Content for TS 23.501 Word version: 18.5.0
1…
3…
4.2.3
4.2.4
4.2.5…
4.2.8…
4.2.8.2.2
4.2.8.2.3…
4.2.8.4…
4.2.9…
4.2.15…
4.3…
4.3.3
4.3.4
4.3.5
4.4…
4.4.6…
4.4.8…
5…
5.3…
5.3.3…
5.4…
5.5…
5.6…
5.6.7…
5.7…
5.7.2…
5.7.3…
5.7.4
5.7.5…
5.8…
5.8.2.11…
5.9…
5.10…
5.11…
5.15…
5.15.11…
5.16…
5.17…
5.18…
5.19…
5.21…
5.22…
5.27…
5.28…
5.29…
5.30…
5.31…
5.32…
5.32.6…
5.33…
5.34…
5.35…
5.38…
5.43…
6…
6.3…
6.3.8…
7…
7.2…
8…
8.2.4
8.2.5…
8.3…
A…
D…
E…
F
G…
G.3
G.4…
H…
J
K…
M…
N…
O…
P…
4.4.6 5G LAN-type Services
4.4.6.1 User plane architecture to support 5G LAN-type service
4.4.6.2 Reference points to support 5G LAN-type service
4.4.7 MSISDN-less MO SMS Service
...
...
4.4.6 5G LAN-type Services |R16| p. 88
4.4.6.1 User plane architecture to support 5G LAN-type service p. 88
The general User Plane architectures described in clause 4.2.3 and clause 4.2.4 apply to 5G LAN-type services, with the additional options described in this clause.
Figure 4.4.6.1-1 depicts the non-roaming user plane architecture to support 5G LAN-type service using local switch.
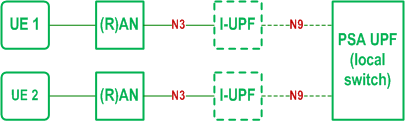
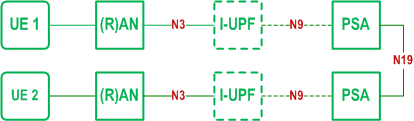
Figure 4.4.6.1-2 depicts the non-roaming user plane architecture to support 5G LAN-type service using N19 tunnel.
4.4.6.2 Reference points to support 5G LAN-type service p. 89
N19:
Reference point between two UPFs for direct routing of traffic between different PDU Sessions without using N6. It has a per 5G VN group granularity.
4.4.7 MSISDN-less MO SMS Service |R16| p. 89
MSISDN-less MO SMS via T4 is subscription based. The subscription provides the information whether a UE is allowed to originate MSISDN-less MO SMS.
The UE is pre-configured with the Service Centre address that points to SMS-SC that performs this MO SMS delivery via NEF delivery procedure. The recipient of this short message is set to the pre-configured address of the AF (i.e. Address of the destination SME). If UE has multiple GPSIs associated to the same IMSI, the GPSI that is associated with an SMS may be determined from the UE's IMSI and the Application Port ID value in the TP-User-Data field (see TS 23.040). The NEF may obtain the GPSI by querying the UDM with the IMSI and application port ID.
UE is aware whether the MO SMS delivery status (success or fail) based on the SMS delivery report from SMS-SC. The network does not perform any storing and forwarding functionality for MO SMS.
See clause 5.2.6 of TS 23.502 for a description of NEF Services and Service Operations.