.
Inputs:
See clause 8.5.3.4.
Outputs:
See clause 8.5.3.5.
See clause 8.5.2.3.2 for details of usage of this operation.
8.5.4.4 Eees_EASDiscovery_Notify operation p. 112
API operation name:
Eees_EASDiscovery_Notify
Description:
The consumer is notified with EAS discovery and/or EAS dynamic information.
Inputs:
See clause 8.5.3.6.
Outputs:
None.
See clause 8.5.2.3.3 for details of usage of this operation.
8.5.4.5 Eees_EASDiscovery_UpdateSubscription operation p. 112
API operation name:
Eees_EASDiscovery_UpdateSubscription
Description:
The consumer updates an existing subscription for EAS discovery information.
Inputs:
See clause 8.5.3.7.
Outputs:
See clause 8.5.3.8.
See clause 8.5.2.3.4 for details of usage of this operation.
8.5.4.6 Eees_EASDiscovery_Unsubscribe operation p. 112
API operation name:
Eees_EASDiscovery_Unsubscribe
Description:
The consumer cancels an existing subscription for EAS discovery information.
Inputs:
See clause 8.5.3.9.
Outputs:
See clause 8.5.3.10.
See clause 8.5.2.3.5 for details of usage of this operation.