Content for TS 23.558 Word version: 19.2.0
0…
5…
6…
6.2a…
6.2b…
6.3…
6.4…
7…
8…
8.3…
8.3.3…
8.3.3.3…
8.4…
8.4.3…
8.4.4…
8.5…
8.6…
8.6.3…
8.6.4…
8.6.6…
8.7…
8.8…
8.8.2.5…
8.8.2A…
8.8.3…
8.8.4…
8.8.5…
8.9…
8.14…
8.14.3…
8.15…
8.17…
8.17.3…
8.17.4…
8.18…
8.19…
8.20…
9…
A…
A.4…
A.5…
B…
E…
6.2b Architecture for Federation support
6.2c Architecture for enabling cloud applications with edge applications
6.2d Architecture for enabling cloud applications with edge applications, with CES support
...
...
6.2b Architecture for Federation support |R18| p. 33
6.2b.1 General p. 33
This clause describes the architecture for support of Federation. To support Federation, EDGE-10 reference point is used between the ECSs to exchange ECS profile and EDN configuration information.
If the ECSP is required to support service provisioning for a certain EAS whose information is not within the pre-configuration or OAM configuration, the ECS can use Edge repository functions as defined in clause 6.3.4 to support ECS discovery via ECS-ER.
6.2b.2 Architecture p. 33
Figure 6.2b.2-1 shows the architecture for support of federation. EDGE-10 reference point is introduced between the ECSs. ECSs interfacing over EDGE-10 reference point can be provided by different or the same ECSP.
EDGE-10 interface is used for exchange of EDN configuration information.
When one of the ECS is enhanced as an edge repository (ECS-ER) as defined in clause 6.3.4, making it the center of information for edge deployments, the ECS-ER receives information about edge deployments from other ECSs and stores it. In such deployments, EDGE-10 interface is used both for exchanging of ECS profile during ECS discovery and for exchanging EDN configuration information during service provisioning information retrieval.
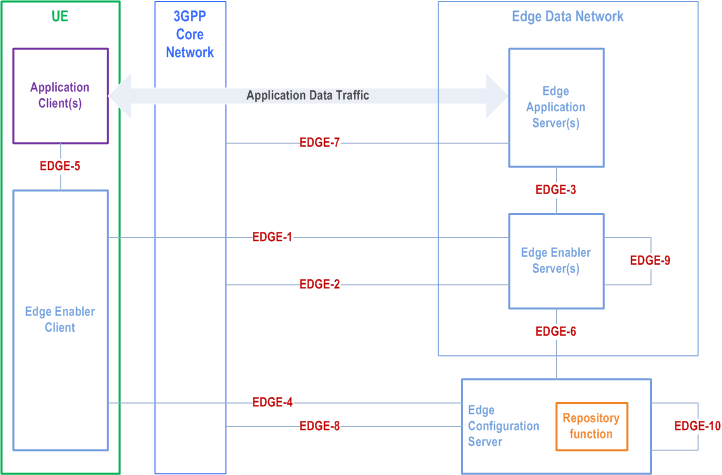
6.2c Architecture for enabling cloud applications with edge applications |R18| p. 34
Figure 6.2c-1 illustrates the architecture for enabling cloud applications along with the edge applications.
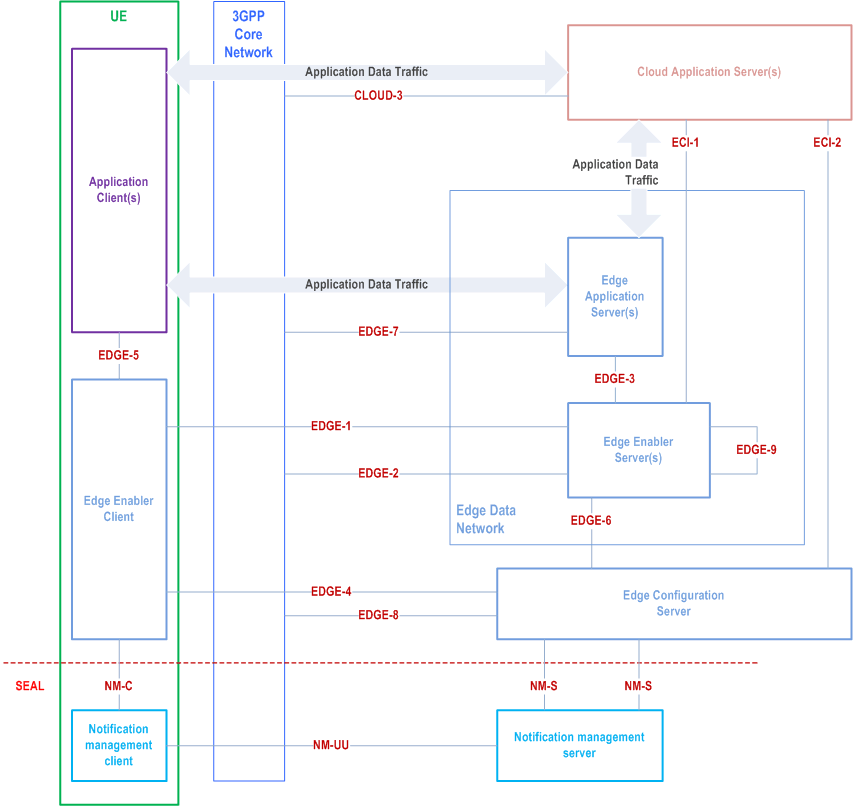
Cloud application server (CAS) residing outside the EDN may need to interact with the EEL entities e.g. for service continuity. The CAS and EAS interaction is Application Data Traffic, which is out-of-scope of this specification.
6.2d Architecture for enabling cloud applications with edge applications, with CES support |R18| p. 35
Figure 6.2d-1 illustrates the architecture for enabling cloud applications along with the edge applications, when CES is used.
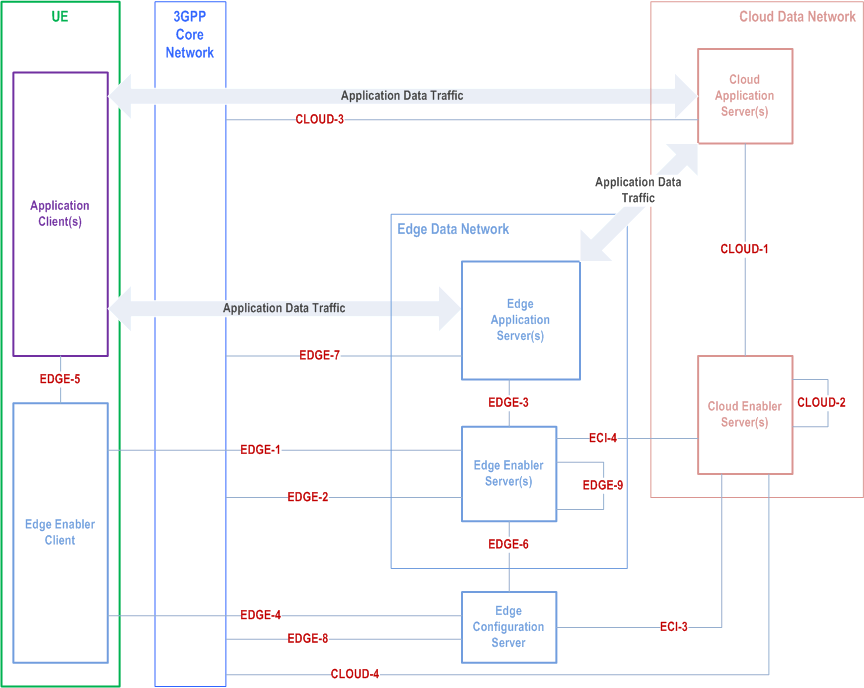
Cloud Application Server (CAS) residing in the cloud DN may need to interact with the Cloud Enabler Server (CES) which is part of the EEL for interworking, e.g. for service continuity. The CAS and EAS interaction is Application Data Traffic, which is out-of-scope of this specification.