Content for TS 23.273 Word version: 18.6.0
1…
4…
4.2…
4.2a…
4.3…
5…
5.5…
6…
6.1.2
6.1.3
6.1.4
6.2
6.3…
6.3.2…
6.4
6.5…
6.7…
6.7.3
6.7.4
6.7.5
6.8
6.9…
6.10…
6.11…
6.12…
6.13…
6.14…
6.15…
6.16…
6.17…
6.18…
6.19…
6.19.3…
6.20…
6.20.4…
6.21…
7…
8…
A…
B…
C…
6.17 Procedures applicable to a PRU
6.17.1 PRU Association Procedure
6.17.2 LMF Initiated PRU Disassociation Procedure
6.17.3 PRU Initiated PRU Disassociation Procedure
6.17.4 Positioning of a target UE
...
...
6.17 Procedures applicable to a PRU |R18| p. 113
6.17.1 PRU Association Procedure p. 113
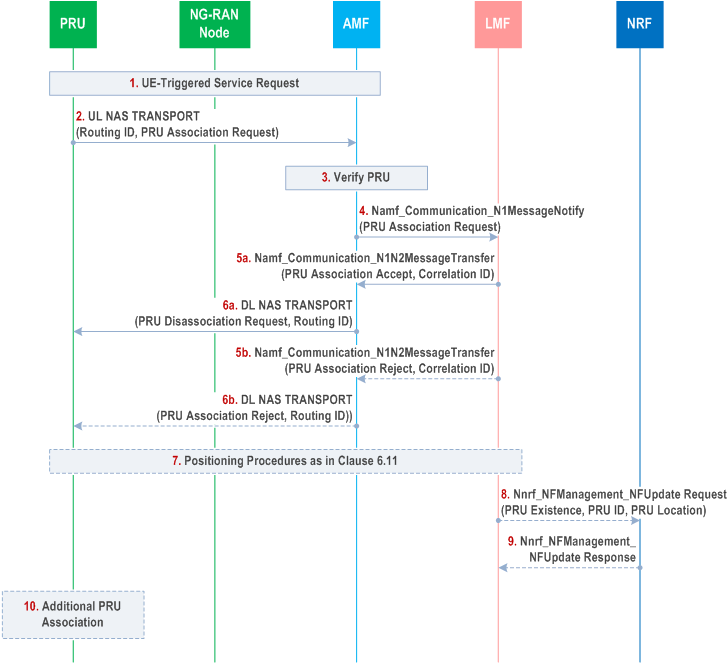
Figure 6.17.1-1 shows a procedure used by a PRU to associate as a PRU with a serving LMF. The procedure is used for initial PRU Association with the serving LMF which may occur when the PRU first starts to access the HPLMN. The procedure can also be used to perform a PRU Association update to inform the serving LMF of the continued availability of the PRU or to inform the serving LMF of some change to the PRU such as a change of location (e.g. a change of tracking area or change of serving AMF) or a change of the PRU positioning capabilities. The PRU shall only perform the Association procedure in the HPLMN.
Precondition:
The PRU is currently registered in the HPLMN. For initial PRU Association, a Routing Identifier may have been configured in the PRU indicating the serving LMF. For subsequent PRU Association, a Routing ID indicating a serving LMF has been returned to the PRU at step 6a or 6b of a previous PRU Association procedure.
Step 1.
The PRU performs a UE Triggered Service Request if in CM IDLE state.
Step 2.
The PRU sends a supplementary services PRU Association Request to the serving AMF in an UL NAS TRANSPORT message and includes any preconfigured Routing ID for an initial Association or the Routing ID if received at step 6a or step 6b for a previous PRU Association procedure. The PRU Association Request is included in the UL NAS TRANSPORT message at the NAS level. The PRU Association Request includes a reason for the PRU Association (e.g. initial PRU Association, or PRU Association update), the PRU's positioning capabilities, location information (if known) or PRU ON/OFF state.
Step 3.
The AMF verifies whether the sender of the PRU Association Request is a PRU using subscription information from the UDM. AMF verifies based on subscription information or local policy if PRU can work as stationary PRU.
Step 4.
The AMF selects the serving LMF based on the criteria defined in clause 5.1 or one of the Routing ID if included in the UL NAS TRANSPORT message of step 2. The AMF may override the Routing ID based on criteria of clause 5.1. The AMF transfers the PRU Association Request to the serving LMF using an Namf_Communication_N1MessageNotify service operation. The AMF includes in the Namf_Communication_N1MessageNotify service operation an indication of whether the request corresponds to a PRU subscription and indication if PRU is stationary. The AMF also includes the SUPI, TAI and cell ID of the PRU.
Step 5a.
If the AMF indicates in step 4 that the request corresponds to a PRU and if the LMF can accept the PRU Association, the serving LMF returns a PRU Association Accept, as a supplementary services message, using Namf_Communication_N1N2MessageTransfer service operation towards the AMF, and a Correlation ID. The Correlation ID is assigned by the serving LMF to identify the serving LMF and optionally the PRU. The PRU Association Accept indicates conditions for performing PRU Association updates with the serving LMF which may include a periodic PRU Association update timer and PRU Association update based on a change of PRU location, change of PRU TAI, change of serving AMF, or change of PRU ON/OFF state. For a PRU whose state is OFF, PRU information is kept at the serving LMF.
Step 6a.
The serving AMF forwards the PRU Association Accept and a Routing ID equal to the Correlation ID to the PRU in a DL NAS TRANSPORT message. The PRU stores the Routing ID which is used for any further PRU Association update with the serving LMF. This Routing ID overrides any Routing ID used in previous Association updates, if any.
Step 5b.
If the AMF indicates in step 4 that the request does not correspond to a PRU subscription or if the serving LMF cannot accept the PRU Association for some other reason (e.g. the serving LMF is not the correct serving LMF for the PRU), the serving LMF returns a PRU Association Reject message, using Namf_Communication_N1N2MessageTransfer service operation towards the AMF, and may include the Routing ID of a new serving LMF if the request at step 4 corresponds to a PRU.
Step 6b.
The serving AMF forwards the PRU Association Reject in a DL NAS TRANSPORT message to the PRU.
Step 7.
If PRU Association is performed successfully as in steps 5a and 6a, the serving LMF may optionally verify any PRU location provided at step 4 or obtain a more accurate location of the PRU using the procedures defined in clause 6.11. The LMF also stores information received for the PRU. If PRU Association update including only a state change is performed, the serving LMF may consider the previously verified PRU location is valid.
Step 8.
If PRU Association is performed successfully as in steps 5a and 6a and if this is an initial PRU Association or if this is a PRU Association update and information for the PRU has changed and if PRU is stationary the serving LMF may optionally instigate an Nnrf_NFManagement_NFUpdate Request service operation towards an NRF and includes an existence indication of a PRU associated with a TAI.
The LMF also indicates to the NRF to remove the TAI associated existence of PRU(s) when there are no longer any PRUs associated in the LMF for this TAI.
Step 9.
If step 8 requested by LMF the NRF returns a confirmation response to the serving LMF.
Step 10.
After being rejected at step 6b, if there are new available Routing ID(s), the PRU may perform a PRU Association procedure with the new serving LMF.
6.17.2 LMF Initiated PRU Disassociation Procedure p. 115
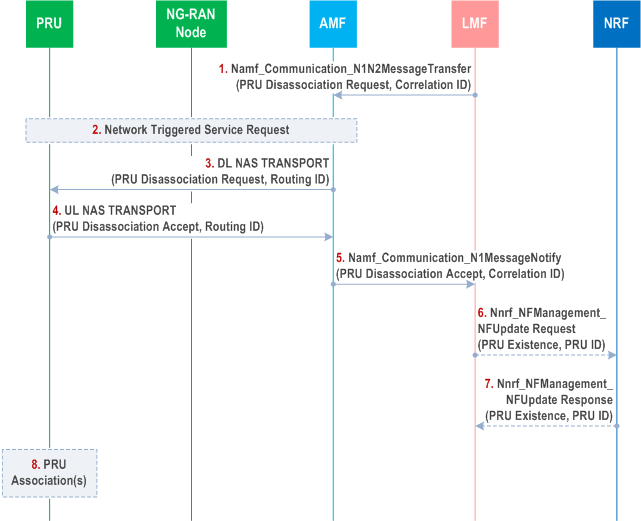
Figure 6.17.2-1 shows a procedure used by a serving LMF to disassociate an already associated PRU. The procedure may be used prior to the serving LMF becoming unavailable (e.g. for maintenance, removal or replacement) or to transfer the PRU to a different serving LMF for other reasons.
Precondition:
The PRU has previously associated with the serving LMF using the procedure in clause 6.17.1.
Step 1.
The serving LMF sends a PRU Disassociation Request as a supplementary services message, using the Namf_Communication_N1N2MessageTransfer service operation, and a Correlation ID identifying the serving LMF. The PRU Disassociation Request may include a Routing ID for a new serving LMF.
Step 2.
If the PRU is in CM IDLE state, the serving AMF performs a Network Triggered service request to place the PRU in CM CONNECTED state.
Step 3.
The serving AMF forwards the PRU Disassociation Request and a Routing ID equal to the Correlation ID to the PRU using DL NAS TRANSPORT message.
Step 4.
The PRU returns a supplementary services PRU Disassociation Accept to the serving AMF in an UL NAS TRANSPORT message and includes the Routing ID received in step 3.
Step 5.
The serving AMF forwards the PRU Disassociation Accept to the serving LMF indicated by the Routing ID received at step 4 and includes a Correlation ID equal to the Routing ID.
Step 6.
If the serving LMF has indicated the PRU to an NRF during PRU Association and if serving LMF does not have any PRU to the TAI, the serving LMF issues an Nnrf_NFManagement_NFUpdate Request service operation towards the NRF and requests an indication of PRU removal. The NRF then removes the TAI associated PRU existence indication.
Step 7.
The NRF returns a confirmation response to the serving LMF.
Step 8.
If the PRU received a new Routing ID for a new serving LMF at step 3, the PRU may perform a PRU Association with the new serving LMF as described in clause 6.17.1.
6.17.3 PRU Initiated PRU Disassociation Procedure p. 116
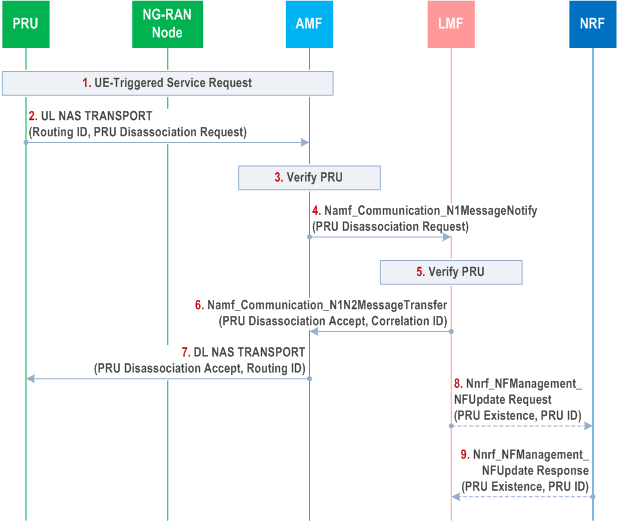
Figure 6.17.3-1 shows a procedure used by a PRU to disassociate from a serving LMF. The procedure may be used prior to the PRU becoming unavailable (e.g. for a software upgrade or power down) or when the PRU will be transferred to a different serving LMF.
Precondition:
The PRU has previously associated with the serving LMF using the procedure in clause 6.17.1 and is currently registered in the HPLMN.
Step 1.
The PRU performs a UE Triggered Service Request if in CM IDLE state.
Step 2.
The PRU sends a supplementary services PRU Disassociation Request to the serving AMF in an UL NAS TRANSPORT message and includes the Routing ID received at step 6a for the procedure in clause 6.17.1 for a previous PRU Association procedure. The PRU also indicates whether an acknowledgment is expected. The PRU Disassociation Request is included in the UL NAS TRANSPORT message at the NAS level.
Step 3.
The AMF verifies whether the sender of the PRU Disassociation Request is a PRU using subscription information from the UDM.
Step 4.
The AMF selects the serving LMF based on the Routing ID and optionally the current TAI and transfers the PRU Disassociation Request to the serving LMF using an Namf_Communication_N1MessageNotify service operation. The AMF includes in the Namf_Communication_N1MessageNotify service operation an indication of whether the sender of the PRU Disassociation Request is a PRU. The AMF also includes the SUPI of the PRU.
Step 5.
The serving LMF verifies that the PRU is currently associated in the serving LMF. If the PRU is not currently associated in the serving LMF, the serving LMF performs steps 6 and 7 but not steps 8 and 9.
Step 6.
If the PRU has indicated that an acknowledgment is expected, the serving LMF returns a PRU Disassociation Accept, as a supplementary services message, using an Namf_Communication_N1N2MessageTransfer service operation towards the AMF, and a Correlation ID.
Step 7.
The serving AMF forwards the PRU Disassociation Accept and a Routing ID equal to the Correlation ID to the PRU in a DL NAS TRANSPORT message.
Step 8.
If the serving LMF has indicated the PRU to an NRF during a previous PRU Association and if serving LMF does not have any PRU to the TAI, the serving LMF invokes an Nnrf_NFManagement_NFUpdate Request service operation towards the NRF and requests an indication of PRU removal. The NRF then removes the TAI associated PRU existence indication.
Step 9.
The NRF returns a confirmation response to the serving LMF.
6.17.4 Positioning of a target UE p. 117
Figure 6.17.4-1 shows a procedure used by a serving LMF for a target UE to obtain a location of the target UE using location information provided by one or more PRUs.
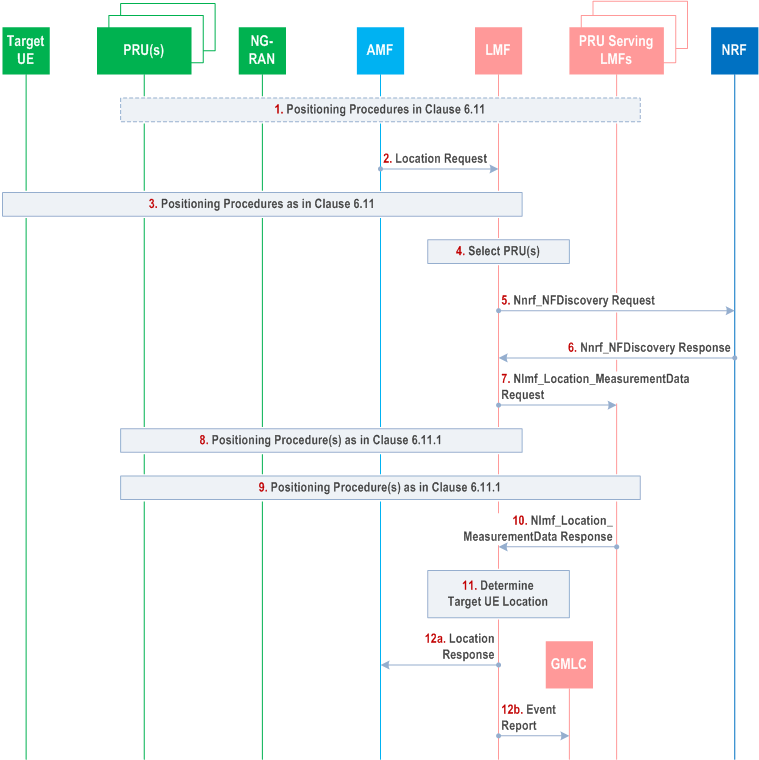
Step 1.
The serving LMF for the target UE and other PRU serving LMFs may use the procedures defined in clause 6.11 to obtain location information from one or more PRUs associated in the serving LMF and in the other PRU serving LMFs that is not related to the target UE. For example, the location information may include location information for the PRU(s) or for the NG-RAN or both.
Step 2.
The serving LMF for the target UE receives a location request from the serving AMF for the target UE. The location request may be included in an Nlmf_Location_DetermineLocation Request service operation for a 5GC-MO-LR, 5GC-MT-LR or 5GC-NI-LR for the target UE. Alternatively, the location request may be implied by receipt of an Namf_Communication_N1MessageNotify service operation carrying a supplementary services event report from the target UE for a periodic or triggered 5GC-MT-LR.
Step 3.
The serving LMF uses the procedures defined in clause 6.11 to obtain location information for the target UE from the target UE and/or from the NG-RAN and may determine pre-calculated location of target UE. During the procedures, the LMF decides to use PRUs to improve the positioning result.
Step 4.
The serving LMF selects one or more PRUs associated with the serving LMF based on the PRU ON/OFF state information to assist in locating the target UE. The selected PRU(s) may be nearby to an initial location estimate for the target UE obtained at step 3 or indicated by a serving cell identifier for the target UE received at step 2.
Step 5.
The serving LMF may optionally invoke an Nnrf_NFDiscovery Request service operation to an NRF. The service operation includes a PRU indication and an area which could be TAs decided by the serving LMF of the target UE based on the serving cell of the target UE.
Step 6.
If step 5 is performed, the NRF selects one or more other PRU serving LMFs based on the PRU indication and the area received in step 5 and sends an Nnrf_NFDiscovery Response to the serving LMF of target UE. The service operation includes the profiles of the other PRU serving LMFs selected by the NRF.
Step 7.
If steps 5 and 6 are performed, the serving LMF of the target UE may send an Nlmf_Location_MeasurementData Request service operation to one or more of the other PRU serving LMFs indicated at step 6. The service operation for each of the other PRU serving LMFs includes target UE cell ID or pre-calculated location of target UE in step 3 and may include time windows for scheduling of PRU measurements.
Step 8.
The serving LMF uses the procedure defined in clause 6.11.1 to obtain location information (e.g. PRU location coordinates, associated location quality/uncertainty of the PRU together with any performed location measurements) related to the target UE from the PRU(s) selected at step 4.
Step 9.
If steps 5-7 are performed and if PRU information is included in the PRU serving LMF profile sent by the NRF to the target UE serving LMF, each of the other PRU serving LMFs for step 7 uses the procedure defined in clause 6.11.1 to obtain the location measurements and/or location requested at step 7 from each of the PRUs identified at step 7 for this LMF.
If steps 5-7 are performed PRU serving LMFs for step 7 selects one or more PRUs based on the locally associated PRU information and information in the location measurements requested (the target UE cell ID, or pre-calculated location of target UE), and uses the procedure defined in clause 6.11.1 to obtain the location measurements requested at step 7 from each of the selected PRUs.
Step 10.
If step 9 is performed, each of the other PRU serving LMFs for step 9 returns the location measurements and the known PRU location obtained from PRUs at step 9 to the serving LMF for the target UE.
Step 11.
The serving LMF for the target UE determines the location of the target UE based on the location information obtained at step 1 (if step 1 is performed), step 3, step 8 and step 10.
Step 12a.
If an Nlmf_Location_DetermineLocation Request service operation for a 5GC-MO-LR, 5GC-MT-LR or 5GC-NI-LR was received at step 2, the serving LMF returns the location estimate of the target UE to the serving AMF.
Step 12b.
If an Namf_Communication_N1MessageNotify service operation carrying a supplementary services event report from the target UE for a periodic or triggered 5GC-MT-LR was received at step 2, the serving LMF sends an event report for the target UE to a GMLC with the location estimate obtained at step 11 as described in clause 6.3.1.