Content for TS 23.502 Word version: 19.0.0
1…
4.2.2.2.2
4.2.2.2.3…
4.2.2.3…
4.2.3…
4.2.3.3
4.2.4…
4.2.6
4.2.7…
4.2.9…
4.2.11…
4.2.11.5…
4.3…
4.3.2.2.2
4.3.2.2.3…
4.3.3…
4.3.3.3
4.3.4…
4.3.4.3
4.3.5…
4.3.5.2…
4.3.5.4…
4.3.5.6…
4.3.6…
4.4…
4.5…
4.9…
4.9.1.3…
4.9.2…
4.11…
4.11.1…
4.11.1.2.2
4.11.1.2.3
4.11.1.3…
4.11.1.3.3…
4.11.1.4…
4.11.1.5…
4.11.2…
4.11.3…
4.12…
4.12.6…
4.12a…
4.12b…
4.13…
4.13.4…
4.13.6…
4.14…
4.15…
4.15.3.2.5…
4.15.4…
4.15.6…
4.15.6.7…
4.15.6.13…
4.15.6.14…
4.15.9…
4.15.9.4…
4.15.13…
4.15.13.4…
4.16…
4.16.4…
4.16.8…
4.16.11…
4.16.14…
4.16.15…
4.17…
4.17.9…
4.18…
4.19…
4.22…
4.23…
4.23.7…
4.23.7.3.3
4.23.7.3.4…
4.23.9…
4.23.9.4…
4.23.11…
4.24…
4.25…
4.25.6…
4.26…
5…
5.2.3…
5.2.5…
5.2.6…
5.2.7…
5.2.8…
5.2.9…
5.2.12…
5.2.18…
A…
E…
F…
G
H…
4.23.7 Inter NG-RAN node N2 based handover
4.23.7.1 General
4.23.7.2 Inter NG-RAN node N2 based handover without I-SMF change/removal
4.23.7.3 Inter NG-RAN node N2 based handover with I-SMF insertion/change/removal
4.23.7.3.1 General
4.23.7.3.2 Preparation phase
...
...
4.23.7 Inter NG-RAN node N2 based handover p. 613
4.23.7.1 General p. 613
The following two scenarios are considered:
- The I-SMF is available for the PDU Session and I-SMF is not changed or removed during the inter NG-RAN node N2 based handover procedure. The procedure to support this scenario is described in clause 4.23.7.2.
- The I-SMF is inserted, changed or removed during inter NG-RAN node N2 based handover procedure. The procedure to support this scenario is described in clause 4.23.7.3.
4.23.7.2 Inter NG-RAN node N2 based handover without I-SMF change/removal p. 613
4.23.7.2.1 General p. 613
When both I-SMF and SMF are available for a PDU Session and no I-SMF change or removal is needed during inter NG-RAN node N2 handover procedure, the procedure defined in clause 4.9.1.3.2, 4.9.1.3.3 are used with the following differences.
4.23.7.2.2 Preparation phase p. 613
Compared to the procedure in clause 4.9.1.3.2, the SMF interacting with the S-UPF, T-UPF, S-AMF and T-AMF is the I-SMF. The difference is following:
- Step 3: The N14 context exchanged between S-AMF and T-AMF contains the SM Context ID at I-SMF, or SM Context ID at SMF if I-SMF is not applicable before.
- Step 4: The T-AMF determines whether Target I-SMF needs to be selected based on UE location and service area of the SMF. In this case no I-SMF change or removal is needed.
- Step 5: The I-SMF checks whether I-UPF needs to be reallocated, i.e. select a T-UPF.
4.23.7.2.3 Execution phase p. 613
Compared to the procedure for execution phase in clause 4.9.1.3.3, the SMF interacting with the S-UPF, T-UPF, S-AMF and T-AMF is the I-SMF. The difference is as following:
-
Step 10a: If I-SMF is available for a PDU Session and the existing intermediate S-UPF is re-allocated, i.e. a new T-UPF is selected, the I-SMF invokes an Nsmf_
PDUSession_ Request (DL CN Tunnel Info of the T-UPF) service operation toward the SMF. The SMF sends N4 Session Modification Request message to PDU Session Anchor UPF, providing DL CN Tunnel Info to the PDU Session Anchor UPF. The PDU Session Anchor sends one or more "end marker" packets for each N3/N9 tunnel on the old path immediately after switching the path, the source NG-RAN shall forward the "end marker" packets to the target NG-RAN.Update -
Step 10b: The SMF responds with the Nsmf_
PDUSession_ Response service operation to I-SMF once the PDU Session Anchor UPF is updated with the DL Tunnel Info of the T-UPF.Update
4.23.7.2.4 Handover Cancel p. 613
The home routed roaming procedure defined in clause 4.9.1.4 is applied, with V-SMF replaced by I-SMF.
4.23.7.3 Inter NG-RAN node N2 based handover with I-SMF insertion/change/removal p. 614
4.23.7.3.1 General p. 614
When I-SMF is inserted or changed or removed during inter NG-RAN node N2 handover, the procedures defined in this clause are used.
To support the EAS session continuity upon UL CL relocation, a N9 forwarding tunnel to support the EAS session continuity is established and released between the Source UL CL and Target UL CL as described in clause 4.23.9.4 or clause 4.23.9.5.
4.23.7.3.2 Preparation phase p. 615
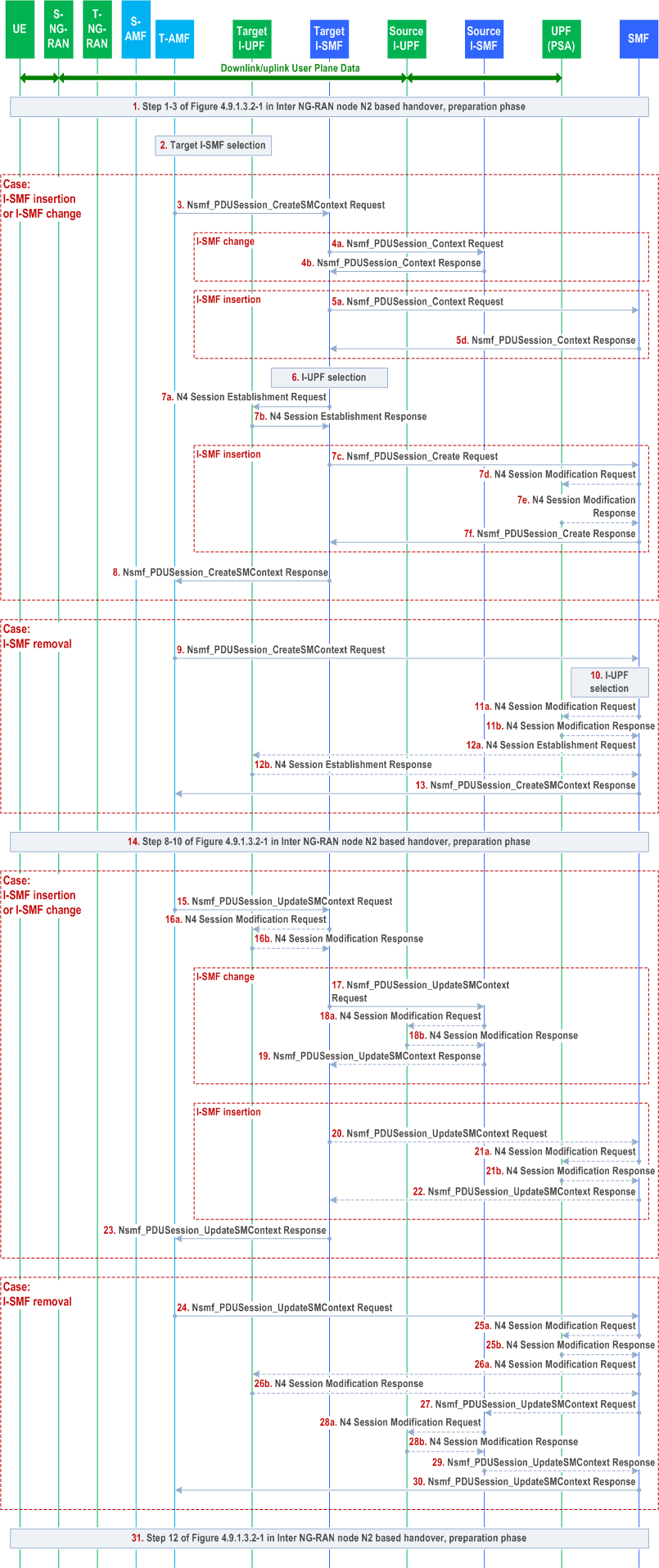
Step 1.
Step 2.
Case: I-SMF insertion, or I-SMF change, step 3~8 are skipped for I-SMF removal case.
Steps 1-3 in clause 4.9.1.3.2 are performed.
Step 2.
For PDU sessions in the UE context, the Target AMF determines whether a (new) Target I-SMF needs to be selected based on Target UE location and service area of the SMF or of the old I-SMF. If Target I-SMF needs to be selected, the AMF selects a Target I-SMF as described in clause 5.34.3 of TS 23.501. If the UE moves from the service area of the I-SMF to the service area of the SMF, the I-SMF will be removed.
The rest of steps are performed for PDU sessions requested to be handed over, i.e. the PDU Sessions with active UP connections.
Step 3.
Case: I-SMF change, steps 4 are skipped for I-SMF insertion case.
T-AMF to Target I-SMF: Nsmf_PDUSession_CreateSMContext (PDU Session ID, Target ID, T-AMF ID, SM Context ID).
The SM Context ID points to the source I-SMF in the case of I-SMF change or to SMF in the case of I-SMF insertion.
Step 4a.
Step 4b.
Case: I-SMF insertion, steps 5 are skipped for I-SMF change case.
(I-SMF change case) Target I-SMF to Source I-SMF: Target I-SMF retrieves SM Context from the source I-SMF by invoking Nsmf_PDUSession_Context Request (SM context type, SM Context ID).
The Target I-SMF uses SM Context ID received from T-AMF for this service operation. SM context type indicates that the requested information is all SM context, i.e. PDN Connection Context and 5G SM context. The SM Context ID is used by the recipient of Nsmf_PDUSession_Context Request in order to determine the targeted PDU Session.
Step 4b.
Source I-SMF to Target I-SMF: Nsmf_PDUSession_Context Response. The source I-SMF responds with the requested SM context.
Step 5a.
Step 5b.
Step 5c.
Step 5d.
Step 6.
Step 7a.
Step 7b.
Case: I-SMF insertion, step 7c~7f are skipped for I-SMF change case.
Target I-SMF to SMF: Target I-SMF retrieves SM Context from the SMF by invoking Nsmf_PDUSession_Context Request (SM context type, SM Context ID).
The Target I-SMF uses SM Context ID received from T-AMF for this service operation. SM context type indicates that the requested information is all SM context, i.e. PDN Connection Context and 5G SM context. The SM Context ID is used by the recipient of Nsmf_PDUSession_Context Request in order to determine the targeted PDU Session.
Step 5b.
Void.
Step 5c.
Void.
Step 5d.
SMF to Target I-SMF: Nsmf_PDUSession_Context Response. The SMF responds with the requested SM context.
Step 6.
The Target I-SMF selects a Target I-UPF: Based on the received SM context, e.g. S-NSSAI and UE location information, the Target I-SMF selects a Target I-UPF as described in clause 6.3.3 of TS 23.501.
Step 7a.
The Target I-SMF to Target I-UPF: N4 Session Establishment Request.
An N4 Session Establishment Request message is sent to the Target I-UPF, providing Packet detection, enforcement and reporting rules to be installed on the Target I-UPF. The UL CN Tunnel Info (on N9) of UPF (PSA) for this PDU Session, which is used to setup N9 tunnel, is also provided to the Target I-UPF.
Step 7b.
Target I-UPF to Target I-SMF or SMF: N4 Session Establishment Response.
The Target I-UPF sends an N4 Session Establishment Response message to the Target I-SMF with DL CN Tunnel Info (i.e. N9 tunnel info) and UL CN Tunnel Info (i.e. N3 tunnel info).
Step 7c.
Step 7d.
Step 7e.
Step 7f.
Step 8.
Case: I-SMF removal, step 9~13 are skipped for I-SMF insertion, or I-SMF change case.
Target I-SMF to SMF: Nsmf_PDUSession_Create Request (PDU Session ID, HO Preparation Indication).
Step 7d.
[Conditional] SMF to UPF (PSA): N4 Session Modification Request.
If different CN Tunnel Info need be used by PSA UPF, i.e. the CN Tunnel Info for N3 and N9 are different, the SMF request CN tunnel information from UPF.
Step 7e.
[Conditional] UPF(PSA) to SMF: N4 Session Modification Response.
The UPF (PSA) sends an N4 Session Modification Response message to the SMF with CN Tunnel Info (on N9).
Step 7f.
SMF to Target I-SMF: Nsmf_PDUSession_Create Response (PDU Session ID, CN Tunnel Info of UPF(PSA) for N9).
The Target I-SMF provides the CN Tunnel Info of UPF(PSA) for N9 to Target I-UPF via N4 Session Modification.
Step 8.
The Target I-SMF to T-AMF: Nsmf_PDUSession_CreateSMContext Response (PDU Session ID, N2 SM Information, Reason for non-acceptance).
If N2 handover for the PDU Session is accepted, the Target I-SMF includes in the Nsmf_PDUSession_CreateSMContext Response the N2 SM Information containing the N3 UP address and the UL CN Tunnel ID of the UPF and the QoS parameters.
Step 9.
Step 10.
Step 11a.
Step 11b.
Step 12a.
Step 12b.
Step 13.
Step 14.
Case: I-SMF insertion, or I-SMF change, step 15~23 are skipped for I-SMF removal case.
T-AMF to SMF: Nsmf_PDUSession_CreateSMContext (PDU Session ID, Target ID, T-AMF ID, SM Context ID). The SM Context ID points to the source I-SMF.
Step 10.
The SMF selects a Target I-UPF if the UE is not in the service area of the PDU Session Anchor UPF. The SMF selects a Target I-UPF as described in clause 6.3.3 of TS 23.501.
Step 11a.
[Conditional] SMF to UPF(PSA): N4 Session Modification Request.
If the Target I-UPF was not selected (i.e. the service area of PSA covers UE location) and different CN Tunnel Info (on N3) need to be used by PSA, the SMF sends N4 Session Modification Request to UPF(PSA).
Step 11b.
[Conditional] UPF(PSA) to SMF: N4 Session Modification Response. The PSA UPF sends UL CN Tunnel Info (i.e. N3 tunnel info) to SMF.
Step 12a.
[Conditional] SMF to Target I-UPF: N4 Session Establishment Request.
If a Target I-UPF is selected by SMF in step 10, the SMF sends N4 Session Establishment Request to Target I-UPF.
An N4 Session Establishment Request message is sent to the Target I-UPF, providing Packet detection, enforcement and reporting rules to be installed on the Target I-UPF. The UL CN Tunnel Info (on N9) of UPF (PSA) for this PDU Session, which is used to setup N9 tunnel, is also provided to the Target I-UPF.
Step 12b.
[Conditional]Target I-UPF to SMF: N4 Session Establishment Response. The Target I-UPF sends an N4 Session Establishment Response message to the SMF with DL CN Tunnel Info (i.e. N9 tunnel info) and UL CN Tunnel Info (i.e. N3 tunnel info).
Step 13.
SMF to T-AMF: Nsmf_PDUSession_CreateSMContext Response (PDU Session ID, N2 SM Information, Reason for non-acceptance).
If N2 handover for the PDU Session is accepted, the Target I-SMF includes in the Nsmf_PDUSession_CreateSMContext Response the N2 SM Information containing the N3 UP address and the UL CN Tunnel ID of the UPF and the QoS parameters.
Step 14.
Same as step 8-10 clause 4.9.1.3.2 are performed.
Step 15.
Step 16a.
Step 16b.
Case: I-SMF change, step 17~19 are skipped for I-SMF insertion case.
T-AMF to Target I-SMF: Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext Request (PDU Session ID, N2 SM response received from T-RAN).
The Target I-SMF stores the N3 tunnel info of T-RAN from the N2 SM response if N2 handover is accepted by T-RAN.
Step 16a.
[Conditional]Target I-SMF to Target I-UPF: N4 Session modification request (T-RAN SM N3 forwarding Information list, indication to allocate DL forwarding tunnel(s) for indirect forwarding).
Indirect forwarding may be performed via a UPF which is different from the Target I-UPF, in which case the Target I-SMF selects another UPF for indirect forwarding.
Step 16b.
[Conditional]Target I-UPF to Target I-SMF: N4 Session Modification Response (Target I-UPF N9 forwarding Information list).
The Target I-UPF allocates Tunnel Info and returns an N4 Session Modification Response message to the Target I-SMF.
The Target I-UPF SM N9 forwarding info list includes Target I-UPF N9 address, Target I-UPF N9 Tunnel identifiers for forwarding data.
Step 17.
Step 18a.
Step 18b.
Step 19.
Case: I-SMF insertion, step 20~22 are skipped for I-SMF change case.
[Conditional]Target I-SMF to Source I-SMF: Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext Request.
Target I-SMF invokes Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext Request (Target I-UPF SM N9 forwarding Information list, Operation type) to the source I-SMF in order to establish the indirect forwarding tunnel. The Target I-SMF uses the SM Context ID received from Target AMF for this service operation. The Operation type indicates the establishment of forwarding tunnel(s) for indirect forwarding.
Step 18a.
[Conditional]The source I-SMF initiates a N4 session modification request (Target I-UPF SM N9 forwarding Information list, indication to allocate DL forwarding tunnel(s) for indirect forwarding) to the source I-UPF to establish indirect forwarding tunnel.
Indirect forwarding may be performed via a UPF which is different from the Source I-UPF.
Step 18b.
[Conditional]The source I-UPF to source I-SMF: N4 Session Modification Response (source I-UPF SM N3 forwarding Information list).
Step 19.
[Conditional]Source I-SMF to Target I-SMF: Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext response (Source I-UPF SM N3 forwarding Information list).
Step 20.
Step 21a.
Step 21b.
Step 22.
Step 23.
Case: I-SMF removal, step 24~30 are skipped for I-SMF insertion, or I-SMF change case.
[Conditional]Target I-SMF to SMF: Nsmf_PDU Session_UpdateSMContext.
The Target I-SMF invokes Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext Request (Target I-UPF SM N9 forwarding Information list, Operation type) to the SMF in order to establish the indirect forwarding tunnel. The Target I-SMF uses the SM Context ID received from Target AMF for this service operation. The Operation type indicates the establishment of forwarding tunnel(s) for indirect forwarding.
Step 21a.
[Conditional]The SMF initiates a N4 session modification request (UPF SM N9 forwarding Information list, indication to allocate DL forwarding tunnel(s) for indirect forwarding) to the UPF(PSA) to establish indirect forwarding tunnel.
Indirect forwarding may be performed via a UPF which is different from the UPF(PSA).
Step 21b.
[Conditional] The UPF(PSA) to SMF: N4 Session Modification Response (UPF SM N3 forwarding Information list).
Step 22.
[Conditional] The SMF to Target I-SMF: Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext response (UPF SM N3 forwarding Information list).
Step 23.
Target I-SMF to T-AMF: Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext Response (N2 SM Information).
Target I-SMF creates an N2 SM information containing the DL forwarding Tunnel Info to be sent to the S-RAN by Source AMF via the Target AMF. Target I-SMF includes this information in the Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext response. The DL forwarding Tunnel Info can be one of the following information:
- If direct forwarding applies, then Target I-SMF includes the T-RAN N3 forwarding information received in step 15.
- If the indirect forwarding tunnel is setup, then the SMF includes Source I-UPF forwarding information containing the N3 UP address and the Tunnel ID of the Source I-UPF.
Step 24.
Step 25a.
Step 25b.
Step 26a.
Step 26b.
Step 27.
Step 28a.
Step 28b.
Step 29.
Step 30.
Step 31.
T-AMF to SMF: Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext Request (PDU Session ID, N2 SM response received from T-RAN).
The SMF stores the N3 tunnel info of T-RAN from the N2 SM response if N2 handover is accepted by T-RAN.
Step 25a.
[Conditional] SMF to UPF (PSA): N4 Session modification Request.
If the Target I-UPF is not selected (i.e. the service area of PSA covers UE location), the SMF sends N4 Session modification request to UPF(PSA) to allocate DL forwarding tunnel(s).
Indirect forwarding may be performed via a UPF which is different from the UPF(PSA), in which case the SMF selects another UPF for indirect forwarding.
Step 25b.
[Conditional] UPF (PSA) to SMF: N4 Session Modification Response (UPF N9 forwarding Information list).
Step 26a.
[Conditional] SMF to Target I-UPF:
If the Target I-UPF is selected, the SMF sends N4 Session modification request to Target I-UPF to allocate DL forwarding tunnel(s) for indirect forwarding;
Indirect forwarding may be performed via a UPF which is different from the Target I-UPF, in which case the SMF selects another UPF for indirect forwarding.
Step 26b.
[Conditional] Target I-UPF to SMF: N4 Session Modification Response (Target I-UPF N9 forwarding Information list).
Step 27.
[Conditional] SMF to Source I-SMF: Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext .
The SMF invokes Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext Request (SM N9 forwarding Information list, Operation type) to the source I-SMF in order to establish the indirect forwarding tunnel. The SMF uses the SM Context ID received from T-AMF for this service operation. The Operation type indicates the establishment of forwarding tunnel(s) for indirect forwarding.
Step 28a.
[Conditional] Source I-SMF to Source I-UPF: N4 Session Modification Request.
The source I-SMF initiates a N4 session modification request (Target I-UPF SM N9 forwarding Information list, indication to allocate DL forwarding tunnel(s) for indirect forwarding) to the source I-UPF to establish indirect forwarding tunnel.
Indirect forwarding may be performed via a UPF which is different from the Source I-UPF.
Step 28b.
[Conditional]The source I-UPF to source I-SMF: N4 Session Modification Response (source I-UPF SM N3 forwarding Information list).
Step 29.
[Conditional]The source I-SMF to SMF: Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext response (Source I-UPF SM N3 forwarding Information list).
Step 30.
SMF to T-AMF: Nsmf_PDUSession_UpdateSMContext Response (N2 SM Information).
The SMF creates an N2 SM information containing the DL forwarding Tunnel Info to be sent to the S-RAN by the Source AMF via the Target AMF. The DL forwarding Tunnel Info can be one of the following information:
- If direct forwarding applies, then the SMF includes the T-RAN N3 forwarding information the SMF received in step 24.
- If the indirect forwarding tunnel is setup, then the SMF includes Source I-UPF forwarding information containing the N3 UP address and the Tunnel ID of the Source I-UPF.
Step 31.
Same as step 12 in clause 4.9.1.3.2 is performed.