Content for TS 23.282 Word version: 19.2.0
1…
5…
6…
6.6…
7…
7.4…
7.4.2.1.10…
7.4.2.2…
7.4.2.5…
7.4.2.8…
7.4.3…
7.5…
7.5.2.1.12…
7.5.2.2…
7.5.2.4…
7.5.2.6…
7.5.2.8…
7.5.2.11…
7.5.2.14…
7.5.3…
7.6
7.7…
7.7.2.1.13…
7.7.2.2…
7.8…
7.9…
7.13…
7.13.3.1.19…
7.13.3.2…
7.13.3.8…
7.13.3.16…
7.13.4…
7.14…
7.14.2.2…
7.17…
7.17.2.13…
7.17.3…
7.17.3.1.4…
7.17.3.2…
7.17.3.2.4…
7.17.3.2.6…
7.17.4…
7.17.6…
A…
B…
6 Functional model
6.1 General
6.2 Description of the planes
6.3 Transmission and reception control aspects
6.4 Generic functional model
6.4.1 On-network functional model
6.4.2 Off-network functional model
6.4.3 Functional entities description
6.4.4 Reference points
6.5 Functional model for short data service
6.5.1 On-network functional model
6.5.2 Off-network functional model
6.5.3 Functional entities description
6.5.4 Reference points
...
...
6 Functional model p. 26
6.1 General p. 26
This clause defines the functional model for MCData service.
The security solution for the MCData service, including end-to-end encryption, is specified in TS 33.180.
6.2 Description of the planes p. 26
The functional model for the support of MCData is defined as a series of planes to allow for the breakdown of the architectural description.
The description of the planes and the relationship between the planes are contained in the common functional architecture to support MC services in TS 23.280.
6.3 Transmission and reception control aspects p. 26
6.3.1 General p. 26
The transmission and reception control are functions of the MCData server.
For small data transmissions there is no need for prior grant of request to transmit. The procedures in the present document describe when data is automatically sent.
For large data transmissions, i.e. large files, the data is transmitted only after request to transmit is granted. The data to be transmitted and/or received may be stored in a data repository associated with the transmission and reception control functions.
6.4 Generic functional model p. 27
6.4.1 On-network functional model p. 27
Figure 6.4.1-1 shows the generic application plane functional model.
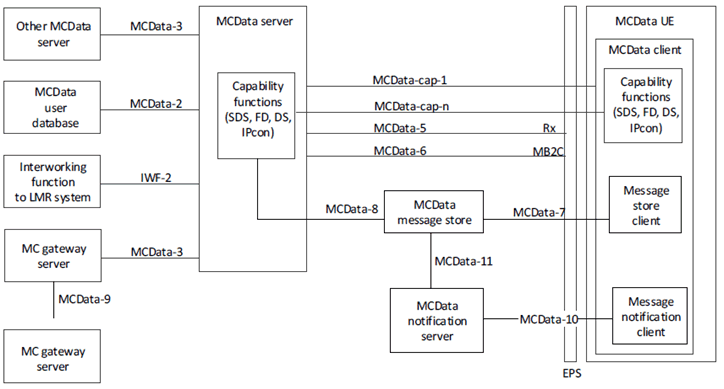
In the model shown in Figure 6.4.1-1, capability functions (SDS, FD, DS, IPcon) of the MCData client and the MCData server along with their reference points (MCData-cap-1 to MCData-cap-n) are described in the respective functional models for each capability.
An MCData server controls the signaling reference points and the corresponding media allowing different paths for media and signalling.The MCData server determines if it needs to stay in the media path based on the feature(s) involved in the MCData communication, e.g., if the MCData message store is required in the MCData communication, the MCData server shall remain in the media path.
6.4.2 Off-network functional model p. 27
6.4.3 Functional entities description p. 27
6.4.3.1 Application plane p. 28
6.4.3.1.1 MCData client p. 28
The MCData client functional entity acts as the user agent for all MCData application transactions. The client supports SDS, file distribution, data streaming and IP connectivity MCData capabilities utilized by MCData services like conversation management, robots control, enhanced status, database enquiries and secured internet.
6.4.3.1.2 MCData server p. 28
The MCData server functional entity provides centralised support for MCData services suite. Conversation management, robots, enhanced status, database enquiries and secured internet MCData services requiring one-to-one or group data communication are realized using SDS, file distribution, data streaming and IP connectivity MCData communication capabilities.
All the MCData clients supporting users belonging to a single group are required to use the same MCData server for that group. An MCData client supporting a user involved in multiple groups can have relationships with multiple MCData servers.
For MBMS delivery, the MCData server functional entity represents a specific instantiation of the GCS AS described in TS 23.468 to control multicast and unicast operations for group communications.
If the MBMS user service architecture is utilized, the MCData server functional entity represents a specific instantiation of the content provider as described in TS 26.346 to control multicast operations for file distribution.
The MCData server functional entity is supported by the SIP AS functional entity of the signalling control plane.
The MCData server shall support the controlling role and the participating role. The MCData server may perform the controlling role for one-to-one and group data communication. The MCData server performing the controlling role for a one-to-one or group data communication may also perform a participating role for the same one-to-one or group data communication. For each one-to-one and group data communication, there shall be only one MCData server assuming the controlling role, while one or more MCData servers in participating role may be involved.
The MCData server performing the controlling role is responsible for:
- handling transmission and reception control (e.g. policy enforcement for participation in the MCData group communication) towards all the MCData users of the one-to-one and group data communication;
- interfacing with the group management server for group policy and affiliation status information of this MCData server's served affiliated users;
- managing SDS and FD data distribution during MCData group communication; and
- managing the MCData transport service for IP connectivity.
- handling transmission control (e.g. authorization for participation in the MCData group communication) to MCData users of the one-to-one and group data communication;
- group affiliation support for MCData user, including enforcement of maximum Nc2 number of simultaneous group affiliations by a user;
- interfacing with the group management server for group policy and affiliation status information of this MCData server's served affiliated users;
- relaying the MCData communication messages between the MCData client and the MCData server performing the controlling role; and
- handling reception control (e.g. temporarily storing the data to present to the MCData user as required) to its MCData users of the one-to-one and group data communication.
6.4.3.1.3 MCData user database p. 29
This functional entity contains information of the MCData user profile associated with an MCData ID that is held by the MCData service provider at the application plane. The MCData user profile is determined by the mission critical organization, the MCData service provider, and potentially the MCData user.
6.4.3.1.4 Interworking function to LMR system |R15| p. 29
The functional entity is specified in TS 23.283.
6.4.3.1.5 MC gateway server |R16| p. 29
The MC gateway server provides support for MCData interconnection services with a partner MCData system in a different trust domain whilst providing topology hiding. It acts as a proxy for one or more MCData servers in the partner MCData system without needing to expose the MCData servers in the primary MCData system outside the trusted domain of the primary MCData system. It may be a role of the MCData server described in subclause 6.4.3.1.2 of the present document.
The MC gateway server is responsible for relaying call control and transmission control signalling messages, and media between MCData servers within the MCData system and the interconnected MCData system.
6.4.3.2 Signalling control plane p. 29
The description of the signalling control plane is contained in the common functional architecture to support MC services as specified in TS 23.280.
6.4.3.3 MCData message store |R16| p. 29
The MCData message store is a network base persistent store that allows Mission Critical Organization to configure their MCData users to permanently store their MCData communications. Once configured a MCData user will be allocated a secured storage area (i.e. size) in the MCData message store that is only accessible by that configured MCData user and any authorized users. The MCData user can manage how and what will be stored in his personal message store with the support of management operations such as creating, deleting and merging folders, moving stored messages and files around and synchronization all used devices to provide the same contxt view etc.
6.4.3.4 Message store client |R16| p. 29
The Message store client is used to support MCData client to manage the MCData communication history stored in MCData message store for a particular MCData user, It supports the secure access to a MCData user's configured MCData message store area and operations relevant to the stored communication history such as folders management and synchronization to the device local message store.
6.4.3.5 MCData notification server |R17| p. 29
The MCData notification server provides the centralized notification function in the network. The MCData notification server allows an application (e.g. resident in the UE) to create a communication channel to receive real-time notifications from the network in either Pull or Push mode. Depending on the channel type created, the MCData notification server provides the application a callback endpoint (i.e. URL) and may also provide a channel endpoint (i.e. URL). The application communicates the callback endpoint information to the application server (i.e. network enabler) for it to use in sending to the MCData notification server the events for delivery to the application. Depending on the type of channel created by the application the delivery of the notifications from the MCData notification server to the application may be via a Pull or Push method. If Pull method is used, then the application shall use the provided channel endpoint to pull the notifications from the MCData notification server. However, if a Push notification delivery is used, then the MCData notification server asynchronously delivers the events received from the application server to the application through a PUSH Enabler server. The MCData notification server provides a consistent way to deliver notifications by all services to reduce the complexity of service logic on the application server.
It depends on deployment, if multiple MCData notification servers aredeployed.
6.4.3.6 Message notification client |R17| p. 30
The Message notification client is used to request the notification service from the MCData notification server. Once the notification service request is authorized by the MCData notification server, the Message notification client will communicate the callback endpoint, received from the MCData notification server, to the MCData message store to be used for notification message delivery.
When multiple MCData notification servers are deployed, the Message notification client shall select one for notification service at any given time. How the Message notification client selects the appropriate MCData notification server from multiple available MCData notification servers for service is implementation specific.
6.4.4 Reference points p. 30
6.4.4.1 Application plane p. 30
6.4.4.1.1 General p. 30
The reference points for the application plane of MCData service are described in the following subclauses.
6.4.4.1.2 Reference point MCData-2 (between the MCData server and the MCData user database) p. 30
The MCData-2 reference point, which exists between the MCData server and the MCData user database, is used by the MCData server to obtain information about a specific user. The MCData-2 reference point utilises a diameter management application protocol as defined in TS 29.283 and shall be intra-network.
6.4.4.1.3 Reference point MCData-3 (between the MCData server and the MCData server) p. 30
The MCData-3 reference point, which exists between the MCData server and the MCData server for MCData application signalling for establishing MCData sessions, shall use the SIP-2 reference point for transport and routing of signalling. If each MCData server is served by a different SIP core then the MCData-3 reference point shall also use the SIP-3 reference point for transport and routing of signalling. Media is also transferred using the MCData-3 reference point.
6.4.4.1.3A Reference point MCData-5 (between the MCData server and the EPS) p. 30
The MCData-5 reference point, which exists between the MCData server and the EPS, is used, subject to the conditions below, by the MCData server to obtain unicast bearers with appropriate QoS from the EPS. It utilises the Rx interface of the EPS according to TS 23.203.
MCData-5 is not used when the MCData service provider and the PLMN operator do not have an operational agreement for QoS control to be provided directly from the MCData service provider domain.
MCData-5 may be used when the MCData service provider and the PLMN operator have an operational agreement where QoS control is provided directly from the MCData service provider domain.
6.4.4.1.4 Reference point MCData-6 (between the MCData server and the EPS) p. 30
The MCData-6 reference point, which exists between the MCData server and the EPS, is used to request the allocation and activation of multicast transport resources for MCData application usage. The MCData-6 reference point uses the MB2-C interface as defined in TS 29.468. The MCData-6 reference point also uses the xMB-C interface as defined in TS 29.116 for file distribution.
6.4.4.1.5 Reference point IWF-2 (between the interworking function to LMR system and the MCData server) |R15| p. 30
The IWF-2 reference point is specified in TS 23.283.
6.4.4.1.6 Reference point MCData-7 (between the Message store client and MCData message store) |R16| p. 31
The MCData-7 reference point, which exists between the Message store client and the MCData message store, is used by the Message store client to manage the information stored in the MCData message store, to subscribe to changes in the MCData message store and to synchronize between the MCData client and the MCData message store.
6.4.4.1.7 Reference point MCData-8 (between the MCData message store and McData server) |R16| p. 31
The MCData-8 reference point, which exists between the MCData server and the MCData message store, is used by the MCData server to access and manage the MCData message store such as creating MCData user folders and depositing the communications history.
6.4.4.1.8 Reference point MCData-9 (between the MC gateway server and the MC gateway server in a different MCData system) |R16| p. 31
The MCData-9 reference point, which exists between the MC gateway server and the MC gateway server in an interconnected MCData system for MCData application signalling for establishing MCData sessions, shall use the SIP-3 reference point for transport and routing of signalling. The MCData-9 reference point also carries application data where the data size is too great to be transferred on the signalling plane.
6.4.4.1.9 Reference point MCData-10 (between the Message notification client and MCData notification server) |R17| p. 31
The MCData-10 reference point, which exists between the Message notification client and the MCData notification server, is used by the Message notification client to create an appropriate notification channel(s) at the MCData notification server in order to direct events from MCData message store to the MCData notification server for subsequent delivery to the Message notification client on the UE.
6.4.4.1.10 Reference point MCData-11 (between the MCData message store and the MCData notification server) |R17| p. 31
The MCData-11 reference point, which exists between the MCData message store and the MCData notification server, is used by the MCData message store to send notification message to the subscribed Message notification client.
6.5 Functional model for short data service p. 31
6.5.1 On-network functional model p. 31
Figure 6.5.1-1 shows the application plane functional model for SDS.
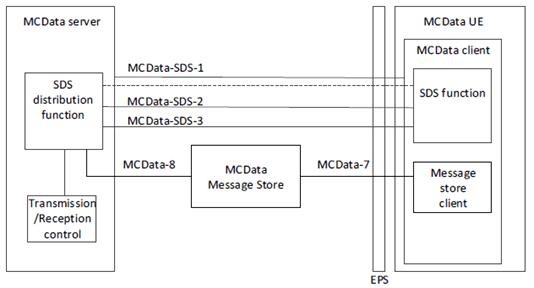
In the model shown in Figure 6.5.1-1, the following apply:
- MCData-SDS-1 reference point is primarily used for MCData application signalling during session establishment in support of SDS data transfer. Secondarily, MCData-SDS-1 reference point is used for uplink and downlink unicast SDS data transaction over signalling control plane by the SDS distribution function of the MCData server and SDS function of the MCData client.
- MCData-SDS-2 reference point carries uplink and downlink unicast SDS data over media plane between the SDS distribution function of the MCData server and the SDS function of the MCData client.
- MCData-SDS-3 reference point carries downlink multicast SDS data over media plane from the SDS distribution function of the MCData server to the SDS function of the MCData client.
- information pertaining to applications e.g. health parameters of MCData user for situational awareness application;
- information pertaining to enhanced status service;
- text or URL data between MCData users;
- application data (e.g. health parameters) to the MCData user;
- location information (independent or along with user or application provided data);
- command instructions to invoke certain operations on the MCData UE e.g. invoking UE specific applications; and
- application plane identities for the MCData user and MCData application.
6.5.2 Off-network functional model p. 32
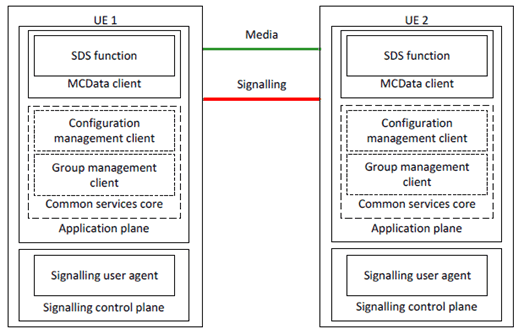
Figure 6.5.2-1 shows the off-network application plane functional model for SDS.
6.5.3 Functional entities description p. 33
6.5.3.1 Application plane p. 33
6.5.3.1.1 SDS function p. 33
SDS function of the MCData client is responsible to handle SDS capability related requests and responses.
6.5.3.1.2 SDS distribution function p. 33
The SDS distribution function of the MCData server is responsible for the SDS data transaction to MCData communication participants. The SDS distribution function of the MCData server provides the following functionality:
- reception of uplink SDS data transaction by means of the MCData-SDS-1 and MCData-SDS-2 reference points;
- replicate the SDS data as needed for distribution to those MCData communication participants using unicast transport;
- distribute downlink data by IP unicast transmission to those MCData communication participants utilizing unicast transport by means of the MCData-SDS-1 and MCData-SDS-2 reference points; and
- distribute downlink SDS data using multicast downlink transport by means of the MCData-SDS-3 reference point.
6.5.3.1.3 Transmission/Reception control p. 33
This functional entity is responsible for transmission and reception control of MCData SDS data transaction between the sending MCData UE, the MCData server, and the receiving MCData UE. For SDS capability, due to small data size, the SDS messages can be automatically sent.
6.5.3.2 Signalling control plane p. 33
The description of the signalling control plane is contained in the common functional architecture to support MC services as specified in TS 23.280.
6.5.4 Reference points p. 34
6.5.4.1 Application plane p. 34
6.5.4.1.1 Reference point MCData-SDS-1 (between the SDS distribution function and the SDS function) p. 34
MCData-SDS-1 reference point is used for uplink and downlink unicast SDS data transaction over signalling control plane by the SDS distribution function of the MCData server and SDS function of the MCData client. This reference point is also used for MCData application signalling during session establishment in support of SDS data transfer.
The MCData-SDS-1 reference point shall use the SIP-1 and SIP-2 reference points for transport and routing of SIP signalling. MCData-SDS-1 reference point can be used when the SDS payload data size does not exceed the configured maximum payload data size for SDS over signalling control plane, otherwise MCData-SDS-2 and MCData-SDS-3 may be used appropriately.
Reference point MCData-SDS-1 also provides support to delivered and read requests and notifications as appropriate.
6.5.4.1.2 Reference point MCData-SDS-2 (unicast between the SDS distribution function and the SDS function) p. 34
The MCData-SDS-2 reference point, which exists between the SDS distribution function and the SDS function of the MCData client, is used unicast SDS data transaction (when the SDS payload data size exceeds the configured maximum payload data size for SDS over signalling control plane) between the MCData server and the MCData client. The MCData-SDS-2 reference point uses the SGi reference point defined in TS 23.002.
Reference point MCData-SDS-2 also provides support to message thread indication using conversation identifier, delivered and read notifications as appropriate.
6.5.4.1.3 Reference point MCData-SDS-3 (multicast between the SDS distribution function and the SDS function) p. 34
The MCData-SDS-3 reference point, which exists between the SDS distribution function of the MCData server and the SDS function of the MCData client, is used by the SDS distribution function of the MCData server to send downlink multicast SDS data to the SDS function of the MCData client. The MCData-SDS-3 reference point uses the MB2-U interface defined in TS 23.468.
6.5.4.2 Signalling control plane p. 34
The description of the signalling control plane reference points is contained in the common functional architecture to support MC services as specified in TS 23.280.