Content for TS 23.284 Word version: 17.0.0
1…
4…
4.2…
4.3…
5
6…
6.3…
6.3.2
6.3.3
6.3.4
6.3.5
7…
7.2.4…
7.2.4.2
7.2.4.3
7.2.4.4
7.2.4.5
7.2.4.6
7.3…
7.3.4…
7.3.4.2
7.3.4.3
7.3.4.4
8…
8.2.3
8.3…
8.3.2
8.4…
8.4.1.1.7…
8.4.1.2…
8.4.2…
8.4.2.2…
8.4.5…
8.4.5.6
8.4.5.7
8.4.5.8…
9…
13…
13.4…
13.4.3…
13.4.4…
13.5…
13.6…
13.7…
14…
16…
A…
A.2…
13.4 Call Forwarding Services
13.4.1 Principles
13.4.2 Call Forwarding Unconditional (CFU)
13.4.2.1 Notification to the Calling Subscriber
13.4.2.2 Initial Addressing
13.4.2.3 Backward LCLS Negotiation
13.4.2.4 LCLS Through-Connection
13.4.2.5 Example
13.4.2.5.1 Connection Model
13.4.2.5.2 Basic Sequence
...
...
13.4 Call Forwarding Services p. 137
13.4.1 Principles p. 137
The procedures specified for the Call Forwarding services in TS 23.205, clause 13.4 for BICC based CS Core Network and in TS 23.231, clause 13.4 for SIP-I based CS Core Network shall be followed. The following clauses describe the additional requirements related to the LCLS functionality.
13.4.2 Call Forwarding Unconditional (CFU) p. 137
13.4.2.1 Notification to the Calling Subscriber p. 137
If the GMSC server determines that a call should be forwarded without being offered to the served mobile subscriber and the served mobile subscriber has requested that the calling subscriber shall receive a notification about the call forwarding, the GMSC server shall send a notification to the preceding node. If the GMSC server supports the LCLS feature and receives the GCR IE, the LCLS-Negotiation Request IE and LCLS-Configuration-Preference IE from the preceding node it may modify the LCLS-Configuration-Preference IE based on its own LCLS configuration requirements, as described in clause 4.2, and it shall return the resulting LCLS-Configuration-Preference IE and the LCLS-Negotiation Response IE to the preceding node.
If the notification is implemented using intermediate tones or announcements the GMSC server requests the MGW to play an announcement/tone to the calling party, as described in clause 14.6, before establishing the call to the forwarded-to subscriber.
13.4.2.2 Initial Addressing p. 137
If the incoming call is to be forwarded without being offered to the served mobile subscriber the call towards the forwarded-to subscriber is established as for a basic call. After the possible generation of in-band information has been completed the initial addressing towards the forwarded-to subscriber is performed as described in the clause 6 for the basic mobile terminating call. If the GMSC server supports the LCLS feature and receives the GCR IE, the LCLS-Negotiation Request IE and LCLS-Configuration-Preference IE from a preceding node in the IAM it shall forward the GCR IE and the resulting LCLS-Configuration-Preference IE and the LCLS-Negotiation Request IE to the succeeding node.
13.4.2.3 Backward LCLS Negotiation p. 137
The procedure specified in clause 6.2.1.2.2 for the intermediate node and in clause 6.1.1.4 for the oMSC server shall be applied.
13.4.2.4 LCLS Through-Connection p. 137
The procedure specified in clause 6.1.1.5 shall be applied.
13.4.2.5 Example p. 137
13.4.2.5.1 Connection Model p. 137
Figure 13.4.2.5.1.1 shows the network model for call forwarding unconditional. The oMSC server seizes one context with two bearer terminations in the oMGW. The bearer termination T1 is used for the bearer towards the oBSS (calling subscriber) and the bearer termination T2 is used for the bearer towards the GMSC selected iMGW. The GMSC server seizes one context with two bearer terminations in the iMGW. The bearer termination T4 is used for the bearer towards the tMSC server selected tMGW and the bearer termination T3 is used for the bearer towards the preceding oMGW. The tMSC server seizes one context with two bearer terminations in the tMGW. The bearer termination T5 is used for the bearer towards the GMSC selected iMGW and bearer termination T6 is used for the bearer towards the tBSS (forwarded-to subscriber).
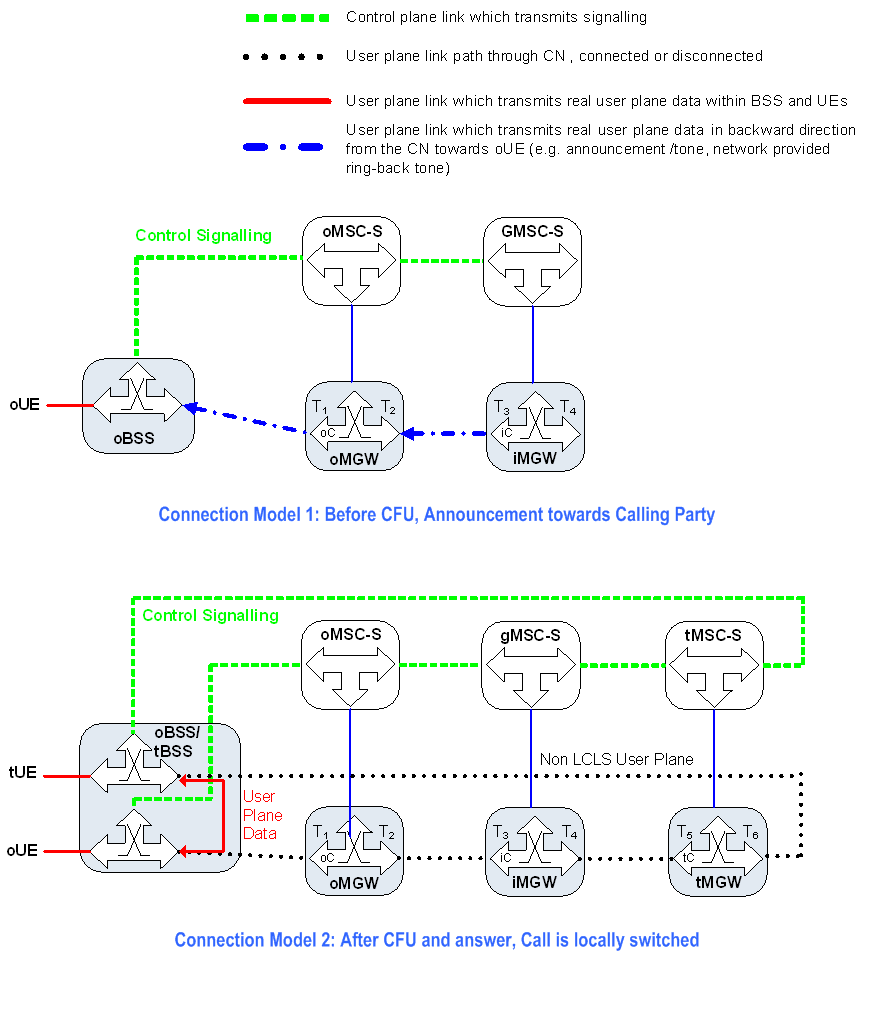
Figure 13.4.2.5.1.1: Connection Model for Call Forwarding Unconditional
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
13.4.2.5.2 Basic Sequence p. 138
Figure 13.4.2.5.2.1 and Figure 13.4.2.5.2.2 show the message sequence example for the call forwarding unconditional with a possible notification to the calling party using an announcement. In the example the GMSC server optionally requests the MGW to play an announcement and to notify the announcement completion, after the bearer to the incoming side has been established. When the possible announcement has completed the GMSC server requests the establishment of the call and the bearer towards the forward-to subscriber.
In this example the calling subscriber (oUE) and the forwarded-to subscriber (tUE) belong to the same BSS (marked as oBSS and tBSS) and the CN permits LCLS. The example is based on examples from clause 6.
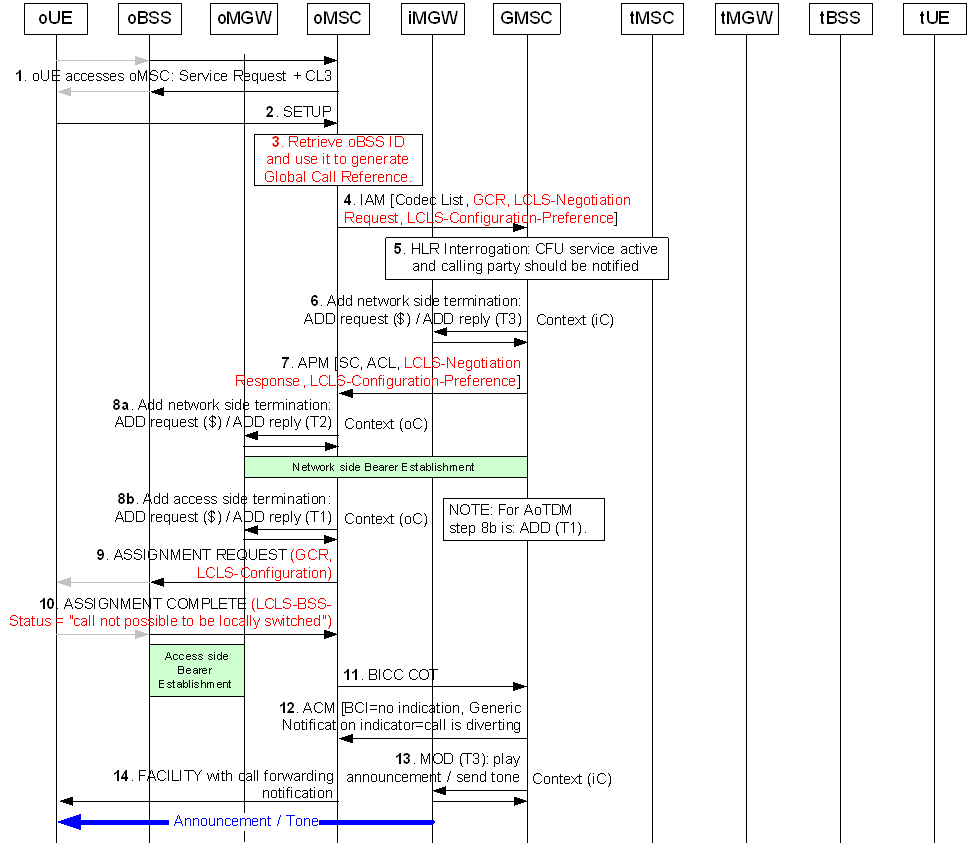
Step 1.
Service Request handling.
Step 2.
Originating Call SETUP.
Step 3.
If the oMSC server supports LCLS it retrieves the oBSS ID and generates the Global Call Reference for the call.
Step 4.
The oMSC server sends the IAM message including supported codecs list, GCR with encapsulated oBSS ID, the LCLS-Negotiation Request IE and the LCLS-Configuration-Preference IE.
Step 5.
The GMSC server determines that call should be forwarded because of the Call Forwarding Unconditional supplementary service and that notification should be send towards the calling party (oUE).
Step 6.
Since bearer must be established for the announcement/tone to be sent to the calling party the GMSC server selects the MGW and requests the seizure of the incoming network side bearer termination (T3).
Step 7.
The GMSC server transfers the APM message with the selected codec and since LCLS is supported the currently negotiated LCLS-Negotiation Response IE and the LCLS-Configuration-Preference IE.
Step 8a.
When the bearer information is received the oMSC server requests the seizure of the network side bearer termination (T2).
Step 8b.
After the network side bearer information is seized the oMSC server requests the seizure of the access side
bearer termination (T1).
During the seizure of the network side or the access side bearer termination the oMSC server will also request the oMGW to through-connect the bearer terminations so that the bearer will be backward through-connected.
Step 9.
The oMSC server determines whether LCLS is allowed in the core network based on the returned LCLS-Negotiation IE and if so the oMSC server includes the LCLS-Configuration IE in the ASSIGNMENT REQUEST message along with the GCR IE.
Step 10.
The oBSS returns the ASSIGNMENT COMPLETE message with the LCLS-BSS-Status IE indicating "call not possible to be locally switched".
Step 11.
When the access assignment is completed the oMSC server sends the Continuity (COT) message to the GMSC server.
Step 12.
The GMSC server sends the ACM message with the Generic Notification Indicator parameter set to "Call is diverting".
Step 13.
The GMSC server provides the iMGW with the announcement/tone identification and requests the iMGW to notify the announcement/tone completion using the Play Announcement or Send Tone procedure.
Step 14.
The oMSC server notifies the calling user (oUE) about call forwarding.
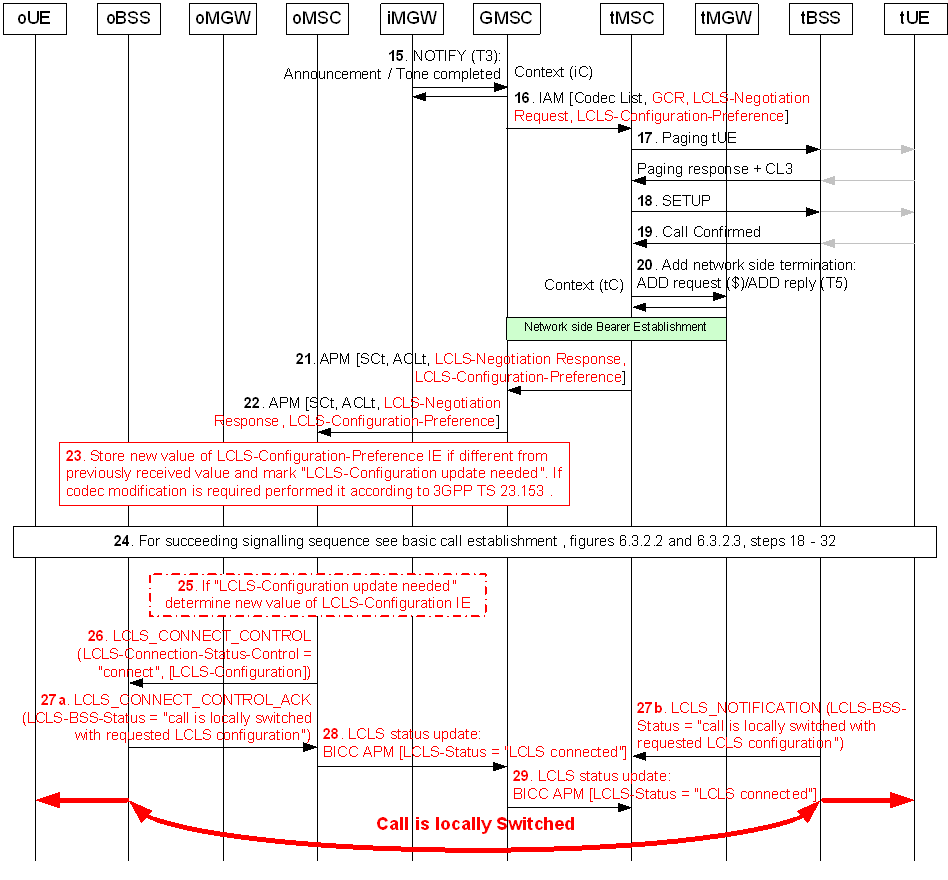
Figure 13.4.2.5.2.2: CFU, Call Establishment Flow (continuation of Figure 13.4.2.5.2.1)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 15.
The iMGW notifies the GMSC server when the announcement/tone is completed using the Announcement Completed or Tone Completed procedure.
Step 16.
If the GMSC server supports LCLS it may modify the LCLS-Negotiation Request IE and the LCLS-Configuration-Preference IE before sending the IAM message containing the GCR with the encapsulated oBSS ID, the LCLS-Negotiation Request IE and the LCLS-Configuration-Preference IE.
Step 17.
The tMSC server pages the forwarded-to subscriber (tUE).
Step 18.
The tMSC server performs call Setup.
Step 19.
The tUE confirms the call.
Step 20.
The tMSC server requests the tMGW to prepare for the network side bearer establishment (T5).
Step 21.
After the tMGW has replied with the bearer address and the binding reference the tMSC server returns the APM message with the selected codec and if LCLS is supported, the LCLS-Negotiation Response IE and the LCLS-Configuration-Preference IE.
Step 22.
The GMSC server transfers the APM message with the LCLS-Negotiation Response IE and the LCLS-Configuration-Preference IE. If codec modification is required then the GMSC server initiates codec negotiation according to TS 23.153, and includes the codec related information within the same APM message.
Step 23.
Based on the returned LCLS-Negotiation Response IE and the LCLS-Configuration-Preference IE the oMSC server determines whether LCLS is allowed in the core network and if LCLS-Configuration update is needed.
If codec modification is required then the oMSC server performs codec negotiation according to TS 23.153.
Step 24.
When performing further call establishment the procedure between the calling subscriber (oUE) and the forwarded-to subscriber (tUE) is the same as specified in steps 18 - 32 of Figure 6.3.2.1.
Step 25.
Since the received ANM message indicated "LCLS is feasible but not yet connected" the oMSC server checks if LCLS-Configuration updated is needed and if so the oMSC server calculates the new LCLS-Configuration value based on the latest received LCLS-Negotiation IE.
Step 26.
The oMSC server requests the oBSS to connect LCLS and if configuration updated is needed, it includes the LCLS-Configuration IE in the LCLS_CONNECT_CONTROL message.
Step 27a.
Since the BSS has received the through connect request for both call legs the oBSS returns the LCLS_CONNECT_CONTROL_ACK message with the LCLS-BSS-Status IE set to "the call is locally switched with requested LCLS configuration".
Step 27b.
Since the BSS has received the through connect request for both call legs the tBSS signals the LCLS status change by sending the LCLS_NOTIFICATION message with the LCLS-BSS-Status IE set to "the call is locally switched with requested LCLS configuration".
Step 28.
The oMSC server signals the change of the LCLS status through the Core Network by sending the APM message with the LCLS-Status IE set to "LCLS connected".
Step 29.
The iMSC server transfers the change of the LCLS status to the tMSC server.