Content for TS 26.501 Word version: 18.6.0
1…
4…
4.0.6…
4.1…
4.2…
4.2.2…
4.3…
4.4
4.5…
4.6…
4.7…
4.7.4…
4.8
4.9…
4.10…
5…
5.2…
5.2.4
5.2.5…
5.3…
5.3.2…
5.4…
5.5…
5.6…
5.7…
5.7.4…
5.7.8
5.8…
5.10…
5.10.5…
5.10.6…
5.11…
5.12…
5.12.4…
5.12.5…
6…
6.2…
6.2.2.2…
6.2.3…
6.3…
6.4…
6.8…
6.9…
6.9.5…
6.9.7
7…
8…
9…
A…
A.4…
A.8
A.9
A.10
A.11
A.12
A.13
A.14
A.15…
A.15.3…
B…
B.3
C…
C.3
C.4
C.5
D…
E…
4.0.6 Dynamic policies
4.0.7 Remote control
4.0.8 Consumption reporting
4.0.9 QoE metrics reporting
4.0.10 Edge processing
4.0.11 eMBMS delivery
4.0.12 Data collection, reporting and exposure
4.0.13 Service URL handling
...
...
4.0.6 Dynamic policies p. 19
The dynamic policies feature is applicable to both downlink media streaming and uplink media streaming. It enables the 5GMS Client in the UE to manipulate the network traffic handling policies for an ongoing media streaming session.
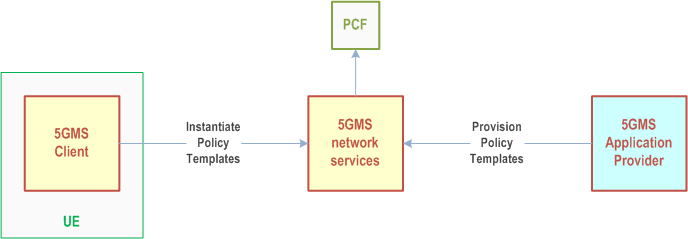
With reference to Figure 4.0.6-2, dynamic policies work as follows:
1.
In addition, the use of dynamic policies by 5GMS Clients is logged by the 5GMS System and, if suitably provisioned, is exposed by it to subscribing 5GMS Application Providers in the form of events (see also clause 4.0.12).
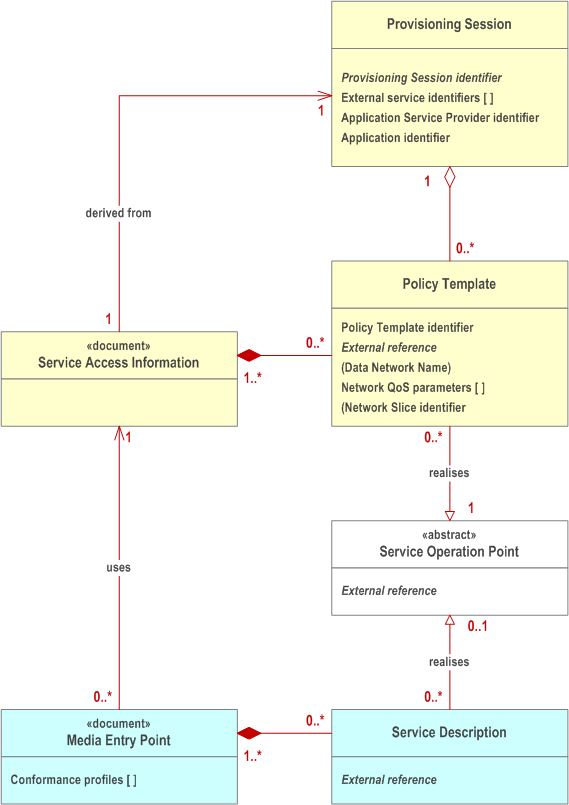
A conceptual Service Operation Point is an abstract set of requirements that support a media streaming service (e.g., SD, HD, UHD). It is identified by an External reference that is used to tag Policy Template resources provisioned in the 5GMS System and Service Descriptions included in Media Entry Point documents.
2.
The Service Operation Point is embodied in the 5G System by a Policy Template which is provisioned in the 5GMS network services by the 5GMS Application Provider within the scope of an umbrella Provisioning Session. A Policy Template may be defined as being applicable to a particular Data Network and/or Network Slice. The Policy Template carries the External reference and Network QoS parameters corresponding to a single Service Operation Point. (Any number of Policy Templates provisioned for different Data Networks and/or Network Slices may reference the same Service Operation Point.) The 5GMS network services may reject attempts to provision a Policy Template that specifies Network QoS parameters outside acceptable bounds imposed by local system configuration.
In addition, the Policy Template may include a reference to an existing Background Data Transfer policy. If no previously defined Background Data Transfer policy exists, the Policy Template may instead include the parameters that are used by the 5GMS network services to provision a Background Data Transfer policy for the current Provisioning Session. These parameters may include desired time windows when Background Data Transfer may be advertised to 5GMS Clients, a quota representing the maximum number of 5GMS Clients that are permitted to take advantage of Background Data Transfers in each such time window and a quota representing a ceiling for the aggregate volume of data that all 5GMS Clients are permitted to transfer in each Background Data Transfer window. Hence, an advertised time window is not a guarantee that a request for Background Data Transfer will actually be granted by the 5GMS System.
3.
The 5GMS Application Provider makes one or more Media Entry Point documents (e.g., DASH MPDs) available for use by the 5GMS Client. To take advantage of the dynamic policies feature, a Media Entry Point document includes one or more Service Descriptions, each identifying the streaming requirements of a presentation that correspond to a single Service Operation Point (e.g., SD, HD, UHD) and identified by means of an External reference. The same Service Description may be included in more than one Media Entry Point document in case a common Service Operation Point is applicable to multiple media presentations.
4.
When a Media Entry Point is selected by the 5GMS Client at the start of a media streaming session, the 5GMS Client retrieves Service Access Information from a network-side component of the 5GMS System describing the set of available Policy Templates provisioned in step 2 and exposes this to a controlling application on the UE.
4a.
If Background Data Transfer was provisioned as part of any Policy Templates in step 2 above, the Service Access Information includes details of the advertised time windows when Background Data Transfers are available and the data volume quota (if any). Maximum bit rates for the 5GMS Client in either or both the uplink and downlink direction may also be nominated by the 5G System and signalled to the 5GMS Client in the Service Access Information. Finally, an endpoint in the 5GMS network services may be provided allowing the 5GMS Client to subscribe to receive real-time notifications of Background Data Transfer warning notifications.
5.
At the start of a media streaming session, the controlling application on the UE selects one of the Service Descriptions listed in the Media Entry Point document that realises its preferred Service Operation Point. Either the Media Player (when the Service Descriptions are within the Media Entry Point document) or the controlling application (when the Service Descriptions are not within the Media Entry Point document) informs the 5GMS Client of its choice by passing the corresponding External reference to it.
6.
If there is a Policy Template available for the current media streaming session with the indicated External reference, the 5GMS Client instantiates this Policy Template by interacting with a network-side component of the 5GMS System in order to realise the Service Operation Point described by the Policy Template and the Service Description. The effect of this is that the corresponding network Quality of Service is applied to the media streaming session.
7.
At any point during one of the advertised Background Data Transfer time windows the 5GMS Client may request a Background Data Transfer by instantiating a Policy Template with a Background Data Transfer specification in the 5GMS network services, including an estimate of the data volume it intends to transfer. The 5GMS network services may grant the request for the Background Data Transfer if the data volume estimate is acceptable and if the quota of requests for the time window in question has not already been exceeded. If the request is granted, the 5GMS network services apply the appropriate Background Data Transfer Quality of Service policy to the media streaming session from the Policy Template in question. The Background Data Transfer grant returned to the 5GMS Client includes an estimate of the time period for which Background Data Transfer is available for the 5GMS Client to use and an indication of the maximum data volume that it is permitted to transfer. After this period has expired, the 5GMS network services automatically revert the network Quality of Service back to its state before the grant.
8.
The 5GMS media services also subscribe to receive Background Data Transfer warning notifications from the PCF related to the individual Background Data Transfer policy as defined in clause 4.16.7.3 of TS 23.502. The 5GMS media services shall notify the 5GMS Client when the network performance of that particular media streaming session degrades below the Background Data Transfer policy currently in force or when the aggregate data volume for all data transfers during the current Background Data Transfer time window has been reached.
4.0.7 Remote control p. 21
The remote control feature is applicable to uplink media streaming only. While high-level procedures for integrating this feature into 5G Media Streaming are specified in clause 6.6 of the present document, it is not further defined in this release.
4.0.8 Consumption reporting p. 21
The consumption reporting feature is applicable to downlink media streaming only in this release. It allows consumption of downlink media streaming to be logged by the 5GMS System and exposed for analysis.
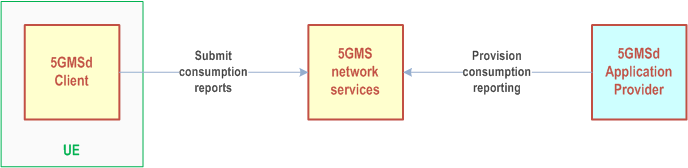
Figure 4.0.8-1: High-level arrangement for consumption reporting feature
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
When a 5GMSd Application Provider has provisioned the consumption reporting feature for downlink media streaming:
- The 5GMSd Client reports consumption of media that is part of downlink media streaming sessions to a network-side component of the 5GMS System.
4.0.9 QoE metrics reporting p. 21
The QoE metrics reporting feature is applicable to downlink media streaming only in this release. It allows the Quality of Experience of media streaming sessions to be logged by the 5GMS System and exposed for analysis.
Two mechanisms for reporting downlink QoE metrics are defined in the present document: one that involves reports being sent to the OAM via the RAN (RAN-based QoE metrics reporting, see clause 5.5.2), the other involving reports sent to the network-based components of the 5GMS System (AF-based QoE metrics reporting, see clause 5.5.3).
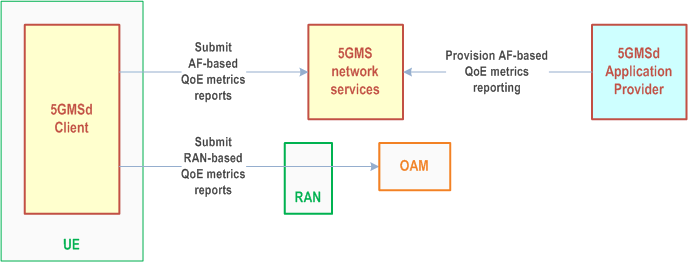
Figure 4.0.9-1: High-level arrangement for QoE metrics reporting feature
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
When a 5GMS Application Provider has provisioned the QoE metrics reporting feature for media streaming:
- The 5GMS Client reports QoE metrics that it has collected during media streaming sessions to a network-side component of the 5GMS System.
4.0.10 Edge processing |R17| p. 22
The edge processing feature is applicable to both downlink media streaming and uplink media streaming. It enables the 5GMS Client in the UE to take advantage of edge computing capabilities in the 5GMS System to support media streaming. This feature is defined in clause 4.5 and high-level procedures are defined in clause 8.
4.0.11 eMBMS delivery |R17| p. 22
The eMBMS delivery feature is applicable to downlink media streaming only. It enables the 5GMS System to provision the delivery of downlink media streaming content via eMBMS User Services sessions. This feature is defined in clause 4.6 and high-level procedures are defined in clause 5.10.
4.0.12 Data collection, reporting and exposure |R17| p. 22
The data collection, reporting and exposure feature is applicable to both downlink media streaming and uplink media streaming. It enables the 5GMS System to log data relating to media streaming sessions and to expose this to subscribers in the form of Events. This feature is defined in clause 4.7 and high-level procedures are defined in clause 5.11 (for downlink media streaming) and clause 6.8 (for uplink media streaming).
4.0.13 Service URL handling |R18| p. 22
Service URL handling is applicable to downlink and uplink media streaming. This feature is defined in clause 4.10 and high-level procedures are defined in clause 9.
The intent of 3GPP Service URL handling is to launch UE functions based on the execution of a URL. This enables 5G Media Streaming services to be announced within a third-party application, a general web page, a messaging service or shared via social messages using a 3GPP Service URL for 5GMS. When a service is launched using a 3GPP Service URL for 5GMS, a 5GMS Client function for media session handling is expected to be launched implicitly alongside, for example, a primary media stream handling function.