Content for TS 23.247 Word version: 18.6.0
1…
4…
4.2…
4.3
5…
6…
6.6…
7…
7.1.1.2
7.1.1.3
7.1.1.4…
7.1.1.6…
7.1.2…
7.2…
7.2.2…
7.2.3…
7.2.4…
7.2.4.3…
7.2.5…
7.2.6…
7.3…
7.3.5…
7.5…
8…
9…
9.2…
9.3…
9.4…
A…
7.3 MBS procedures for broadcast Session
7.3.1 MBS Session Start for Broadcast
7.3.1a MBS Session Start for resource sharing across multiple broadcast MBS Sessions during network sharing
7.3.2 MBS Session Release for Broadcast
7.3.2a MBS Session Release for resource sharing across multiple broadcast MBS Sessions during network sharing
7.3.3 MBS Session Update for Broadcast
7.3.4 Support for Location dependent Broadcast Service
...
...
7.3 MBS procedures for broadcast Session p. 98
7.3.1 MBS Session Start for Broadcast p. 98
The Broadcast MBS Session Start follows the common procedure specified in clause 7.1.1.2 or clause 7.1.1.3, which consist of TMGI Allocation and MBS Session Create. It is possible for AF to allocate TMGI once but create the MBS Session for multiple times. A combined procedure to perform both TMGI allocation and MBS Session Create is available.
The TMGI Allocation is used by AF to obtain the TMGI as MBS Session ID (i.e. TMGI) and perform service announcement towards UEs.
The MBS Session Create (with MBS service type set to broadcast service) is used by the AF to indicate the impending start of the transmission of MBS data, and to provide the session attributes, so that resources for the MBS Session are set up in the MB-UPF and in the NG-RAN for 5GC Shared MBS traffic delivery. The MBS Session Create can be used if TMGI has not been allocated. In this case, MB-SMF will allocate a unique TMGI for the AF and then start the MBS Session.
To receive the data of broadcast communication service, the UE is either preconfigured with needed configuration (see TS 24.575 for UE pre-configuration) for the UE to receive MBS service, or provisioned with the configuration of Broadcast MBS session on application level (service announcement as described in TS 26.502 and TS 26.517). If the needed configuration is pre-configured, the UE does not need to interact with network.
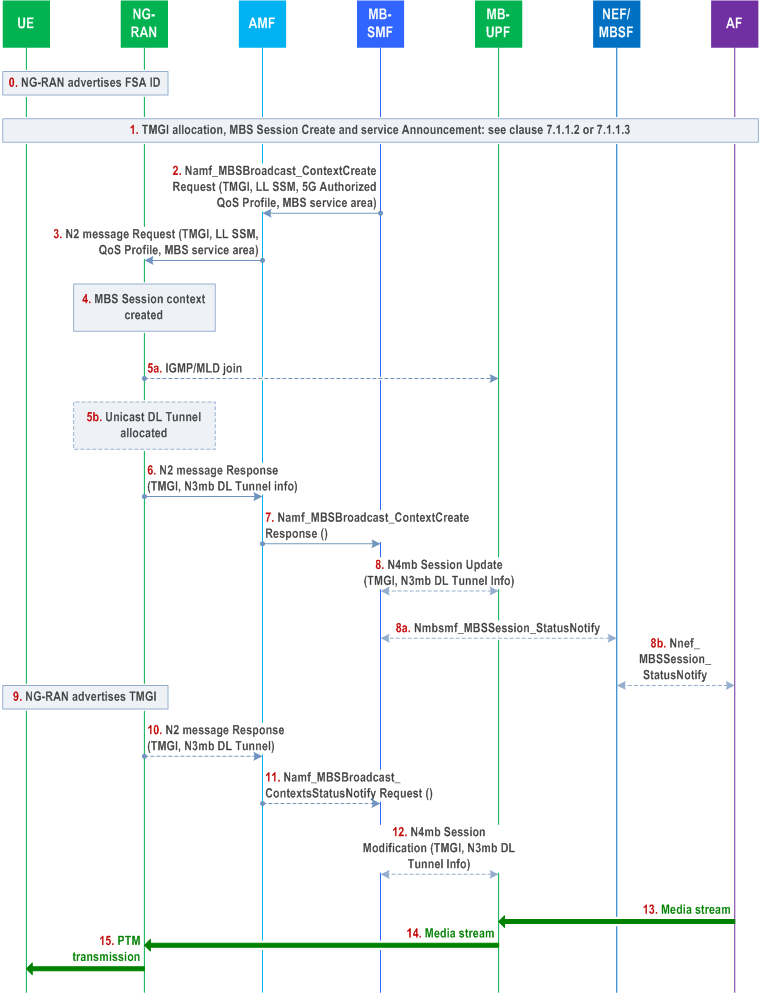
Step 0.
Depending on the NG-RAN's preference to use multicast or unicast transport over N3mb and the availability of the LL SSM, step 5a or step 5b is executed.
Based on OAM configuration, RAN nodes announce in SIBs over the radio interface information about the MBS FSA IDs and frequencies of neighbouring cells.
Step 1.
To establish broadcast MBS session, the AF performs TMGI allocation and MBS session creation as specified in clause 7.1.1.2 or clause 7.1.1.3. The MBS service type indicates to be broadcast service. The MBS FSA ID(s) of a broadcast MBS session are communicated in the service announcement towards the UE. The UE compares those MBS FSA IDs(s) with the MBS FSA ID(s) in SIBs for frequency selection.
Step 2.
The MB-SMF may use NRF to discover the AMF(s) supporting MBS based on the MBS service area and select the appropriate one(s). Then the MB-SMF sends the Namf_MBSBroadcast_ContextCreate (TMGI, N2 SM information ([LL SSM], 5G QoS Profile, [NR RedCap UE Information]), MBS service area, [MBS FSA ID(s)]) messages to the selected AMF(s) in parallel if the service type is broadcast service. The MB-SMF may include a maximum response time in the request.
If the MB-SMF receives the "NR RedCap UE Information" parameter (as defined in clause 6.19) from the AF (which may be via NEF/MBSF), the MB-SMF includes the "NR RedCap UE Information" parameter in N2 SM information.
Step 3.
The AMF transfers the MBS Session Resource Setup Request message, which contains the N2 SM information in the received Namf_MBSBroadcast_ContextCreate Request to all NG-RANs which support MBS in the MBS service area. The AMF includes the MBS service area.
Step 4.
NG-RAN creates a Broadcast MBS Session Context and stores the TMGI and the QoS Profile in the MBS Session Context. The LL SSM are optional parameters and only provided by MB-SMF to NG-RAN if N3mb multicast transport is configured to be used in the 5GC. If MBS FSA ID(s) were received, the NG-RAN may use those MBS FSA ID(s)s to determine cells/frequencies within the MBS service area to broadcast MBS session data based on OAM configuration about the MBS FSA IDs and related frequencies.
If N2 SM information contains "NR RedCap UE Information", the NG-RAN determines that the related MBS service is intended to be received by NR RedCap UEs only, or both by NR RedCap UEs and non-RedCap UEs, and allocates the appropriate radio resources as defined in TS 38.331.
Step 5a.
If NG-RAN prefers to use N3mb multicast transport (and if LL SSM is available in NG-RAN), the NG-RAN joins the multicast group (i.e. LL SSM).
Step 5b.
If NG-RAN prefers to use N3mb unicast transport (or if the LL SSM is not available in NG-RAN) between the NG-RAN and MB-UPF, NG-RAN allocates its N3mb DL Tunnel endpoint to receive downlink MBS session data.
Step 6.
The NG-RAN reports successful establishment of the MBS Session resources (which may include multiple MBS QoS Flows) by sending MBS Session Resource Setup Response (TMGI, N2 SM information ([N3mb DL Tunnel Info])) message(s) to the AMF. If NG-RAN prefers to use N3mb unicast transport (or if the LL SSM is not available in NG-RAN) between the NG-RAN and MB-UPF, NG-RAN provides its N3mb DL Tunnel Info as part of the N2 SM information. For more details, refer to TS 38.413.
Step 7.
The AMF transfers the Namf_MBSBroadcast_ContextCreate Response () to the MB-SMF. The AMF should respond success when it receives the first success response from the NG-RAN(s). And if all NG-RAN(s) report failure, the AMF should respond failure. The MB-SMF stores the AMF(s) which responds success in the MBS Session Context as the downstream nodes. If the AMF receives the NG-RAN response(s) from all involved NG-RAN(s), the AMF should include an indication of completion of the operation in all NG-RANs. If received from NG-RAN node, the N3mb DL Tunnel Info and NG-RAN ID are included in the response.
Step 8.
[Conditional] If N3mb unicast transport is to be used (i.e. N3mb DL Tunnel Info is present in the Namf_MBSBroadcast_ContextCreate Response message from AMF) in a deployment where NG-RAN nodes share a common user plane entity, the MB-SMF only establishes the shared tunnel towards the DL GTP tunnel endpoint if the shared tunnel has not yet been established (as determined based on the stored DL GTP Tunnel endpoint(s) for the MBS session). The MB-SMF also stores the received DL GTP Tunnel and corresponding NG-RAN Node ID for the MBS session. For the deployment where NG-RAN nodes do not share a common user plane entity, the DL GTP tunnel will not be used by other NG-RAN nodes. In a deployment where NG-RAN nodes do not share a common user plane entity, the MB-SMF always establishes the shared tunnel towards the DL GTP tunnel endpoint.
To establish the shared tunnel towards the DL GTP tunnel endpoint, the MB-SMF sends an N4mb Session Modification Request to the MB-UPF to allocate the N3mb unicast transport tunnel for a replicated MBS stream for the MBS Session.
Step 8a-8b.
If the AF subscribed to a Delivery Status Indication (see clause 7.3.5), the MB-SMF notifies the AF as specified in step 2 of clause 7.3.5. The MB-SMF notifies the AF directly by invoking Nmbsmf_MBSSession_StatusNotify service operation, or the MB-SMF notifies the AF via NEF/MBSF (if deployed) by invoking Nmbsmf_MBSSession_StatusNotify service operation to the NEF/MBSF which then invokes Nnef_MBSSession_StatusNotify service operation to the AF.
Step 9.
NG-RAN broadcasts the TMGI representing the MBS service over radio interface. Step 9 can take place in parallel with step 6.
Step 10.
Another NG-RAN may report successful establishment of the MBS Session resources (which may include multiple MBS QoS Flows) by sending MBS Session Resource Setup Response (TMGI, N2 SM information ([N3mb DL Tunnel Info])) message after the AMF transferred the Namf_MBSBroadcast_ContextCreate Response () to the MB-SMF.
Step 11.
The AMF transfers the Namf_MBSBroadcast_ContextStatusNotify request () to the MB-SMF. When the AMF receives the response from all NG-RAN nodes, the AMF includes an indication of the completion of the operation. If the AMF does not receive responses from all NG-RAN nodes before the maximum response time elapses since the reception of the Namf_MBSBroadcast_ContextCreate Request, then the AMF should transfer the Namf_MBSBroadcast_ContextStatusNotify request () which indicates partial success or failure.
Step 12.
[Conditional] If N3mb unicast transport is to be used (i.e. N3mb DL Tunnel Info is present in the MBS Session Start Response message from AMF), the handling in MB-SMF and MB-UPF is the same as specified in step 8.
Step 13.
The AF starts transmitting the DL media stream to MB-UPF using the N6mb Tunnel, or optionally un-tunnelled i.e. as an IP multicast stream using the HL MC address.
Step 14.
The MB-UPF transmits the media stream to NG-RAN via N3mb multicast transport or unicast transport.
Step 15.
The NG-RAN transmits the received DL media stream using DL PTM resources.
7.3.1a MBS Session Start for resource sharing across multiple broadcast MBS Sessions during network sharing |R18| p. 101
To support resource sharing across multiple broadcast MBS Sessions during network sharing (see clause 6.18), in addition to clause 7.3.1, the following enhancement applies:
-
Step 2: The MB-SMF includes Associated Session ID in the N2 SM information in Namf_
MBSBroadcast_ .ContextCreate - Step 4: A shared NG-RAN node identifies the associated MBS sessions as specified in clause 6.18. The associated MBS sessions share radio resource configuration based on the existing Broadcast MBS Session context.
- Step 5a: If the NG-RAN determines there is already an existing broadcast MBS session delivering the same content, the NG-RAN may skip joining the multicast group based on operator policy, i.e. step 5a can be skipped.
- Step 5b: If the NG-RAN determines there is already an existing broadcast MBS session delivering the same content, a shared NG-RAN node may decide not to allocate N3mb DL tunnel endpoint.
-
Step 6:
- For N3mb multicast transport, when the NG-RAN node decides to skip joining the multicast group in step 5a, the NG-RAN still reports successful establishment of the MBS Session resource.
- For N3mb unicast transport, when the NG-RAN decides not to allocate N3mb DL Tunnel endpoint in step 5b, the NG-RAN still reports successful establishment of the MBS Session resource but the N3mb DL Tunnel Info is not included in MBS Session Resource Setup Response.
- Step 8: If the N3mb unicast transport is used but N3mb DL Tunnel Info is not present in MBS Session Resource Setup Response, the MB-SMF accepts the response and skips step 8.
- Step 9: If the NG-RAN determines that radio resource has been allocated for another broadcast MBS Session delivering the same content as specified in clause 6.18, the NG-RAN advertises the TMGI of the broadcast MBS session, and reuses such already allocated radio resource for the MBS data transmission for the broadcast MBS session.
- Step 10 ~ step 12: The handling is the same as steps 5, 6, 7 and 8.
- Step 14: If the user plane of a broadcast MBS session from its MB-UPF to the shared NG-RAN is not established, the NG-RAN will not receive the MBS packets from the MB-UPF.
- Step 15: If the NG-RAN receives multiple DL media streams for the same content represented by the same Associated Session ID via multiple CNs, the NG-RAN should deliver only one DL media stream.
7.3.2 MBS Session Release for Broadcast p. 101
The MBS Session Release for broadcast follows the MBS Session Deletion (e.g. TMGI De-allocation and MBS Session Deletion) so that resource for shared MBS delivery is released. It is possible for AF to stop MBS Session but keep TMGI allocated.
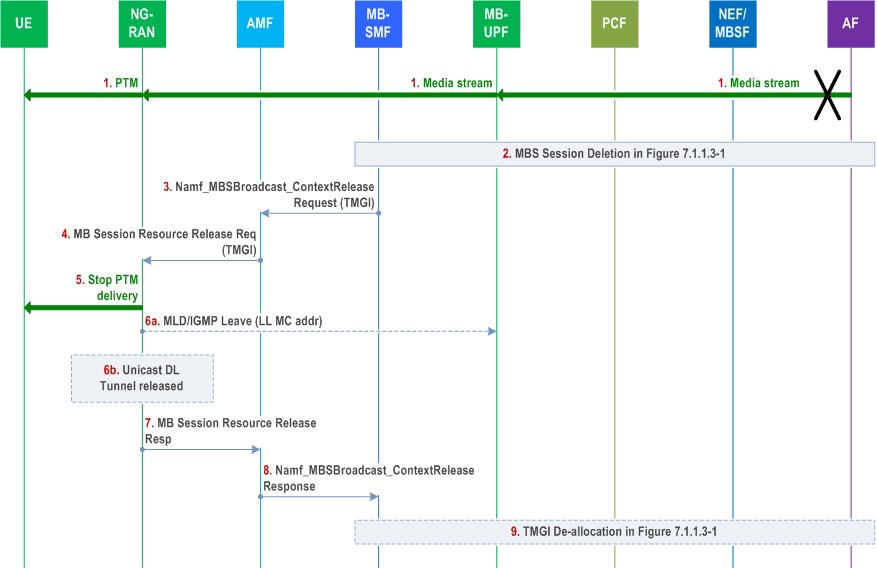
Step 1.
Depending on whether multicast or unicast transport is used over N3mb, step 6a or step 6b is executed.
The AF/AS may stop the media stream before sending the MBS Session Release Request (TMGI) message to the 3GPP network.
Step 2.
The AF/AS performs MBS Session Deletion procedure to request release of MBS Session (steps 1 ~ 10 in Figure 7.1.1.4-1, or steps 1 ~ 15 in Figure 7.1.1.5-1).
Step 3.
MB-SMF sends Namf_MBSBroadcast_ContextRelease request (TMGI) to the AMF(s) that has been involved in the MBS Session.
Step 4.
The AMF sends an N2 message to all RAN nodes that have been involved to release MBS session. If a NG-RAN node receives multiple N2 message to release the MBS Session for the same TMGI (e.g. from several AMFs the NG-RAN is connected to), NG-RAN only performs step 5 and step 6 once.
Step 5.
The NG-RAN stops the PTM transmission and stops TMGI advertisement for the MBS Session.
Step 6a.
If N3mb multicast transport has been used, the NG-RAN sends a Leave message (LL SSM) to stop the media stream to this NG-RAN node.
Step 6b.
If N3mb unicast transport has been used, the NG-RAN releases its unicast DL N3mb Tunnel endpoint.
Step 7.
NG-RAN deletes the MBS Session Context of the broadcast MBS Session. The NG-RAN reports successful release of resources for the MBS Session by sending MBS Session Resource Release Response (TMGI) message(s) to the AMF(s).
Step 8.
The AMF sends Namf_MBSBroadcast_ContextRelease response (TMGI) to the MB-SMF.
Step 9.
The AF may start a TMGI de-allocation procedure (steps 11 ~ 14 in Figure 7.1.1.4-1, or steps 16 ~ 19 in Figure 7.1.1.5-1).
7.3.2a MBS Session Release for resource sharing across multiple broadcast MBS Sessions during network sharing |R18| p. 102
To support resource sharing across multiple broadcast MBS Sessions, in addition to clause 7.3.2, the following enhancement applies:
-
Step 5:
- If the NG-RAN determines there are other associated broadcast MBS Sessions based on the Associated Session Identifier, the step 5 is skipped.
-
Step 6a:
- If the NG-RAN skipped joining the multicast group (LL SSM) in clause 7.3.1a, the NG-RAN does not send a Leave message (LL SSM),
- Otherwise, if the NG-RAN joined the multicast group (LL SSM) previously, and if the NG-RAN determines there are other associated broadcast MBS Sessions based on the Associated Session Identifier, the NG-RAN may trigger procedure of Transport change for resource sharing across broadcast MBS Sessions during network sharing as specified in clause 7.3.7.
-
Step 6b:
- If the DL N3mb Tunnel for the broadcast MBS Session was not allocated previously in clause 7.3.1a, step 6b is skipped.
- Otherwise, if the DL N3mb Tunnel for the broadcast MBS Session was allocated previously, and if the NG-RAN determines there are other associated broadcast MBS Sessions based on the Associated Session Identifier, the NG-RAN may trigger the procedure of Transport change for resource sharing across broadcast MBS Sessions during network sharing as specified in clause 7.3.7.
7.3.3 MBS Session Update for Broadcast p. 103
The MBS Session Update for broadcast is used by the AF to update the broadcast area or service requirements of the MBS Session which may lead to addition of new MBS QoS Flow(s), removal of existing MBS QoS Flow(s) or update of existing MBS QoS Flow(s).
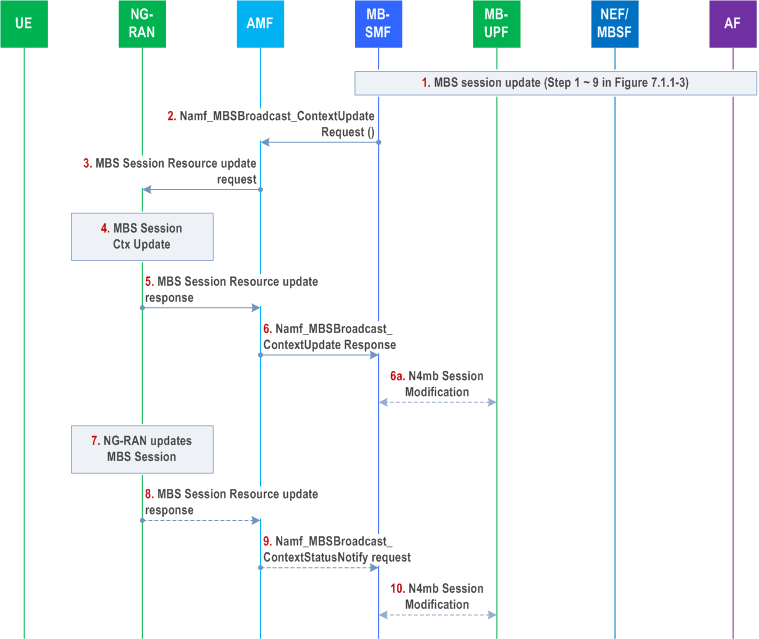
Step 1.
The AF starts MBS session update procedure by sending Nnef_MBSSession_Update Request to the NEF/MBSF with TMGI (steps 1-6 and steps 9-10 in Figure 7.1.1.6-1, or steps 1-12 and steps 15-16 in Figure 7.1.1.7-1). The AF may adjust service requirement and/or broadcast area. The service requirements adjustment may lead to addition of new MBS QoS Flow(s), removal of existing MBS QoS Flow(s) or update of existing MBS QoS Flow(s).
Step 2.
The MB-SMF sends Namf_MBSBroadcast_ContextUpdate Request (TMGI, N2 SM information (MBS Session ID, [MBS QoS profile], [service area(s)], [Area Session ID(s)], [MBS IP Multicast Tunnel Info(s)], [MBS FSA ID(s)], [NR RedCap UE Information]), [updated MBS service area]) to the AMFs. For a location dependent service, the MB-SMF may provide information about several location areas. If the broadcast area is updated, the MB-SMF may use NRF to discover the AMF(s) based on the new broadcast area and select the appropriate one(s). The MB-SMF may include a maximum response time in the request.
Depending on the change of the MBS service area, the MB-SMF may send Namf_MBSBroadcast_ContextCreate to some AMFs in the new MBS service area, Namf_MBSBroadcast_ContextRelease to some other AMFs in the old MBS service area.
The MB-SMF includes the "NR RedCap UE Information" parameter in N2 SM information, if received.
Step 3.
The AMF sends MBS Session Resource Update to NG-RANs with TMGI, the updated 5G QoS Profile and the updated MBS service area.
Depending on the change of the MBS service area, the AMF may send MBS Session Resource Setup to some NG-RANs in new MBS service area (see clause 7.3.1) and MBS Session Resource Release to some other NG-RANs in old MBS service area.
Step 4.
The NG-RAN updates MBS Session Context.
If N2 SM information contains "NR RedCap UE Information" for the broadcast MBS session, the NG-RAN may update the radio resources accordingly as specified in TS 38.331.
Step 5.
The NG-RAN reports successful update of the MBS Session resources (which may include multiple MBS QoS Flows) by sending MBS Session Resource Update Response (TMGI, N2 SM information ([N3mb DL Tunnel Info])) message(s) to the AMF. N3mb DL Tunnel Info is only available when unicast transport applies between MB-UPF and NG-RAN and the NG-RAN wants the transport to be changed. The NG-RAN should be ready to receive using the N3mb DL tunnel. For more details, refer to TS 38.413.
Step 6.
The AMF sends Namf_MBSBroadcast_ContextUpdate Response to the MB-SMF. If the AMF received the NG-RAN responses from all involved NG-RAN(s), the AMF should include an indication of completion of the operation in all NG-RANs. If received from NG-RAN node, the N3mb DL Tunnel Info and corresponding NG-RAN ID are included in the response.
Step 6a.
[Conditional] If MBS service area is changed in such a manner that NG-RAN nodes are added or removed from handling the MBS session, and N3mb unicast transport is used.
Step 7.
-
In a deployment where NG-RAN nodes share a common user plane entity, the MB-SMF perform as following:
- For the NG-RAN node to be added, the MB-SMF only establishes the shared tunnel towards the DL GTP tunnel endpoint if the shared tunnel has not yet been established (as determined based on the stored DL GTP Tunnel endpoint(s) for the MBS session). The MB-SMF also stores the received DL GTP Tunnel and corresponding NG-RAN Node ID for the MBS session.
- For the NG-RAN node to be removed, the MB-SMF removes the received NG-RAN Node ID and possibly DL GTP tunnel endpoint from the stored NG-RAN Node ID(s) for the DL GTP tunnel endpoint for the MBS session, and checks whether the DL GTP tunnel is in use by other NG-RAN nodes based on the stored NG-RAN Node ID(s) for DL GTP tunnel endpoint for the MBS session. If the related DL GTP tunnel is not in use by other NG-RAN nodes, the N3mb unicast transport tunnel shall be removed.
- In a deployment where NG-RAN nodes do not share a common user plane entity, the MB-SMF always establishes or releases the shared tunnel towards the DL GTP tunnel endpoint if NG-RAN nodes are added or removed from handling the MBS session.
The NG-RAN updates the MBS Session. It takes place in parallel with step 5 to step 6.
Step 8.
Another NG-RAN may report successful update of the MBS Session resources (which may include multiple MBS QoS Flows) by sending MBS Session Resource Update Response (TMGI, N2 SM information ([N3mb DL Tunnel Info])) message after the AMF transferred the Namf_MBSBroadcast_ContextUpdate Response () to the MB-SMF. N3mb DL Tunnel Info is only available when unicast transport applies between MB-UPF and NG-RAN and the NG-RAN wants the transport to be changed. The NG-RAN should be ready to receive using the N3mb DL tunnel. For more details, refer to TS 38.413.
Step 9.
The AMF transfers the Namf_MBSBroadcast_ContextStatusNotify request () to the MB-SMF. When the AMF receives the response from all NG-RAN nodes, the AMF should include an indication of completion of the operation in all NG-RANs. If the AMF does not receive responses from all NG-RAN nodes before the maximum response time elapses since the reception of the Namf_MBSBroadcast_ContextUpdate Request, then the AMF should transfer the Namf_MBSBroadcast_ContextStatusNotify request () which indicates partial success or failure. If received from NG-RAN node, the N3mb DL Tunnel Info and corresponding NG-RAN ID are included in the request.
Step 10.
[Conditional] If MBS service area is changed in such a manner that NG-RAN nodes are added or removed from handling the MBS session, and N3mb unicast transport is used, the MB-SMF establishes or releases the shared delivery tunnel via unicast N3mb transport for the MBS Session in the same manner as described in step 6a.
7.3.4 Support for Location dependent Broadcast Service p. 105
The clause describes procedures to support the Location dependent broadcast service as described in clause 6.2.
The MBS session creation procedure is performed as defined in clause 7.1.1.2 with the following additions:
- Multiple AFs may start the same Broadcast MBS session with different content in different MBS service areas. The NEF selects MB-SMF as ingress control node(s) for different MBS service areas.
- If presented, the NEF maps possible external identifiers for MBS service areas to network-internal identifiers (e.g. list of cells, TAIs).
- An NEF/MBSF uses the service area to discover the MB-SMF. If different MB-SMFs are assigned for different MBS service areas belonging to different MB-SMF service areas for an MBS session as specified in clause 6.2.3, an MB-SMF shall accept TMGIs allocated by other MB-SMF.
- For Location dependent Broadcast Service, MB-SMF allocates Area Session ID, and updates its NF profile towards the NRF with the TMGI and Area Session ID.
- The MB-SMF may select the MB-UPF based on the MBS service area.
- The MBS service area(s) are indicated to the UE in the Service Announcement as defined in clause 6.11.
- MB-SMF requests the AMF to transfer an N2 message (i.e. MBS Session Resource Setup Request) to the NG-RAN nodes of the MBS service area with Broadcast MBS session information which additionally includes the Area Session IDs and MBS service areas.
- The NG-RAN uses the received MBS Session ID and Area Session IDs to determine the local Broadcast MBS session contexts.
- The NG-RAN responds for service areas it handles with the Area Session ID(s) and DL tunnel endpoint(s) for the DL tunnel(s) from MB-SMF if unicast transport applies over N3mb between MB-UPF and NG-RAN.
- According to the Area Session ID(s) and DL tunnel endpoint(s) provided by NG-RAN, the MB-SMF instructs the MB-UPF to send location dependent content.
- The AF transmits the DL media streams to MB-UPF via tunnels to differentiate the content delivered to different areas.