Content for TS 23.502 Word version: 19.0.0
1…
4.2.2.2.2
4.2.2.2.3…
4.2.2.3…
4.2.3…
4.2.3.3
4.2.4…
4.2.6
4.2.7…
4.2.9…
4.2.11…
4.2.11.5…
4.3…
4.3.2.2.2
4.3.2.2.3…
4.3.3…
4.3.3.3
4.3.4…
4.3.4.3
4.3.5…
4.3.5.2…
4.3.5.4…
4.3.5.6…
4.3.6…
4.4…
4.5…
4.9…
4.9.1.3…
4.9.2…
4.11…
4.11.1…
4.11.1.2.2
4.11.1.2.3
4.11.1.3…
4.11.1.3.3…
4.11.1.4…
4.11.1.5…
4.11.2…
4.11.3…
4.12…
4.12.6…
4.12a…
4.12b…
4.13…
4.13.4…
4.13.6…
4.14…
4.15…
4.15.3.2.5…
4.15.4…
4.15.6…
4.15.6.7…
4.15.6.13…
4.15.6.14…
4.15.9…
4.15.9.4…
4.15.13…
4.15.13.4…
4.16…
4.16.4…
4.16.8…
4.16.11…
4.16.14…
4.16.15…
4.17…
4.17.9…
4.18…
4.19…
4.22…
4.23…
4.23.7…
4.23.7.3.3
4.23.7.3.4…
4.23.9…
4.23.9.4…
4.23.11…
4.24…
4.25…
4.25.6…
4.26…
5…
5.2.3…
5.2.5…
5.2.6…
5.2.7…
5.2.8…
5.2.9…
5.2.12…
5.2.18…
A…
E…
F…
G
H…
4.11.3 Handover procedures between EPS and 5GC-N3IWF
4.11.3a Handover procedures between EPS and 5GC-TNGF
4.11.4 Handover procedures between EPC/ePDG and 5GS
4.11.4.1 Handover from EPC/ePDG to 5GS
4.11.4.2 Handover from 5GS to EPC/ePDG
4.11.4.3 Impacts to EPC/ePDG Procedures
4.11.5 Impacts to 5GC Procedures
4.11.6 Interworking for common network exposure
...
...
4.11.3 Handover procedures between EPS and 5GC-N3IWF p. 325
4.11.3.1 Handover from EPS to 5GC-N3IWF p. 325
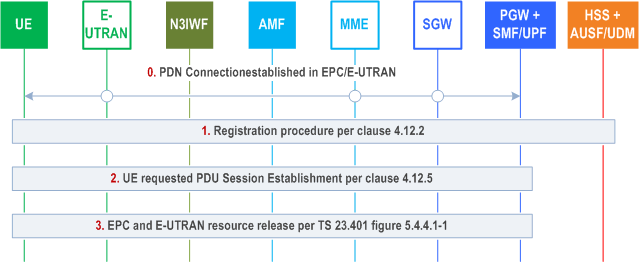
Step 0.
Initial status: one or more PDN connections have been established in EPC between the 5G capable UE and the PGW via E-UTRAN.
Step 1.
The UE initiates Registration procedure on untrusted non-3GPP access via N3IWF (with 5G-GUTI is available or SUCI if not) per clause 4.12.2.
Step 2.
The UE initiates a UE requested PDU Session Establishment with Existing PDU Session indication in 5GC via Untrusted non-3GPP Access via N3IWF per clause 4.12.5.
If the Request Type indicates "Existing Emergency PDU Session", the AMF shall use the Emergency Information received from the HSS+UDM which contains SMF+PGW-C FQDN for S5/S8 interface for the emergency PDN connection established in EPS and the AMF shall use the S-NSSAI locally configured in Emergency Configuration Data.
The combined PGW+SMF/UPF initiates a PDN GW initiated bearer deactivation as described in clause 5.4.4.1 of TS 23.401 to release the EPC and E-UTRAN resources.
4.11.3.2 Handover from 5GC-N3IWF to EPS p. 325
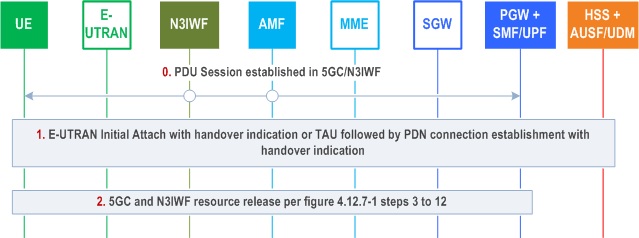
Step 0.
Initial status: one or more PDU Sessions have been established in 5GC between the UE and the SMF/UPF via untrusted non-3GPP access and N3IWF. During PDU Session setup and in addition to what is specified in clause 4.3.2.2.1 and clause 4.3.2.2.2, the AMF includes an indication that EPS interworking is supported to the SMF+PGW-C as specified in clause 4.11.5.3 and the SMF+PGW-C sends the FQDN related to the S5/S8 interface to the HSS+UDM which stores it as described in clause 4.11.5.
Step 1.
For the UE to move PDU session(s) from 5GC/N3IWF to EPC/E-UTRAN, the UE's behaviour is as follows:
Step 2.
-
If the UE is operating in single-registration mode (as described in clause 5.17.2.1 of TS 23.501) and the UE is registered via 3GPP access to 5GC;
- the UE behaves as specified in clause 4.11.1 or 4.11.2 and moves its PDU session from 5GC/N3IWF to EPC/E-UTRAN using the PDN connection establishment with "Handover" indication procedure as described in TS 23.401.
- otherwise, i.e. either the UE is operating in single registration mode and is not registered via 3GPP access to 5GC, or the UE is operating in dual registration mode; and
-
if the UE is not attached to EPC/E-UTRAN,
- the UE initiates Handover Attach procedure in E-UTRAN as described in TS 23.401 for a non-3GPP to EPS handover with "Handover" indication, except note 17.
- otherwise (i.e. the UE is attached to EPC/E-UTRAN), the UE initiates the PDN Connection establishment with "Handover" indication procedure as described in TS 23.401.
The combined PGW+SMF/UPF initiates a network requested PDU Session Release via untrusted non-3GPP access and N3IWF according to Figure 4.12.7-1 steps 3 to 12 to release the 5GC and N3IWF resources with the following exception:
-
the H-SMF indicates in the Nsmf_
PDUSession_ Request that the UE shall not be notified. This shall result in the V-SMF not sending the N1 SM Container (PDU Session Release Command) to the UE.Update -
Nsmf_
PDUSession_ service operation invoked by H-SMF to V-SMF indicates the PDU Session is moved to a different system;StatusNotify -
Nsmf_
PDUSession_ service operation invoked by the (V-)SMF indicates the PDU Session is moved to another system.SMContexStatusNotify -
The Npcf_
SMPolicyControl_ service operation to PCF shall not be performed.Delete
4.11.3a Handover procedures between EPS and 5GC-TNGF |R16| p. 326
4.11.3a.1 Handover from EPS to 5GC-TNGF p. 326
The handover procedure from EPS to 5GC-TNGF is supported as specified in clause 4.11.3.1 for handover procedure from EPS to 5GC-N3IWF with the following differences:
- The untrusted non-3GPP access is substituted by trusted non-3GPP access point (TNAP).
- The N3IWF is substituted by TNGF.
- The registration procedure via trusted non-3GPP access as specified in clause 4.12a.2 shall be performed in step 1.
- The UE requested PDU Session Establishment with Existing PDU Session indication in 5GC via trusted non-3GPP access is performed in step 2 as specified clause 4.12a.5.
4.11.3a.2 Handover from 5GC-TNGF to EPS p. 326
The handover procedure from 5GC-TNGF to EPS is supported as specified in clause 4.11.3.2 for handover procedure from 5GC-N3IWF to EPS with the following differences:
- The untrusted non-3GPP access is substituted by trusted non-3GPP access point (TNAP).
- The N3IWF is substituted by TNGF.
- The network requested PDU Session Release via TNAP and TNGF shall be initiated as specified in clause 4.12a.7 from steps 3 to 12.
4.11.4 Handover procedures between EPC/ePDG and 5GS p. 327
4.11.4.1 Handover from EPC/ePDG to 5GS p. 327
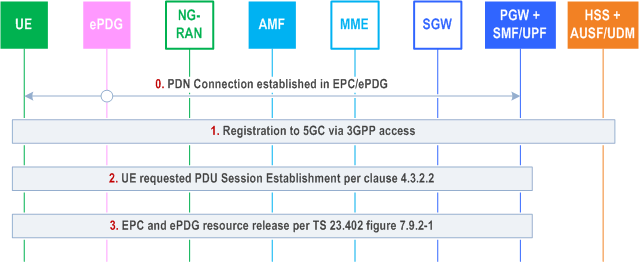
Step 0.
Initial status: one or more PDN Connections have been established between the UE and the EPC/ePDG via untrusted non-3GPP access as specified in clauses 7.2.4 and 7.6.3 of TS 23.402 with modification described in clauses 4.11.4.3.3 and 4.11.4.3.5.
Step 1.
For the UE to move its PDU session(s) from EPC/ePDG to 5GC/3GPP access, the UE's behaviour is as follows:
Step 2.
-
If the UE is operating in single-registration mode (as described in clause 5.17.2.1 of TS 23.501) and the UE is attached to EPC/E-UTRAN:
- the UE behaves as specified in clause 4.11.1 or clause 4.11.2 and gets registered to 5GC via 3GPP access.
- otherwise i.e. either the UE is operating in single registration mode and is not attached to EPC/E-UTRAN, or the UE is operating in dual registration mode; and
-
if the UE is already registered in 5GS via 3GPP access,
- the UE skips to step 2.
- otherwise (i.e. UE is not registered in 5GS via 3GPP access), the UE performs Registration procedure of type initial registration in 5GS via 3GPP access as described in clause 4.2.2.2.
The UE initiates a UE requested PDU Session Establishment via 3GPP Access according to clause 4.3.2.2 and includes the "Existing PDU Session" indication or "Existing Emergency PDU Session" and the PDU Session ID.
For Request Type "Existing PDU Session", the UE provides a DNN, the PDU Session ID and S-NSSAI corresponding to the existing PDN connection it wants to transfer from EPC/ePDG to 5GS. The S-NSSAI and PLMN ID sent to the UE are set in the same way as for EPS to 5GS mobility as specified in clause 5.15.7.1 of TS 23.501.
If the Request Type indicates "Existing Emergency PDU Session", the AMF shall use the Emergency Information containing SMF+PGW-C FQDN for the S2b interface it has received from the HSS+UDM. The SMF+PGW-C FQDN was sent by PGW-C when the Emergency PDN connection was established in EPC via ePDG and the AMF shall use the S-NSSAI locally configured in Emergency Configuration Data.
Step 3.
The combined PGW+SMF/UPF initiates a PDN GW initiated Resource Allocation Deactivation with GTP on S2b as described in clause 7.9.2 of TS 23.402 to release the EPC and ePDG resources when S6b is used. When S6b is not used between SMF+PGW-C and AAA, impacts to step 5 of TS 23.402 Figure 7.9.2-1 are captured in clause 4.11.4.3.6.
4.11.4.2 Handover from 5GS to EPC/ePDG p. 328
Figure 4.11.4.2-1 describes the procedure for handing over a PDU Session from 5GS to EPC/ePDG. The UE shall not request a handover of a PDU session with SSC mode 2 or SSC mode 3 to EPC/ePDG.
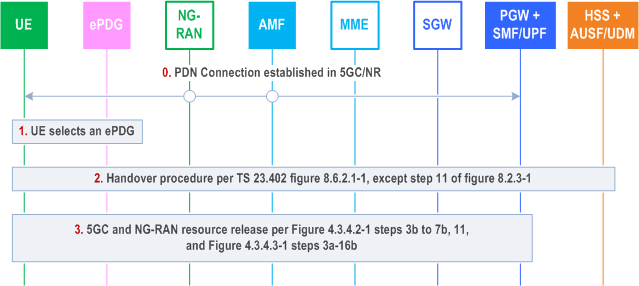
Step 0.
Initial status: one or more PDU Sessions have been established between the UE and the SMF/UPF via NG-RAN.
Step 1.
The UE connects to an untrusted non-3GPP access and the N3IWF-ePDG selection process results in selecting an ePDG.
Step 2.
The UE initiates a Handover procedure as described in clause 8.6.2.1 of TS 23.402, except step 11 of referenced Figure 8.2.3-1 that corresponds to the release of resources in source system.
Step 3.
The combined PGW+SMF/UPF initiates a network requested PDU Session Release via 3GPP access according to Figure 4.3.4.2-1 steps 3b to 7b, step 11 or Figure 4.3.4.3-1 steps 3a-16b to release the 5GC and NG-RAN resources with the following exception:
-
For non-roaming or local breakout in clause 4.3.4.2, the SMF does not include N1 SM Container in Namf_
Communication_ service operation.N1N2MessageTransfer -
For home routing roaming in clause 4.3.4.3, the H-SMF indicates in the Nsmf_
PDUSession_ Request that the UE shall not be notified. This shall result in the V-SMF not sending the N1 SM Container (PDU Session Release Command) to the UE.Update -
Nsmf_
PDUSession_ service operation invoked by H-SMF to V-SMF and Nsmf_StatusNotify PDUSession_ service operation invoked by the (V-)SMF to the AMF indicate that the PDU Session is moved to a different system.SMContexStatusNotify -
The Npcf_
SMPolicyControl_ service operation to PCF shall not be performed.Delete
4.11.4.3 Impacts to EPC/ePDG Procedures |R16| p. 328
4.11.4.3.1 General p. 328
This clause captures enhancements to procedures in TS 23.402 to support interworking with 5GS. The architecture for interworking is shown in clause 4.3.4 of TS 23.501. with the ePDG connected to SMF+PGW-C and UPF+PGW-U using GTP based S2b.
4.11.4.3.2 ePDG FQDN construction p. 328
Clause 4.5.4.2 of TS 23.402 applies with the following modification:
- Tracking/Location Area Identity FQDN: When the 5GC NAS capable UE uses the Tracking Area of the NG-RAN when the UE is registered with the 5GC when constructing the Tracking Area Identity FQDN.
4.11.4.3.3 Initial Attach with GTP on S2b p. 329
The procedure in clause 7.2.4 of TS 23.402 applies with the following modifications:
- In Step A.1 IKEv2 tunnel establishment procedure, the 5GC NAS capable UE shall indicate its support of 5GC NAS in IKEv2. The UE allocates a PDU Session ID and also includes it in IKEv2 signalling sent to the ePDG. For 5GC NAS capable UE even if the NAS capability is currently disabled (i.e. N1 mode is disabled), the UE may also allocate a PDU Session ID and include it in IKEv2 signalling sent to the ePDG.
- In Step A.1, UE's mobility restriction parameters related to 5GS or indication of support for interworking with 5GS for this APN or both as defined for MME in clause 4.11.0a.3 apply to the ePDG and are obtained by the ePDG as part of the reply from the HSS via the 3GPP AAA Server. These parameters and the 5G NAS support indicator from the UE, may be used by the ePDG to determine if a combined SMF+PGW-C or a standalone PGW should be selected.
- In Step B.1, if the PDN connection is not restricted to interworking with 5GS by user subscription and if PDU Session ID is received from the UE, the ePDG shall send the 5GC Not Restricted Indication, 5GS Interworking Indication and the PDU Session ID to the SMF+PGW-C.
- In Step B.1, if the SMF+PGW-C supports more than one S-NSSAI and the APN is valid for more than one S-NSSAI, the SMF+PGW-C selects S-NSSAI as specified in clause 4.11.0a.5.
- In Step D.1 (Create Session Response), if the PDU Session ID is present and 5GC Not Restricted Indication is set, the SMF+PGW-C assigns a S-NSSAI to be associated with the PDN connection as specified in clause 5.15.7.1 of TS 23.501. The SMF+PGW-C sends the S-NSSAI to the ePDG together with a PLMN ID that the S-NSSAI relates to.
- In Steps B.1 and D.1, if the UE does not support 5GC NAS but has 5GS subscription and a SMF+PGW-C is selected and interaction with UDM, PCF and UPF is required, the SMF+PGW-C assigns PDU Session ID as specified in clause 4.11.0a.5. The SMF+PGW-C shall not provide any 5GS related parameters to the UE.
- In the IKEv2 Authentication Response message, the ePDG sends S-NSSAI and the PLMN ID that the S-NSSAI relates to, to the UE. The UE associates the received S-NSSAI and the PLMN ID that the S-NSSAI relates to, with the PDN Connection.
-
After step D.1, the SMF+PGW-C provides the PCF ID selected for the PDN connection in the UDM using the Nudm_
UECM_ service operation.Registration
4.11.4.3.3a Initial Attach for emergency session (GTP on S2b) p. 329
The procedure in clause 7.2.5 of TS 23.402 applies with the following modification:
- Step 3 (Create Session Request): ePDG determines if interworking with 5GC is supported based on UE's 5G NAS capability and local configuration. In SMF+PGW-C, only one S-NSSAI is configured for the emergency APN. An emergency SMF+PGW-C identity should be configured as part of the Emergency Configuration Data specified in clause 13.5 of TS 23.402.
- Step 6 (Create Session Response), compared to step D.1 of clause 4.11.4.3.3, SMF+PGW-C does not include S-NSSAI in PCO for emergency PDN connection.
4.11.4.3.4 Interaction with PCC p. 329
When interworking with 5GS is supported and a SMF+PGW-C is selected by the ePDG, policy interactions between PDN GW and PCRF specified in TS 23.402 are replaced by equivalent interactions between SMF+PGW-C and PCF as captured in clause 4.11.0a.2.
If SMF+PGW-C is selected and interaction with PCF is required for a UE that does not support 5GC NAS, the SMF+PGW-C determines the PDU Session ID and S-NSSAI in the same way as for PDN connection via MME as specified in clause 4.11.0a.5.
4.11.4.3.5 UE initiated Connectivity to Additional PDN with GTP on S2b p. 330
The procedure in clause 7.6.3 of TS 23.402 references the Initial Attach procedure with GTP on S2b. Impacts to the initial attach procedure with GTP on S2b are captured in clause 4.11.4.3.3 above. If the additional PDN connection is for emergency service, impact as captured in clause 4.11.4.3.3a applies.
4.11.4.3.6 Use of N10 interface instead of S6b p. 330
This clause applies to scenarios when ePDG is connected to SMF+PGW-C and S6b in not used. It is applicable for procedures specified in TS 23.402 including mobility between EPC/ePDG and EPC/EUTRAN and also for mobility between EPC/ePDG and 5GS.
When S6b, as specified in TS 23.402, is not deployed between SMF+PGW-C and AAA and the UE creates and deletes a PDN connection via ePDG connected to SMF+PGW-C, the registration and de-registration of PDN GW is performed on the N10 interface instead of the S6b interface.
If SMF+PGW-C is selected for a UE that does not support 5GC NAS, the SMF+PGW-C determines the PDU Session ID and S-NSSAI in the same way as for PDN connection via EPC/EUTRAN as specified in clause 4.11.0a.5.
For roaming scenario with local-breakout (TS 23.501, Figure 4.3.4.2-1), the use of N10 interface instead of S6b interface may be based on support of this feature from HSS+UDM to SMF+PGW-C on N10 interface.
The specific impacts to procedures in clauses 7 and 8 of TS 23.402 are as follows:
7.2.4 Initial Attach with GTP on S2b
7.4.3.1
7.4.4.1 Non-Roaming, Home Routed Roaming and Local Breakout Case
-
Instead of Step C.1 in Figure 7.2.4-1 of TS 23.402, step 16c (Nudm_
UECM_ with an optional indication that access is from ePDG) from Figure 4.3.2.2.1-1 are performed between the SMF+PGW-C and HSS+UDM. Based on this indication, the HSS+UDM does not send notification of PGW-C assignment on SWx to AAA.Registration
-
Instead of step 5 in Figure 7.2.5-1 of TS 23.402, step 16c (Nudm_
UECM_ with an optional indication that access is from ePDG) from Figure 4.3.2.2.1-1 are performed between the SMF+PGW-C and HSS+UDM. Based on this indication, the HSS+UDM does not send notification of PGW-C assignment on SWx to AAA. The indication of access from ePDG is forwarded on the interface between UDM and HSS.Registration
Non-Roaming, Home Routed Roaming and Local Breakout Case
-
Instead of Step A.2 in Figure 7.4.3-1 of TS 23.402, step 12 (Nudm_
UECM_ ) from Figure 4.3.4.2-1 is performed between the SMF+PGW-C and HSS+UDM.Deregistration
-
Instead of step 3 in Figure 7.4.1-1 of TS 23.402 (referenced by Figure 7.4.4-1 of TS 23.402), Step 12 (Nudm_
UECM_ ) from Figure 4.3.4.2-1 is performed between the SMF+PGW-C and HSS+UDMDeregistration
-
Instead of step 5 in Figure 7.9.2-1 of TS 23.402, Step 12 (Nudm_
UECM_ ) from Figure 4.3.4.2-1 is performed between the SMF+PGW-C and HSS+UDM.Deregistration
-
Step 18 of clause 8.6.1.1 of TS 23.402 refers to clause 7.9.2 of TS 23.402. The Nudm_
UECM_ in the impacted referenced clause 7.9.2 above is not performed as resources in the SMF+PGW-C are not released.Deregistration
-
In Step B.2 of clause 8.6.2.1 of TS 23.402, if the registration of the SMF+PGW-C in the HSS+UDM is not already done, step 16c (Nudm_
UECM_ with an optional indication that access is from ePDG) from Figure 4.3.2.2.1-1 is performed between the SMF+PGW-C and HSS+UDM.Registration
- For step 0, the impacts to clause 7.2.4 of TS 23.402 are captured above.
- In step 2, if the Request Type indicates "Existing Emergency PDU Session", the AMF shall use the Emergency Information containing SMF+PGW-C FQDN for the S2b interface and the S NSSAI locally configured in Emergency Configuration Data.
-
In step 3, the impacts to clause 7.9.2 of TS 23.402 are captured above. Nudm_
UECM_ is not performed by SMF+PGW-C, as resources in the SMF+PGW-C are not released.Deregistration
- For step 2, impacts to clause 8.6.2.1 (3GPP Access to Untrusted Non-3GPP IP Access Handover with GTP on S2b) of TS 23.402 are captured above and Step 16c of Figure 4.3.2.2.1-1 is not performed as SMF+PGW-C already registered in the HSS+UDM when the UE is in 5GS.
4.11.4.3.7 5GC NAS capability (re-)enabled and disabled |R17| p. 331
When 5G NAS (i.e. N1 mode) capability is (re-)enabled, the UE does not report the UE capability change to ePDG.
When N1 is re-enabled, how to handle PDN connection(s) established over EPC/ePDG and without a mapped S-NSSAI is defined in TS 24.501.
4.11.5 Impacts to 5GC Procedures p. 331
4.11.5.1 General p. 331
This clause captures impacts to 5GC procedures in other clauses of this specification to support interworking with EPS. These impacts are applicable to interworking based on N26 and interworking without N26 for PDU Session via 3GPP access and for PDU Session via non-3GPP access.
This clause also captures the impact to 5GC if the UE was previously in GERAN/UTRAN as specified in clause 5.17.2.4 of TS 23.501.
4.11.5.2 Registration procedure p. 331
The following impacts are applicable to clause 4.2.2.2 (Registration procedure):
- Step 1: If the Registration type is set to "Initial Registration", the UE is not registered in EPS and the UE provides the 5G-GUTI mapped from EPS GUTI as the old GUTI, then the UE includes complete EPS Attach Request in the Registration request message.
- Step 4: If the Registration type is "Initial Registration" as in step 1 of the Registration Procedure captured in clause 4.2.2.2.2, the target AMF may perform Identification Request towards MME along with complete EPS Attach Request message for MME to verify it as in step 3 as specified in clause 5.3.2.1 of TS 23.401.
-
Step 14a:
-
If the AMF does not have event subscription information from the UDM, the AMF indicates it in Nudm_
UECM_ . The UDM then provides event subscriptions (possibly retrieved from UDR) if any.Registration -
If mobility between GERAN/UTRAN and 5GS is required (as specified in clause 5.17.2.4 of TS 23.501), at Initial Registration, the AMF serving 3GPP access shall also register with the Nudm_
UECM_ even if the AMF has a valid context.Registration
-
If the AMF does not have event subscription information from the UDM, the AMF indicates it in Nudm_
- Step 14d: If mobility between GERAN/UTRAN and 5GS is required (as specified in clause 5.17.2.4 of TS 23.501), when the UDM stores the associated 3GPP Access Type together with the serving AMF as indicated in step 14a, it will also cause cancellation of any other previously registered serving node (e.g. MME if AMF does not indicate not to cancel or SGSN) via HSS/HLR.
- At the end of registration procedure, the AMF may initiate synchronization of event subscriptions with the UDM if the AMF does not indicate unavailability of event subscription in step 14a.
In clause 4.3.2.2.1 Non-roaming and Roaming with Local Breakout:
For PDU Session via non-3GPP access, the AMF determines if EPS interworking is supported and sends the indication to the SMF in the same way as for PDU Session via 3GPP access. The SMF makes the final decision on the EPS interworking in the same way as for PDU Session via 3GPP access with the following modification:
-
Step 17: Additional trigger for step 17 Nsmf_
PDUSession_ are:UpdateSMContext -
If status of interworking with EPS for a PDU session changes, e.g. due to change of 5GMM capability (e.g. "S1 mode supported"), the UE subscription data change (e.g. Core Network Type Restriction to EPC), the AMF invokes Nsmf_
PDUSession_ (EPS Interworking Indication with N26 or without N26) to SMF. The SMF determines whether the PDU session supports interworking with EPS need be changed. If it needs to be changed, the SMF invokes Nudm_UpdateSMContext UECM_ service operation to add or remove the PGW-C FQDN for S5/S8 interface from the UE context in SMF data stored at the UDM.Update
-
If status of interworking with EPS for a PDU session changes, e.g. due to change of 5GMM capability (e.g. "S1 mode supported"), the UE subscription data change (e.g. Core Network Type Restriction to EPC), the AMF invokes Nsmf_
If the SMF does not receive the interworking indication, the SMF makes its decision based on subscription.
4.11.5.3 UE Requested PDU Session Establishment procedure p. 332
For PDU Session via 3GPP, the following impacts are applicable to clause 4.3.2.2 (UE Requested PDU Session Establishment procedure) to support interworking with EPS:
In clause 4.3.2.2.1 Non-roaming and Roaming with local breakout:
For non-emergency PDU Session via non-3GPP, the AMF determines if EPS interworking is supported and sends the indication to the SMF in the same way as for PDU Session via 3GPP. The SMF makes the final decision on the EPS interworking in the same way as for PDU Session via 3GPP with the following modification:
- Step 1: In PDU Session Establishment Request message, the UE includes also the UE capability of Ethernet PDN type support in EPS to the SMF (or H-SMF in home routing roaming);
-
Step 3: The AMF determines that a PDU Session supports EPS interworking with N26 or without N26, based on e.g. 5GMM capability (e.g. "S1 mode supported"), UE subscription data (e.g. Core Network Type Restriction to EPS, EPC interworking support per (S-NSSAI, subscribed DNN)) and network configuration if EPS interworking with N26 or without N26 is supported. The AMF then includes in the Nsmf_
PDUSession_ an indication whether the PDU Session supports EPS Interworking and whether EPS Interworking is done with N26 or without N26. For PDU Session with Request Type "initial emergency request", the AMF decides the EPS interworking with N26 or without N26 based on 5GMM capability and local configuration. For PDU Session with Request Type "Existing Emergency PDU Session", the AMF shall use Emergency Information received from HSS+UDM and the S-NSSAI locally configured in Emergency Configuration Data. If the Request Type indicates "Existing PDU Session" the AMF selects the SMF based on SMF-ID or SMF+PGW-C FQDN received from UDM during the Registration or Subscription Profile Update Notification procedure. The case where the AMF does not recognize the PDU Session ID or the subscription context that the AMF received from UDM neither contains an SMF ID nor a SMF+PGW-C FQDN corresponding to the PDU Session ID constitutes as an error case. If the AMF has stored APN Rate Control Status and the PDU Session is considered a new first PDU Session to a DNN that is the same as the APN in stored APN Rate Control Status and interworking with EPC is enabled for this PDU Session, then the AMF sends the APN Rate Control Status to the SMF. The AMF indicates to the SMF whether the UE support User Plane Integrity Protection with EPS and whether the AMF has associated functionality.CreateSMContext -
Step 4: If the EPS Interworking indication received from AMF indicates that the UE supports EPS interworking and the SMF determines, based on the EPS interworking support indication from the AMF and additional UE subscription data (e.g. whether UP integrity protection of UP Security Enforcement Information is not set to required, EPS interworking is allowed for this DNN and S-NSSAI), that the PDU Session supports EPS interworking and the PDU Session is using SSC mode 1, the SMF+PGW-C FQDN for S5/S8/S2b interface is included in the Nudm_
UECM_ Request. The SMF+PGW-C also includes the SMF+PGW-C FQDN for S5/S8/S2b interface if the PDU Session is using SSC mode 1 and mobility to ePDG/EPC is allowed based on operator's policy.Registration - Step 10a: If APN Rate Control Status is received from the AMF then the SMF provides the configured APN Rate Control Status to the PGW-U+UPF.
- Step 11: if the SMF+PGW-C supports URSP delivery in EPS and ePCO it provides the Indication of URSP Provisioning Support in EPS in the PDU Session Establishment Accept (see clause 5.17.8 of TS 23.501).
- Step 13: In PDU Session Establishment Accept message, the SMF also includes indication of Ethernet PDN type supported if the Ethernet PDN type is supported by both the UE and the SMF+PGW-C. The SMF and the UE stores the information if Ethernet PDN type is supported for later use when UE moves from 5GS to EPS.
-
Step 16c: For PDU Session establishment with Request Type "initial PDU Session", if the SMF+PGW-C selects the same PCF as the PCF ID received from AMF as specified in clause 4.3.2.2.1 and if the PDU Session supports EPC interworking, the SMF provide the selected PCF ID in the UDM using the Nudm_
UECM_ service operation.Registration
- Step 3a: Same impact as for step 3 for the non-roaming and roaming with local breakout case above.
- Step 5: Same impact as for step 10a for the Non-roaming and Roaming with Local Breakout case above.
-
Step 6: The V-SMF pass the EPS interworking support indication received from the AMF to the H-SMF in Nsmf_
PDUSession_ .Create -
Step 7: If the EPS interworking indication received from V-SMF indicates that the PDU Session supports EPS interworking and the H-SMF determines, based on the EPS interworking support indication from the AMF and additional information such as UP integrity protection of UP Security Enforcement Information as described in clause 4.11.1.1, that the PDU Session supports EPS interworking, the SMF+PGW-C FQDN for S5/S8 interface is included in the Nudm_
UECM_ Request.Registration - Step 15: Same impact as in step 13 for the non-roaming and roaming with local breakout case above with the difference that it's the home SMF+PGW-C that includes the indication of Ethernet PDN type supported.
- If the SMF does not receive the interworking indication, the SMF makes its decision based on subscription.
4.11.5.4 UE or Network Requested PDU Session Modification procedure p. 334
For PDU Session via 3GPP, the following impacts are applicable to clause 4.3.3.2 (UE or network requested PDU Session Modification (non-roaming and roaming with local breakout)) to support interworking with EPS:
-
Step 1: In addition to the triggers listed in step 1 of clause 4.3.3.2, the procedure may be also triggered by the following event:
-
AMF initiated modification: If the support of EPS Interworking for this PDU Session has changed, e.g. the change of the UE's subscription data (e.g. Core Network Type Restriction to EPS), or change of 5GMM capability (e.g. "S1 mode supported"), the AMF invokes Nsmf_
PDUSession_ update the status of EPS interworking support in the to SMF.UpdateSMContext
-
AMF initiated modification: If the support of EPS Interworking for this PDU Session has changed, e.g. the change of the UE's subscription data (e.g. Core Network Type Restriction to EPS), or change of 5GMM capability (e.g. "S1 mode supported"), the AMF invokes Nsmf_
-
Step 3a: This step also applies to AMF initiated modification. For AMF initiated modification, the SMF may determines whether the PDU session supports EPS interworking need be changed. If it need be changed, the SMF invokes Nudm_
UECM_ service operation to add or remove the PGW-C FQDN for S5/S8 interface from the UE context in SMF data stored at the UDM,Update
- Step 1a (AMF to V-SMF): Same impact as for step 1 of clause 4.3.3.2 above.
- Step 1a (V-SMF to H-SMF): The V-SMF pass the status of EPS interworking support to the H-SMF.
- Step 1a (H-SMF to V-SMF): Same impact as for step 3a of clause 4.3.3.2 above.
If the SMF does not receive the interworking indication, the SMF makes its decision based on subscription.
4.11.5.5 Xn based inter NG-RAN handover p. 334
The following impacts are applicable to clause 4.9.1.2.1 (General) to support interworking with EPS:
- If there is Mapping between EBI(s) and QFI(s) for the UE in the source NG-RAN, the source NG-RAN sends the Mapping to target NG-RAN during handover.
4.11.5.6 Inter NG-RAN node N2 based handover p. 335
The following impacts are applicable to clause 4.9.1.3.2 (Preparation phase) to support interworking with EPS:
- Step 7: If the PDU session supports EPS interworking, the N2 SM information contains the Mapping between EBI(s) and QFI(s).
4.11.5.7 UE or Network Requested PDU Session Release procedure |R16| p. 335
The following impacts are applicable to clause 4.3.4.2 (UE or network requested PDU Session Release for Non-Roaming and Roaming with Local Breakout) to support interworking with EPS:
- Step 2b: If the released PDU Session used APN Rate Control in EPC then the PGW-U+UPF provides the APN Rate Control Status to the SMF if the released PDU Session supported interworking with EPC and it is the last PDU Session to the DNN that is the same as the APN identified in the APN Rate Control Status.
- Step 3: If the PGW-U+UPF provided APN Rate Control Status to the SMF then the SMF provides the APN Rate Control Status to the AMF.
- Step 2b: Same impact as for step 2b for the Non-roaming and Roaming with Local Breakout case above.
- Step 3: Same impact as for step 3 for the Non-roaming and Roaming with Local Breakout case above.
4.11.5.8 Network Configuration |R16| p. 335
To avoid the need for identifier coordination between AMFs and MMEs, the AMF provides to the NG-RAN its served GUAMIs by separating the values between native AMF values and the values mapped from MME.
4.11.5.9 Network Slice Admission Control |R17| p. 335
Support of NSAC in conjunction with interworking with EPC is described in clause 5.15.11.5 of TS 23.501.
If EPS counting is required for a network slice, the SMF+PGW-C performs NSACF discovery that supports controlling the maximum number of PDU sessions per network slice as described in clause 6.3.22 of TS 23.501 and in clause 5.2.7.3.2.
The following impacts are applicable to clause 4.2.11.4 (Number of PDU Sessions per network slice availability check and update procedure):
- The SMF+PGW-C invokes this procedure to perform network slice availability check on the number of PDU Sessions and update for S-NSSAI associated with the PDN connection during PDN connection establishment. In this case the SMF in Figure 4.2.11.2-1 is replaced with SMF+PGW-C.
- Step 3, The NSACF determines whether or not to accept the request as described in clause 5.15.11.5 of TS 23.501.
- The SMF+PGW-C invokes this procedure to perform network slice availability check on the number of PDU Sessions and update for S-NSSAI associated with the PDN connection during PDN connection establishment and PDN connection release. In this case the SMF in Figure 4.2.11.4-1 is replaced with SMF+PGW-C.
- Step 3: The NSACF determines whether or not to accept the request as described in clause 5.15.11.5 of TS 23.501.
- The SMF+PGW-C invokes this procedure to perform network slice availability check on the number of PDU Sessions and update for S-NSSAI associated with the PDN connection during PDN connection establishment. In this case the SMF in figure 4.2.11.4a-1 is replaced with SMF+PGW-C.
- Step 8: The NSACF determines whether or not to accept the request as described in clause 5.15.11.5 of TS 23.501. When the local maximum number is reached, the NSACF may interact with the Primary NSACF before it returns the response back to the SMF+PGW-C as defined in clause 4.2.11.4a.
- The SMF+PGW-C invokes this procedure to perform network slice availability check on the number of UEs and update for S-NSSAI associated with the PDN connection during PDN connection establishment. In this case the AMF in figure 4.2.11.2-1 is replaced with SMF+PGW-C.
- Step 2: The SMF+PGW-C includes in the message the S-NSSAI, identity of SMF+PGW-C, UE ID and update flag. In a centralized NSAC architecture, the SMF+PGW-C additionally includes the NSAC service area if available.
- Step 3: The AMF ID is replaced by the SMF + PGW-C ID.
- Step 3: The NSACF determines whether or not to accept the request as described in clause 5.15.11.5 of TS 23.501.
- The SMF+PGW-C invokes perform network slice availability check on the number of UEs and update for S-NSSAI associated with the PDN connection during PDN connection establishment. In this case the AMF in figure 4.2.11.2a-1 is replaced with SMF+PGW-C.
- Step 2: The SMF+PGW-C includes in the message the S-NSSAI, identity of SMF+PGW-C, UE ID and update flag.
- Step 3: The AMF ID is replaced by the SMF + PGW-C ID.
- Step 8: The NSACF determines whether or not to accept the request as described in clause 5.15.11.5 of TS 23.501. When the local maximum number is reached the NSACF may interact with the Primary NSACF before it returns the response back to the SMF+PGW-C as defined in clause 4.2.11.2a.
4.11.5.9a Network Slice Admission Control in 5GS for maximum number of UE with at least one PDU session and one PDN connection |R18| p. 336
Support of NSAC in conjunction with interworking with EPC for maximum number of UE with at least one PDU session/PDN connection is described in clause 5.15.11.5a of TS 23.501.
For option 1, the same mechanisms in clause 4.2.11.2 (Number of UEs per network slice availability check and update procedure) is used with the following additions:
- The SMF+PGW-C invokes this procedure when the UE establishes the first PDU Session/PDN Connection and when the last PDU Session/PDN Connection associated with the network slice is released. In this case, the AMF in figure 4.2.11.2-1 is replaced with SMF+PGW-C.
- Step 2: The SMF+PGW-C includes in the message the S-NSSAI, identity of SMF+PGW-C, UE ID and update flag. The update flag may include either 'increase', 'decrease' or 'update' values.
- Step 2: The AMF ID is replaced by the SMF+PGW-C ID.
-
Step 3: The 'update' value indicates that for existing UE registration the Access Type is to be replaced with a new Access Type during inter access mobility. If the update flag parameter from the SMF+PGW-C indicates update value, the NSACF locates the existing entry with UE ID and NF ID and replaces the Access Type in the existing entry. The NSACF may take the Access Type into account for UE counting based on local policy. If there was one UE entry in the new Access Type with same NF ID then NSACF may not increase the count again. If there was one UE entry in the new Access Type with different NF ID then NSACF may add this new NF ID in the UE entry and not increase the count. If there was one entry with same NF ID in the old Access Type then NSACF may remove the UE entry and decrease the count.
- The NSACF determines whether or not to accept the request as described in clause 5.15.11.5a of TS 23.501
- The NSACF also counts the maximum number UE with at least one PDU session/PDN connection based on the update value received from SMF+PGW-C.
- If the update flag parameter from the SMF/SMF+PGW-C anchoring the PDU session/PDN connections indicates update, the NSACF locates the existing entry with UE ID and NF ID and replaces the Access Type in the existing entry. The NSACF may take the Access Type into account for UE counting based on local policy. If there was one UE entry in the new Access Type with same NF ID then NSACF may not increase the count again. If there was one UE entry in the new Access Type with different NF ID then NSACF may add this new NF ID and not increase the count. If there was one entry with same NF ID in the old Access Type then NSACF may remove the UE entry and decrease the count.
- The NSACF determines whether to accept the request as described in clause 5.15.11.5a of TS 23.501.
- The NSACF performs other actions in addition to the above to keep track of the last PDU Session/Connection released so as to decrease the count for the number of Registered UEs with at least one PDU Session/one PDN Connection.
- For option 2, the NSAC for the number of UEs with at least one PDU session/PDN connections and the NSAC for the number of PDU sessions shall be handled within the same NSACF.
- For both options, when the local maximum number of UEs with at least one PDU Session/PDN Connection or local threshold is reached, the NSACF may interact with the Primary NSACF before it returns the response back to the SMF+PGW-C. For more details on handling between the NSACF and Primary NSACF see clause 4.2.11.2a.
- For NSAC for number of PDU Sessions, when the local maximum number is reached, the NSACF may interact with the Primary NSACF before it returns the response back to the SMF+PGW-C. For more details on handling between the NSACF and Primary NSACF see clause 4.2.11.4a.
4.11.5.10 UE Policy Association control |R18| p. 337
4.11.5.10.1 UE Policy Association Establishment for URSP delivery in EPS p. 337
The following impacts are applicable to clause 4.16.11 (UE Policy Association Establishment procedure) during initial registration or during UE registration with 5GS when the UE moves from EPS to 5GS:
-
In addition to step 3 in clause 4.16.11, if the indication about the support of provisioning of URSP rules in EPS is received in step 2 within Npcf_
UEPolicyControl_ Request, that indication is added in the list of parameters to be stored in UDR using Nudr_Create DM_ .Create
4.11.6 Interworking for common network exposure |R16| p. 337
4.11.6.1 Subscription and Notification of availability or expected level of support of a service API p. 337
Figure 4.11.6.1-1 represent the information flow subscribing and notifying the availability or expected level of support of a service API.
For the subscription to Nnef_APISupportCapability service, the subscription request may include the Duration of Reporting. If the Duration of Reporting is expired, the SCEF+NEF deletes the subscription without any explicit signalling interaction.
For the CN type Change Event subscription to the HSS+UDM, the subscription request may include the Duration of Reporting. If the Duration of Reporting is expired, the HSS+UDM locally unsubscribe the CN Type Change Event without any explicit signalling interaction.
The SCEF+NEF informs the AF of the API Indication which indicates list of available north-bound API(s).
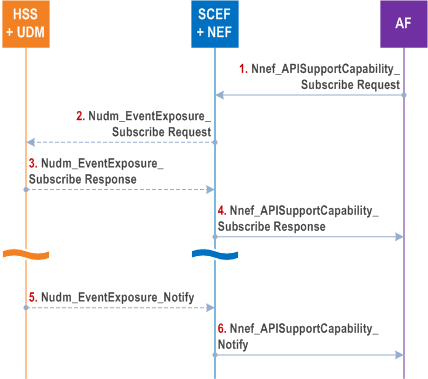
Step 1.
The AF subscribes to Nnef_APISupportCapability service for a UE or a group of UEs by sending Nnef_APISupportCapability_Subscribe Request (UE ID or External Group ID, Report Type, callback URI, Duration of Reporting) message.
The callback URI parameter is optional and is used in step 6 if provided.
The Report Type can be either One-time report or Continuous report. If this is a subscription for Continuous report type, then the Duration of Reporting may be included. The Duration of Reporting is optional and is used to indicate when the subscription is invalid. If the SCEF+NEF has established direct connection with MME or AMF or SMF, steps 2 - 3 and step 5 are omitted. If this is a subscription for One-time report type and if the Freshness Timer of last One-time report type subscribe request is not expired or a direct connection has been set up with MME or AMF or SMF, the SCEF+NEF determines the CN type locally, steps 2 - 3 are omitted.
Step 2.
SCEF+NEF subscribes the CN Type Change Event to HSS+UDM by sending Nudm_EventExposure_Subscribe Request (CN Type Change, Report Type, UE ID or External Group ID, Duration of Reporting) message.
If Duration of Reporting is received at step 1, it shall include Duration of Reporting in this message.
Step 3.
The HSS+UDM determines the CN type that is serving the indicated UE or the indicated group of UEs based on the registered MME or AMF. The HSS+UDM informs SCEF+NEF of the CN type by sending Nudm_EventExposure_Subscribe Response (CN Type) message. If the Report Type indicates One-time report, the HSS+UDM delete the CN Type Change Event subscription after sending the response with CN Type. The Freshness Timer is set in SCEF+NEF per operator's policy, e.g. based on the statistics of UE activities. If the Report Type indicates Continuous report, HSS+UDM stores the CN Type Change Event subscription.
Step 4.
According to the CN type received or local stored, the SCEF+NEF determines the availability or expected level of support of common north-bound APIs for the indicated UE or the indicated group of UEs. SCEF+NEF responds to AF by sending Nnef_APISupportCapability_Subscribe Response (API Indication).
If the subscription is for One-time report type, then steps 5 - 6 are omitted.
Step 5.
When HSS+UDM detects that the indicated UE is switching between EPC and 5GC the HSS+UDM determines the CN type that is serving the indicated UE or the indicated group of UEs. The HSS+UDM informs SCEF+NEF of the CN type by sending Nudm_EventExposure_Notify (CN type).
The CN type denotes the 5GC or EPC or 5GC+EPC serving the UE or the group of UEs.
Step 6.
According to the CN type received and local detected, the SCEF+NEF node determines the availability or expected level of support of common north-bound APIs for the indicated UE or the indicated group of UEs. SCEF+NEF inform AF of such API information by sending Nnef_APISupportCapability_Notify (API Indication) message.
If callback URI is provided at step 1, then SCEF+NEF will send the Nnef_APISupportCapability_Notify (API Indication) message to the node addressed by callback URI.
Upon reception of API Indication in step 4 or step 6, the AF obtains the availability or expected level of support of a given service for the indicated UE or the indicated group of UEs. If required, the AF can select the valid north-bound API based on such API information.
4.11.6.2 Unsubscribing to N11otification of availability or expected level of support of a service API p. 339
Figure 4.11.6.2-1 represent the information flow unsubscribing to Continuous report type subscription of the availability or expected level of support of a service API.
If the AF invokes Nnef_APISupportCapability_Subscribe service to SCEF+NEF node with the Duration of Reporting parameter for Continuous report type, the subscription on the SCEF+NEF and HSS+UDM are implicitly unsubscribed if the Duration of Reporting timer expires, i.e. the explicit unsubscribe service operation is not needed.
If the explicit unsubscribe operation is needed, the information flow is as follows.
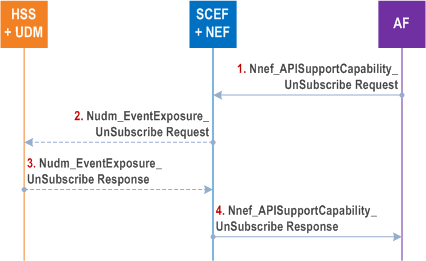
Step 1.
The AF unsubscribes to Nnef_APISupportCapability service for a UE or a group of UEs by sending APISupportCapability_Unsubscribe Request (UE ID or External Group ID) message.
Step 2.
If SCEF+NEF has subscribed to CN Type Change Event for the indicated UE or the indicated group of UEs, SCEF+NEF unsubscribes the CN Type Change Event by sending Ndum_EventExposure_Unsubscribe Request (CN Type Change, UE ID or External Group ID) message to HSS+UDM.
Step 3.
HSS+UDM deletes the CN Type Change Event subscription for the indicated UE or the indicated group of UEs, HSS+UDM responses to the SCEF+NEF by sending Ndum_EventExposure_Unsubscribe Response (Operation execution result indication) message.
Step 4.
If result indication indicates the operation is successful, the SCEF+NEF deletes the subscription to Nnef_APISupportCapability service. SCEF+NEF acknowledges the operation result by sending Nnef_APISupportCapability_Unsubscribe Response (Operation execution result indication) to AF.
4.11.6.3 Configuration of monitoring events for common network exposure p. 339
Figure 4.11.6.3-1 represent the information flow to configure monitoring events applicable to both EPC and 5GC using 5GC procedures towards UDM in scenarios where interworking between 5GS and EPC is possible.
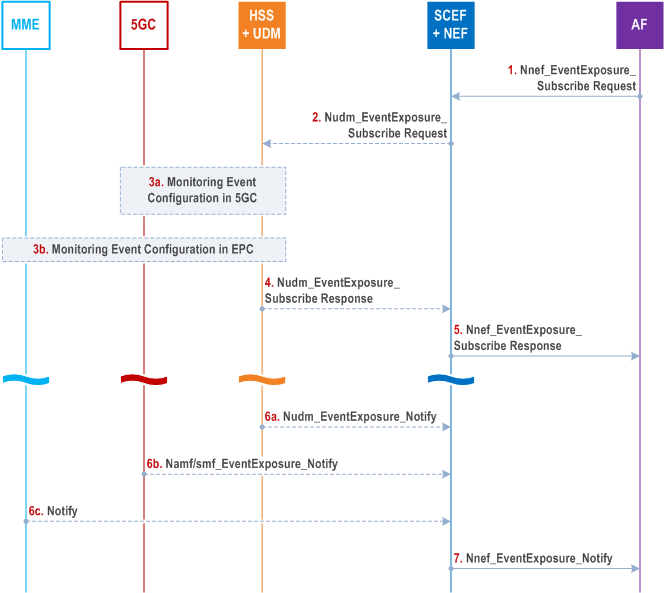
Step 1.
The AF configures a monitoring event via the SCEF+NEF using the Nnef_EventExposure_Subscribe service operation.
Step 2.
SCEF+NEF configures the monitoring event in the UDM+HSS using the Nudm_EventExposure_Subscribe service operation.
The combined SCEF+NEF indicates that the monitoring event is also applicable to EPC (i.e. the event must be reported both by 5GC and EPC). Depending on the type of event, the SCEF+NEF may include a SCEF address (i.e. if the event needs to be configured in the MME and the corresponding notification needs to be sent directly to the SCEF).
Step 3.
The HSS+UDM configures the monitoring event. For events that need to be reported from a serving node (e.g. location change) the HSS+UDM requests the configuration of the monitoring event to the corresponding serving node in the 5GC and EPC. The HSS+UDM uses the corresponding Event Exposure Subscribe service operation to configure monitoring events in 5GC serving NFs (e.g. Namf_EventExposure_Subscribe or Nsmf_EventExposure_Subscribe ). The HSS+UDM uses the procedures defined in TS 23.682 to configure monitoring events in MME. The HSS+UDM provides the MME with the SCEF address during the configuration of the monitoring event in EPC. If the HSS and UDM are deployed as separate network entities, UDM shall use HSS services to configure the monitoring event in EPC as defined in TS 23.632.
Step 4.
The HSS+UDM replies the SCEF+NEF with the indication that the monitoring event was successfully configured in 5GC and EPC by sending the Nudm_EventExposure_Subscribe Response.
Step 5.
The SCEF+NEF responds to AF by sending Nnef_EventExposure_Subscribe Response.
Step 6.
The SCEF+NEF is notified when HSS+UDM or the serving node at the 5GC or EPC detects the corresponding event. The HSS+UDM notifies the SCEF+NEF using the Nudm_EventExposure_Notify service operation. A serving NF in the 5GC notifies the SCEF+NEF using the corresponding Event Exposure Notify service operation (e.g. Namf_EventExposure_Notify or Nsmf_EventExposure_Notify ). The MME notifies the SCEF+NEF using the procedures defined in TS 23.682 using the SCEF address provided by the HSS+UDM in step 3.
Step 7.
The SCEF+NEF notifies the AF using the Nnef_EventExposure_Notify service operation.