Content for TS 24.501 Word version: 18.7.0
1…
3…
4…
4.4…
4.4.3…
4.5…
4.5.3…
4.6…
4.7…
4.9…
4.15…
5…
5.2…
5.3…
5.3.2…
5.3.7…
5.3.19…
5.4…
5.4.1.3…
5.4.2…
5.4.4…
5.4.5…
5.4.6…
5.5…
5.5.1.2.4
5.5.1.2.5…
5.5.1.3…
5.5.1.3.4
5.5.1.3.5…
5.5.2…
5.6…
5.6.2…
6…
6.1.4…
6.2…
6.3…
6.3.2…
6.3.3…
6.4…
6.4.1.4…
6.4.2…
6.5…
7…
8…
8.2.9…
8.3…
9…
9.11.2…
9.11.2.10…
9.11.3…
9.11.3.4…
9.11.3.8…
9.11.3.14…
9.11.3.18C…
9.11.3.29…
9.11.3.33…
9.11.3.39…
9.11.3.45…
9.11.3.50…
9.11.3.53A…
9.11.3.68…
9.11.3.75…
9.11.4…
9.11.4.10…
9.11.4.13…
9.11.4.16…
9.11.4.30…
9.12
10…
A…
B…
C…
D…
D.6…
D.6.3…
D.6.8
D.7…
D.6.3 UE policy section management result
D.6.4 UPSI list
D.6.5 UE policy classmark
D.6.6 UE OS Id
D.6.7 UE policy network classmark
...
...
D.6.3 UE policy section management result p. 1123
The purpose of the UE policy section management result information element is to transfer from the UE to the PCF information about instructions for UE policy section management which the UE could not execute successfully.
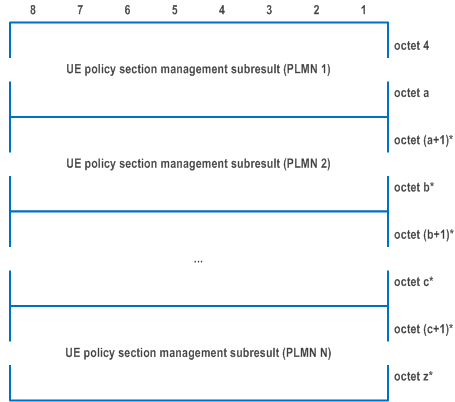
The UE policy section management result information element is coded as shown in Figure D.6.3.1, Figure D.6.3.2, Figure D.6.3.3, Figure D.6.3.4, Figure D.6.3.5 and Table D.6.3.1.
The UE policy section management result information element has a minimum length of 12 octets and a maximum length of 65534 octets.
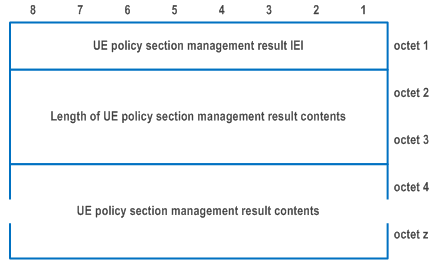
| Value part of the UE policy section management result information element (octets 4 to z) | |
| The value part of the UE policy section management result information element consists of one or several UE policy section management subresults. | |
| UE policy section management subresult: | |
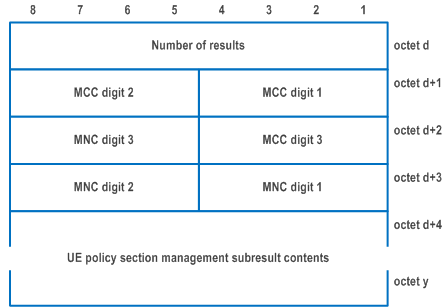
| Number of results (octet d) | |
| This field contains the binary encoding of number of results included in the UE policy section management subresult. | |
| MCC, Mobile country code (octet d+1, and bits 4 to 1 of octet d+2) | |
| The MCC field is coded as in ITU-T Recommendation E.212 [42], Annex A. | |
| MNC, Mobile network code (bits 8 to 5 of octet d+2, and octet d+3) | |
| The coding of this field is the responsibility of each administration but BCD coding shall be used. The MNC shall consist of 2 or 3 digits. If a network operator decides to use only two digits in the MNC, MNC digit 3 shall be coded as "1111" (NOTE). | |
| UE policy section management subresult contents (octets d+4 to y) | |
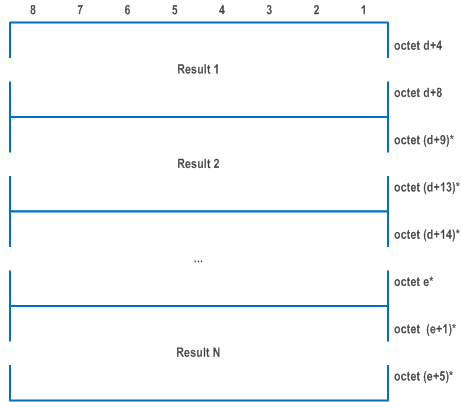
| The UE policy section management subresult contents consist of one or several results. | |
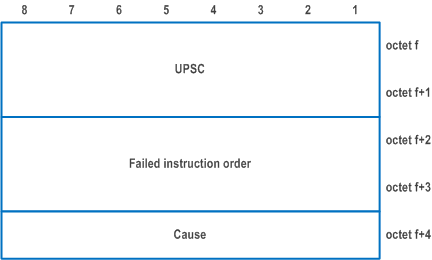
| Result (octet f to f+4) | |
| UPSC (octet f to f+1) | |
| This field contains the binary encoding of the UPSC. The value of the UPSC is set by the PCF | |
| Failed instruction order (octets f+2 to f+3) | |
| This field contains the binary encoding of the order of the instruction in the UE policy section management sublist contents as specified in Figure D.6.2.4, which could not be executed successfully. The value of failed instruction order set to one indicates that the first instruction in the UE policy section management sublist contents could not be executed successfully. | |
| Cause (octet f+4) | |
| Bits
8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 | |
| 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 | Protocol error, unspecified |
| The receiving entity shall treat any other value as 0110 1111, "Protocol error, unspecified". | |
|
NOTE:
The UE operating in the SNPN access operation mode shall include the PLMN ID part of the SNPN identity of the SNPN in the UE policy section management subresult.
|
|
D.6.4 UPSI list p. 1125
The purpose of the UPSI list information element is to transfer from the UE to the PCF a list of UPSIs.
The UPSI list information element is coded as shown in Figure D.6.4.1, Figure D.6.4.2, and Table D.6.4.1.
The UPSI list information element has a minimum length of 3 octets and a maximum length of 65532 octets.
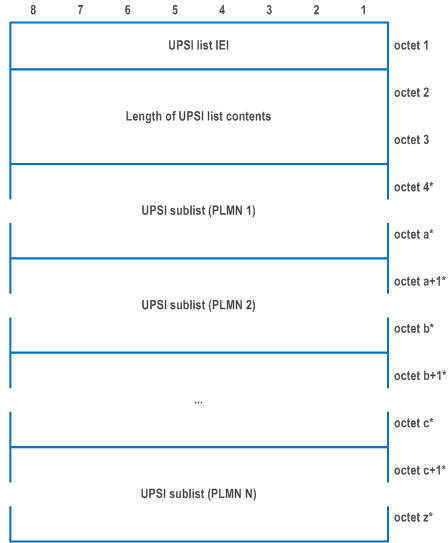
| Length of UPSI list contents (octets 2 to 3) | |
| This field indicates the length of the UPSI list contents. If no UPSIs are included in the UPSI list, the UE shall set the length of UPSI list contents to zero. | |
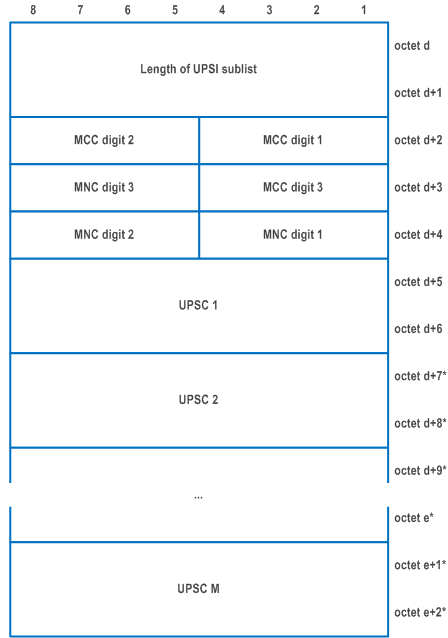
| MCC, Mobile country code (octet d+2, and bits 4 to 1 of octet d+3) | |
| The MCC field is coded as in ITU-T Recommendation E.212 [42], Annex A. | |
| MNC, Mobile network code (bits 8 to 5 of octet d+3, and octet d+4) | |
| The coding of this field is the responsibility of each administration but BCD coding shall be used. The MNC shall consist of 2 or 3 digits. If a network operator decides to use only two digits in the MNC, MNC digit 3 shall be coded as "1111" (NOTE). | |
| UPSC (octets d+5 to d+6) | |
| This field contains the binary encoding of the UPSC. The value of the UPSC is set by the PCF. | |
|
NOTE:
The UE operating in the SNPN access operation mode shall include the PLMN ID part of the SNPN identity in the UPSI sublist.
|
D.6.5 UE policy classmark p. 1127
The purpose of the UE policy classmark information element is to provide the network with information about the policy aspects of the UE.
The UE policy classmark information element is coded as shown in Figure D.6.5.1 and Table D.6.5.1.
The UE policy classmark is a type 4 information element with a minimum length of 3 octets and a maximum length of 5 octets.
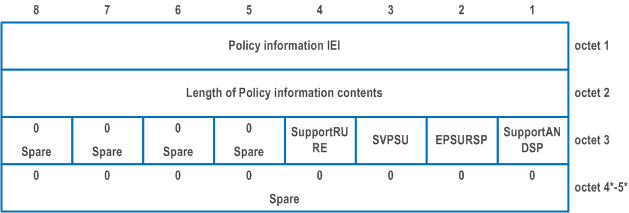
| Support of ANDSP by the UE (SupportANDSP) (octet 3, bit 1) | |
| Bit
1 | |
| 0 | ANDSP not supported by the UE |
| 1 | ANDSP supported by the UE |
| All other bits in octet 3 to 5 are spare and shall be coded as zero, if the respective octet is included in the information element. | |
| Support of URSP provisioning in EPS by the UE (EPSURSP) (octet 3, bit 2) (see NOTE) | |
| Bit
2 | |
| 0 | URSP provisioning in EPS not supported by the UE |
| 1 | URSP provisioning in EPS supported by the UE |
| Support of VPS URSP (SVPSU) (octet 3, bit 3) | |
| Bit
3 | |
| 0 | VPS URSP not supported by the UE |
| 1 | VPS URSP supported by the UE |
| Support of Reporting URSP Rule Enforcement by the UE (SupportRURE) (octet 3, bit 4) | |
| Bit
3 | |
| 0 | Reporting URSP rule enforcement not supported by the UE |
| 1 | Reporting URSP rule enforcement supported by the UE |
|
NOTE:
This indicator shall be ignored by an EPS receiving entity as the UE in EPS providing UE STATE INDICATION message, supports URSP provisioning in EPS.
|
|
D.6.6 UE OS Id p. 1128
The purpose of the UE OS Id information element is to provide the network with information about the OS of the UE.
The UE OS Id information element is coded as shown in Figure D.6.6.1 and Table D.6.6.1.
The UE OS Id is a type 4 information element with a minimum length of 18 octet and a maximum length of 242 octets.
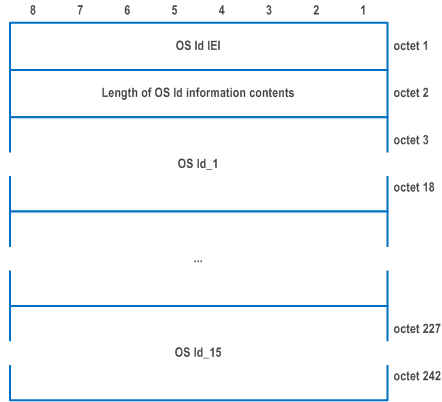
| OS Id: | |
| The OS Id is coded as a sequence of a sixteen octet OS Id value field. The OS Id value field is defined as Universally Unique IDentifier (UUID) as specified in RFC 4122. | |
D.6.7 UE policy network classmark |R17| p. 1129
The purpose of the UE policy network classmark information element is to provide the UE with information about the policy aspects of the network.
The UE policy network classmark information element is coded as shown in Figure D.6.7.1 and Table D.6.7.1.
The UE policy network classmark is a type 4 information element with a minimum length of 3 octets and a maximum length of 5 octets.
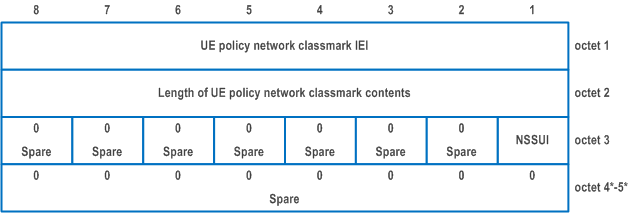
| Non-subscribed SNPN signalled URSP handling indication (NSSUI) (octet 3, bit 1) (see NOTE) | |
| Bit
1 | |
| 0 | UE is allowed to accept URSP signalled by non-subscribed SNPNs |
| 0 | UE is not allowed to accept URSP signalled by non-subscribed SNPNs |
| All other bits in octet 3 to 5 are spare and shall be coded as zero, if the respective octet is included in the information element. | |
|
NOTE:
Receiving UE shall ignore this bit, if i) UE has an empty or non-present EHPLMN list and the bit is received from the RPLMN which is not the HPLMN, ii) UE has non-empty EHPLMN list and the bit is received from the RPLMN which is not an EHPLMN or iii) the bit is received from the RSNPN which is not the subscribed SNPN.
|
|