Content for TS 23.203 Word version: 18.0.0
0…
4…
5…
6…
6.1.4…
6.1.7…
6.1.10…
6.1.17…
6.2…
6.2.2…
6.2.3…
6.3
6.4…
6.8…
7…
7.3…
7.4…
7.7…
7.7.3…
7.8…
A…
A.4…
D…
P…
P.4.2.4…
P.7…
P.7.5…
P.8
Q…
S…
S.7…
S.8.8
T…
P.7.5 Gateway Control Session Procedures
P.7.6 PCRF Discovery and Selection
P.7.7 BPCF Discovery and Selection
P.7.8 TDF Discovery and Selection for NS-WLAN offloaded traffic
...
...
P.7.5 Gateway Control Session Procedures p. 232
P.7.5.1 BBERF-Initiated Gateway Control Session Establishment p. 232
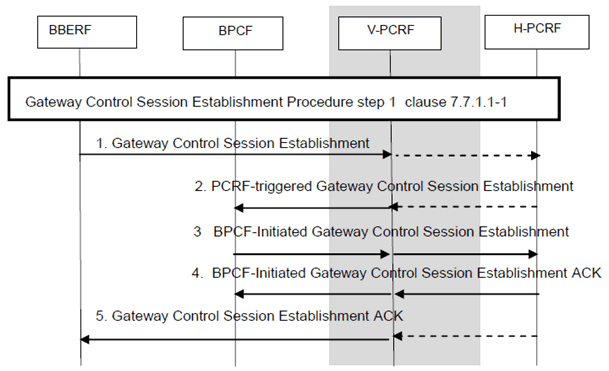
Figure P.7.5.1: PCRF-triggered Gateway Control Session Establishment for EPC routed traffic
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
This procedure is applicable for both WLAN and H(e)NB PMIP. This procedure is the same as described in clause 7.7.1.1 with the additions described below:
Step 1.
For the WLAN case, the ePDG (BBERF) initiates a Gateway Control Session Establishment as defined in clause 7.7.1 with the PCRF (for non-roaming) and with the V-PCRF (for home routed and visited access roaming cases) including the IMSI, APN (if available), the UE Local IP address, the UDP port number if available, while for H(e)NB case the SGW (BBERF) initiates a Gateway Control Session Establishment as defined in clause 7.7.1 with the PCRF (for non-roaming) and with V-PCRF (for home routed and visited access roaming case) including the H(e)NB local IP address and the UDP port number (if available) in the Fixed Broadband Access at which the H(e)NB is connected to.
Step 2.
For WLAN case, the PCRF (non-roaming case) or the V-PCRF (home routed and visited access roaming cases) triggers Gateway Control Session establishment with the BPCF over S9a, if this is the first Gateway Control Session for the same IMSI, the PCRF includes in the request message to BPCF the IMSI, the UE local IP address and the UDP port number (if available) and the ePDG IP address (for S2b-PMIP and untrusted S2c access).
For the H(e)NB case, the PCRF (non-roaming case) or the V-PCRF (home routed and visited access roaming cases) triggers Gateway Control Session establishment with the BPCF over S9a, if this is the first Gateway Control Session for the same H(e)NB, the PCRF includes in the request message to BPCF the IMSI, the H(e)NB IP address and the UDP port number (if available).
Step 3.
The BPCF Initiates the Gateway Control session establishment to the PCRF (for non-roaming case), to the V-PCRF (for visited access and home routed roaming case) including in the request message the IMSI. Triggered by the BPCF-initiated Gateway Control Session establishment over S9a the V-PCRF sends the Gateway Control Session Establishment over S9.
Step 4.
The PCRF in non-roaming and the V-PCRF for roaming cases reply message contains the result code.
Step 5.
For H(e)NB case, the PCRF provisions QoS Rules to the BBERF, while for the WLAN case, the PCRF sends a result code in the reply message.
No QoS Rules and no event triggers are provided to the BBERF for WLAN scenarios.
P.7.5.2 GW (BBERF)-Initiated Gateway Control Session Termination p. 233
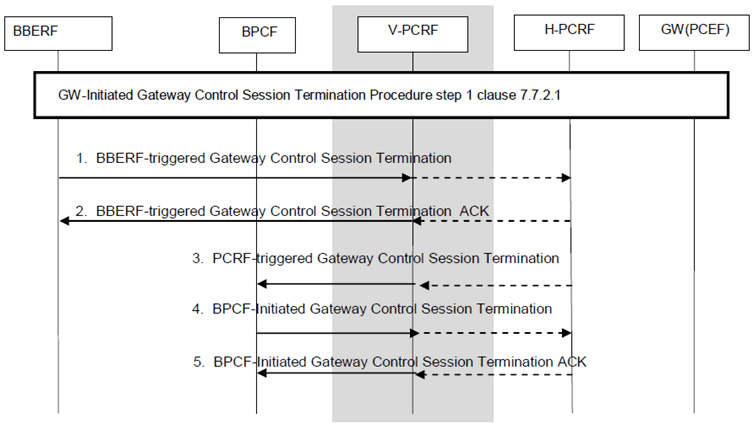
This procedure is applicable for both WLAN and H(e)NB scenarios. This procedure is the same as described in clause 7.7.2.1 with the additions described below:
Step 1.
For WLAN scenarios, the ePDG (BBERF) initiates a Gateway Control Session Termination with the PCRF (for non-roaming) and with the V-PCRF (for home routed and visited access roaming cases).
For H(e)NB scenarios, the SGW (BBERF) initiates a Gateway Control Session Termination as defined with the PCRF (for non-roaming) and with the V-PCRF (for home routed and visited access roaming cases).
Step 2.
The PCRF sends a response code.
Step 3.
The PCRF (non-roaming case) or the V-PCRF (roaming case) initiates a Gateway Control Session Termination over S9a with the BPCF to terminate the Gateway Control Session with the BPCF if this is the last Gateway Control Session bound to the Gateway Control session over S9a.
Step 4.
The BPCF terminates the Gateway Control Session over S9a to the PCRF. In the roaming scenario, V-PCRF (for both home routed and visited access) sends a Gateway Control Session Termination over S9 to the PCRF.
Step 5.
The PCRF sends a response code.
P.7.5.3 Gateway Control and QoS Rule Request from ePDG/Serving GW p. 234
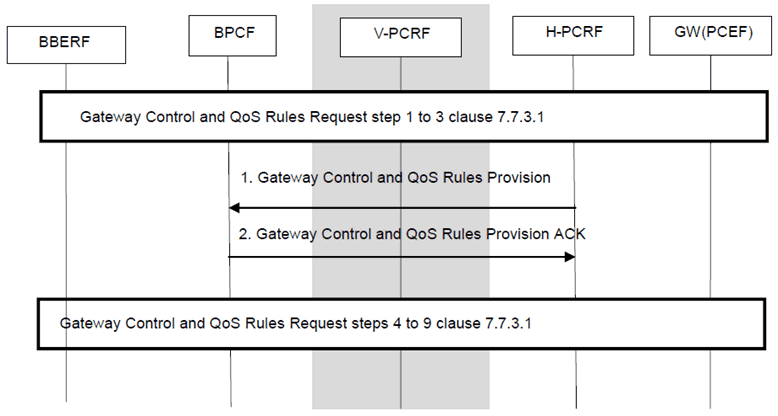
Figure P.7.5.3: Gateway Control and QoS Rule Request for EPC Routed Traffic
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
This procedure is applicable for both WLAN and H(e)NB PMIP. This procedure is the same as described in clause 7.7.3.1 with the exceptions described below:
In case 2b and case 2a for WLAN scenario, the ePDG (BBERF) may initiate a Gateway Control and QoS Rules Request Procedure to provide the updated UE local IP address and the UDP port number, if available, while for H(e)NB scenario the SGW (BBERF) may initiate a Gateway Control and QoS Rule Procedure to provide the updated H(e)NB local IP address and the UDP port number (if available) in the Fixed Broadband Access at which the H(e)NB is connected to.
Step 1.
For the WLAN scenario, triggered by the Gateway Control and QoS Rules Request Procedure in step 2 of clause 7.7.3.1, the PCRF (non-roaming case) or the v-PCRF (roaming case) initiates Gateway Control and QoS Rules Provision Procedure. The updated UE local IP address and/or the UDP port number are provided in the procedure if available, while for H(e)NB scenario the PCRF (non-roaming) or the H-PCRF (for visited access and home routed) may initiate a Gateway Control and QoS Rule Procedure to provide the updated H(e)NB local IP address and the UDP port number (if available) in the Fixed Broadband Access at which the H(e)NB is connected to.
For H(e)NB PMIP scenario, the PCRF may provide:
Step 2.
- QoS-Rule with the QoS control information (i.e. QCI, GBR, MBR, ARP) and SDF information.
- Information (e.g. Session ID) that allows the BPCF to associate the request with the existing Gateway Control Session on S9a so that the fixed access can identify the traffic plane resources that are affected.
The BPCF replies with a response code, when QoS Rules were provided by the PCRF, the BPCF translates the QoS rule as received of the S9a interface into access specific QoS parameters applicable in the BBF domain . The BPCF may respond with a "counter-offer" in form of acceptable bandwidth and/or QoS for one or more SDFs if it cannot provide the requested QoS from the PCRF. The BPCF provides the acceptable QoS in the BBF access using 3GPP QoS parameters on S9a interface (i.e. QCI, GBR) in the reply if the QoS validation for admission control fails. The PCRF may make a new policy decision, e.g. decide to modify or remove the affected QoS rules.
P.7.5.4 PCRF-Initiated Gateway Control Session Termination p. 235
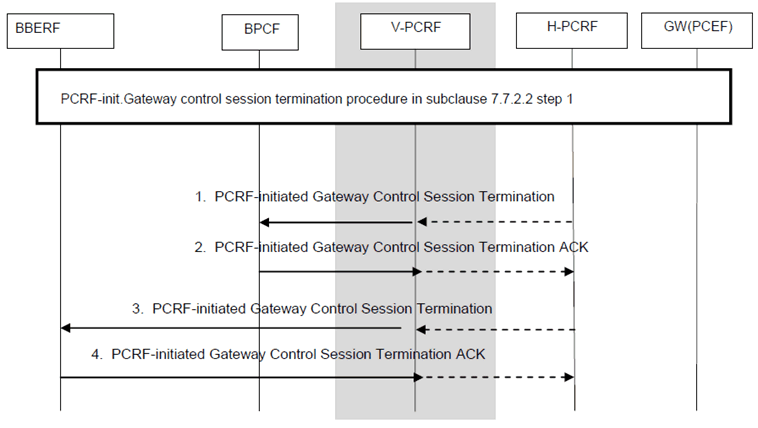
This procedure is applicable for WLAN scenario. This procedure is the same as described in clause 7.7.2.2 steps 1 with the additions described below:
Step 1.
For the non-roaming and roaming home routed cases, triggered by step 1 in clause 7.7.2.2, the (h)PCRF sends a PCRF-initiated Gateway Control Session termination procedure with BPCF over S9a. For the roaming LBO case, triggered by step 1 in clause 7.7.2.2, the (v)PCRF sends a PCRF-Initiated Gateway control session termination procedure with BPCF over S9a.
Step 2.
The BPCF sends PCRF-Initiated Gateway Control Session Termination acknowledgement.
Step 3.
Triggered by step 1 in clause 7.7.2.2, the (h)PCRF (for non-roaming case and home routed roaming case) sends a PCRF-initiated Gateway Control Session Termination over Gxb* with the ePDG (BBERF). Triggered by the Gateway Control Session Termination over S9a and S9 with the BPCF, the V-PCRF (roaming LBO case) sends a PCRF-initiated Gateway Control Session Termination over Gxb* with the ePDG (BBERF).
Step 4.
The ePDG (BBERF) sends a sends PCRF-Initiated Gateway Control Session Termination acknowledgement.
P.7.6 PCRF Discovery and Selection p. 236
P.7.6.1 PCRF Discovery and Selection by BPCF p. 236
When the BPCF knows that a 3GPP UE attached via a Fixed Broadband access network and learns the IMSI and the NSWO-APN, the BPCF initiates the IP-CAN session establishment for NSWO offloaded traffic, the BPCF finds the PCRF using the DRA as described in clause 7.6.1.
When the BPCF is requested to establish a Gateway Control Session over S9a by PCRF, the BPCF uses the PCRF address provided in the request to establish the Gateway Control Session over S9a.
In roaming scenarios, the selected V-PCRF shall belong to the same V-PLMN selected during the 3GPP access authentication procedure. The BPCF uses the VPLMN id to find the V-DRA in the VPLMN. The V-PCRF finds the DRA in the HPLMN based on the IMSI and the APN if available as described in clause 7.6.1.
P.7.6.2 PCRF Discovery and Selection by AF/TDF unsolicited application reporting for NS-WLAN offloaded traffic p. 236
For PCRF discovery and selection by AF/TDF unsolicited application reporting for NS-WLAN offloaded traffic the procedure described in clause 7.6.1 applies.
P.7.6.3 PCRF Discovery and Selection by HNB GW p. 236
When the DRA receives a request for a certain S15 Session establishment from the HNB GW, the DRA selects a suitable PCRF for the S15 Session based on HNB local IP address. When the S15 Session terminates, the DRA shall remove the information about the S15 Session.
P.7.7 BPCF Discovery and Selection p. 236
For PCRF-triggered Gateway Control Session establishment, the PCRF (for non-roaming case) and the V-PCRF (for home routed and visited access roaming cases) is configured with IP address range mappings { (IPx..IPy) > BBF network entry point}. The PCRF (for non-roaming) and the V-PCRF (for roaming cases) selects the correct BBF network entry point based on UE Local IP address for WLAN access and based on H(e)NB Local IP address received from the PCEF/BBERF for H(e)NB case. The implementation of a BBF network entry point is out-of-scope for 3GPP e.g. be a BPCF or a DRA. The H-PCRF sends the H(e)NB/UE local IP address to the V-PCRF over the S9 interface.
For WLAN and H(e)NB in Home Routed roaming case, for PCRF-triggered Gateway Control Session establishment, H-PCRF finds V-DRA according to the VPLMN ID if received via Gx session, and then discovers V-PCRF by V-DRA. V-PCRF selects the correct BBF network entry point with the given UE local IP address and the H(e)NB Local IP address in the BBF access network at which the H(e)NB is connected to respectively.
P.7.8 TDF Discovery and Selection for NS-WLAN offloaded traffic p. 236
For the solicited application reporting, the TDF address may be preconfigured in the PCRF. Alternatively, the PCRF may receive the TDF address as a part of IP-CAN session signalling for NS-WLAN offloaded traffic over S9a.