Content for TS 38.401 Word version: 18.2.0
1…
5…
6…
6.1.4
6.1.5…
6.2…
7…
8…
8.2…
8.2.1.4…
8.2.2…
8.2.3…
8.2.4
8.2.5
8.3…
8.4…
8.4.4…
8.5…
8.9…
8.9.4…
8.9.6…
8.9.7…
8.10
8.11…
8.12…
8.13…
8.14…
8.15…
8.15.2…
8.16…
8.17…
8.17.3…
8.17.4
8.18…
8.19…
8.19.2
8.19.3
8.19.4…
8.21…
8.22…
8.23…
8.24…
9…
A…
8.9.7 Trace activation/deactivation over F1 and E1
8.9.8 BH RLC channel establishment procedure
8.9.9 Traffic Mapping
8.9.9.1 Traffic Mapping from IP-layer to Layer-2
8.9.9.2 BH RLC Channel Mapping on BAP Layer
8.9.10 IAB-node release
8.9.10.1 IAB-node orderly release
8.9.10.2 IAB-node disorderly release
8.9.11 IAB-node OAM
8.9.12 Handling of IAB-MTs in INACTIVE State
8.9.13 IP Address Allocation for IAB-nodes
8.9.14 Mobile IAB-node authorization
8.9.15 IAB-donor-CU-based NR Cell Identity (NCI) (re-)configuration for mobile IAB cells
8.9.16 TAC/RANAC (re-)configuration for mobile IAB
8.9.17 IAB-node authorization
8.9.17.1 IAB-node in NSA
8.9.17.2 IAB-node with single IAB-donor in SA
8.9.17.2.1 IAB-node is single-connected
8.9.17.2.2 IAB-node is NR dual-connected
8.9.17.3 IAB-node is served by two IAB-donors in SA
...
...
8.9.7 Trace activation/deactivation over F1 and E1 |R16| p. 78
Figure 8.9.7-1 shows the procedure used for the activation and the deactivation of UE traces in the gNB-DU, the gNB-CU-UP or both.
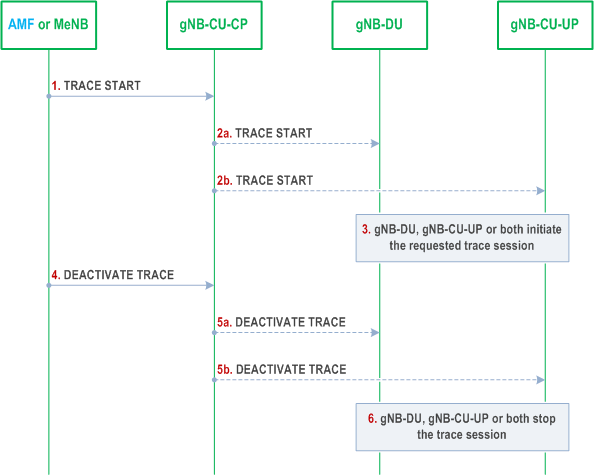
Step 1.
The gNB-CU-CP receives a TRACE START message from the AMF or the MeNB (in case of EN-DC).
Step 2.
The gNB-CU-CP initiates the Trace Start procedure by sending a TRACE START message to the gNB-DU, the gNB-CU-UP or both.
Step 3.
Upon reception of the TRACE START message, the gNB-DU, the gNB-CU-UP or both initiate the requested trace session and report it as described in TS 32.422.
Step 4.
The gNB-CU-CP receives a DEACTIVATE TRACE message from the AMF or the MeNB (in case of EN-DC).
Step 5.
The gNB-CU-CP initiates the Deactivate Trace procedure by sending a DEACTIVATE TRACE message to the gNB-DU, the gNB-CU-UP or both.
Step 6.
Upon reception of the DEACTIVATE TRACE message, the gNB-DU, the gNB-CU-UP or both stop the trace session for the indicated trace reference.
8.9.8 BH RLC channel establishment procedure |R16| p. 78
The BH RLC channel is an RLC channel used for backhauling between IAB-node and IAB-donor-DU, or between different IAB-nodes. The BH RLC channel establishment may be triggered by a UE accessing the network and establishing a DRB.
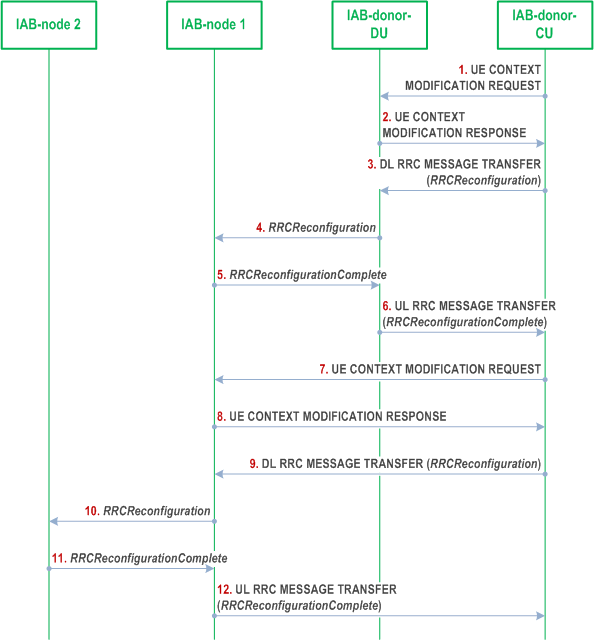
Step 1.
The IAB-donor-CU uses the existing CU-DU split principles and the UE Context Setup procedure or UE Context Modification procedure to configure the parent IAB-DU side of the BH RLC channel. The IAB-donor-CU uses RRC signaling (which is encapsulated in the DL RRC MESSAGE TRANSFER message terminating at the parent node IAB-DU side of the BH RLC channel) to configure the child node IAB-MT side of the BH RLC channel.
The IAB-donor-CU configures the IAB-DU with a mapping to the BH RLC channel to be used for a specific UL F1-U tunnel during the UE Context Setup procedure or the F1-AP UE Context Modification procedure for the UE.
The IAB-donor-CU sends to the IAB-donor-DU a UE CONTEXT MODIFICATION REQUEST message for setting up the parent-node IAB-DU side of the BH link between IAB-donor-DU and IAB-node 1. This step is optional and is required only when a new BH RLC channel needs to be established on the BH link between IAB-donor-DU and IAB-node 1.
Step 2.
The IAB-donor-DU sends the UE CONTEXT MODIFICATION RESPONSE message to the IAB-donor-CU.
Step 3.
The IAB-donor-CU sends to the IAB-donor-DU a DL RRC MESSAGE TRANSFER message encapsulating the RRCReconfiguration message for configuring the IAB-MT of IAB-node 1. This step is optional and is required only when a new BH RLC channel needs to be established on the BH link between IAB-donor-DU and IAB-node 1.
Step 4.
The IAB-donor-DU decapsulates and forwards the RRCReconfiguration message to the IAB-MT of IAB-node 1. This step is optional and is required only when a new BH RLC channel needs to be established on the BH link between IAB-donor-DU and IAB-node 1.
Step 5.
The IAB-MT of IAB-node 1 sends to the IAB-donor-DU an RRCReconfigurationComplete message destined to the IAB-donor-CU. This step is optional and is required only when a new BH RLC channel needs to be established on the BH link between IAB-donor-DU and IAB-node 1.
Step 6.
The IAB-donor-DU sends the UL RRC MESSAGE TRANSFER message encapsulating the RRCReconfigurationComplete message to the IAB-donor-CU. This step is optional and is required only when a new BH RLC channel needs to be established on the BH link between IAB-donor-DU and IAB-node 1.
Step 7.
The IAB-donor-CU sends to the IAB-DU of IAB-node 1 a UE CONTEXT MODIFICATION REQUEST message for setting up the parent node IAB-DU side of the BH link between IAB-node 1 and IAB-node 2. This step is optional and is required only when a new BH RLC channel needs to be established on the BH link between IAB-node 1 and IAB-node 2.
Step 8.
The IAB-node 1 sends the UE CONTEXT MODIFICATION RESPONSE message to the IAB-donor-CU.
Step 9.
The IAB-donor-CU sends to the IAB-DU of IAB-node 1 a DL RRC MESSAGE TRANSFER message encapsulating the RRCReconfiguration message for configuring the IAB-MT of IAB-node 2. This step is optional and is required only when a new BH RLC channel needs to be established on the BH link between IAB-node 1 and IAB-node 2.
Step 10.
The IAB-DU of IAB-node 1 decapsulates and forwards the RRCReconfiguration message to the IAB-MT of IAB-node 2. This step is optional and is required only when a new BH RLC channel needs to be established on the BH link between IAB-node 1 and IAB-node 2.
Step 11.
The IAB-MT of IAB-node 2 sends to IAB-node 1 an RRCReconfigurationComplete message destined to the IAB-donor-CU. This step is optional and is required only when a new BH RLC channel needs to be established on the BH link between IAB-node 1 and IAB-node 2.
Step 12.
IAB-node 1 sends the UL RRC MESSAGE TRANSFER message encapsulating the RRCReconfigurationComplete message to the IAB-donor-CU. This step is optional and is required only when a new BH RLC channel needs to be established on the BH link between IAB-node 1 and IAB-node 2.
8.9.9 Traffic Mapping |R16| p. 80
8.9.9.1 Traffic Mapping from IP-layer to Layer-2 p. 80
When forwarding IP packets, the IAB-donor-DU performs the traffic mapping from IP-layer to layer-2 as defined in TS 38.340. The traffic mapping information is configured by the IAB-donor-CU, which contains the IP header information, and the BH information including the BAP routing ID and a list of egress link and BH RLC channel pairs.
Multiple traffic mappings can contain the same BAP routing ID and/or list of egress link and BH RLC channel pairs.
The traffic mappings can be configured as part of the UE Context Setup or UE Context Modification procedures. They may also be configured via the non-UE-associated BAP Mapping Configuration procedure.
The traffic mapping from IP-layer to layer-2 may include IPv6 Flow Label information. For DL F1 or X2 traffic, the IPv6 Flow Label information is set by the IAB-donor-CU or MeNB, respectively. When this traffic is protected via IPsec tunnel mode, the IPv6 Flow Label is set on the inner header by the IAB-donor-CU or MeNB, and the security gateway shall copy the IPv6 Flow Label from the inner IP header to the outer IP header to ensure that the IAB-donor-DU can perform the traffic mapping considering the IPv6 Flow Label.
8.9.9.2 BH RLC Channel Mapping on BAP Layer p. 80
When traffic is forwarded on BAP layer as described in TS 38.300, the IAB-node performs the BH RLC channel mapping as defined in TS 38.340. The BH RLC channel mapping information is configured by the IAB-donor-CU.
The BH RLC channel mappings can be configured as part of the UE Context Setup or UE Context Modification procedures. They may also be configured via the non-UE-associated BAP Configuration procedure.
8.9.10 IAB-node release |R16| p. 80
An IAB-node may depart the network either in an orderly fashion, which implies that both the network and the IAB-node are aware in advance, or in a disorderly fashion (e.g. due to an RLF with failed recovery).
8.9.10.1 IAB-node orderly release p. 81
For orderly release, the IAB-donor-CU can remove the F1 interface connection to the IAB-DU without releasing the IAB-MT. If the IAB-MT needs to be released, IAB-MT will perform the deregistration procedure. If both F1 interface and IAB-MT need to be released, the IAB-donor-CU should remove the F1 interface to the IAB-DU before it releases the collocated IAB-MT. The deregistration procedure is the same as the UE deregistration procedure. The IAB-donor-CU hands over the UEs or child IAB-nodes currently connected to the IAB-node's cell(s) to another cell(s), or releases the UEs and may stop accepting incoming handovers or connections to the IAB-node that is about to be released. The IAB-donor-CU may also update/release the BH RLC channels in the intermediate hops. At this point, the F1 interface will be released and the corresponding SCTP associations will be removed.
8.9.10.2 IAB-node disorderly release p. 81
For the disorderly release case, how to remove the IAB-node context is up to network implementation.
8.9.11 IAB-node OAM |R16| p. 81
The IAB-node receives commands, configuration data and software downloads (e.g. for equipment software upgrades) from its OAM system. The IAB-node can also send alarms and traffic counter information to its OAM system. The transport connection between the IAB-node and its OAM, using IP, is provided by the IAB-MT's PDU session via 5G network, or the IAB-MT's PDN connection via LTE network when IAB-MT uses EN-DC.
Alarms in the IAB generate bursts of high-priority traffic, to be transported in real time. Traffic counters generate bursts of traffic, but their transport need not be real-time. Configuration messages from OAM to the IAB will also generate small bursts of traffic, possibly with lower priority than alarms but still delay-sensitive: when a configuration is committed on the OAM, the time interval between the commitment and the effect on the equipment shall be small. Alarm messages and commands should be transported on a high-priority bearer, while counters may be transported on a lower priority bearer.
OAM software download to the IAB may generate larger amounts of data, but both the required data rate and the priority of this kind of traffic are much lower than in the case of alarms, commands and counters.
For different types of OAM traffic, it is necessary to use different DRBs between the IAB-MT and the serving DU, and different BH RLC channels for intermediate hops, with different QoS parameters. Aggregation of F1-U traffic for OAM with other F1-U traffic on the same BH RLC channels is not precluded. The QoS parameters are provided to the IAB-donor during the IAB-MT's PDU session establishment, or the IAB-MT's PDN connection establishment when IAB-MT uses EN-DC.
The continuity of OAM connectivity needs to be ensured as the mobile IAB-node moves across the mobile network.
8.9.12 Handling of IAB-MTs in INACTIVE State |R16| p. 81
The IAB-MT optionally supports the RRC INACTIVE state. Upon the IAB-MT entering the RRC INACTIVE state, it is up to implementation to keep or release the F1 connection of the collocated IAB-DU.
8.9.13 IP Address Allocation for IAB-nodes |R16| p. 82
An IAB-node may obtain IP address(es) either from the IAB-donor or from the OAM system. The IP address(es) is(are) used by the IAB-node for F1 and non-F1 traffic exchange via the backhaul. In case IPsec tunnel mode is used to protect this F1 and non-F1 traffic, the IP address(es) refer to the outer tunnel addresses. The allocation of the inner tunnel IP address(es) is outside of 3GPP scope.
In case of IAB-donor-based IP address allocation, the IP address(es) is(are) allocated by the IAB-donor-CU or IAB-donor-DU. In both cases, the IAB-node requests the IP address(es) via RRC from the IAB-donor-CU. It includes a separate IP address request for each usage, where the usages defined are all traffic, F1-U, F1-C and non-F1. The IAB-donor-CU may initiate the IAB TNL Address Allocation procedure to obtain IP addresses from the IAB-donor-DU. The IAB-donor-CU sends the IP addresses allocated for each usage to the IAB-node via RRC. r each usage to the IAB-node via RRC. In case of IAB inter-CU topology management, the F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU may obtain the IP addresses for each usage in the non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU's topology from the non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU for the boundary IAB-node and the descendant IAB-nodes of the boundary IAB-node.
The IAB-node may be allocated one or multiple IPv6 addresses or one 64-bit IPv6 prefix for each usage and/or one or multiple IPv4 addresses for each usage. Each allocated IP address/IPv6 prefix is unique within the IAB network and routable from the wireline network.
In case of OAM-based IP address allocation, the IAB-node informs the IAB-donor-CU via an UL RRC message about the IP address(es) it received for each purpose. The mapping between the IP addresses assigned to the IAB-node and the BAP address(es) of the corresponding IAB-donor-DU(s) anchoring these IP addresses should be known by the IAB-node and the IAB-donor-CU based on implementation. This occurs before the IAB node uses the IP address(es) for UL and/or DL traffic.
The IAB-donor-CU configures the IAB-donor-DU with mappings between IP header fields and L2 parameters (BAP Routing ID, BH RLC channels) used for DL traffic. Each mapping configuration may hold an IPv4 address, IPv6 address or a 64-bit IPv6 prefix. In case of two mapping entries matching the same IP header where one holds an IPv6 prefix and the other holds a full IPv6 address, the one with full IPv6 address takes precedence at the IAB-donor-DU.
In case of IAB-donor-allocated IP addresses, the IAB-node's IP address(es) can be updated using DL RRC signalling.
For F1-C traffic transfer for NSA IAB, the LTE leg and NR leg should use separate IP address pairs {IAB-DU's IP address, IAB-donor-CU's IP address}. How the IAB-DU gets the remote IP end point(s) and its own IP address for LTE leg is not specified in this release.
8.9.14 Mobile IAB-node authorization |R18| p. 82
During the mobile IAB-node integration procedure or mobile IAB-MT migration via NG handover, the RRC-terminating IAB-donor-CU receives the authorization status of the mobile IAB-node from the 5GC. During the mobile IAB-MT migration procedure and the mobile IAB-node RLF recovery procedure, the target/new RRC-terminating IAB-donor-CU receives the authorization status of the mobile IAB-node from the source/initial RRC-terminating IAB-donor-CU as well as from the 5GC during Path Switch Request procedure. If the authorization status is "not authorized", the RRC-terminating IAB-donor-CU does not establish any backhaul resources. Additionally, the RRC-terminating IAB-donor-CU does not allocate any BAP address, TNL address(es) or default BAP configuration for this mobile IAB-node. If the authorization status for the mobile IAB-node changes, the 5GC sends an updated authorization status to the RRC-terminating IAB-donor-CU.
In case the mobile IAB-MT and its co-located mobile IAB-DU connect to same IAB-donor-CU, and the updated authorization status received from the 5GC is "not authorized", the IAB-donor-CU performs the following actions in the following order: it attempts to hand over the UEs served by the mobile IAB-node to other cell(s), releases the F1 interface towards the mobile IAB-DU, and then releases all backhaul resources, the BAP address, TNL address and default BAP configuration for this mobile IAB-node.
In case the mobile IAB-MT and its co-located mobile IAB-DU connect to different IAB-donor-CUs, the RRC-terminating IAB-donor-CU sends the updated authorization status to the F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU via the IAB TRANSPORT MIGRATION MODIFICATION REQUEST message. The F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU confirms the reception of the updated authorization status via the IAB TRANSPORT MIGRATION MODIFICATION RESPONSE message.
If the updated authorization status for the mobile IAB-node is set to "not authorized", the F1-terminating IAB-donor attempts to hand over the UEs served by the mobile IAB-node to other cell(s), and then releases the F1 interface towards the mobile IAB-DU. After that, the F1-terminating IAB-donor requests from the RRC-terminating IAB-donor the release of all the offloaded traffic via the IAB TRANSPORT MIGRATION MANAGEMENT REQUEST message. The RRC-terminating IAB-donor releases the offloaded traffic and all backhaul resources, BAP address, TNL address and default BAP configuration for this mobile IAB-node. The RRC-terminating IAB-donor may send an indication that the mobile IAB-MT can be deregistered via a UE CONTEXT RELEASE REQUEST message, to the AMF.
If the authorization status is changed back from "not authorized" to "authorized", the phase 2 and phase 3 of the mobile IAB-node integration procedure as defined in clause 8.12.3 are carried out.
8.9.15 IAB-donor-CU-based NR Cell Identity (NCI) (re-)configuration for mobile IAB cells |R18| p. 83
The NCIs of the cells served by a mobile IAB-DU configured by the OAM can be reconfigured by the F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU serving the mobile IAB-DU, in case of an NCI collision with cells of other gNB-DUs served by the IAB-donor-CU. The reconfiguration of NCI pertains to the reconfiguration of the cellLocalId part of the NCI, where the new cellLocalId(s) are based on a list of NCIs that has been configured at the F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU.
The value change of cellLocalId(s) shall be indicated to the OAM system of the mobile IAB-DU following the NCI reconfiguration. The mobile IAB-DU can notify OAM about the reconfigured cellLocalId(s) using notifications specified in TS 28.532.
8.9.16 TAC/RANAC (re-)configuration for mobile IAB |R18| p. 83
The TAC/RANAC of mobile IAB-DU's cell is configured by the OAM, and it can be reconfigured by the OAM during the mobile IAB-node mobility. The TAC/RANAC of the mobile IAB-DU's cell may be same as or different than the TAC/RANAC of the co-located mobile IAB-MT's serving cell. The TAC/RANAC broadcasted by the mobile IAB-DU cell can be changed in order to reflect the mobile IAB-node's physical location.
8.9.17 IAB-node authorization |R16| p. 83
8.9.17.1 IAB-node in NSA p. 83
During the IAB-node integration procedure, the eNB receives the authorization status of the IAB-node from the EPC. The eNB forwards the authorization status to the IAB-donor-CU in the SGNB ADDITION REQUEST message. If the authorization status is "not authorized", the IAB-donor-CU neither establishes the backhaul resources nor allocates any BAP address, TNL address or default BAP configuration for this IAB-node.
When the authorization status for the IAB-node changes, the EPC sends an updated authorization status to the IAB-MT's eNB. The eNB forwards the authorization status to the IAB-donor-CU in the SGNB ADDITION REQUEST message or SGNB MODIFICATION REQUEST message.
In case the updated authorization status is "not authorized", the IAB-donor-CU performs the following actions in this order: it attempts to hand over the UEs and descendant nodes served by the IAB-node to other cell(s), releases the F1 interface towards the IAB-DU, and releases all backhaul resources (including the BAP address, TNL address and default BAP configuration) for this IAB-node. The IAB-donor-CU may indicate to the eNB that the actions described above have been completed, by sending a SGNB MODIFICATION REQUIRED or SGNB RELEASE REQUIRED message with the corresponding cause value included. Then, the eNB may indicate to the EPC that the IAB-MT can be de-registered.
8.9.17.2 IAB-node with single IAB-donor in SA p. 84
8.9.17.2.1 IAB-node is single-connected |R17| p. 84
During the IAB-node network integration or RLF recovery, the IAB-donor-CU receives the authorization status of the IAB-node from the 5GC. Also, during the inter-CU topology adaptation procedure, the target IAB-donor-CU receives the authorization status of the IAB-node from the source IAB-donor-CU as well as from the 5GC when performing the Path Switch Request procedure. If the authorization status is "not authorized", the IAB-donor-CU neither establishes the backhaul resources nor allocates any BAP address, TNL address or default BAP configuration for this IAB-node. When the authorization status for the IAB-node changes, the 5GC sends an updated authorization status to the IAB-donor-CU. When the authorization status received by the IAB-donor-CU changes, the IAB-donor-CU performs the SA equivalent of the steps described for NSA in clause 8.9.17.1.
In case the updated authorization status is "not authorized", after actions described in clause 8.9.17.1 have been completed, the IAB-donor-CU may indicate to the 5GC that the IAB-MT can be de-registered.
8.9.17.2.2 IAB-node is NR dual-connected |R17| p. 84
In case the IAB-node is dual-connected to the IAB-donor-CU, the IAB-donor-CU receives the authorization status of the IAB-node from the 5GC. Upon reception of the authorization status, the IAB-donor-CU performs the same steps described in clause 8.9.17.2.1.
In case the IAB-node is dual-connected to a non-IAB-capable gNB and to an IAB-donor-CU, the MN receives the authorization status of the IAB-node from the 5GC. If the MN is the non-IAB-capable gNB and the SN is the IAB-donor-CU, the MN forwards the authorization status to the IAB-donor-CU in the S-NODE ADDITION REQUEST message or S-NODE MODIFICATION REQUEST message. Upon reception of the authorization status, the IAB-donor-CU performs the same steps described in clause 8.9.17.2.1. If the updated authorization status is "not authorized", the SN may indicate to the MN that the actions of removing the UEs and descendant nodes, releasing the F1 interface and backhaul resources for the IAB-node have been completed, by sending a S-NODE MODIFICATION REQUIRED or S-NODE RELEASE REQUIRED message with the corresponding cause value included. Then, the MN may indicate to the 5GC that the IAB-MT can be de-registered. If the MN is the IAB-donor-CU and the SN is not the non-IAB-capable gNB, the IAB-donor-CU performs the same steps described in clause 8.9.17.2.1.
8.9.17.3 IAB-node is served by two IAB-donors in SA |R17| p. 84
In case the IAB-MT only connects to the non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU or in case the IAB-MT is NR dual-connected with the non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU as the MN, the non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU sends the authorization status received from the 5GC to the F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU in the IAB-TRANPORT MIGRATION MODIFICATION REQUEST message. Upon reception of the authorization status, the F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU performs the same steps described in clause 8.9.17.2.1. If the authorization status is "not authorized", the F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU sends to the non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU an IAB TRANSPORT MIGRATION MANAGEMENT REQUEST message requesting the release of all offloaded traffic, after which the non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU releases the offloaded traffic and all backhaul resources, BAP address, TNL address and default BAP configuration for the IAB-node. The non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU then may indicate to the 5GC that the IAB-MT can be de-registered.
In case the IAB-MT is NR dual-connected, where the MN is the F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU and the SN is a non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU, upon reception of the authorization status, the IAB-node's authorization procedure follows the same steps as described in clause 8.9.17.2.1.