TS 23.402
Architecture enhancements for non-3GPP Accesses
V18.3.0 (PDF)
2023/12 319 p.
V17.0.0
2021/03 317 p.
V16.0.0
2019/06 317 p.
V15.3.0
2018/03 310 p.
V14.7.0
2018/03 310 p.
V13.9.0
2018/03 300 p.
V12.10.0
2016/06 293 p.
V11.10.0
2014/12 255 p.
V10.10.0
2014/12 234 p.
V9.13.0
2014/06 202 p.
V8.10.0
2012/03 201 p.
- Rapporteur:
- Mr. Ali, Irfan
Nokia Networks
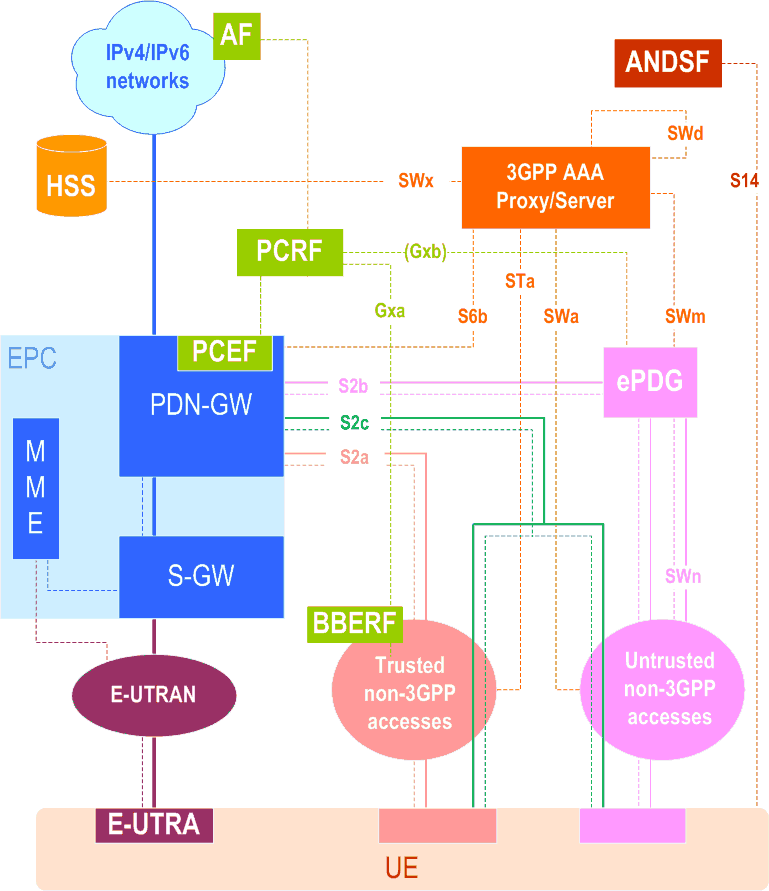
essential Table of Contents for TS 23.402 Word version: 18.3.0
each title, in the "available" or "not available yet" area, links to the equivalent title in the CONTENT