Content for TS 23.558 Word version: 19.2.0
0…
5…
6…
6.2a…
6.2b…
6.3…
6.4…
7…
8…
8.3…
8.3.3…
8.3.3.3…
8.4…
8.4.3…
8.4.4…
8.5…
8.6…
8.6.3…
8.6.4…
8.6.6…
8.7…
8.8…
8.8.2.5…
8.8.2A…
8.8.3…
8.8.4…
8.8.5…
8.9…
8.14…
8.14.3…
8.15…
8.17…
8.17.3…
8.17.4…
8.18…
8.19…
8.20…
9…
A…
A.4…
A.5…
B…
E…
6 Application layer architecture p. 28
6.1 General p. 28
This clause provides the overall architecture description:
- Clause 6.2 describes the functional architecture and corresponding considerations to support roaming and federation scenarios as well as interactions with cloud services;
- Clause 6.3 describes the functional entities;
- Clause 6.4 describes the service-based interfaces;
- Clause 6.5 describes the reference points;
- Clause 6.6 describes the cardinality of functional entities and reference points; and
- Clause 6.7 describes the capabilities exposed for enabling edge applications.
6.2 Architecture p. 29
This clause describes the architecture for enabling edge applications in the following representations:
- A service-based representation, where the Edge Enabler Layer functions (e.g. ECS) enable other authorized Edge Enabler Layer functions (e.g. EES) to access their services. This representation also includes point-to-point reference points where necessary;
- A service-based representation as specified in TS 23.501, where the Network Functions (e.g. NEF) enable authorized Edge Enabler Layer functions (e.g. ECS) i.e. Application Functions, to access their services;
- A service-based representation, where the Core Network Northbound APIs as specified in TS 23.501 and TS 23.502, are utilized by authorized Edge Enabler Layer functions via CAPIF core function specified in TS 23.222; and
- A reference point representation, where existing interactions between any two functions (e.g. EES, ECS) is shown by an appropriate point-to-point reference point (e.g. EDGE-6, EDGE-7).
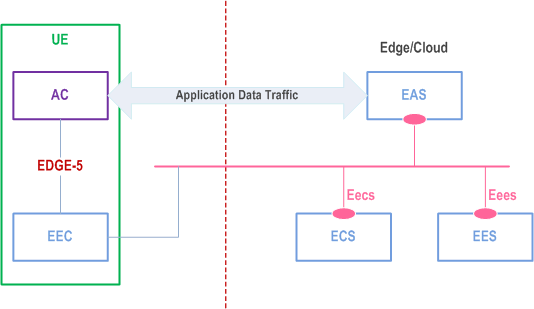
The mechanisms for service discovery in the service-based representation depicted in Figure 6.2-1 are as follows:
- The EES discovers the ECS via pre-configuration or by using CAPIF as specified in TS 23.222;
- The EAS discovers the EES via pre-configuration or by using CAPIF as specified in TS 23.222;
- The EAS discovers the other EAS(s) as specified in clause 8.8.3.2;
- The EEC discovers the ECS as specified in clause 8.3.2; and
- The EEC discovers the EES via service provisioning as specified in clause 8.3.3.
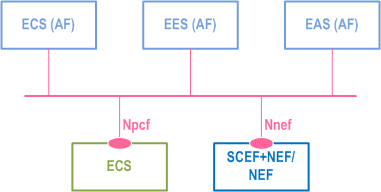
The ECS, EES and EAS act as AFs for consuming network services from the 3GPP 5G Core Network entities over the Service Based Architecture specified in TS 23.501.
Figure 6.2-3 illustrates the service-based representation for utilization of the Core Network (5GC, EPC) northbound APIs via CAPIF.
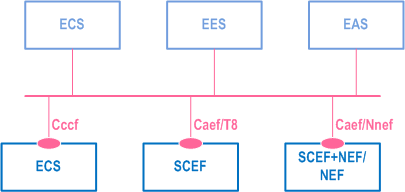
The ECS, EES and EAS act as authorized API invoker to consume services from the Core Network (5GC, EPC) northbound API entities like SCEF, NEF, SCEF+NEF which act as API Exposing Function as specified in TS 23.222.
The mechanism for northbound APIs discovery using the service-based interfaces depicted in Figure 6.2-3 is as specified in TS 23.222.
Figure 6.2-4 illustrates the reference point representation of the architecture for edge enabling applications.
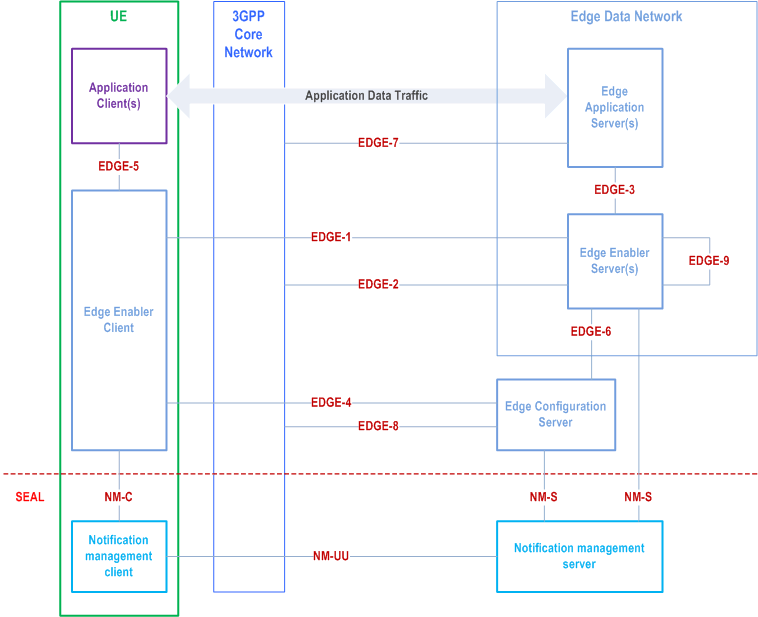
The EDN is a local Data Network. EAS(s) and the EES are contained within the EDN. The ECS provides configurations related to the EES, including details of the EDN hosting the EES. The UE contains AC(s) and the EEC. The EAS(s), the EES and the ECS can interact with the 3GPP Core Network. When SEAL notification management service is used, the EES and the ECS interact with the SEAL notification management server and the SEAL EEC interacts with SEAL Notification management client.