Content for TS 23.502 Word version: 19.0.0
1…
4.2.2.2.2
4.2.2.2.3…
4.2.2.3…
4.2.3…
4.2.3.3
4.2.4…
4.2.6
4.2.7…
4.2.9…
4.2.11…
4.2.11.5…
4.3…
4.3.2.2.2
4.3.2.2.3…
4.3.3…
4.3.3.3
4.3.4…
4.3.4.3
4.3.5…
4.3.5.2…
4.3.5.4…
4.3.5.6…
4.3.6…
4.4…
4.5…
4.9…
4.9.1.3…
4.9.2…
4.11…
4.11.1…
4.11.1.2.2
4.11.1.2.3
4.11.1.3…
4.11.1.3.3…
4.11.1.4…
4.11.1.5…
4.11.2…
4.11.3…
4.12…
4.12.6…
4.12a…
4.12b…
4.13…
4.13.4…
4.13.6…
4.14…
4.15…
4.15.3.2.5…
4.15.4…
4.15.6…
4.15.6.7…
4.15.6.13…
4.15.6.14…
4.15.9…
4.15.9.4…
4.15.13…
4.15.13.4…
4.16…
4.16.4…
4.16.8…
4.16.11…
4.16.14…
4.16.15…
4.17…
4.17.9…
4.18…
4.19…
4.22…
4.23…
4.23.7…
4.23.7.3.3
4.23.7.3.4…
4.23.9…
4.23.9.4…
4.23.11…
4.24…
4.25…
4.25.6…
4.26…
5…
5.2.3…
5.2.5…
5.2.6…
5.2.7…
5.2.8…
5.2.9…
5.2.12…
5.2.18…
A…
E…
F…
G
H…
4.15.4 Core Network Internal Event Exposure
4.15.4.1 General
4.15.4.2 Exposure of Mobility Events from AMF
4.15.4.3 Exposure of Communication trends from SMF
4.15.4.4 Internal Event Exposure Subscription/Unsubscription via UDM
4.15.4.5 Exposure of Events from UPF for UPF Data Collection
4.15.4.5.1 General
4.15.4.5.2 Information flow for subscription to UPF event exposure service for certain UE(s) via SMF
4.15.4.5.3 Information flow for UPF event exposure service for any UE
4.15.4.5.4 Information flow for subscription via SMF to UPF event exposure service related with AOI
...
...
4.15.4 Core Network Internal Event Exposure p. 420
4.15.4.1 General p. 420
The exposure of events internally within the 5GC NFs is explained in the following clauses. Only the event notifications that are independent of the ongoing system procedure are specified in this clause. For the event notifications that are part of the system procedure, see the system procedure descriptions under clause 4.2 to clause 4.14.
4.15.4.2 Exposure of Mobility Events from AMF p. 421
The AMF invokes the Namf_EventExposure_Notify to provide mobility related events to NF consumers that have subscribed for the events by invoking Namf_EventExposure_Subscribe , in the following scenarios listed below and after Namf_EventExposure_Subscribe service operation.
EventExposure_Subscribe .
- During Registration procedure, Inter NG-RAN node N2 based handover procedure, when there is a change of AMF (within the same AMF Set or across the AMF Set), the new AMF receives all event subscriptions from old AMF or UDSF. For each event subscription: if the event subscription only applies to the UE, the new AMF allocates a new Subscription Correlation ID and notify the NF consumer of the new Subscription Correlation ID associated with the change of Subscription Correlation ID event. if the event subscription applies to a group of UE(s) and there is no corresponding subscription for this group (identified by the internal group Id and notification endpoint) at the new AMF, the new AMF shall create corresponding event subscription, allocate a new Subscription Correlation Id and send it to the received notification endpoint, i.e. Notification Target Address (+Notification Correlation Id), associated with the addition of Subscription Correlation ID event. The new AMF does not need to allocate another Subscription Correlation ID for any subsequent registrations of the members of the same group. The initial Maximum number of reports and the remaining number of reports within the Maximum number of reports quota for the UE is transferred from the old AMF.
- During Registration procedure, when there is a change of AMF, the new AMF notifies each NF that has subscribed for UE reachability event about the UE reachability status.
- During Registration, Handover, UE Triggered Service Request procedure in CM-IDLE state, Location Reporting, N2 Notification and AN Release procedures, the AMF determines the UE presence in Area Of Interest (i.e. IN, OUT or UNKNOWN status ) as described in Annex D.1 and notifies the NF Consumers of the UE presence in an Area Of Interest if the NF consumers (e.g. SMF) had subscribed for this Area Of Interest and if the UE presence in Area Of Interest is different from the one reported earlier.
- During Registration and Handover procedure or during Service Area Restriction update by UDM or PCF, if the UE is moving from an Allowed Area to a Non-Allowed Area, then the AMF informs all the NF consumers (e.g. SMF), that have subscribed for UE reachability event, that the UE is reachable only for regulatory prioritized service. The SMF shall explicitly subscribe UE reachability unless the established PDU Session is related to regulatory prioritized service.
- If the AMF had notified an SMF of the UE being reachable only for regulatory prioritized service earlier, the AMF informs the NF consumers (e.g. SMF), that have subscribed for UE reachability event, that the UE is reachable if the UE enters into Allowed Area.
-
During Registration procedure and Service Request procedure, if the AMF had notified an SMF earlier of the UE being unreachable and that SMF need not invoke Namf_
Communication_ to the AMF due to DL data notifications, the AMF informs the SMF when the UE becomes reachable.N1N2MessageTransfer -
During Registration procedure and Service Request procedure, if the AMF had notified an SMF earlier that the UE is unreachable together with an Estimated Maximum Wait time, then the AMF informs the SMF when the UE becomes reachable. When the SMF learns that the UE is reachable and:
-
if the SMF performs Extended Buffering for a PDU session, the SMF sends the buffered data to the UPF and invokes the Namf_
Communication_ service operation to the AMF to establish the User Plane(s) for the PDU Sessions, or the buffered data is delivered to the UE as per the procedure in clause 4.24.2 starting from step 2g for a PDU session using Control Plane CIoT 5GS Optimisation;N1N2MessageTransfer -
if the UPF performs Extended Buffering for a PDU session, the SMF invokes the Namf_
Communication_ service operation to the AMF to establish the User Plane(s) for the PDU Sessions, or the buffered data is delivered to the UE as per the procedure in clause 4.24.2 starting from step 8a for a PDU session using Control Plane CIoT 5GS Optimisation.N1N2MessageTransfer
-
if the SMF performs Extended Buffering for a PDU session, the SMF sends the buffered data to the UPF and invokes the Namf_
-
If NEF had subscribed for UE reachability event notification for Extend Buffering, then the AMF informs the NEF when the UE becomes reachable. When the NEF learns that the UE is reachable, it invokes the Nsmf_
NIDD_ service operation of the corresponding SMF to deliver the buffered data to the UE as per the procedure in clause 4.25.5 starting from step 2 for a PDU session using Control Plane CIoT 5GS Optimisation.Delivery - During Registration procedure, Handover without Registration procedure and Service Request procedure, if the NF consumers had subscribed for UE reachability status, the AMF notifies the UE reachability status changes.
- If the Mobile Reachable Timer expires the AMF notifies the NF consumers that have subscribed for the corresponding events that the UE is not reachable.
- If the UDM had subscribed for UE reachability event notification either to be reported to the UDM or to an NF consumer directly, then the AMF notifies the UE reachability event to the UDM or to the NF consumer as specified in clause 4.2.5.2.
- If UE's TAC is already known by the AMF, then, the AMF notifies UE TAC to the NF consumers (e.g. to NWDAF). If UE TAC is unknown, then the AMF notifies the UE TAC when it obtained the UE TAC from the UE.
| Information | Description |
|---|---|
| UE Identity | SUPI |
| List of state transitions | |
| > State transition type | State transition identifier:
|
| > Spacing | Average and variance of the time interval separating two consecutive occurrences of the state transition. |
| > Duration | Average and variance of duration in the resulting state. |
| Information | Description |
|---|---|
| UE Identity | SUPI |
| List of location information (1..N) | |
| > UE Location | TAI, Cell-ID (if available), non-3GPP access identity. |
| > Spacing | Average and variance of the time interval separating two consecutive arrivals at this location. |
| > Duration | Average and variance of duration of stay in the location. |
| > Timestamp | Timestamp of last arrival in the location. |
|
NOTE:
The maximum size of the list (N) is defined per configuration and only the N entries with the highest average value of "Duration" are kept in the list. The list is ordered by descending order of "Duration".
|
|
4.15.4.3 Exposure of Communication trends from SMF |R17| p. 422
During Session Management procedures, the SMF may store and update the UE access behaviour trends specified in Table 4.15.4.3-1 and the UE communication trends specified in Table 4.15.4.3-2. Each metrics is updated incrementally, e.g. using exponential moving average. This information is exposed to consumer NFs (e.g. NWDAF) that subscribe for the event ID "UE session behaviour trends" and/or "UE communication trends", respectively, by invoking Nsmf_EventExposure_Subscribe .
| Information | Description |
|---|---|
| UE Identity | SUPI |
| List of state transitions | |
| > State transition type | State transition identifier:
|
| > Spacing | Average and variance of the time interval separating two consecutive occurrences of the state transition. |
| Information | Description |
|---|---|
| UE Identity | SUPI |
| List of communication information (1..N) | |
| > Communication characteristics | S-NSSAI and DNN |
| > Spacing | Average and variance of the time interval separating two consecutive PDU Session Establishment procedures corresponding to the communication characteristics. |
| > Duration | Average and variance of duration of PDU Sessions corresponding to the communication characteristics. |
| > Timestamp | Timestamp of the last PDU Session Establishment procedure corresponding to the communication characteristics. |
|
NOTE:
The maximum size of the list (N) is defined per configuration and only the N entries with the highest average value of "Duration" are kept in the list. The list is ordered by descending order of "Duration".
|
|
4.15.4.4 Internal Event Exposure Subscription/Unsubscription via UDM |R17| p. 423
This clause describes an indirect method of event exposure subscription in AMF and SMF via UDM for a UE or group of UEs. This can be used after the removal of UE context in the AMF including event exposure subscriptions, or the creation of new UE context in AMF or SMF. In this case, the UDM is responsible for (re)creating event exposure subscriptions in AMF and SMF.
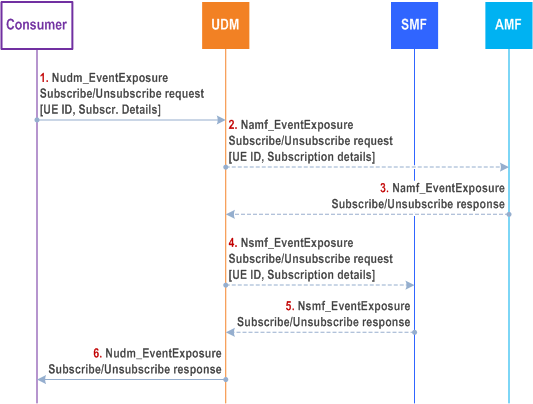
Step 1.
A consumer of event exposure for events detected in AMF or SMF (e.g. NWDAF) sends an Nudm_EventExposure Subscribe/Unsubscribe request to the UDM for a UE or group of UEs, including the subscription details (Event ID, Event filters, etc.).
Step 2.
UDM examines the event type and subscription details to determine whether one or more events are to be detected by the AMF. In this case, for those applicable events that are detected by the AMF, if an AMF is registered in UDM for the UE (or for a UE that is member of the group of UEs), UDM creates an Namf_EventExposure Subscribe/Unsubscribe request and sends it to the AMF of the UE, including the subscription details.
Step 3.
AMF answers with an Namf_EventExposure Subscribe/Unsubscribe response.
Step 4.
UDM examines the event type and subscription details to determine whether one or more events are to be detected by the SMF. In this case, for those applicable events that are detected by the SMF, if one or more SMFs are registered in UDM for the UE (or for a UE that is member of the group of UEs), UDM creates an Nsmf_EventExposure Subscribe/Unsubscribe request and sends it to each applicable SMF of the UE, including the subscription details.
Step 5.
SMF answers with an Nsmf_EventExposure Subscribe/Unsubscribe response.
Step 6.
UDM sends an Nudm_EventExposure Subscribe/Unsubscribe response to the consumer of event exposure.
4.15.4.5 Exposure of Events from UPF for UPF Data Collection |R18| p. 424
4.15.4.5.1 General p. 424
This clause contains the detailed description and the procedures for how the UPF event exposure service (see clause 5.2.26.2) is used for UPF data collection.
The list of NF consumer which may receive UPF event notifications is defined in clause 5.8.2.17 of TS 23.501.
To get exposure data from UPF, NF consumer may subscribe to the UPF directly or indirectly via SMF. This is further defined in clause 5.8.2.17 of TS 23.501.
The UPF event exposure events are described in clause 5.2.26.2. In this Release of the specification, the following events are used for UPF Data collection:
EventExposure_Notify service operation when sending reports. Otherwise, the SMF may accept the request and indicate in the response that reporting will be activated when the measurements are enabled by a PCC rule or the SMF may reject the subscription request for that Application Identifier.
A consumer of UPF event exposure such as NWDAF may subscribe to User Data Usage events (i.e. User Data Usage Measures and User Data Usage Trends) directly to UPF (under the conditions defined in clause 5.8.2.17 of TS 23.501) or via SMF, and UPF sends the event notifications directly to this consumer. For these events, the interaction between SMF and UPF is over SBI. For User Data Usage events, the subscription request targets the traffic matching Event Filter Information (details are described in clause 5.2.26.2.1) for a user's PDU Session or for each PDU Session served by the UPF. The subscription request may indicate the granularity requested, that is whether the measurement reports should be provided per data flow, per application, or per PDU Session.
If the event notification can be delayed, i.e. delay tolerant, Reporting suggestion information is included. The Reporting suggestion information includes Report urgency and Reporting time information. Reporting urgency information indicates whether this event report can be delay tolerant, i.e. the event report can be delayed. If the Reporting urgency information indicates "delay tolerant", the Reporting time is also provided, which defines the last valid reporting time and UPF shall report the detected event before the last valid time.
If a consumer subscribes to an UPF event via the SMF including an AoI ("Area of Interest"), the SMF starts the subscription to the UPF only when the UE is located in the requested AoI. When the UE leaves the AoI, the SMF stops the subscription on the UPF. The SMF may subscribe to AMF about UE moving in or out of an AoI for this purpose. Clause 4.15.4.5.4 describes an alternative procedure for subscription via SMF to UPF event exposure service related with AOI.
- QoS Monitoring: This event provides QoS Flow performance information.
- User DataUsage Measures: This event provides information of user data usage of the User PDU Session.
- User DataUsage Trends: This event provides statistics related to user data usage of the User PDU Session.
| Information | To SMF | To UPF
(NOTE 4) |
|---|---|---|
| UE identification (NOTE 5) | Y | Y |
| GroupID | Y | N |
| AnyUE | Y | Y (NOTE 6) |
| DNN | Y | Y (NOTE 6) |
| S-NSSAI | Y | Y |
| AOI | Y | N |
| BSSID/SSID | Y | N |
| DNAI (NOTE 3) | Y | N |
| UPF Id (NOTE 3) | Y | not applicable |
| Type of Measurement | Y | Y |
| Granularity of Measurement (NOTE 2) | Y | Y |
| Application ID (NOTE 1) | Y | Y |
| Traffic Filtering Information (NOTE 1), (NOTE 2) | Y | Y |
| Reporting suggestion information | Y | Y |
|
NOTE 1:
Application ID and Traffic Filtering Information are exclusive.
NOTE 2:
This parameter does not apply to QoS monitoring event.
NOTE 3:
This parameter is used to indicate a UP Path as defined in Table 6.4.1-1 of TS 23.288.
NOTE 4:
This column is not applicable to events where SMF-UPF interactions are using PFCP (e.g. QoS Monitoring event). That interaction is described in clause 5.8.5 of TS 23.501.
NOTE 5:
Input parameter when the target is a UE. SUPI is the input to SMF and UE IP address is the input to UPF.
NOTE 6:
In a deployment where UPF reporting filtered per DNN and /or S-NSSAI is expected, the SMF should provide UPF with the necessary information over N4. If the SMF is not configured to provide UPF with this information then such UPF reporting filtering is not possible.
|
||
4.15.4.5.2 Information flow for subscription to UPF event exposure service for certain UE(s) via SMF p. 426
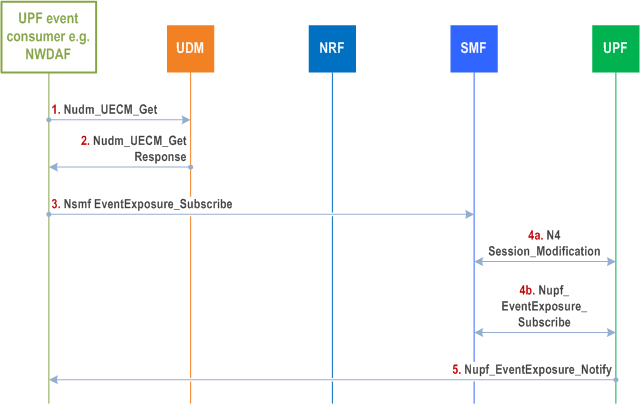
In the case of a group of UEs, the UPF event consumer (e.g. NWDAF) first issues an Nnrf_NFDiscovery_Request service operation to find the UDM providing the target Group ID and gets the NF profile of the UDM serves this group. Then, NWDAF obtains the list of SUPIs that correspond to the Group ID from UDM using Nudm_SDM_Get
Then, for each SUPI:
Step 1.
The UPF event consumer (e.g. NWDAF) invokes Nudm_UECM_Get service operation to retrieve the appropriate SMF by providing UE ID, DNN, S-NSSAI and NF type = SMF.
Step 2.
The UDM provides a Nudm_UECM_Get response with the corresponding SMF.
Step 3.
The UPF event consumer sends the Nsmf_EventExposure Subscription request to the SMF to subscribe to UPF data, including the following information:
Step 4.
- Notification Target Address (UPF event consumer address), Notification Correlation Information.
- UPF Event Id.
- Event Filter Information, i.e. one or more of the following parameters: S-NSSAI, DNN, DNAI, UPF Id, either Application Id(s) or Traffic Filtering Information, Area of Interest, SSID/BSSID.
- Target of Event Reporting: a UE.
- Reporting suggestion information.
- Type of Measurement and Granularity of Measurement.
The SMF selects the PDU session(s) and the UPFs it has to send the request to. The SMF sends the request to the UPF including the UPF event consumer address, UPF Event Id, Notification Correlation Information, Event Filter Information (but only Application Id(s) or Traffic Filtering Information, if received in step 3), Reporting suggestion information, Target of Event Reporting, Type of Measurement and Granularity of Measurement as required. Target of Event Reporting indicates the PDU Session of the UE. The interaction mechanism used between SMF and UPF depends on UPF exposure event and which mechanism applies for each event as described in clause 5.2.26.2.1. For some events, the SMF shall contact UPF (4a) with N4 Session Modification with PFCP (TS 29.244), for other events (4b) with Nupf_event exposure subscribe request (as defined in clause 5.2.26.2.3).
Step 5.
Per Reporting suggestion information (if available), the UPF sends the locally collected UPF data by invoking Nupf_EventExposure_Notify service operation to the UPF event consumer.
4.15.4.5.3 Information flow for UPF event exposure service for any UE p. 427
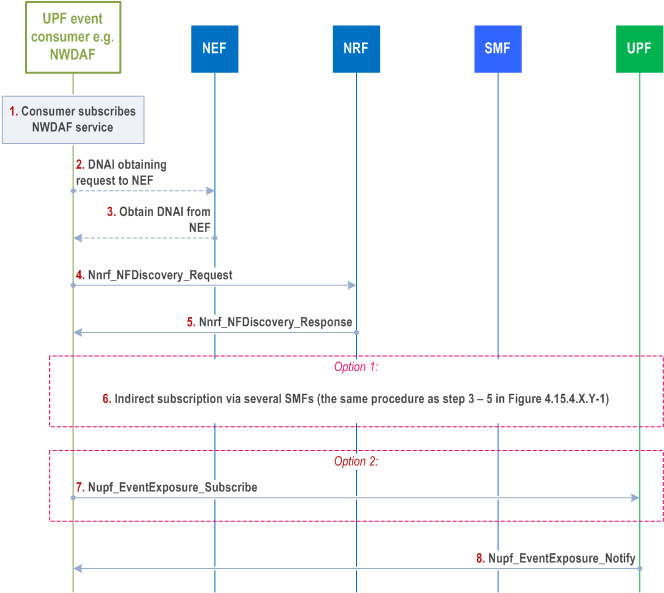
Step 1.
(For the case when the UPF event consumer is NWDAF) The analytics consumer sends a request to the NWDAF for analytics on any UE. The analytics consumer provides the value "any UE" in the Target of Analytics Reporting. Analytics Filter Information optionally contains DNN, S-NSSAI, Area of Interest, Application server IP address/FQDN, Application ID, DNAI, etc.
Step 2.
(Optional and only when the UPF event consumer is NWDAF) If the Analytic Filter Information does not contain DNN/S-NSSAI, but only includes application server IP address/FQDN, the NWDAF should first obtain the DNAI from NEF. The NWDAF invokes Nnef_DNAIMapping_Subscribe service to request the DNAI information. The request includes EAS IP/IP range and/or FQDN.
Step 3.
(Conditional, if step 2 took place) The NEF determines the suitable DNAI(s) and provides them to NWDAF.
Step 4.
The UPF event consumer triggers the SMF(s)/UPF(s) discovery to NRF by Nnrf_NFDiscovery_Request providing the DNN, S-NSSAI, DNAI etc. This procedure is to discover the related SMF(s)/UPF(s) associated with any UE and support the indicated DNAI. Either SMF(s) or UPF(s) are discovered depending on whether the subscription request to UPF events meets the criteria for direct subscription to UPF as defined in clause 5.8.2.17 of TS 23.501).
Step 5.
The NRF provides Nnrf_NFDiscovery_Response that may refer to several SMFs/UPFs.
Step 6.
(Option 1) If the subscribed UPF events needs the SMF(s) to do a third-party subscription onto UPF (as defined in clause 5.8.2.17 of TS 23.501), the same procedure as Indirect subscription via several SMFs (steps 3 - 5 in Figure 4.15.4.5.2-1(for single UE)) takes place via each discovered SMF.
Step 7.
(Option 2) If the subscribed UPF events allows to directly subscribe to UPF (as defined in clause 5.8.2.17 of TS 23.501), the UPF event consumer (e.g. NWDAF) triggers the Nupf_EventExposure_Subscribe to all discovered UPFs. The information included in the subscription is:
Step 8.
- Notification Target Address (UPF event consumer address), Notification Correlation Information.
- UPF Event Id.
- Event Filter Information, i.e. one or more of the following parameters: S-NSSAI, DNN, either Application Id(s) or Traffic Filtering Information.
- Target of Event Reporting: any UE.
- Reporting suggestion information.
- Type of Measurement and Granularity of Measurement.
Each of the UPFs invokes Nupf_EventExposure_Notify service operation directly to the UPF event consumer (e.g. NWDAF).
4.15.4.5.4 Information flow for subscription via SMF to UPF event exposure service related with AOI p. 428
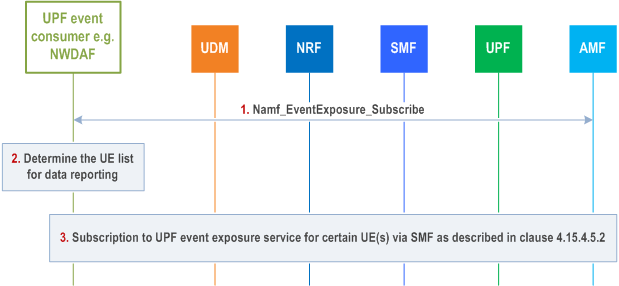
If the subscription is related to AOI, the UPF event consumer (e.g. NWDAF) firstly get the UE list which includes the UE(s) located in the AOI from the AMF(s), then subscribe to UPF via SMF as described in clause 4.15.4.5.2. If the UPF event consumer (e.g. NWDAF) further needs to filter certain UE(s) out from the UE list get from the AMF(s), the UPF event consumer (e.g. NWDAF) locally decides the final UE list.
Step 1.
The UPF event consumer (e.g. NWDAF) determines the AMF(s) based on the AOI, i.e. TAIs and possibly on the target S-NSSAI and obtains the UE list which includes the UE(s) located in the AoI from AMF(s) by invoking Namf_EventExposure_Subscribe service operation to get the presence of UE(s) and moving in or out status in Area of Interest as described in clause 5.2.2.3 and in clause 5.3.4.4 of TS 23.501. The target of Namf_EventExposure_Subscribe depends on whether the UPF event consumer (e.g. NWDAF) targets one UE a group of UE or Any UE.
Step 2.
The UPF event consumer (e.g. NWDAF) locally computes the final UE list by comparing the UE list from AMF(s) and its own target UE list if it exists.
Step 3.
For each UE in the final UE list, the UPF event consumer (e.g. NWDAF) issues a subscription to UPF event exposure service via the SMF serving the UE (Nsmf_EventExposure Subscription) to get UPF data as described in clause 4.15.4.5.2. When an AMF reports a change of the list of UE(s) in the AoI (Namf_EventExposure_Notify ), the UPF event consumer (e.g. NWDAF) may need to cancel the Nsmf_EventExposure Subscription or to issue a new Nsmf_EventExposure Subscription.