Content for TS 23.222 Word version: 19.2.0
0…
4…
5…
6…
6.3…
6.4…
7…
8…
8.5…
8.8…
8.9…
8.13…
8.17…
8.21…
8.25…
8.26…
8.28…
8.30…
9…
10…
10.4…
10.7…
11…
A
B…
B.2…
B.3…
C…
D…
8.26 Update API invoker's API list
8.26.1 General
8.26.2 Information flows
8.26.2.1 Update API invoker API list request
8.26.2.2 Update API invoker API list response
8.26.3 Procedure
8.27 Dynamically routing service API invocation
8.27.1 General
8.27.2 Information flows
8.27.2.1 Obtain routing information request
8.27.2.2 Obtain routing information response
8.27.3 Procedure
...
...
8.26 Update API invoker's API list |R16| p. 90
8.26.1 General p. 90
The procedure in this subclause corresponds to the architectural requirements for updating the API invoker's API list on the CAPIF core function. The CAPIF enables API invoker to update its own API list e.g. subsequent to discovering new API(s).
8.26.2 Information flows p. 90
8.26.2.1 Update API invoker API list request p. 90
Table 8.26.2.1-1 describes the information flow update API invoker API list request from the API invoker to the CAPIF core function.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| API invoker identity information | M | Identity information of the API invoker requesting update |
| APIs for update | M | List of APIs that need update (e.g. enroll new API(s), disenroll API(s)). |
8.26.2.2 Update API invoker API list response p. 90
Table 8.26.2.2-1 describes the information flow update API invoker API list response from the CAPIF core function to the API invoker.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Result | M | Indicates the completely successful or partially successful or failure of the update operation |
| API information | O (see NOTE 1) | List of APIs and the categories of service APIs that the API invoker can access. |
| Reason | O (see NOTE 2) | This element indicates the reason when update status is failure and for which API(s). |
|
NOTE 1:
Information element shall be present when update API invoker API list status is partial or completely successful.
NOTE 2:
Information element shall be present when update API invoker API list status is partial successful or failure.
|
||
8.26.3 Procedure p. 91
Figure 8.26.3-1 illustrates the procedure for updating the API invoker API list on the CAPIF.
Pre-conditions:
- The API invoker has been onboarded as a recognized user of the CAPIF and associated API invoker profile is provisioned.
- The API invoker has visibility to new APIs information (e.g. updates on API catalogue or dashboard, API discovery).
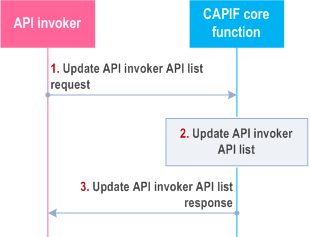
Step 1.
For updating of the API invoker API list on the CAPIF, the API invoker triggers update API invoker API list request towards the CAPIF core function, providing the information to be updated (e.g. enroll new APIs, disenroll APIs).
Step 2.
The CAPIF core function updates the API invoker API list of the requesting API invoker, according to the grant from the CAPIF administrator or the API management.
Step 3.
The update API invoker API list response provides partial success or complete success or failure indication. Partial success and complete success result will include APIs information that the API invoker can access. When the update status is failure, the reason for failure and information for which API(s) the update operation has failed is included.
8.27 Dynamically routing service API invocation |R16| p. 92
8.27.1 General p. 92
The procedure in this subclause corresponds to the architectural requirements for dynamic routing of service API invocation. The CAPIF enables dynamically routing the service API invocation request based on the detailed information of the invocation.
8.27.2 Information flows p. 92
8.27.2.1 Obtain routing information request p. 92
Table 8.27.2.1-1 describes the information flow dynamic routing information request from the API exposing function to the CAPIF core function.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Service API identification | M | The identification information of the service API for which invocation is requested. The service API identification is part of the specific service API invocation request. |
| AEF identity information | M | Identity information of the entity requesting the routing information |
8.27.2.2 Obtain routing information response p. 92
Table 8.27.2.2-1 describes the information flow dynamic routing information response from the CAPIF core function to the API exposing function.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Service API identification information | M | The identification information of the service API for which invocation is requested. |
| Routing rule(s) information for service API invocation | M | Indicates the routing rule(s) for service API invocation, e.g., mapping of IP address range and AEF identity, or mapping of area serving the service API and AEF information. |
8.27.3 Procedure p. 92
Figure 8.27.3-1 illustrates the procedure for dynamically routing the service API invocation from the AEF acting as service communication entry point to the destination AEF for handling service API.
Pre-conditions:
- The API invoker has performed the service discovery and received the details of the service API which includes the information about the service communication entry point of the AEF-1 in the CAPIF.
- The API invoker is authenticated and authorized to use the service API.
- The AEF-1 iis the AEF acting as service communication entry point for the service API, and AEF-2 is one of the multiple destination AEF which provides the service API.
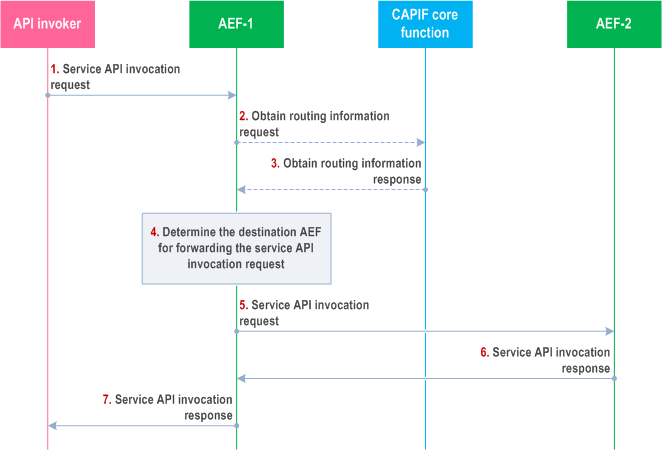
Step 1.
The API invoker performs service API invocation according to the interface of the service API by sending a service API invocation request towards the AEF-1 which exposes the service API towards the API invoker, and acts as topology hiding entity.
Step 2.
If the routing rule information for the service API invocation is not available, the AEF-1 sends obtain routing information request to the CAPIF core function.
Step 3.
The CAPIF core function creates routing rule information for the service API and sends obtain routing information response with the routing rule information.
Step 4.
The AEF-1 further resolves the actual destination of the service API address information (AEF-2) according to the routing rule information and the invocation parameters in service API invocation request.
Step 5.
The AEF-1 forwards the incoming service API invocation request to AEF-2.
Step 6.
The AEF-2 returns the service API invocation response to AEF-1.
Step 7.
The AEF-1 sends the service API invocation response to the API invoker.