Content for TS 23.222 Word version: 19.2.0
0…
4…
5…
6…
6.3…
6.4…
7…
8…
8.5…
8.8…
8.9…
8.13…
8.17…
8.21…
8.25…
8.26…
8.28…
8.30…
9…
10…
10.4…
10.7…
11…
A
B…
B.2…
B.3…
C…
D…
8.30 Deregistering the API provider domain functions on the CAPIF
8.30.1 General
8.30.2 Information flows
8.30.2.1 Deregistration request
8.30.2.2 Deregistration response
8.30.3 Procedure
8.31 API invoker obtaining authorization from resource owner
8.31.1 General
8.31.2 Information flows
8.31.3 Procedure
8.32 Reducing authorization information inquiry in a nested API invocation
8.32.1 General
8.32.2 Information flows
8.32.3 Procedure
...
...
8.30 Deregistering the API provider domain functions on the CAPIF |R16| p. 97
8.30.1 General p. 97
The procedure in this subclause corresponds to the architectural requirements for deregistering the API provider domain functions on the CAPIF. This procedure deregisters the API provider domain functions as authorized users of the CAPIF functionalities.
8.30.2 Information flows p. 97
8.30.2.1 Deregistration request p. 97
Table 8.30.2.1-1 describes the information flow, deregistration request, from the API management function to the CAPIF core function.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Security information | M | Information for CAPIF core function to validate the deregistration request |
8.30.2.2 Deregistration response p. 97
Table 8.30.2.2-1 describes the information flow, deregistration response, from the CAPIF core function to the API management function.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Result | M | Indicates the success or failure of the deregistration operation |
8.30.3 Procedure p. 97
Figure 8.30.3-1 illustrates the procedure for deregistering API provider domain functions on the CAPIF core function.
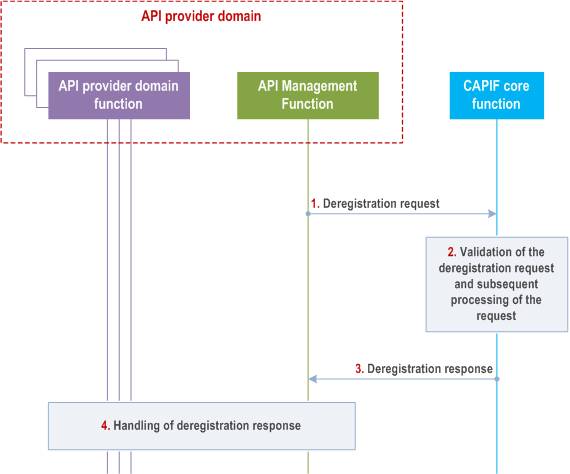
Step 1.
For deregistration of API provider domain functions on the CAPIF core function, the API management function sends a deregistration request to the CAPIF core function.
Step 2.
The CAPIF core function validates the received request and processes the deregistration request.
Step 3.
The CAPIF core function sends a deregistration response message to the API management function.
Step 4.
The API management function processes the deregistration to the individual API provider domain functions.
8.31 API invoker obtaining authorization from resource owner |R18| p. 98
8.31.1 General p. 98
CAPIF may authorize the API invoker to invoke the service API based on the authorization information from the resource owner given before the API invocation.
Clause 8.31.3 shows the procedure for obtaining the authorization information.
8.31.2 Information flows p. 98
8.31.3 Procedure p. 98
Figure 8.31.3-1 illustrates the procedure for API invoker obtaining authorization from resource owner.
Pre-conditions:
- The resource owner function can communicate with the API invoker.
- The service API access requires obtaining authorization from resource owner.
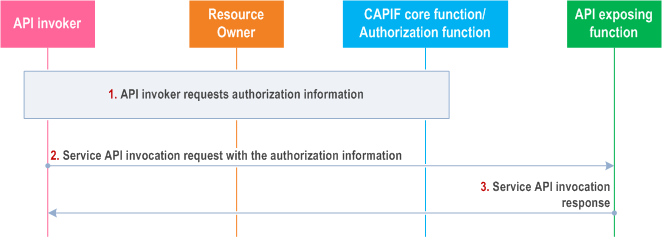
Step 1.
The API invoker requests to obtain resource owner authorization information to invoke the service API exposed by the API exposing function. The authorization function provides the authorization by interacting with the resource owner via the resource owner function.
Step 2.
The API invoker sends service API invocation request to the API exposing function with the resource owner authorization information received in step 1.
Step 3.
The API invoker receives the service API invocation response resulting from the service API invocation once the API exposing function has checked whether the API invoker is authorized to invoke that service API based on the authorization information.
8.32 Reducing authorization information inquiry in a nested API invocation |R18| p. 99
8.32.1 General p. 99
The nested API invocation scenario is a scenario where an API invocation towards a first API exposing function triggers that API exposing function to request an API invocation towards a second API exposing function, which is in the same API provider domain as the first API exposing function. This scenario addresses the situation in which a service API may require the services of other service APIs. For example, if the API invoker invokes SEAL SS_LocationInfoRetrieval API (clause 9.4.4 of TS 23.434), the location management server (acting as an API exposing function for the API invoker and as an API invoker for the NEF) may invoke NEF API to retrieve UE location information from 5GC. In this scenario, the CAPIF may reduce the authorization information inquiries for a nested API invocation using procedure described in clause 8.32.3.
8.32.2 Information flows p. 99
8.32.3 Procedure p. 99
Figure 8.32.3-1 illustrates the procedure to obtain authorization information in a nested API invocation, in which an API exposing function receiving the service API invocation request interacts with another API exposing function to provide the service.
Pre-conditions:
- The resource owner function can communicate with the API invoker.
- The API exposing functions 1 and 2 are in the same trust domain.
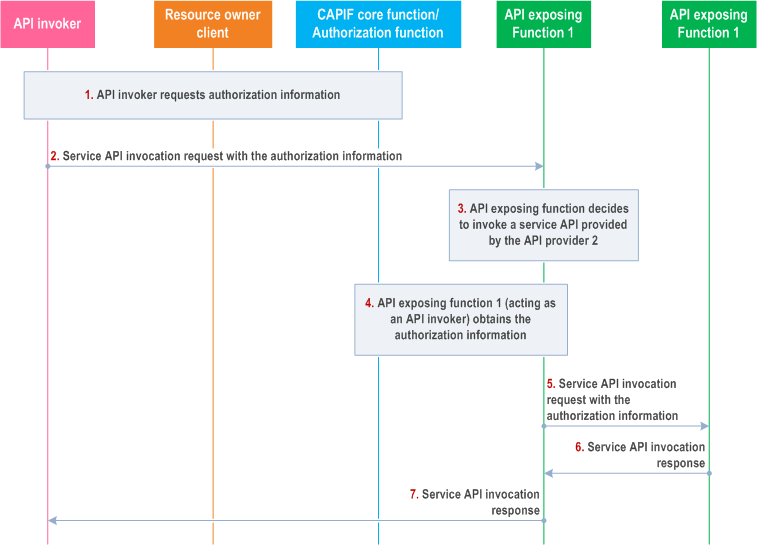
Step 1.
The API invoker requests authorization information to invoke the service API exposed by API exposing function 1.
Step 2.
The API invoker sends a service API invocation request to API exposing function 1 with the authorization information received in step 1.
Step 3.
Based on the service API invocation request, API exposing function 1 decides to invoke another service API exposed by API exposing function 2.
Step 4.
API exposing function 1, acting as an API invoker, obtains from the CCF the authorization information to access the service API exposed by API exposing function 2.
Step 5.
API exposing function 1, acting as an API invoker sends a service API invocation request to API exposing function 2 with the authorization information received in step 4.
Step 6.
The API exposing function 1 receives the service API invocation response resulting from the service API invocation once API exposing function 2 has checked whether the API invoker is authorized to invoke that service API based on the authorization information.
Step 7.
The API invoker receives the service API invocation response resulting from the service API invocation.