Content for TS 23.558 Word version: 19.2.0
0…
5…
6…
6.2a…
6.2b…
6.3…
6.4…
7…
8…
8.3…
8.3.3…
8.3.3.3…
8.4…
8.4.3…
8.4.4…
8.5…
8.6…
8.6.3…
8.6.4…
8.6.6…
8.7…
8.8…
8.8.2.5…
8.8.2A…
8.8.3…
8.8.4…
8.8.5…
8.9…
8.14…
8.14.3…
8.15…
8.17…
8.17.3…
8.17.4…
8.18…
8.19…
8.20…
9…
A…
A.4…
A.5…
B…
E…
8.14 EDGE-5 APIs
8.14.1 General
8.14.2 Procedures
8.14.2.1 General
8.14.2.2 Registration
8.14.2.2.1 General
8.14.2.2.2 AC registration
8.14.2.2.3 AC registration update
8.14.2.2.4 AC deregistration
8.14.2.3 EAS discovery
8.14.2.4 ACR trigger request
8.14.2.5 EEC services subscription
8.14.2.5.1 General
8.14.2.5.2 Subscribe
8.14.2.5.3 EEC services notification
8.14.2.5.4 EEC services subscription update
8.14.2.5.5 Unsubscribe
8.14.2.6 UE ID request
...
...
8.14 EDGE-5 APIs |R18| p. 227
8.14.1 General p. 227
EEC exposes EDGE-5 APIs corresponding to EEC's capabilities, for the AC to request EEC's services for edge enablement. Using these APIs, ACs request the EEC for EEL services. EDGE-5 APIs include one-time request/response operations for EAS discovery, retrieval of UE ID and ACR operations. Additionally, the AC can request for an AC subscription. The EEC creates the subscription and when required, performs necessary operations such as EAS discovery, ACR etc., delivering notifications to the AC as required.
8.14.2 Procedures p. 227
8.14.2.1 General p. 227
Following procedures are specified for EDGE-5:
- Registration;
- EAS discovery;
- ACR trigger request;
- EEC services subscription; and
- UE ID request.
8.14.2.2 Registration p. 228
8.14.2.2.1 General p. 228
Following are supported for AC registration:
- AC registration procedure;
- AC registration update procedure; and
- AC de-registration procedure.
8.14.2.2.2 AC registration p. 228
Figure 8.14.2.2.2-1 illustrates AC registration procedure.
Pre-conditions:
- AC can communicate with the EEC.
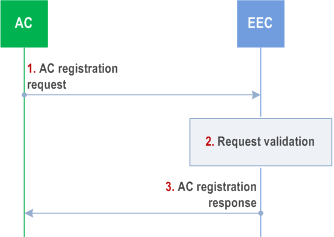
Step 1.
The AC sends an AC registration request to the EEC. The request includes the AC profile, AC's security credentials and optionally the EAS characteristics. The request may also include a list of EEC's services that AC requires the EEC to handle. The request additionally includes ECS configuration information if the AC is edge-aware and configured with the ECS configuration information.
Step 2.
The EEC checks AC's security credentials and validates the request.
Step 3.
If the request is successfully validated, the EEC registers the information provided in the request and responds back to the AC with AC registration response. The AC registration response includes the list of EEC's services that AC is authorized for.
8.14.2.2.3 AC registration update p. 229
Figure 8.14.2.2.3-1 illustrates AC registration update procedure.
Pre-conditions:
- AC is registered with the EEC.
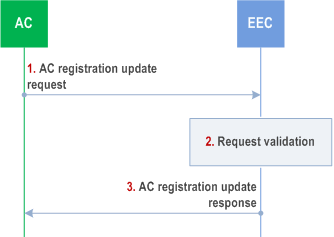
Step 1.
The AC sends an AC registration update request to the EEC. The request includes the registration ID, AC's security credentials, and may include the updated AC profile, EAS discovery filters, list of requested EEC services and list of ECS information.
Step 2.
The EEC checks AC's security credentials and validates the request.
Step 3.
If the request is successfully validated, the EEC sends a successful registration update response, which includes an updated list of EEC services that AC is authorized for.
8.14.2.2.4 AC deregistration p. 229
Figure 8.14.2.2.4-1 illustrates AC deregistration procedure.
Pre-conditions:
- AC is registered with the EEC.
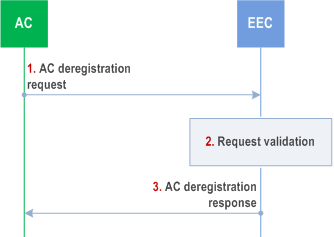
Step 1.
The AC sends an AC deregistration request to the EEC. The request includes the registration ID and AC's security credentials.
Step 2.
The EEC checks AC's security credentials and validates the request.
Step 3.
Upon successful authorization, the EEC deregisters the AC and sends a successful de-registration response.
8.14.2.3 EAS discovery p. 230
Pre-conditions:
- The AC can communicate with the EEC.
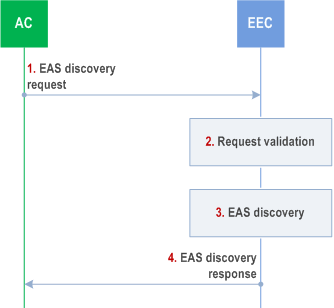
Step 1.
The AC sends an EAS discovery request to the EEC. The request includes AC profile and AC's security credentials and may include EAS discovery filters.
Step 2.
The EEC checks AC's security credentials and validates the request.
Step 3.
If the request is successfully validated, the EEC determines if the required EAS is available or not. The EEC may use information cached or preconfigured at the EEC or may use the EAS discovery procedures to query the EES. If step 1 includes the AC profile or EAS discovery filters, then the EEC may utilize the provided AC profile and filters, to form the EAS discovery request towards EES. If step 1 does not include any of the optional IEs of the AC profile and EAS discovery filters, and AC registration was performed, the EEC may utilize the AC profile provided by the AC during AC registration. The EEC also needs to take user privacy requirements, e.g., regarding the disclosure of location information towards the network into account. If required, e.g., when EAS discovery procedures returns a list of EASs, the EEC performs EAS selection based on the information received in step 1 and the AC profile. The EEC can perform EAS discovery with different EESs before selecting an EAS.
Step 4.
The EEC responds back to the AC with the EAS discovery response. The response includes the EAS profile(s) of the available EAS(s).
8.14.2.4 ACR trigger request p. 231
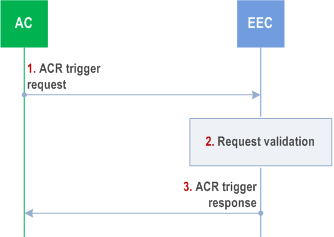
Step 1.
The AC sends an ACR trigger request to the EEC. The request includes AC profile, AC's security credentials, type of requested operation (i.e., ACR detection, ACR initiation) and S-EAS information as described in clause 8.14.3.10. If the request is to initiate the ACR, the request may also include the target EAS information.
Step 2.
The EEC checks AC's security credentials and validates the request.
Step 3.
If the request is successfully validated, the EEC sends an ACR trigger response to the AC indicating if the request was successful as described in clause 8.14.3.11. The EEC process the request from the AC. If the type of requested operation in the request received in step 1 is:
- ACR detection, then the EEC determines if ACR is required or not. If it is required, the EEC uses one of the EEC initiated ACR scenarios or launches ACR with action "determination", leading to S-EES executed ACR;
- ACR initiation, then the EEC uses one of the EEC initiated ACR scenarios and initiate ACR. If the request in step 1 also includes target information, the EEC uses it to select the ACR targets;
8.14.2.5 EEC services subscription p. 232
8.14.2.5.1 General p. 232
Following are supported for EEC services subscription:
- Subscribe;
- Notify;
- Subscription update; and
- Unsubscribe.
8.14.2.5.2 Subscribe p. 232
Pre-conditions:
- The AC can communicate with the EEC.
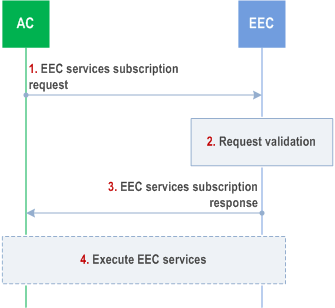
Step 1.
The AC sends an EEC services subscription request to the EEC. The request includes AC profile, AC's security credentials, a list of EEC's services that AC requires the EEC to handle, and related parameters as described in clause 8.14.3.12. If the subscription request includes:
Step 2.
- EAS discovery or EAS dynamic information subscription, then the request may include a list of EAS characteristics and a list of EAS dynamic information filters respectively;
-
ACR, then the request includes a list of S-EAS information and corresponding type of ACR operations:
- ACR notifications, where the EEC notifies the AC with respect to the "ACR detection" and "ACR initiation" requests as specified in clause 8.14.2.5.3;
- ACR monitoring, where the EEC monitors the need for ACR and notifies the AC as and when required e.g., on receiving ACR related notifications on EDGE-1 interface; and
- EEC managed ACR, where the EEC monitors the need for ACR. If need for ACR is detected, then the EEC decides and initiates ACR using one of the EEC initiated ACR scenarios. The EEC notifies the AC about the imminent ACR and may include the target information.
The EEC checks AC's security credentials and validates the request.
Step 3.
If the request is successfully validated, the EEC creates the subscription and sends an EEC services subscription response message to the AC. The response includes the list of services that the EEC will handle and related details.
Step 4.
The EEC executes the services e.g., EAS discovery, ACR, and notifies the AC with information as necessary. The EEC may use locally cached information or configurations while providing services to the AC.
8.14.2.5.3 EEC services notification p. 233
Pre-conditions:
- The AC has subscribed to the EEC.
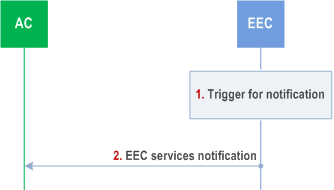
Step 1.
An event occurs at the EEC that satisfies the trigger conditions for notifying a AC e.g., EEC detects a need for Application Context Relocation, unavailability of suitable T-EES and/or unavailability of suitable T-EAS.
Step 2.
The EEC sends an EEC services notification to the AC with relevant information related to the event triggered in step 1.
8.14.2.5.4 EEC services subscription update p. 233
Figure 8.14.2.5.4-1 illustrates EEC services subscription update procedure.
Pre-conditions:
- The AC has subscribed to the EEC.
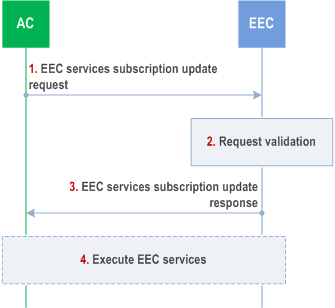
Step 1.
The AC sends an EEC services subscription update request to the EEC. The request includes the subscription ID, AC's security credentials, and may include updated notification related details or updated list of required EEC services.
Step 2.
The EEC checks AC's security credentials and validates the request.
Step 3.
If the request is successfully validated, the EEC updates the subscription and sends a successful subscription update response.
Step 4.
The EEC executes the services e.g., EAS discovery, ACR, and notifies the AC with information as necessary. The EEC may use locally cached information or configurations while providing services to the AC.
8.14.2.5.5 Unsubscribe p. 234
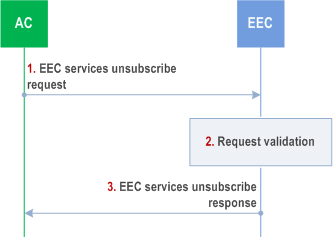
Figure 8.14.2.5.5-1 illustrates the unsubscribe procedure.
Pre-conditions:
- The AC has subscribed to the EEC.
Step 1.
The AC sends EEC services unsubscribe request to the EEC. The request includes the subscription ID and AC's security credentials.
Step 2.
The EEC checks AC's security credentials and validates the request.
Step 3.
Upon successful authorization, the EEC sends a successful de-registration response.
8.14.2.6 UE ID request p. 235
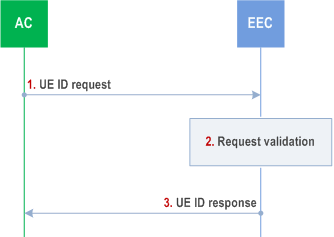
Pre-conditions:
- The AC can communicate with the EEC.
Step 1.
The AC sends an UE ID request to the EEC. The request includes AC's security credentials and the EAS ID list for which the AC needs to know the associated Edge UE ID or AF-specific UE ID(s).
Step 2.
The EEC checks AC's security credentials and validates the request.
Step 3.
If the request is successfully validated, the EEC process the request from the AC. The EEC uses the UE Identifier API procedure (see clause 8.6.5) to query the EES.