Content for TR 21.917 Word version: 17.0.1
0…
5…
5.2
6…
6.3…
6.3.2…
6.3.3…
6.3.4…
7…
7.4…
8…
9…
10…
11…
11.9…
12…
13…
14…
15…
15.6…
16…
17…
18…
18.10…
19…
6 Services to "verticals"
6.1 Introduction
6.2 Generic functionalities, to all verticals
6.2.1 Network and application enablement for verticals
6.2.1.1 Enhanced Service Enabler Architecture Layer for Verticals
6.2.1.2 Enhancements for Cyber-physical control Applications in Vertical domains (eCAV)
6.2.1.3 Enhancements of 3GPP Northbound Interfaces and APIs
6.2.2 Location and positioning
6.2.2.1 RAN aspects of NR positioning enhancements
6.2.2.2 Enhancement to the 5GC LoCation Services-Phase 2
6.2.3 Support of Non-Public and Private Networks
6.2.3.1 Enhanced support of Non-Public Networks
6.2.3.2 Enhancement of Private Network support for NG-RAN
...
...
6 Services to "verticals" p. 21
6.1 Introduction p. 21
A key segment of the Rel-17 improvements of the 5G System (5GS) refers to the services provided by 5GS to segments of the industry other than telecommunications, e.g. factory automation, agriculture, electricity distribution, etc. These segments are referred to as "verticals", as explained in TR 21.915.
The boundary of "verticals" is unclear, in the sense that whether a Feature can be classified as offered to verticals or not can be arguable - besides, a Feature can be usable both for verticals and for the wide audience.
References
Related CRs:
set "TSG Status = Approved" in: https://portal.3gpp.org/ChangeRequests.aspx?q=1&workitem=920049,900024,920006,920050
6.2 Generic functionalities, to all verticals p. 21
6.2.1 Network and application enablement for verticals p. 21
6.2.1.1 Enhanced Service Enabler Architecture Layer for Verticals p. 21
| UID | Name | Acronym | WG | WID | WI rapporteur name/company |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 920049 | Enhanced Service Enabler Architecture Layer for Verticals | eSEAL | SP-200987 | Basavaraj (Basu) Pattan, Samsung | |
| 900024 | Stage 2 of eSEAL | eSEAL | S6 | SP-200987 | Basavaraj (Basu) Pattan, Samsung |
| 920006 | CT1 aspects of eSEAL | eSEAL | C1 | CP-212098 | Sapan Shah (Samsung Electronics) |
| 920050 | CT3 aspects of eSEAL | eSEAL | C3 | CP-212098 | Sapan Shah (Samsung Electronics) |
Summary based on the input provided by Samsung in SP-220623.
In Rel-16, Service Enabler Architecture Layer (SEAL) was specified, in TS [1] to [8]. SEAL offers a set of common services to the verticals industry applications and to V2X applications. These services include the management of Groups, Configurations, Keys, Identities, Locations and Network Resource. SEAL is further described in clause 9.4 of TR 21.916.
In Rel-17, enhancements are made to several SEAL services, namely:
- The SEAL architecture is enhanced to support Light Weight Protocol (LWP) for constrained devices.
- The "Configuration Management" capability is enhanced to support generic container to carry Vertical Application Layer (VAL) service-specific information.
- The "Group Management" capability is enhanced to support temporary groups in a VAL system, to remove the limitation where VAL service specific data cannot be sent to group members, to add location criteria in the group creation, to support management of 5G VN groups, to control notification rate, to control group communication messages, support for external group Id and group fetch procedure.
- The "Location Management" capability is enhanced to support the tracking of UE and obtaining dynamic UE information at a location, to distinguish the VAL services, to obtain list of UEs based on location area, monitoring location deviation, to include supplementary location information to verticals, to add timestamp for location report and off-network location management.
- The "Network resource management" is enhanced to add local MBMS support, to allow NRM server to use TSN and 5G native TSC for resource management, to subscribe to unicast QoS monitoring, to Subscribe to Unicast QoS Monitoring and real-time monitoring status information.
References
Related CRs:
set "TSG Status = Approved" in: https://portal.3gpp.org/ChangeRequests.aspx?q=1&workitem=920049,900024,920006,920050
[6.2.1.1-1]
TS 23.434: "Service Enabler Architecture Layer for Verticals; Functional architecture and information flows".
[6.2.1.1-2]
TS 33.434: "Security aspects of Service Enabler Architecture Layer (SEAL) for verticals".
[6.2.1.1-3]
TS 24.544: "Group Management - SEAL; Protocol specification".
[6.2.1.1-4]
TS 24.545: "Location Management - SEAL; Protocol specification".
[6.2.1.1-5]
TS 24.546: "Configuration management - SEAL; Protocol specification".
[6.2.1.1-6]
TS 24.547: "Identity management - SEAL; Protocol specification".
[6.2.1.1-7]
TS 24.548: "Network Resource Management - SEAL; Protocol specification".
[6.2.1.1-8]
TS 29.549: "SEAL; Application Programming Interface (API) specification".
[6.2.1.1-9]
TR 21.916: "Release 16 Description; Summary of Rel-16 Work Items"
[6.2.1.1-10]
TS 24.549: "Network slice capability enablement- SEAL; Protocol specification; Stage 3".
6.2.1.2 Enhancements for Cyber-physical control Applications in Vertical domains (eCAV) p. 22
| UID | Name | Acronym | WG | WID | WI rapporteur name/company |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 840050 | Enhancements for cyber-physical control applications in vertical domains | eCAV | SP-190310 | Bahr, Michael, Siemens AG | |
| 830020 | Study on eCAV | FS_eCAV | S1 | SP-190092 | Michael Bahr, Siemens AG |
| 840041 | Stage 1 of eCAV | eCAV | S1 | SP-191043 | Bahr, Michael, Siemens AG |
Summary based on the input provided by Siemens in SP-220458.
Cyber-physical control applications in vertical domains (CAV) was introduced in Rel-16 [2]. As a reminder, "cyber-physical control applications" refers to applications that control physical processes over a network, using algorithms. Communication for cyber-physical control applications supports operation in various vertical domains, for instance industrial automation, Smart Grid. CAV requires very high levels of communication service availability and some of them also require a very low end-to-end latency as well as real-time capabilities.
Rel-17's enhancements for CAV (eCAV) refines the service requirements for CAV and specifies new service requirements for specific aspects (Stage 1): additional service performance requirements (KPIs, influencing parameters) have been provided for enhanced and new use cases of cyber-physical control applications: control-to-control communication, wired-to-wireless link replacement (100 Mbit/s, 1 Gbit/s), cooperative carrying, mobile operation panels, and industrial wireless sensors.
eCAV addresses further and enhanced service requirements for industrial Ethernet integration, which includes time synchronization, clock synchronization performance requirements, different time domains, integration scenarios, and support for time-sensitive networking (TSN).
An essential requirement specifies: "The 5G system shall support clock synchronization (e.g. IEEE 802.1AS) through the 5G network if the sync master and the sync devices are served by different UEs". See Figure 6.2.1.2-1. The flow of clock synchronization messages is in either direction, UL and DL, and can contain two wireless links on its path.
![Copy of original 3GPP image for 3GPP TS 21.917, Fig. 6.2.1.2-1: 5G network on path of synchronization messages with two wireless links (both, UL and DL) [1]](../img/tinv-21-917-6.2.1.2-1.gif)
Figure 6.2.1.2-1: 5G network on path of synchronization messages with two wireless links (both, UL and DL) [1]
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Service requirements on direct device communication (ProSe communication) for cyber-physical control applications are provided (general, network performance, clock synchronization, service continuity, aspects of indirect communication), many of them supporting the use case of cooperative carrying.
Furthermore, high-level requirements for enhancements in network operation and maintenance in 5G non-public networks for cyber-physical control applications in vertical domains and enhancements and clarifications for positioning have been provided.
References
Related CRs:
set "TSG Status = Approved" in: https://portal.3gpp.org/ChangeRequests.aspx?q=1&workitem=840050,830020,840041
[6.2.1.2-1]
TR 22.832: "Study on enhancements for cyber-physical control applications in vertical domains"
[6.2.1.2-2]
TS 22.104: "Service requirements for cyber-physical control applications in vertical domains"
[6.2.1.2-3]
TS 22.261: "Service requirements for the 5G system"
6.2.1.3 Enhancements of 3GPP Northbound Interfaces and APIs p. 23
| UID | Name | Acronym | WG | WID | WI rapporteur name/company |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 920058 | Rel-17 Enhancements of 3GPP Northbound Interfaces and Application Layer APIs | NBI17 | CP-220058 | Abdessamad EL MOATAMID, Huawei | |
| 920013 | CT1 aspects of NBI17 | NBI17 | C1 | CP-220058 | Abdessamad EL MOATAMID, Huawei |
| 920053 | CT3 aspects of NBI17 | NBI17 | C3 | CP-220058 | Abdessamad EL MOATAMID, Huawei |
| 920054 | CT4 aspects of NBI17 | NBI17 | C4 | CP-220058 | Abdessamad EL MOATAMID, Huawei |
Summary based on the input provided by Huawei in CP-220394.
The 3GPP Northbound Interfaces and APIs are specified as to enable external entities and third party Application Servers/Functions to access a set of exposed 3GPP network services and capabilities in a secure and controlled manner. The 3GPP application layer APIs are defined by 3GPP as to allow the support of various applications/services (e.g. V2X, UAS, EDGE, etc.) over 3GPP networks and to ensure the efficient use and deployment of these applications/services over 3GPP systems via an optimized application layer framework. 3GPP northbound interfaces/APIs as well as application layer APIs are used and supported by various external entities including third party Application Servers/Functions.
This work relates to the introduction of pure stage 3 (i.e. there are no related stage 1 nor stage 2 requirements) technical improvements and enhancements, i.e. improvement of the overall efficiency, reliability and flexibility, enhancement of the signalling efficiency, consolidation of the common protocol aspects, alignment with the 5GC service based principles and guidelines when relevant, corrections/changes missed in the previous 3GPP Releases, etc., especially that such enhancements may not be covered by the other more dedicated and functionality-driven work items.
References
Related CRs:
set "TSG Status = Approved" in: https://portal.3gpp.org/ChangeRequests.aspx?q=1&workitem=920058,920013,920053,920054
[6.2.1.3-1]
TS 24.558: "Enabling Edge Applications; Protocol specification".
[6.2.1.3-2]
TS 29.122: "T8 reference point for Northbound APIs".
[6.2.1.3-3]
TS 29.222: "Common API Framework for 3GPP Northbound APIs"
[6.2.1.3-4]
TS 29.257: "Application layer support for Uncrewed Aerial System (UAS); UAS Application Enabler (UAE) Server Services; Stage 3".
[6.2.1.3-5]
TS 29.486: "V2X Application Enabler (VAE) Services; Stage 3".
[6.2.1.3-6]
TS 29.522: "5G System; Network Exposure Function Northbound APIs; Stage 3".
[6.2.1.3-7]
TS 29.549: "Service Enabler Architecture Layer for Verticals (SEAL); Application Programming Interface (API) specification; Stage 3".
[6.2.1.3-8]
TS 29.558: "Enabling Edge Applications; Application Programming Interface (API) specification; Stage 3".
6.2.2 Location and positioning p. 24
6.2.2.1 RAN aspects of NR positioning enhancements p. 24
| UID | Name | Acronym | WG | WID | WI rapporteur name/company |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 900060 | RAN aspects of NR positioning enhancements | NR_pos_enh | RP-210903 | Intel | |
| 860034 | Study on NR positioning enhancements | FS_NR_pos_enh | R1 | RP-202094 | CATT |
| 900160 | Core part: NR positioning enhancements | NR_pos_enh-Core | R1 | RP-210903 | Intel |
| 900260 | Perf. part: NR positioning enhancements | NR_pos_enh-Perf | R4 | RP-210903 | Intel |
Summary based on the input provided by Intel in RP-220919.
This Work Item specifies solutions for NR Positioning enhancements, including improvement of positioning accuracy and latency of Rel-16 NR positioning methods, improvements of network efficiency (On-Demand PRS transmission), improvement of device efficiency (positioning in RRC_INACTIVE), providing high integrity and reliability requirements (GNSS integrity) and enhancements of A-GNSS positioning (BDS B2a,/B3I and NavIC to NR).
All these aspects are detailed below.
Improvement of positioning accuracy
To improve positioning accuracy, several solutions were considered:
Mitigation of gNB/UE Tx/Rx timing delay errors: For mitigation of gNB/UE Tx/Rx timing delay errors, multiple enhancements are introduced in Rel-17:
- For DL-TDOA, a UE can be requested to provide the Rx TEG IDs together with RSTD measurements and a TRP can be requested to provide TRP Tx TEG association information of DL PRS resources to mitigate UE Rx timing errors and TRP Tx timing errors. A UE can also be requested to measure the same DL PRS resource of a TRP with different UE Rx TEGs and report the corresponding multiple RSTD measurements to mitigate UE Rx timing errors.
- For UL-TDOA, Rel-17 supports a TRP to provide the Rx TEG IDs together with RTOA measurements and a UE to provide UE Tx TEG association information of UL positioning SRS resources to mitigate TRP Rx timing errors and UE Tx timing errors. A TRP can also be requested to measure the same UL SRS resource of a UE with different TRP Rx TEGs and report the corresponding multiple RTOA measurements to mitigate TRP Rx timing errors.
- Multi-RTT, Rel-17 supports a UE/TRP to provide the RxTx TEG IDs, or combination of {Rx TEG ID, Tx TEG ID} together with UE/gNB Rx-Tx time difference measurements and a UE/gNB to provide its Tx TEG association information for mitigating UE/TRP Rx/Tx timing errors;
Improvement of positioning latency
To improve the positioning latency, following solutions were considered:
Preconfigured measurement gap: To reduce latency of procedures for DL PRS processing with measurement gaps, the set of measurement gap patterns can be pre-configured to UE and activated/deactivated by gNB using new DL MAC CE signalling designed to control DL PRS measurement by UE. The UE can request activation and deactivation of the pre-configured MG using new UL MAC CE signalling introduced in Rel-17. The LMF can request activation of pre-configured MG using new NRPPa signalling introduced in Rel-17.
Preconfigured PRS processing window: To further reduce latency of DL PRS processing, UEs can perform DL PRS measurement outside measurement gaps and inside the active DL BWP with PRS having the same numerology as the active DL BWP. The gNB can use RRC signalling to pre-configure PRS processing window and DL MAC CE signalling for activation of PRS processing window, respectively. gNB can indicate the DL PRS processing priority relative to other DL signals/channels within the PRS processing window for PRS measurement outside MG.
M-sample measurement (M = 1): In Rel-17, LMF can request UE and/or TRP to perform measurement over either a single RS transmission period (M=1) or four RS transmission periods (M=4). Configuring M=1 for a UE reduces UE measurement period comparing to Rel.16 (In Rel-16, UE is expected to measure DL PRS over four periods (M = 4)). An AGC sample, in addition to the M=1 sample may be required at the UE subject to measurement conditions.
Lower Rx beam sweeping factor: In Rel-17, a new UE capability on lower Rx beam sweeping factor (<8) is introduced to reduce the PRS measurement latency for FR2 positioning frequency layers.
Storing LPP capability in AMF: The LMF may interact with the AMF to provide (updated) UE Positioning Capability to AMF and to receive stored UE Positioning Capability from AMF as described in TS 23.273. The LPP procedures to transfer UE LPP positioning capabilities may be skipped if the LMF already obtained the UE positioning capabilities from the AMF.
Preconfigured assistance data: Preconfigured assistance data is the DL-PRS assistance data (with associated validity criteria, i.e. area ID) that can be provided to the UE (before or during an ongoing LPP positioning session), to be then utilized for potential positioning measurements at a future time (e.g. for deferred MT-LR). Pre-configured DL-PRS assistance data may consist of multiple instances, where each instance is applicable to a different area within the network.
Scheduled location time: During positioning procedure, the LMF may obtain the scheduled location time from the AMF. Based on the obtained scheduled location time, the LMF may schedule location measurements by the UE and/or location measurement by the NG-RAN to occur at or near to the scheduled location time.
On-Demand PRS transmission
On-Demand PRS transmission procedure allows the LMF to control and decide whether PRS should be transmitted or not and whether the characteristics of an ongoing PRS transmission should be changed or not.
In case of UE-initiated On-Demand PRS, the LMF may configure the UE with pre-defined PRS configurations via LPP Provide Assistance Data message or via posSI. The UE sends an On-Demand PRS request to the LMF via LPP Request Assistance Data message. The On-Demand PRS request can be the request for a defined PRS configuration with PRS configuration ID or explicit parameter for PRS configuration and may be a request for PRS transmission or change to the PRS transmission characteristics for positioning measurements.
In case of LMF-initiated On-Demand PRS, the LMF and the UE may exchange LPP messages e.g., to obtain UE measurements or the DL-PRS positioning capabilities of the UE, etc).
The actual PRS changes are requested by the LMF irrespective of whether the procedure is UE- or LMF-initiated.
Positioning in RRC_INACTIVE state
Positioning may be performed when a UE is in RRC_INACTIVE. Any uplink LCS or LPP message can be transported in RRC_INACTIVE. If the UE initiated data transmission using UL SDT, the network can send DL LCS, LPP and RRC message (e.g. to configure SRS for UL positioning, if it is supported) to the UE. UE may also receive PRS or transmit SRS in RRC_INACTIVE. Support of all NR positioning measurements and support of NR positioning methods such as NR E-CID, DL-TDOA, DL-AOD, UL-AOA, UL-TDOA, Multi-RTT and RAT-independent positioning methods are extended for UEs in RRC_INACTIVE state.
GNSS Integrity
Positioning integrity is a measure of the trust in the accuracy of the position-related data and the ability to provide associated alerts. UE based GNSS integrity is supported in Rel-17. It allows the UE to determine and report the integrity results of the calculated location, where only protection level (PL) reporting mode is supported; the UE can use the integrity requirements and assistance data obtained via NG-RAN, together with its own measurements, to determine the integrity results of the calculated location.
For integrity operation, the network will ensure that:
P(Error > Bound for longer than TTA | NOT DNU) ≤ Residual Risk + IRallocation
(Equation 8.1.1a-1)
for all values of IRallocation in the range irMinimum ≤ IRallocation ≤ irMaximum
for all the errors in Table 8.1.2.1b-1 as specified in clause 8.1.2.1b of TS 38.305, which have corresponding integrity assistance data available and where the corresponding DNU flag(s) are set to false.
Enhancements of A-GNSS positioning
Enhancements of A-GNSS positioning specified: BDS B2a signal; BDS B3I signal; NavIC to NR.
References
Related CRs:
set "TSG Status = Approved" in: https://portal.3gpp.org/ChangeRequests.aspx?q=1&workitem=900060,860034,900160,900260
[6.2.2.1-1]
RP-220803: "Status Report to TSG on NR Positioning Enhancements", Intel Corporation
[6.2.2.1-2]
TR 38.857: "Study on NR positioning enhancements" v17.0.0
6.2.2.2 Enhancement to the 5GC LoCation Services-Phase 2 p. 26
| UID | Name | Acronym | WG | WID | WI rapporteur name/company |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 910052 | Enhancement to the 5GC LoCation Services-Phase 2 | 5G_eLCS_ph2 | SP-200082 | Ming Ai, CATT | |
| 870001 | Stage 2 of 5G_eLCS_ph2 | 5G_eLCS_ph2 | S2 | SP-200082 | Ming Ai, CATT |
| 910006 | CT aspects of 5G_eLCS_ph2 | 5G_eLCS_ph2 | ct | CP-211090 | Chenxi Bao, CATT |
| 910053 | CT1 aspects of 5G_eLCS_ph2 | 5G_eLCS_ph2 | C1 | CP-211090 | Chenxi Bao, CATT |
| 910054 | CT3 aspects of 5G_eLCS_ph2 | 5G_eLCS_ph2 | C3 | CP-211090 | Chenxi Bao, CATT |
| 910055 | CT4 aspects of 5G_eLCS_ph2 | 5G_eLCS_ph2 | C4 | CP-211090 | Chenxi Bao, CATT |
6.2.3 Support of Non-Public and Private Networks p. 27
6.2.3.1 Enhanced support of Non-Public Networks p. 27
| UID | Name | Acronym | WG | WID | WI rapporteur name/company |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 840024 | Study on enhanced support of Non-Public Networks | FS_eNPN | S2 | SP-200094 | Peter Hedman |
| 910065 | Enhanced support of Non-Public Networks | eNPN | SP-200980 | Hedman, Peter, Ericsson | |
| 900015 | Stage 2 for eNPN | eNPN | S2 | SP-200980 | Hedman, Peter, Ericsson |
| 910016 | CT aspects of eNPN | eNPN | ct | CP-212103 | Sedlacek, Ivo, Ericsson |
| 910066 | CT1 aspects of eNPN | eNPN | C1 | CP-212103 | Sedlacek, Ivo, Ericsson |
| 910067 | CT3 aspects of eNPN | eNPN | C3 | CP-212103 | Sedlacek, Ivo, Ericsson |
| 910068 | CT4 aspects of eNPN | eNPN | C4 | CP-212103 | Sedlacek, Ivo, Ericsson |
| 920025 | Security Aspects of eNPN | eNPN | S3 | SP-210422 | Jost, Christine, Ericsson |
| 880008 | Study on enhanced security support for Non-Public Networks | FS_eNPN_SEC | S3 | SP-200353 | Normann, Henrik, Ericsson |
| 870023 | Management of non-public networks (NPN) | OAM_NPN | S5 | SP-200189 | ZHANG, Kai, Huawei |
Summary based on the input provided by Ericsson in SP-220584.
The support of non-public networks (NPN) was introduced in Rel-16 by the WI Vertical_LAN with UID 830042. Deployments of NPN to provide coverage within a specific geographic area for non-public use is a key demand of emerging 5G applications and verticals.
This Rel-17 work item enables the four following enhancements:
Support for accessing an SNPN using credentials from a Credential Holder (CH): A UE can be configured with user or CH controlled prioritized list of information, SNPN identifiers or Group IDs for Network selection (GINs), enabling the UE to discover SNPNs supporting access using credentials from a CH. If the UE selects and accesses the SNPN, the CH is involved in the primary authentication and for authorizing the access to the SNPN. The CH can either include 5GC NFs e.g. AUSF and UDM (if the CH is an SNPN or a PLMN) or include a AAA server.
Support for Onboarding of UEs: Onboarding of UEs allows the UE to access an Onboarding Network (ONN) for the purpose of provisioning the UE with SNPN credentials and other information to enable the UE to select and access a desired SNPN. It also allows provisioning the UE with credentials for Network Slice-Specific Authentication and Authorization (NSSAA) or secondary authentication/authorization. Provisioning of the UE is done via User Plane connectivity.
To be able to provision SNPN credentials in a UE, as the 5GS requires security to be enabled the UE needs to use some already available credentials to access a 5GS, i.e. either:
- The UE has Default UE credentials in which case the UE selects an SNPN as ONN and then the UE registers using Registration Type set to "SNPN Onboarding" that enables the 5GC to restrict the connectivity to Onboarding service e.g. using a dedicated S-NSSAI within the network.
- The UE uses existing PLMN or SNPN credentials in which case the UE uses the existing credentials to get access connectivity to a PLMN or SNPN.
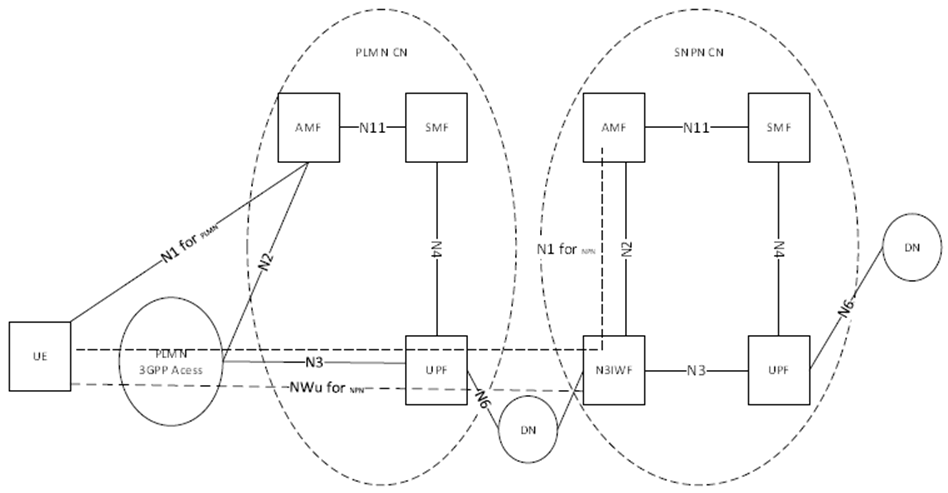
Figure 6.2.3.1-1: Example with a PLMN acting as underlay network and SNPN as overlay network
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Management aspects (from Huawei, SP-220570):
The management part is covered in TS 28.557 "Management and orchestration; Management of NPN; Stage 1 and stage 2". TS 28.557 specifies concepts, use cases, requirements and solutions for management of non-public networks. To support management of non-public networks, the following are addressed: Roles related to NPN management; Different management modes of NPN; Generic solutions for management of NPN; Solutions for management of SNPN; Solutions for management of PNI-NPN.
References
Related CRs:
set "TSG Status = Approved" in: https://portal.3gpp.org/ChangeRequests.aspx?q=1&workitem=840024,910065,900015,910016,910066,910067,910068,920025,880008,870023
[6.2.3.1-1]
TS 23.501: "System architecture for the 5G System (5GS)"
[6.2.3.1-2]
TS 23.502: Procedures for 5G System; Stage 2.
[6.2.3.1-3]
TS 23.503: Policy and Charging Control Framework for the 5G System; Stage 2 Service Enabler Architecture Layer for Verticals
[6.2.3.1-4]
TS 24.501: "Non-Access-Stratum (NAS) protocol for 5G System (5GS); Stage 3".
[6.2.3.1-5]
TS 23.122: "Non-Access-Stratum (NAS) functions related to Mobile Station in idle mode".
[6.2.3.1-6]
TS 33.501: "Security architecture and procedures for 5G system".
[6.2.3.1-7]
TS 28.557: Management and orchestration; Management of non-public networks; Stage 1 and stage 2
6.2.3.2 Enhancement of Private Network support for NG-RAN p. 28
| UID | Name | Acronym | WG | WID | WI rapporteur name/company |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 890049 | Enhancement of Private Network support for NG-RAN | NG_RAN_PRN_enh | R3 | RP-212585 | China Telecom |
| 890149 | Core part: Enhancement of Private Network support for NG-RAN | NG_RAN_PRN_enh-Core | R3 | RP-212585 | China Telecom |
Summary based on the input provided by China Telecom in RP-220562.
This Work Item, specified by RAN2 and RAN3, enables:
For this feature, the term "Credentials Holder (CH)" is used for the external entity providing subscription or credential for SNPNs and the term "Group IDs for Network Selection (GINs)" is used for the service provider Group IDs.
In TS 38.331, the following statement is added: "An SNPN may allow access to UEs being authorized using credentials or subscription owned by a separate credential holder (CH). The support of this feature is uniform across the SNPN as specified in TS 23.501 [3]."
For Uu interface, the indication of SNPN access with subscription of a Credentials Holder is broadcast in SIB1 per SNPN.
Optionally, Group IDs for Network selection (GINs) could be broadcast in SIBXY. Each GIN may be assigned to one or more SNPNs. There is a common list of GINs for both onboarding and SNPN access using external CHs.
For each SNPN there is a vector that describes which GINs are supported, the maximum number of GINs is 24 per cell.
For cell selection/reselection, since SA2 has the conclusion the indication of SNPN access with subscription of a Credentials Holder should be set uniformly, there is no impact on cell (re)selection to support SNPN with subscription or credentials by a separate entity.
No UE impact was identified on connected mode mobility for external CH.
Support UE onboarding and provisioning for NPN
For onboarding support, the section "Support of UE onboarding and remote provisioning" is added in TS 38.331.
The procedure of AMF selection in TS 38.410 is modified for supporting onboarding as follow: "Therefore, a NAS node selection function is located in the NG-RAN node to determine the AMF association of the UE, based on the UE's temporary identifier, which was assigned to the UE by the AMF. When the UE's temporary identifier has not been yet assigned or is no longer valid the NG-RAN node may instead take into account other information (e.g. slicing information, onboarding indication) to determine the AMF."
For Uu interface, the indication of UE onboarding and remote provisioning is broadcast in SIB1 per SNPN.
As for "on-boarding support" indicator, cell selection and suitability criteria of a SNPN cell are not affected. NAS will anyway allow access for onboarding only if the cell/SNPN supports onboarding.
Toggling the 1-bit onboarding indication in SIB1 allows to control congestion due to onboarding request.
No UE impact was identified on connected mode mobility for onboarding.
For NG interface, the new "Onboarding Support" IE is included within the same PLMN Support Item IE in the NG SETUP RESPONSE/AMF CONFIGURATION UPDATE message, the related statement for NG SETUP procedure, in TS 38.413, is added as follows:
"If the Onboarding Support IE is also included within the same PLMN Support Item IE, the NG-RAN node shall, if supported, consider that the AMF supports UE onboarding for the identified SNPN, as specified in TS 23.501 [9]."
Support of IMS voice and emergency services for SNPN
Emergency services are supported for SNPN in Rel-17, which is the new feature compared with Rel-16. UE in SNPN access mode could select the SNPN with imsEmergencySupportForSNPN=true for emergency services.
For Uu interface, the indication of support for emergency services is broadcast in SIB1 per SNPN.
Support of PWS for SNPN
PWS over SNPN is supported in Rel-17. In TS 38.300, the statement that ETWS and CMAS are not supported over SNPN is removed.
- Support SNPN along with subscription / credentials owned by an entity separate from the SNPN including: broadcasting of information to enable SNPN selection for UEs with subscription/credentials owned by an entity separate from the SNPN; associated cell selection/reselection and connected mode mobility support; necessary modifications over network interfaces (e.g. NG, Xn, F1, E1 etc)
- Support UE onboarding and provisioning for NPN including: The UE onboarding relevant parameter broadcast from SIB; associated cell selection/reselection, cell access control and the connected mode mobility support; necessary modifications over network interfaces (e.g. NG, Xn, F1, E1 etc)
- Support of IMS voice and emergency services for SNPN: Broadcasting of relevant parameters
- Support of PWS for SNPN
References
Related CRs:
set "TSG Status = Approved" in: https://portal.3gpp.org/ChangeRequests.aspx?q=1&workitem=890049,890149
[6.2.3.2-1]
RP-200732: Status report of WI: Private Network Support for NG-RAN; rapporteur: China Telecom.