Content for TS 23.273 Word version: 18.6.0
1…
4…
4.2…
4.2a…
4.3…
5…
5.5…
6…
6.1.2
6.1.3
6.1.4
6.2
6.3…
6.3.2…
6.4
6.5…
6.7…
6.7.3
6.7.4
6.7.5
6.8
6.9…
6.10…
6.11…
6.12…
6.13…
6.14…
6.15…
6.16…
6.17…
6.18…
6.19…
6.19.3…
6.20…
6.20.4…
6.21…
7…
8…
A…
B…
C…
6.14 Procedures for Broadcast of Assistance Data
6.14.1 Broadcast of Assistance Data by an LMF
6.14.2 Delivery of Ciphering Keys to UEs for Broadcast Assistance Data
...
...
6.14 Procedures for Broadcast of Assistance Data p. 106
6.14.1 Broadcast of Assistance Data by an LMF p. 106
The following procedure is used by the LMF to support broadcasting of network assistance data to target UEs. This procedure is not associated with a UE location session. It is used in an AMF to send network assistance data to an NG-RAN node for broadcasting by the NG-RAN node to target UEs. NG-RAN positioning procedures related to LMF and NG-RAN node communication are specified in TS 38.455.
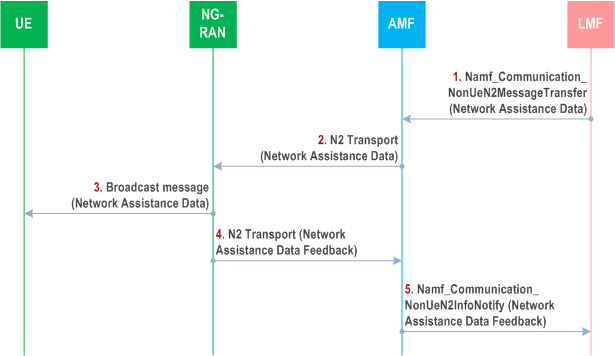
Step 1.
The LMF invokes the Namf_Communication_NonUeN2MessageTransfer service operation towards the AMF to request the transfer of a Network Assistance Data message to an NG-RAN node (gNB or ng-eNB) in the NG-RAN. The service operation includes the Network Assistance Data message and the target NG-RAN node identity. The Network Assistance Data message includes assistance data which may be optionally ciphered. LMF may send one or multiple sets of GNSS assistance data to the target NG-RAN node.
LMF receives the GNSS assistance data by means of describing in clause 6.15, or other means not specified in the present document.
Step 2.
The AMF forwards the Network Assistance Data message to the target NG-RAN node indicated in step 1 in an N2 Transport message. The AMF includes a Routing identifier, in the N2 Transport message, identifying the LMF.
Step 3.
The NG-RAN node broadcasts the assistance data contained in the Network Assistance Data message.
Step 4.
The target NG-RAN node may return feedback on assistance information broadcasting to the AMF in a Network Assistance Feedback message. The target NG-RAN node shall also include the Routing identifier in the N2 Transport message received in step 2.
Step 5.
The AMF invokes the Namf_Communication_NonUeN2InfoNotify service operation towards the LMF indicated by the routing identifier received in step 4. The service operation includes the Network Assistance Data Feedback message received in step 4.
6.14.2 Delivery of Ciphering Keys to UEs for Broadcast Assistance Data p. 107
The following procedure is used by the LMF and the AMF to distribute ciphering keys to UEs to enable UEs to decipher broadcast assistance data that was ciphered by the LMF. This procedure is not associated with a UE location session. The procedure makes use of the Registration procedure defined in TS 23.502.
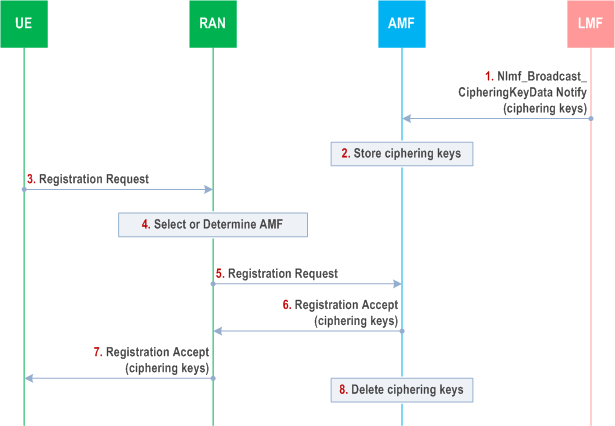
Step 1.
The LMF invokes the Nlmf_Broadcast_CipheringKeyData Notify service operation towards the AMF carrying one or more ciphering keys used to cipher network assistance data that is broadcast to UEs according to the procedure in clause 6.14.1. For each ciphering key, the LMF includes a ciphering key value, a ciphering key identifier, a validity period, a set of applicable tracking areas and a set of applicable types of broadcast assistance data.
Step 2.
The AMF stores the ciphering keys including the validity periods, applicable tracking areas and the types of applicable broadcast assistance data.
Step 3.
A UE sends a Registration Request to a RAN node. The Registration Request may be sent as part of normal mobility management, A Registration Request may also be sent specifically to request and obtain ciphering keys. The UE includes in the Registration Request an indication that ciphering keys are requested. Other details of the Registration Request are as defined in TS 23.502.
Step 4.
The RAN node selects the AMF if the UE is in CM IDLE state or determines the AMF for CM CONNECTED state.
Step 5.
The RAN node forwards the Registration Request to the AMF.
Step 6.
The AMF returns a Registration Accept to the RAN node as defined in TS 23.502. If the UE is subscribed to receive ciphered broadcast data, the AMF includes in the Registration Accept one or more ciphering keys applicable to the current tracking area for the UE. The AMF also includes for each ciphering key the ciphering key value, the ciphering key identifier, the validity period, the set of applicable tracking areas and the set of applicable types of broadcast assistance data.
Step 7.
The RAN node forwards the Registration Accept to the UE. The UE may start to use each ciphering key to decipher network assistance data that is broadcast according to the procedure in clause 6.14.1 once the validity period for the ciphering key has started and if the UE is currently in an applicable tracking area. The UE shall cease using a ciphering key when entering a tracking area not applicable to the ciphering key. The UE shall cease using and shall delete a ciphering key when the validity period for the ciphering key has expired.
Step 8.
The AMF deletes all information for a ciphering key when the validity period has expired.