Content for TS 23.203 Word version: 18.0.0
0…
4…
5…
6…
6.1.4…
6.1.7…
6.1.10…
6.1.17…
6.2…
6.2.2…
6.2.3…
6.3
6.4…
6.8…
7…
7.3…
7.4…
7.7…
7.7.3…
7.8…
A…
A.4…
D…
P…
P.4.2.4…
P.7…
P.7.5…
P.8
Q…
S…
S.7…
S.8.8
T…
P.4.2.4 Reference architecture - Non-Roaming with non-seamless WLAN offload in Fixed Broadband Access Network; scenario with AF
P.4.2.5 Reference architecture - Roaming with non-seamless WLAN offload in Fixed Broadband Access Network: scenario with AF
P.4.2.6 Reference architecture - Non-Roaming with non-seamless WLAN offload in Fixed Broadband Access Network: scenario with TDF
P.4.2.7 Reference architecture - Roaming with non-seamless WLAN offload in Fixed Broadband Access Network: scenario with TDF
P.5 Functional description
P.6 Functional Entities
P.6.1 Policy Control and Charging Rules Function (PCRF)
P.6.2 Broadband Policy Control Function (BPCF)
P.6.3 Bearer Binding and Event Reporting Function (BBERF)
P.6.4 Policy and Charging Enforcement Function (PCEF)
...
...
P.4.2.4 Reference architecture - Non-Roaming with non-seamless WLAN offload in Fixed Broadband Access Network; scenario with AF p. 218
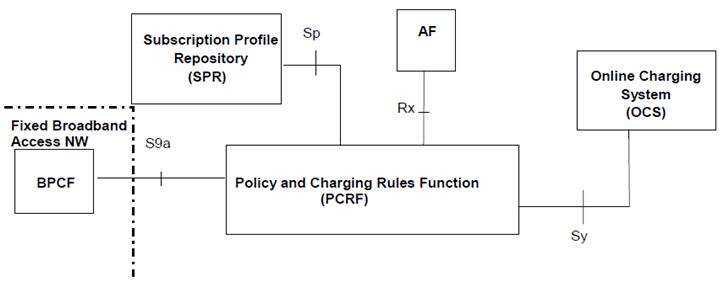
Figure P.4.2.4-1: PCC Reference architecture for Fixed Broadband Access Interworking (non-roaming with non-seamless WLAN offload in Fixed Broadband Access Network)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
P.4.2.5 Reference architecture - Roaming with non-seamless WLAN offload in Fixed Broadband Access Network: scenario with AF p. 218
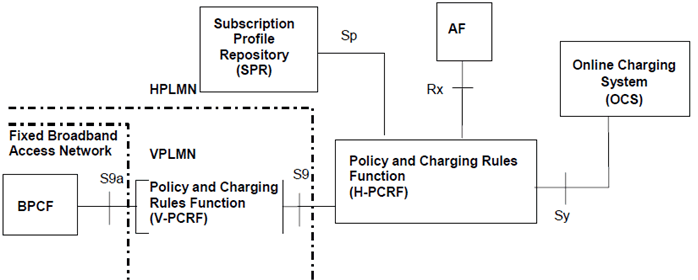
Figure P.4.2.5-1: PCC Reference architecture for Fixed Broadband Access Interworking (roaming with non-seamless WLAN offload in Fixed Broadband Access Network)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
P.4.2.6 Reference architecture - Non-Roaming with non-seamless WLAN offload in Fixed Broadband Access Network: scenario with TDF p. 219
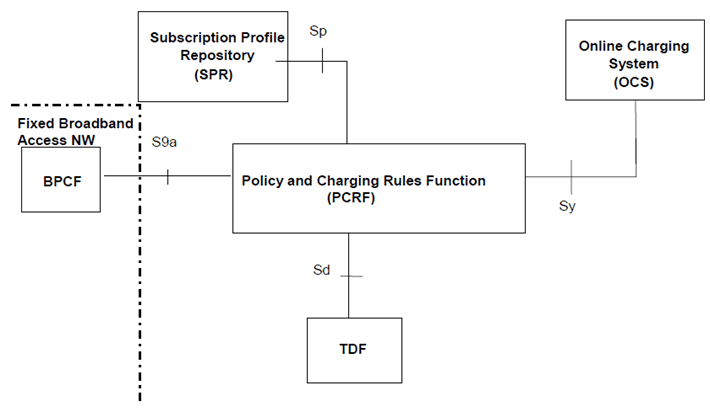
Figure P.4.2.6-1: PCC Reference architecture for Fixed Broadband Access Interworking (non-roaming with non-seamless WLAN offload in Fixed Broadband Access Network)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
P.4.2.7 Reference architecture - Roaming with non-seamless WLAN offload in Fixed Broadband Access Network: scenario with TDF p. 220
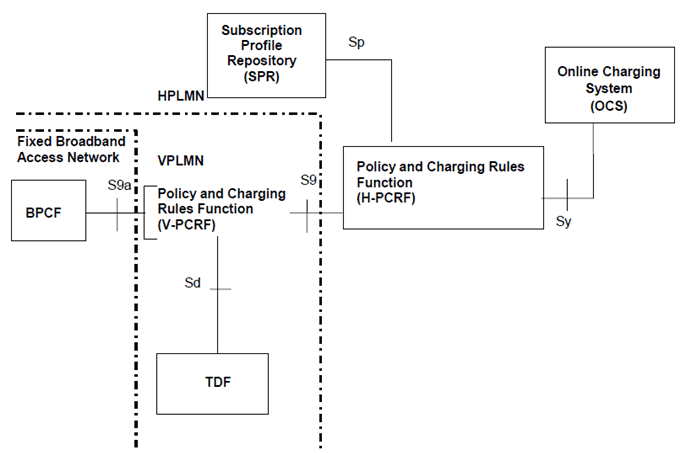
Figure P.4.2.7-1: PCC Reference architecture for Fixed Broadband Access Interworking (roaming with non-seamless WLAN offload in Fixed Broadband Access Network)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
P.5 Functional description p. 220
P.5.1 Overall description p. 220
For EPC based Fixed Broadband Access Interworking with EPC-routed traffic the credit management, reporting, usage monitoring, termination actions, service data flow prioritization and standardized QoS characteristics as defined in clause 6.1 shall apply.
For non-seamless WLAN offloaded traffic service data flow prioritization as defined in clause 6.1 applies. For scenario with TDF, usage monitoring as defined in clause 6.1 applies. For NSWO traffic in other scenarios, without TDF, usage monitoring is out of scope of this specification. For all scenarios, credit management, termination actions and reporting for NSWO traffic are out of scope of this specification.
The purpose of policy interworking via S9a for non-seamless WLAN offloaded traffic (PCC Rules provisioned for the UE local IP address) is to enable policy control in the BBF domain in two different ways:
- Gate enforcement. The BPCF is expected to provide information over R interface to control whether a service data flow, which is subject to policy control, pass through the BNG if and only if the corresponding gate is open.
- QoS enforcement: The BPCF is expected to provide information over R interface to control the authorized QoS of a service data flow according to the QoS information received over S9a interface.
| Event trigger | Description | Reported from | Conditions for reporting |
|---|---|---|---|
| UE local IP address change | Either the UE local IP address or the UDP port number or both assigned by Fixed Broadband Access have changed | PCEF, BBERF | Always set |
| H(e)NB local IP address change | Either the H(e)NB IP address or the UDP port number or both assigned by Fixed Broadband Access have changed | PCEF, BBERF | PCRF |
P.5.1.1 Binding Mechanism p. 221
P.5.1.1.1 EPC-routed traffic p. 221
For EPC routed traffic, binding mechanisms apply as defined in clause 6.1.1 by PCRF, PCEF and BBERF. In addition, the PCC and QoS Rule generation is performed by PCRF as specified in clause 6.1.1, in addition when:
- Both a Gx and associated Gateway Control Session exist for the same IP-CAN session; the PCRF shall generate QoS Rules for all the authorized PCC rules in this step.
P.5.1.1.2 Non-seamless WLAN offloaded traffic p. 221
The binding mechanism includes two steps for the non-seamless WLAN offloaded traffic:
- Session binding.
- PCC rule authorization.
P.5.1.2 S9a, Gx and S15 Session Linking p. 221
For WLAN, PCRF and BPCF both need to support session linking function. Depending on the deployment there may be one or multiple PCRF that have a Gateway Control Session on S9a for a given UE. The PCRF shall be able to perform the linking between IP-CAN sessions on Gx and the Gateway Control Session on S9a for the same UE based on IMSI and UE local IP address.
For H(e)NB scenarios a Gateway Control Session on S9a may be linked to:
- IP-CAN Sessions on Gx for all UEs connected to the H(e)NB;
- Gateway Control Sessions on S9 and/or IP-CAN Sessions on S9 (in roaming cases);
- S15 Session;
P.6 Functional Entities p. 222
P.6.1 Policy Control and Charging Rules Function (PCRF) p. 222
P.6.1.1 General p. 222
The PCRF functionality defined in clause 6.2.1.0 shall apply. In addition, to support interworking with Fixed Broadband networks, the PCRF shall:
- Send the QoS rules to the BPCF over S9a to request admission control in the fixed access.
- Send to the BPCF the UE local IP address and UDP port number for the WLAN scenario to allow the Fixed Broadband Access to identify UE traffic.
- Send to the BPCF the HeNB Local IP address and UDP port number for the Femto scenario. This allows the Fixed Broadband Access to identify IP flows corresponding to the IPSec tunnel from the HeNB GW to the SeGW which transports H(e)NB UE traffic.
- Be able to be configured with the relation of IP address ranges to Fixed Broadband Access, to allow BPCF discovery.
- Be able to receive from PDN GW the H(e)NB Local IP address and the UDP source port, if available, in the Fixed Broadband access network at which the H(e)NB is connected.
- Be able to receive the UE local IP address and UDP source port from the ePDG (case 2a and case 2b) and PDN GW (case 1).
- Be able to receive the HNB local IP address and UDP source port from HNB GW (case 1) for the HNB CS scenario.
- Handle incoming request of IP-CAN session establishment received over S9a.
- Perform session binding of the AF session information received via Rx or via S9a with an existing IP-CAN session using the UE local IP address and the IMSI (if available).
- Initiate IP-CAN Session Modification and also QoS information provision for Non-seamless WLAN offloaded traffic.
- Establish an Sd session with the TDF when an indication of IP-CAN session establishment is received over S9a for the UE local IP address in case of architecture variant C the solicited mode.
P.6.1.2 V-PCRF p. 222
The V-PCRF functionality defined in clause 6.2.1.3 shall apply. For the purpose of Fixed Access interworking the V-PCRF functionalities for EPC routed traffic, the following are applicable:
- If a BPCF-Initiated Gateway Control Session termination is received over S9a, then the V-PCRF shall terminate a Gateway Control session over S9 with the H-PCRF.
-
For home routed roaming case, in case 1:
- If a Gateway Control Session termination indication is received over S9 from the H-PCRF, then the V-PCRF shall trigger a Gateway Control Session termination to the BPCF.
- If a Gateway Control and QoS Rules Request is received over S9 from the H-PCRF, then the V-PCRF shall trigger a Gateway Control and QoS Rules Request to the BPCF.
-
For both home routed and visited access roaming cases, in case 2b:
- If a Gateway Control Session establishment from the BBERF (ePDG) occurs, then the V-PCRF shall establish a Gateway Control Session with the BPCF over S9a and with the H-PCRF over S9.
- If the last Gateway Control Session from the BBERF (ePDG) is terminated, then the V-PCRF shall terminate the Gateway Control Session with the BPCF over S9a and with the H-PCRF over S9.
- When the last PDN connection over the HNB has been terminated the V-PCRF initiates the GW Control Session Termination to the BPCF if there is no S15 session bound to the Gateway control session over S9a interface session. Otherwise, if there is a S15 session bound to the Gateway control session over S9a interface session the V-PCRF initiates the GW Control QoS rule Provision procedure to the BPCF to release the resources in the fixed broadband network.
- For roaming scenario, V-PCRF shall handle incoming request of IP-CAN session establishment received over S9a.
- If an IP-CAN session establishment request is received for a roaming user over the S9a reference point, then the V-PCRF shall conclude that the IP-CAN session is used for NSWO and acts as visited access network as described in clause 6.2.1.3.3.
P.6.1.3 H-PCRF p. 223
The H-PCRF functionality defined in clause 6.2.1.4 shall apply. For the purpose of Fixed Access interworking, the H-PCRF functionalities defined in the following are applicable to the home routed scenario:
- For case 1, if an IP-CAN Session Establishment indication is received over Gx, then if this is the first IP-CAN session for this UE the H-PCRF shall establish a Gateway Control Session to the V-PCRF over S9.
- For case 1, if an IP-CAN Session Termination indication is received over Gx then if this is the last IP-CAN session for this UE, the H-PCRF shall terminate the Gateway Control session to the V-PCRF over S9.
- If a PCC Rule is generated, the H-PCRF shall send QoS rules to the V-PCRF to request admission control over S9.
- If a PCEF-Initiated IP-CAN Session Modification Procedure occurs over Gx to update, for WLAN scenario, the UE local IP Address and UDP port number, or, for the HeNB scenario, the HeNB local IP Address and UDP port number, then the H-PCRF shall send them to the V-PCRF.
- For the purpose of BBF interworking for NSWO traffic, in case of roaming, the H-PCRF shall determine PCC rules based on home operator policy for the specific UE when it receives the IP-CAN session establishment request from V-PCRF.
P.6.2 Broadband Policy Control Function (BPCF) p. 224
The BPCF is the policy Control entity in the Fixed Broadband Access network. The complete specification of the BPCF is defined in BBF TR-134 [31] and BBF TR-203 [30] and it is out of the scope of the 3GPP.
For the purpose of interworking with 3GPP network the BPCF is expected to:
- Perform admission control in fixed access or delegates admission control decision to other BBF nodes. Based on the admission control, the BPCF accepts or rejects the request received from PCRF over S9a. As with current S9, the BPCF may include the acceptable QoS in the reply if the request is rejected.
- Translate the 3GPP QoS rule as received from PCRF over S9a interface into access specific QoS parameters applicable in the Fixed Broadband access network.
- Support PCRF-triggered Gateway Control session establishment procedure over S9a.
- Support Gateway Control session modification and termination procedures over S9a.
- Support BPCF-initiated IP-CAN Session Establishment procedure over S9a only after successfully checking the local policies indicating that policy control for NSWO is provided.
- Support IP-CAN Session Modification procedure over S9a.
- Support IP-CAN Session Termination procedure over S9a.
- Bind the request received on E/G from AF in the Fixed Broadband access network with an existing IP-CAN session on S9a using the UE local IP address and the IMSI ( if available).
P.6.3 Bearer Binding and Event Reporting Function (BBERF) p. 224
For case 2a and case 2b, the BBERF in the ePDG supports only reporting of the UE's Local IP address and UDP port number to the PCRF. Bearer binding, uplink bearer binding verification functions are not supported.
For case 2b, the BBERF in the Serving GW supports those functions specified in clause 6.2.7.1
P.6.4 Policy and Charging Enforcement Function (PCEF) p. 224
PCEF supports those functions specified in clause 6.2.2.1. Case 1 additionally supports the reporting of the UE / H(e)NB Local IP address and the UDP port number, if available, in the Fixed Broadband Access at which the H(e)NB is connected to the PCRF.