Content for TS 23.060 Word version: 18.0.0
1…
5…
5.3.8…
5.4…
5.4.2…
5.4.9…
5.6…
5.6.2
5.6.3…
5.6.3.7…
5.7…
6…
6.3…
6.5…
6.6…
6.8…
6.9…
6.9.1.3
6.9.2…
6.9.2.2…
6.9.2.2.2
6.9.2.2.3…
6.9.2.2.5…
6.9.3…
6.10…
6.12…
6.13…
6.13.1.2…
6.13.2…
6.13.2.2
6.14…
8…
8.2
9…
9.2.2…
9.2.2.2
9.2.2.3…
9.2.3…
9.2.3.2…
9.2.3.3…
9.2.4…
9.2.4.2…
9.2.5…
12…
12.5…
12.6…
12.7…
12.8…
13…
14…
15…
15.3…
16…
16.2…
A…
B…
5.4.2 Packet Domain PLMN Backbone Networks
5.4.3 HLR/HSS
5.4.4 SMS-GMSC and SMS-IWMSC
5.4.5 Mobile Stations (A/Gb mode)
5.4.6 Mobile Stations (Iu mode)
5.4.7 Charging Gateway Functionality
5.4.8 PCRF
...
...
5.4.2 Packet Domain PLMN Backbone Networks p. 55
There are two kinds of backbone networks. These are called:
- intra-PLMN backbone network; and
- inter-PLMN backbone network.
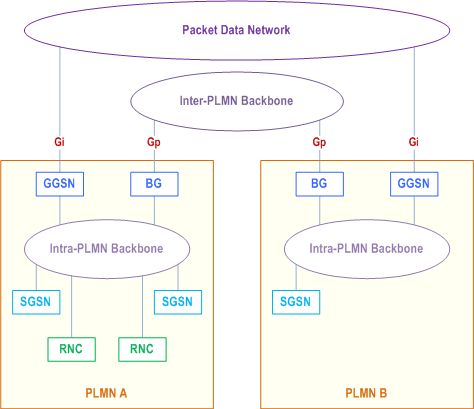
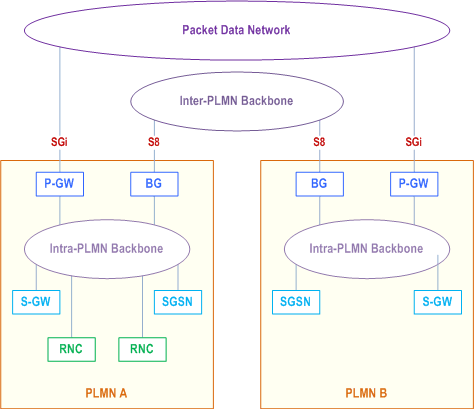
Every intra-PLMN backbone network is a private IP network intended for GPRS packet domain data and signalling only. A private IP network is an IP network to which some access control mechanism is applied in order to achieve a required level of security. Two intra-PLMN backbone networks are connected via the Gp interface using Border Gateways (BGs) and an inter-PLMN backbone network. The inter-PLMN backbone network is selected by a roaming agreement that includes the BG security functionality. The BG is not defined within the scope of GPRS. The inter-PLMN backbone can be a Packet Data Network, e.g. the public Internet or a leased line.
5.4.3 HLR/HSS p. 56
The HLR/HSS contains GPRS and EPS subscription data and routeing information. The HLR/HSS is accessible from the Gn/Gp SGSN via the Gr interface, from the S4-SGSN via the S6d interface and from the GGSN via the Gc interface. For roaming MSs, the HLR/HSS may be in a different PLMN than the current SGSN.
5.4.4 SMS-GMSC and SMS-IWMSC p. 56
The SMS GMSC and SMS IWMSC are connected to the SGSN via the Gd or the Gdd interface to enable the SGSN to support SMS.
5.4.5 Mobile Stations (A/Gb mode) p. 56
An A/Gb mode MS operates in one of three modes of operation. The mode of operation depends on the network domains that the MS is attached to, i.e. only PS or both PS and CS domain, and upon the MS's capabilities to operate PS and CS domain services simultaneously.
- Class A mode of operation: The MS is attached to both PS and CS domain, and the MS supports simultaneous operation of PS and CS domain services.
- Class B mode of operation: The MS is attached to both PS and CS domain, but the MS can only operate one set of services, PS or CS services, at a time.
- Class C mode of operation: The MS is exclusively attached to the PS domain.
5.4.6 Mobile Stations (Iu mode) p. 57
An Iu mode MS operates in one of three modes of operation. However, these operation modes are different from the ones of an A/Gb mode MS due to the capabilities of an Iu mode RAN to multiplex CS and PS connections, due to paging co-ordination for PS services and CS services that are offered by the CN or the UTRAN/GERAN-Iu, etc. The different Iu mode MS operation modes are defined as follows:
- CS/PS mode of operation: The MS is attached to both the PS domain and CS domain, and the MS is capable of simultaneously signalling with the PS and CS core network domains. This mode of operation is comparable to the class A mode of operation defined for A/Gb mode. The ability to operate CS and PS services simultaneously depends on the MS capabilities (for example an A/Gb mode MS of class B, which can not operate simultaneously CS and PS services, may have the same limitations when changing to Iu mode and CS/PS mode of operation).
- PS mode of operation: The MS is attached to the PS domain only and may only operate services of the PS domain. However, this does not prevent CS-like services to be offered over the PS domain (e.g. VoIP). This mode of operation is equivalent to the A/Gb mode GPRS class C mode of operation.
- CS mode of operation: The MS is attached to the CS domain only and may only operate services of the CS domain. However, this does not prevent PS-like service to be offered over the CS domain. The CS mode of operation is outside the scope of this specification.
5.4.7 Charging Gateway Functionality p. 57
The Charging Gateway Functionality (CGF) described in TS 32.251 is a function of the Offline Charging System (OFCS) which is described in TS 32.240.
5.4.8 PCRF |R8| p. 57
The PCRF is the policy and charging control element. PCRF functions are described in more detail in TS 23.203.