Content for TS 26.501 Word version: 18.0.0
1…
4…
4.2…
4.2.2…
4.3…
4.5…
4.6…
4.7…
5…
5.2…
5.3…
5.3.2
5.4…
5.5…
5.5.3…
5.6…
5.7…
5.7.3
5.7.4…
5.8
5.9…
5.10…
5.10.5
5.10.6
5.11…
6…
6.2…
6.3…
6.5…
6.8…
7…
8…
8.2
A…
A.3…
A.5…
A.7…
A.9
A.10
A.11
A.12
A.13
A.14
A.15
B…
B.3
C…
C.3
C.4
C.5
D…
8 Procedures for 5GMS Edge Processing
8.1 Procedure for client-driven management of 5GMS Edge Processing
...
...
8 Procedures for 5GMS Edge Processing |R17| p. 102
8.1 Procedure for client-driven management of 5GMS Edge Processing p. 102
Figure 8.1-1 outlines a detailed call flow for client-driven session establishment.
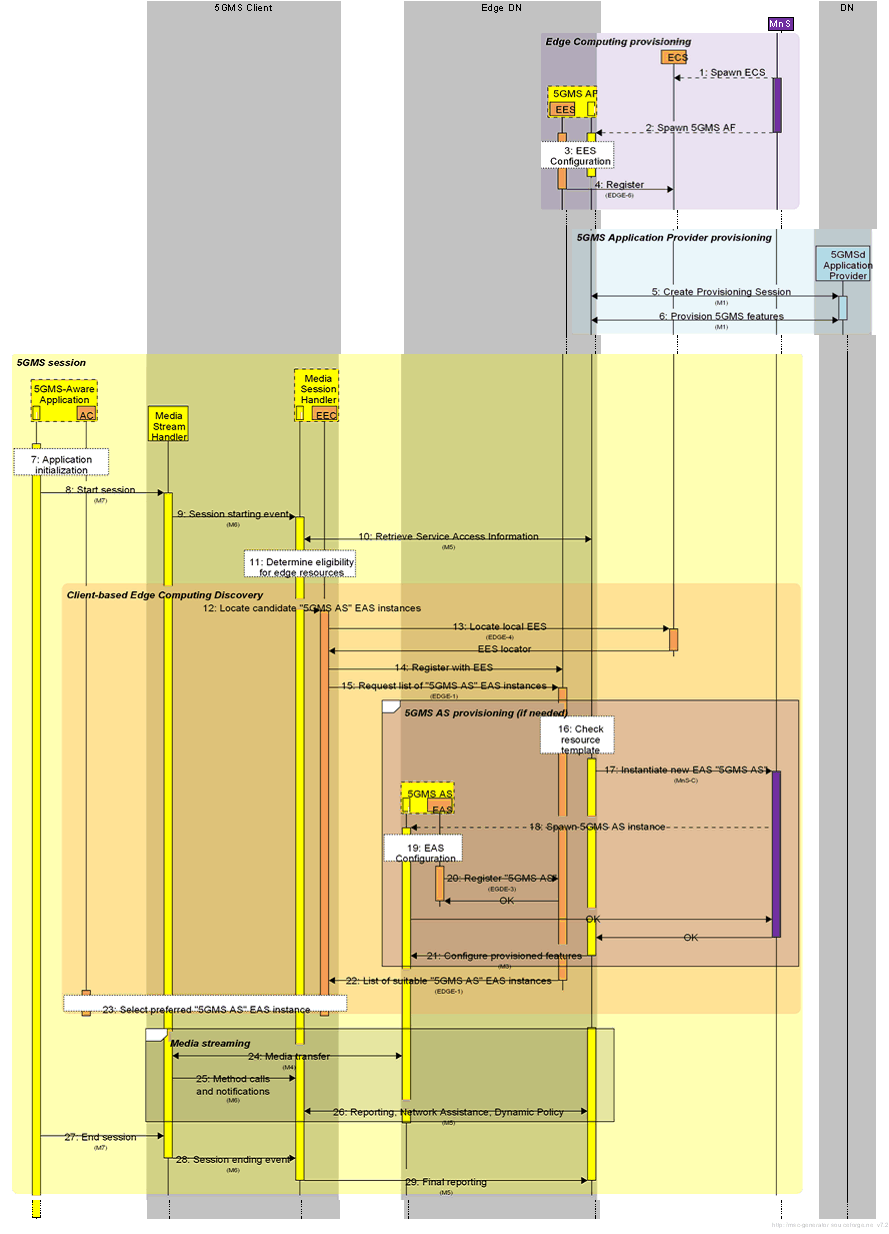
The Edge Computing Provisioning phase is a provisioning phase, that may be repeated several times (e.g. to extend edge processing coverage to new geographical areas or to increase the capacity of an already provisioned area). All steps in this phase are optional and performed on need basis. The steps are:
The 5GMS Application Provider Provisioning phase is performed prior to the establishment of any related media streaming sessions by the 5GMS Application Provider. Subsequent updates to the provisioning session are possible.
The 5GMS-Aware Application initiates a new media streaming session:
If the eligibility criteria are met in the previous step, the UE discovers an EAS instance offering 5GMS AS functionality in the Client-based Edge Computing Discovery phase:
The optional sub-flow is for provisioning an additional 5GMS AS instance if a suitable EAS instance offering the "5GMS AS" capability cannot be located. The steps are:
Completion of Client-based Edge Computing Discovery phase:
After the successful discovery of a "5GMS AS" EAS instance, the actual streaming session may start:
Step 1.
Spawn ECS: In this step, a new ECS is instantiated to manage new or increased demand for edge processing.
Step 2.
Spawn 5GMS AF: In this step, a new 5GMS AF that is edge-enabled is instantiated to handle new or increased demand for media sessions with edge processing.
Step 3.
EES Configuration: The EES is configured for a specific Edge Data Network.
Step 4.
EES Registration with ECS: The EES registers with the ECS that is in authority over the target EDN.
Step 7.
Application Initialization: The user launches the 5GMS-Aware Application. The application performs any required initialization steps.
Step 8.
Start session: The 5GMS-Aware Application invokes the Media Streamer with appropriate streaming access parameters.
Step 9.
Session starting event: The application informs the Media Session Handler about the start of a new 5GMS session.
Step 10.
Retrieve Service Access Information: The Media Session Handler retrieves Service Access Information from the 5GMS AF appropriate to the 5GMS session.
Step 11.
Determine eligibility for requesting edge resources: Using information from the Service Access Information, the Media Session Handler determines whether the media streaming session is eligible for requesting edge resources.
Step 12.
Locate candidate "5GMS AS" EAS instances: The Media Session Handler (potentially triggered by a request from the 5GMS-Aware Application) asks its embedded EEC to discover the location of one or more suitable EAS instances offering the "5GMS AS" capability that are able to serve the application.
Step 13.
Locate local EES: The EEC queries the ECS for a suitable EES.
Step 14.
Register with EES: The EEC registers with the selected EES.
Step 15.
Request list of "5GMS AS" EAS instances: The EEC contacts the EES to query for one or more EAS instances offering the "5GMS AS" capability that can serve the session, using EAS discovery filters (see Table 8.5.4.2-2 in TS 23.558) obtained as a part of the Service Access Information and/or provided by the Application Client, e.g. "5GMS AS" for EAS type, appropriate values for service feature(s), and other EAS characteristics.
Step 16.
Check resource template: The 5GMS AF checks the provisioned edge processing resource template for the related application to determine the edge resource requirements of the application.
Step 17.
Instantiate new EAS/5MGS AS: The 5GMS AF requests the MnS to instantiate a new "5GMS AS" EAS instance using the specified requirements in the provisioned edge processing resource template and parameters provided in the query by the EEC.
Step 18.
Spawn 5GMS AS instance: The MnS creates a new instance of the EAS offering "5GMS AS" capability with the requested placement and resources.
Step 19.
EAS configuration: The newly instantiated "5GMS AS" EAS instance is configured, after which it is discoverable through DNS procedures or the discovery procedures as defined in TS 23.558.
Step 20.
Register EAS with EES: The newly instantiated EAS instance registers itself with the triggering EES.
Step 21.
Configure provisioned features: This may include configuring and launching the server-side application in the 5GMS AS.
Step 22.
List of suitable "5GMS AS" EAS instances: The EES/5GMS AF responds to the EEC with a list of "5GMS AS" EAS instances and their characteristics in an EAS discovery response (see Table 8.5.3.3-1 in TS 23.558). Every EAS instance in the list satisfies the requirements defined in the provisioned edge processing resource template.
Step 23.
Select preferred "5GMS AS" EAS instance: The AC and/or EEC/Media Session Handler select(s) a "5GMS AS" EAS instance from the provided list, based on the AC's desired criteria.
In the case where the media entry point provided in the Service Access Information includes a host name, the EEC/Media Session Handler inserts a record into the UE's local DNS resolver that resolves this host name to the IP address of the chosen EAS instance.
Step 24.
Media transfer: The 5GMS-Aware Application connects to the selected EAS "5GMS AS" and the streaming starts.
In the case where the media entry point provided in the Service Access Information includes a host name, before connecting, the Media Stream Handler first resolves this to the IP address of the EAS instance selected in step 23.
Step 25.
Method calls and notifications: Supporting information about the 5GMS session is passed from the Media Stream Handler to the Media Session Handler.
Step 26.
Reporting, network assistance, and dynamic policy: The Media Session Handler exchanges supporting information about the 5GMS session with the 5GMS AF.
Step 27.
End session: the 5GMS-Aware Application informs the Media Session Handler that the 5GMS session has ended.
Step 28.
Session ending event: The Media Streamer informs the Media Session Handler about the end of the 5GMS session.
Step 29.
Final reporting: The Media Session Handler performs any final reporting to the 5GMS AF.