Content for TS 23.247 Word version: 18.7.0
1…
4…
4.2…
4.3
5…
6…
6.6…
7…
7.1.1.2
7.1.1.3
7.1.1.4…
7.1.1.6…
7.1.2…
7.2…
7.2.2…
7.2.3…
7.2.4…
7.2.4.3…
7.2.5…
7.2.6…
7.3…
7.3.5…
7.5…
8…
9…
9.2…
9.3…
9.4…
A…
5 Architecture model
5.1 General architecture
5.2 General architecture for interworking with EPS
5.3 Service-based interfaces, Reference point and functional entities
5.3.0 Service-based interfaces
5.3.1 Reference point
5.3.2 Functional entities
5.3.2.1 PCF
5.3.2.2 MB-SMF
5.3.2.3 SMF
5.3.2.4 MB-UPF
5.3.2.5 UPF
5.3.2.6 AMF
5.3.2.7 NG-RAN
5.3.2.8 UE
5.3.2.9 AF
5.3.2.10 NEF
5.3.2.11 MBSF
5.3.2.12 MBSTF
5.3.2.13 UDM
5.3.2.14 UDR
5.3.2.15 NRF
...
...
5 Architecture model p. 20
5.1 General architecture p. 20
Figure 5.1-1 depicts the MBS reference architecture. Service-based interfaces are used within the Control Plane. Support for interworking at reference points xMB and MB2 is described in Annex C.
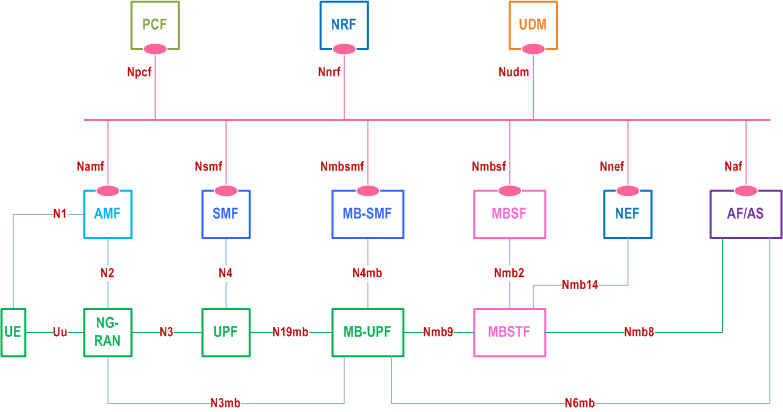
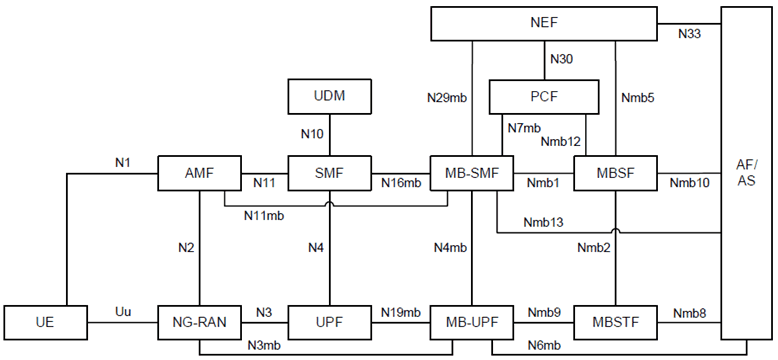
Figure 5.1-2 depicts the 5G system architecture for MBS using the reference point representation.
5.2 General architecture for interworking with EPS p. 21
Interworking between MBS and eMBMS at service layer functionality applies in cases where the same Multicast/Broadcast service is provided via eMBMS and MBS. Figure 5.2-1 depicts the system architecture for interworking between E-UTRAN/EPC eMBMS and MBS at service layer, with collocated BM-SC and MBSF/MBSTF functionalities.
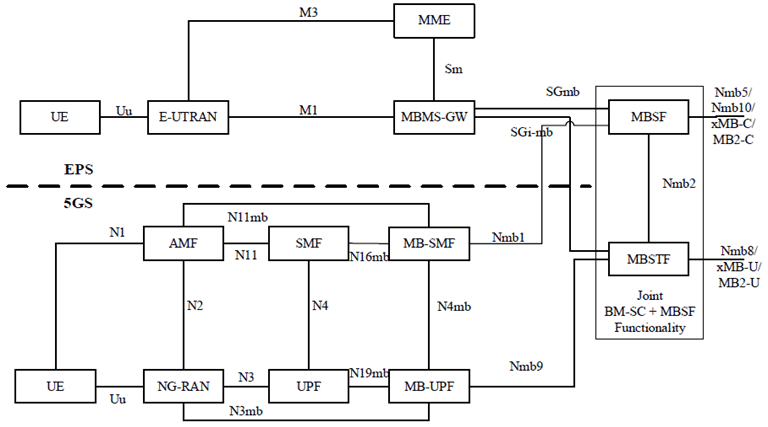
The BM-SC+MBSF/MBSTF exposes common Nmb5/Nmb10/xMB-C/MB2-C and Nmb8/xMB-U/MB2-U reference points to the NEF and/or AF/AS. A common TMGI is used towards the AF/AS. The TMGI is also used as identifier for transport over E-UTRAN/EPC. The MBSTF distributes the received data to the MB-UPF at reference point Nmb9 and/or the MBMS-GW at reference point SGi-mb, when supported by operator network configuration.
5.3 Service-based interfaces, Reference point and functional entities p. 22
5.3.0 Service-based interfaces p. 22
The 5G System Architecture for MBS contains the following service-based interfaces:
Nmbsmf:
Service-based interface exhibited by MB-SMF. Further details are described in clause 9.1.
Npcf:
Service-based interface exhibited by PCF. Further details are described in clause 9.2.
Namf:
Service-based interface exhibited by AMF. Further details are described in clause 9.3.
Nnef:
Service-based interface exhibited by NEF. Further details are described in clause 9.4.
Nmbsf:
Service-based interface exhibited by MBSF. Further details are described in clause 9.5.
5.3.1 Reference point p. 22
The 5G System Architecture for MBS contains the following new reference points:
N3mb:
Reference point between the RAN and the MB-UPF.
N4mb:
Reference point between the MB-SMF and the MB-UPF.
N6mb:
Reference point between the MB-UPF and the AF/AS.
N7mb:
Reference point between the MB-SMF and the PCF.
N11mb:
Reference point between the AMF and the MB-SMF.
N16mb:
Reference point between the SMF and the MB-SMF.
N19mb:
Reference Point between the UPF and the MB-UPF.
N29mb:
Reference point between the MB-SMF and the NEF.
Nmb1:
Reference point between the MB-SMF and the MBSF.
Nmb2:
Reference point between the MBSF and the MBSTF.
Nmb5:
Reference point between the MBSF and the NEF.
Nmb8:
Reference point between the MBSTF and the AF/AS.
Nmb9:
Reference point between the MB-UPF and the MBSTF.
Nmb10:
Reference point between the MBSF and the AF/AS.
Nmb12:
Reference point between the MBSF and the PCF.
Nmb13:
Reference point between the MB-SMF and the AF/AS.
Nmb14:
Reference point between the NEF and the MBSTF.
N101:
Reference point between the MB-SMF and the CHF.
5G System Architecture for MBS reuses the existing reference points of N1, N2, N4, N5, N10, N11, N30, N33 and N40 with enhancement to support MBS.
5.3.2 Functional entities p. 23
5.3.2.1 PCF p. 23
In addition to the functions defined in TS 23.501, the PCF performs the following functions to support MBS if dynamic PCC for MBS is needed:
- Supporting QoS handling for MBS Session.
- Providing policy information regarding the MBS Session to MB-SMF for authorizing the related QoS profiles.
- Interacting with UDR for QoS information retrieval.
- The PCF can receive MBS information from AF, NEF or MBSF, e.g. based on the different configuration options in Annex A.
5.3.2.2 MB-SMF p. 23
The MB-SMF performs the following functions to support MBS:
-
General for Multicast and Broadcast MBS sessions:
- Supporting MBS session management (including QoS control).
- Configuring the MB-UPF for multicast and broadcast data transport, based on the policy rules for multicast and broadcast services from PCF or local policy.
- Allocating and de-allocating TMGIs.
-
Specific for Broadcast MBS sessions:
- Interacting with RAN (via AMF) to control data transport using 5GC Shared MBS traffic delivery method.
-
Specific for Multicast MBS sessions:
- Interacting with SMF to provide the SMF with MBS Session Context information.
- Interacting with RAN (via AMF) to establish data transmission resources between MB-UPF and RAN nodes for 5GC Shared MBS traffic delivery method.
- Controlling the MB-UPF for multicast data transport using 5GC Individual MBS traffic delivery method.
5.3.2.3 SMF p. 24
In addition to the functions defined in TS 23.501, the SMF performs the following functions to support MBS:
- Discovering MB-SMF for a Multicast MBS session.
- Authorizing Multicast MBS session join operation for served UEs if needed.
- Interacting with MB-SMF to obtain multicast Session Context information used as input to modify the PDU Session associated with MBS session.
- Interacting with RAN to provide information about a Multicast MBS session that a UE is participating in.
- Interacting with RAN and UPF for multicast data transport using 5GC Individual MBS traffic delivery method.
- Interacting with RAN to provide MBS Assistance Information for the MBS session.
5.3.2.4 MB-UPF p. 24
The MB-UPF performs the following functions to support MBS:
-
General for Multicast and Broadcast MBS sessions:
- Packet processing of incoming downlink packets for multicast and broadcast flows.
- QoS enforcement (MFBR) based on existing means.
- Interaction with MB-SMF for receiving multicast and broadcast data.
- Delivery of multicast and broadcast data to RAN nodes for 5GC Shared MBS traffic delivery method.
-
Specific for Multicast MBS sessions:
- Delivery of multicast data to UPF for 5GC Individual MBS traffic delivery method.
5.3.2.5 UPF p. 24
In addition to the functions defined in TS 23.501, the UPF performs the following functions to support MBS:
- Interacting with SMF for receiving multicast data from MB-UPF for 5GC Individual MBS traffic delivery method.
- Delivering multicast data to UEs via PDU Session for 5GC Individual MBS traffic delivery method.
5.3.2.6 AMF p. 25
In addition to the functions defined in TS 23.501, the AMF performs the following functions to support MBS:
- Signalling with NG-RAN and MB-SMF for MBS Session management.
- Selection of NG-RANs for notification of multicast session activation toward UEs in CM-IDLE state.
- Selection of NG-RANs for broadcast traffic distribution.
5.3.2.7 NG-RAN p. 25
In addition to the functions defined in TS 23.501, the NG-RAN performs the following functions to support MBS:
- Management of MBS QoS flows via N2.
- Delivery of MBS data packets for multiple UEs over radio using PTM or PTP.
- Configuration of UE for MBS QoS flow reception at AS layer.
- Control switching between PTM and PTP delivery per UE.
- Support for multicast session service continuity during Xn Handover and N2 Handover.
- Support group paging at multicast session activation over radio toward UEs in CM-IDLE state and CM-CONNECTED with RRC_INACTIVE state.
- Reception of MBS data packets from 5GC via shared MBS traffic delivery.
- Support for efficient radio resource utilization for multiple broadcast MBS Sessions via multiple CNs to deliver the same broadcast content in the case of network sharing.
- If supported, determine to move UE(s) receiving multicast MBS data from RRC_CONNECTED state to CM-CONNECTED with RRC_INACTIVE state if the UE(s) are capable of receiving MBS data in RRC_INACTIVE state.
5.3.2.8 UE p. 25
In addition to the functions defined in TS 23.501, the UE may perform the following functions to support MBS:
- Reception of multicast data using PTM/PTP in RRC_CONNECTED state.
- If supported, reception of multicast data using PTM in RRC_INACTIVE state.
- Reception of broadcast data using PTM.
- Handling of incoming MBS QoS flows.
- Support of signalling for joining and leaving a Multicast MBS session.
- MBS resource management support at AS layer.
- Reception of notification in CM-IDLE state and CM-CONNECTED with RRC_INACTIVE state for multicast data transmission.
- Support of the aforementioned functions for UE using power saving functions.
5.3.2.9 AF p. 25
The AF performs the following functions to support MBS:
- Requesting multicast or broadcast service from the 5GC by providing service information including QoS requirement to 5GC.
- Instructing MBS session operation towards 5GC if needed.
- Interacting with NEF for MBS related service exposure.
- Interacting with NEF for group message delivery to the UE(s).
5.3.2.10 NEF p. 26
In addition to the functions defined in TS 23.501, the NEF performs the following functions to support MBS:
- Providing an interface to AFs for MBS procedures including service provisioning, MBS session and QoS management.
- Interacting with AF and NFs in 5GC, e.g. MB-SMF for MBS session operations, determination of transport parameters.
- Selection of MB-SMF to serve an MBS Session.
- Support of provisioning the optional MBS Session Assistance Information related to the reception of multicast MBS data in RRC_INACTIVE state.
- Interacting with AF and MBSF/MBSTF for group message delivery.
5.3.2.11 MBSF p. 26
The MBSF performs the following functions to support MBS:
- Service level functionality to support MBS, and interworking with LTE MBMS
- Interacting with AF and MB-SMF for MBS session operations, determination of transport parameters, and session transport.
- Selection of MB-SMF to serve an MBS Session.
- Controlling MBSTF if the MBSTF is used.
- Determination of destination IP multicast address for the MBS session if IP multicast address is sourced by MBSTF.
5.3.2.12 MBSTF p. 26
The MBSTF performs the following functions to support MBS if deployed:
- Media anchor for MBS data traffic if needed.
- Sourcing of IP Multicast if needed.
- Generic packet transport functionalities available to any IP multicast enabled application such as framing, multiple flows, packet FEC (encoding).
- Multicast/broadcast delivery of input files as objects or object flows.
5.3.2.13 UDM p. 27
In addition to the functions defined in TS 23.501, the UDM performs the following functions to support MBS:
- Support management of subscription for authorization for multicast MBS sessions.
- Support management of subscription MBS Assistance Information related to the reception of multicast MBS data in RRC_INACTIVE state.
5.3.2.14 UDR p. 27
In addition to the functions defined in TS 23.501, the UDR performs the following functions to support MBS if deployed:
- Support storage or retrieval of MBS subscription data by the UDM for UE authorization information for multicast MBS sessions and MBS Assistance Information.
- Support storage and retrieval of policy data by the PCF for Multicast or Broadcast MBS sessions.
5.3.2.15 NRF p. 27
5.3.2.15.1 General p. 27
In addition to the functions defined in TS 23.501, the NRF performs the following functions to support MBS:
- Support of new NF types MB-SMF and MBSF and their corresponding NF profiles.
- For both multicast and broadcast MBS sessions, support of MB-SMF discovery based on parameters such as DNN, S-NSSAI and MBS service area, at MBS Session creation.
- For multicast MBS sessions, support of MB-SMF discovery based on MBS Session ID by SMF serving the multicast Session at UE join.
5.3.2.15.2 Extensions to NF profile at NRF p. 27
In addition to the NF profile contents defined in clause 6.2.6.2 of TS 23.501, the NF profile in the NRF contains the following content:
- For MB-SMF, the NF profile may include MB-SMF service area, MBS Session ID(s), Area Session ID(s) and corresponding MBS service area(s) if available.