Content for TS 38.305 Word version: 18.1.0
1…
4…
5…
6…
6.5…
6.7…
7…
7.3A…
7.4…
7.6…
7.11…
7.12…
8…
8.1.2.1a…
8.1.3…
8.2…
8.3…
8.4…
8.5…
8.6…
8.7…
8.8…
8.9…
8.10…
8.11…
8.12…
8.13…
8.14…
8.15…
A…
6.5 Signalling between an LMF and NG-RAN node
6.5.1 Protocol Layering
6.5.2 NRPPa PDU Transfer for UE Positioning
6.5.3 NRPPa PDU Transfer for Positioning Support
6.5.4 NRPPa PDU Transfer for Assistance Information Broadcast
...
...
6.5 Signalling between an LMF and NG-RAN node p. 38
6.5.1 Protocol Layering p. 38
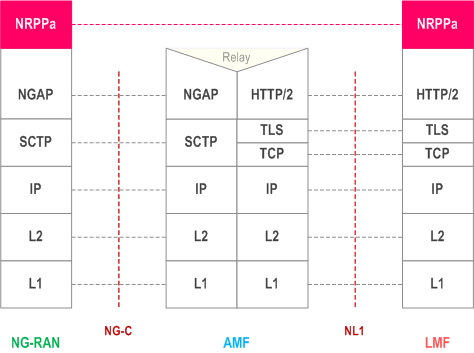
Figure 6.5.1-1 shows the protocol layering used to support transfer of NRPPa PDUs between an LMF and NG-RAN Node.
The NRPPa protocol is transparent to the AMF. The AMF routes the NRPPa PDUs transparently based on a Routing ID which corresponds to the involved LMF node over the NG interface without knowledge of the involved NRPPa transaction. It carries the NRPPa PDUs over NG interface either in UE associated mode or non-UE associated mode.
6.5.2 NRPPa PDU Transfer for UE Positioning p. 38
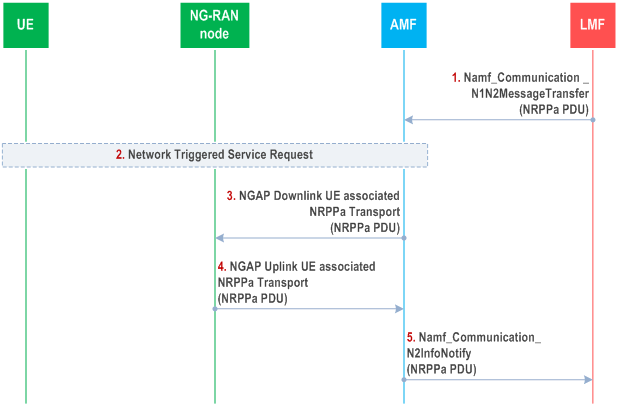
Figure 6.5.2-1 shows NRPPa PDU transfer between an LMF and NG-RAN Node to support positioning of a particular UE.
Step 1.
Steps 1 to 3 are triggered when the LMF needs to send an NRPPa message to the serving NG-RAN Node for a target UE as part of a NRPPa positioning activity. The LMF then invokes the Namf_Communication_N1N2MessageTransfer service operation towards the AMF to request the transfer of a NRPPa PDU to the serving NG-RAN Node for the UE. The service operation includes the NRPPa PDU together with the LCS Correlation ID in the N2 Message Container as defined in TS 29.518.
Step 2.
If the UE is in CM-IDLE state (e.g. if the NG connection was previously released due to data and signalling inactivity), the AMF performs a network triggered service request as defined in TS 23.502 in order to establish a signalling connection with the UE and assign a serving NG-RAN Node.
Step 3.
The AMF forwards the NRPPa PDU to the serving NG-RAN Node in an NGAP Downlink UE Associated NRPPa Transport message over the NG signalling connection corresponding to the UE and includes the Routing ID related to the LMF. The AMF need not retain state information for this transfer - e.g. can treat any response in step 4 as a separate non-associated transfer.
Step 4.
Steps 4 and 5 are triggered when a serving NG-RAN Node needs to send an NRPPa message to the LMF for a target UE as part of an NRPPa positioning activity. The NG-RAN Node then sends an NRPPa PDU to the AMF in an NGAP Uplink UE Associated NRPPa Transport message and includes the Routing ID received in step 3.
Step 5.
The AMF invokes the Namf_Communication_N2InfoNotify service operation towards the LMF indicated by the Routing ID received in step 4. The service operation includes the NRPPa PDU received in step 4 together with the LCS Correlation ID in the N2 Info Container as defined in TS 29.518. Steps 1 to 5 may be repeated.
6.5.3 NRPPa PDU Transfer for Positioning Support p. 39
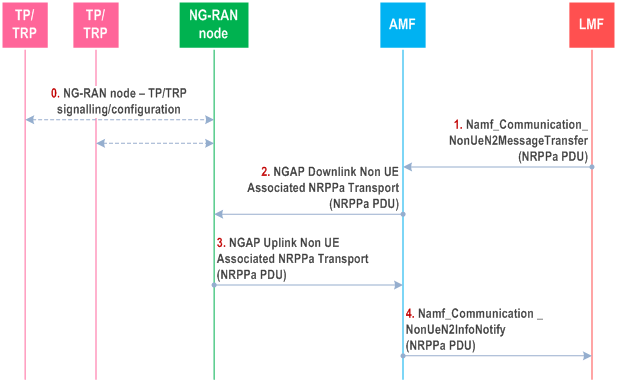
Figure 6.5.3-1 shows NRPPa PDU transfer between an LMF and NG-RAN Node when related to gathering data from the NG-RAN Node for positioning support for all UEs.
Step 0.
An ng-eNB in the NG-RAN may communicate with several TPs (including PRS-only TPs in case of PRS-based TBS is supported) to configure TPs, obtain TP configuration information, etc.
A gNB in the NG-RAN may communicate with several TRPs (including PRS-only TPs) to configure TRPs, obtain TRP configuration information, etc.
Step 1.
Steps 1 and 2 are triggered when the LMF needs to send an NRPPa message to an NG-RAN Node to obtain data related to the NG-RAN Node, and possibly associated TPs. The LMF invokes the Namf_Communication_NonUeN2MessageTransfer service operation towards the AMF to request the transfer of a NRPPa PDU to a NG-RAN node (gNB or ng-eNB) in the NG-RAN. The service operation includes the target NG-RAN node identity and the NRPPa PDU in the N2 Information Container as defined in TS 29.518.
Step 2.
The AMF forwards the NRPPa PDU to the identified NG-RAN Node in an NGAP Downlink Non UE Associated NRPPa Transport message and includes a Routing ID identifying the LMF. The AMF need not retain state information for this transfer - e.g. can treat any response in step 3 as a separate non-associated transfer.
Step 3.
Steps 3 and 4 are triggered when an NG-RAN Node needs to send an NRPPa PDU to an LMF containing data applicable to the NG-RAN Node, and possibly associated TPs. The NG-RAN Node then sends an NRPPa PDU to the AMF in an NGAP Uplink Non UE Associated NRPPa Transport message and includes the Routing ID received in step 2.
Step 4.
The AMF invokes the Namf_Communication_NonUeN2InfoNotify service operation towards the LMF indicated by the Routing Identifier received in step 3. The service operation includes the NRPPa PDU received in step 3 in the N2 Info Container as defined in TS 29.518. Steps 1 to 4 may be repeated.
6.5.4 NRPPa PDU Transfer for Assistance Information Broadcast |R16| p. 40
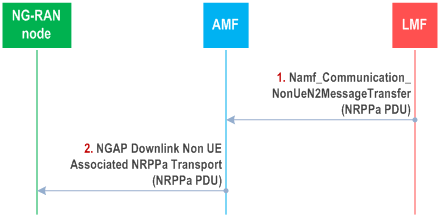
Figure 6.5.4-1 shows NRPPa PDU transfer between an LMF and NG-RAN node to support broadcast of assistance data.
Step 1.
Figure 6.5.4-2 shows NRPPa PDU transfer between an NG-RAN node and LMF for providing feedback to the LMF on assistance data broadcasting.
Step 1 is triggered when the LMF needs to send new or updated assistance information to an NG-RAN node for broadcasting in positioning system information messages. The LMF invokes the Namf_Communication_NonUeN2MessageTransfer service operation towards the AMF to request the transfer of a NRPPa PDU to a NG-RAN node (gNB or ng-eNB) in the NG-RAN. The service operation includes the target NG-RAN node identity and the NRPPa PDU in the N2 Information Container as defined in TS 29.518.
Step 2.
The AMF forwards the NRPPa PDU to the identified NG-RAN node in an NGAP Downlink Non UE Associated NRPPa Transport message and includes the Routing ID identifying the LMF. The AMF need not retain state information for this transfer.
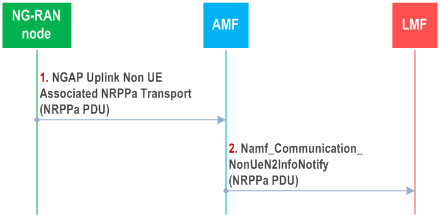
Step 1.
Step 1 is triggered when an NG-RAN node needs to send an NRPPa PDU to an LMF for providing feedback on assistance data broadcasting. Step 1 may only be triggered if the procedure in Figure 6.5.4-1 has already been performed. The NG-RAN node sends an NRPPa PDU to the AMF in an NGAP Uplink Non UE Associated NRPPa Transport message. The NG-RAN node includes the previously received Routing ID related to the LMF (Figure 6.5.4-1).
Step 2.
The AMF invokes the Namf_Communication_NonUeN2InfoNotify service operation towards the LMF indicated by the Routing identifier received at step 1. The service operation includes the NRPPa PDU received in step 1 in the N2 Info Container as defined in TS 29.518.