Content for TS 23.247 Word version: 18.6.0
1…
4…
4.2…
4.3
5…
6…
6.6…
7…
7.1.1.2
7.1.1.3
7.1.1.4…
7.1.1.6…
7.1.2…
7.2…
7.2.2…
7.2.3…
7.2.4…
7.2.4.3…
7.2.5…
7.2.6…
7.3…
7.3.5…
7.5…
8…
9…
9.2…
9.3…
9.4…
A…
A Configuration options at Service and/or Application for MBS
B Service levels for multicast communication service
C Interworking at reference points MB2 and xMB
$ Change history
A (Normative) Configuration options at Service and/or Application for MBS p. 130
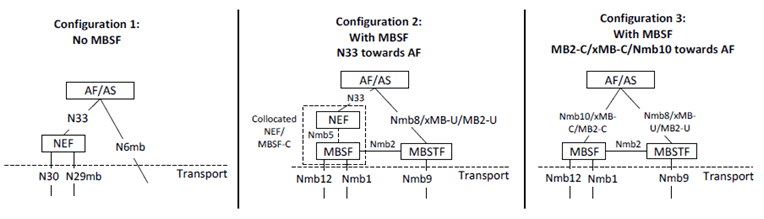
Figure A-1 provides the reference architecture with all configuration variants for Application Function interaction with 5G Core Network, usage of NEF or MBSF in the control plane, and usage of N6, MB2-U or xMB-U in user plane.
The following characteristics describe each of the Configuration options:
-
Configuration Option 1: No MBSF:
- This configuration is used for Transport Only Mode (i.e. MBS provides only transport of MBS data in a transparent manner without modifying the data), when the Multicast service or Broadcast service does not require service layer interworking with LTE MBMS.
- The control plane entry point for the Application Function outside the trusted domain towards 5GC to request establishment of an MBS session is the NEF via N33.
- An application function within the trusted domain can directly use the N30, N5 and N29mb service based interfaces. In this case some NEF functionality related to PCF and MB-SMF interaction is incorporated in AF.
- The user plane entry point for the Application Function towards 5GC is the MB-UPF via N6mb.
-
Configuration Option 2: MBSF, N33 towards AF:
- This configuration may be used for Service Mode (i.e. MBS provides service layer capability, allows to modify the data), or when service layer interworking with LTE MBMS is required, or when the functionalities of MBS security is used (see clause 6.13).
- When interworking with LTE MBMS for Transport Only Mode services, N33/Nmb5 and Nmb8 provide the same functionalities as N33/N13mb and N6mb respectively.
- The control plane entry point from the Application Function to request establishment of an MBS session is the NEF via N33.
- The user plane entry point for the Application Function towards 5GC is the MBSTF via MB2-U, xMB-U or Nmb8.
- The NEF and MBSF may be collocated.
- If the MBSF is not collocated with the NEF, the reference point between the NEF and MBSF is Nmb5.
- An application function within the trusted domain may be collocated with MBSF.
-
Configuration Option 3: MBSF, MB2-C/xMB-C/Nmb10 towards AF:
- This configuration may be used for Service Mode (xMB-C or Nmb10), or when interworking with LTE MBMS is required (MB2-C, xMB-C or Nmb10), or when the functionalities of MBS security is used (see clause 6.13).
- When interworking with LTE MBMS for Transport Only Mode services, Nmb10 and Nmb8 provide the same functionalities as Nmb13 and N6mb respectively.
- The control plane entry point from the Application Function to request establishment of an MBS session is the MBSF via MB2-C, xMB-C or Nmb10.
- The user plane entry point for the Application Function is the MBSTF via MB2-U, xMB-U or Nmb8.
- If interworking with LTE MBMS at 5GC is required for the service, MBSF and MBSTF shall be used, i.e. either Configuration 2 or Configuration 3 shall be used.
- If interworking with LTE MBMS is not required for the service, MBSF and MBSTF are optional.
B Service levels for multicast communication service p. 132
The following service levels for the multicast communication service are defined:
-
Basic service level. The following requirements are defined:
- Media transported transparently through the 5GS.
- Interactions between UE and network for receiving the multicast communication service.
- Packet distribution from the 5GS ingress to NG-RAN node(s).
- Data delivery from NG-RAN node(s) to the UE.
-
Enhanced service level, with additional requirements on top of basic service level. Different requirements out of the set below may be necessary to address each use case:
- Local MBS service.
- User authentication and authorization for Multicast MBS session.
- Explicit configuration of Multicast MBS session by AF, including group member information.
- Enhanced QoS support. E.g. to differentiate MBS data flow with different QoS over 5GS.
C (Normative) Interworking at reference points MB2 and xMB p. 133
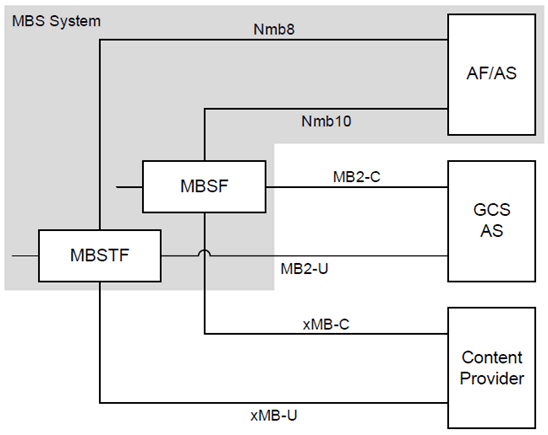
To allow the MBS System to interwork with a GCS AS supporting the MB2 interfaces defined in TS 23.468:
- In addition to supporting the Nmbsf service-based API at Nmb10 (as defined in clause 5.1) the MBSF shall support interfaces MB2 C.
- In addition to supporting content ingest interfaces defined in TS 26.502 at Nmb8 (as defined in clause 5.1) the MBSTF shall support interfaces MB2 U.
- In addition to supporting the Nmbsf service-based API at Nmb10 (as defined in clause 5.1) the MBSF shall support interface xMB C.
- In addition to supporting content ingest interfaces defined in TS 26.502 at Nmb8 (as defined in clause 5.1) the MBSTF shall support interface xMB U.