Content for TS 23.009 Word version: 18.0.0
1…
4…
4.3…
6…
6.2…
6.2.3
6.3…
7…
7.2…
8…
8.1.3…
8.2…
8.2.2…
8.2.4
8.3…
8.3.2…
9…
10…
11…
12…
12.8…
12.8.2
12.8.3
13…
14…
15…
4.3 3G_MSC-A
4.4 3G_MSC-B
4.5 MSC server enhanced for SRVCC features
5 Handover initiation conditions
...
...
4.3 3G_MSC-A p. 18
For roles and functional composition of the 3G_MSC-A working as pure GSM MSC, please see previous clause ("MSC-A").
4.3.1 Role of 3G_MSC-A p. 19
In the Intra-3G_MSC-A handover/relocation case, 3G_MSC-A controls the call, the mobility management and the radio resources before, during and after an Intra-3G_MSC-A handover/relocation. When RANAP or BSSMAP procedures have to be performed, they are initiated and driven by 3G_MSC-A.
In a network implementing the "Flexible Iu interface for handover/relocation" option, 3G_MSC-A may optionally use a global title based on the Global RNC-Id for the addressing of the Iu interface messages towards the target RNC.
For handover/relocation to an area where "Intra Domain Connection of RAN Nodes to Multiple CN Nodes" is applied, 3G_MSC-A can have multiple target CN nodes for each handover/relocation target in a pool-area as specified in TS 23.236.
In the case of intra-3G_MSC-A handover of a speech call, 3G_MSC-A controls the transcoder in the core network. The 3G_MSC-A determines, if a transcoder is required to be inserted or released in the CN.
If AoIP is supported by 3G_MSC-A and BSS, then the BSS or the 3G_MSC-A may initiate a "BSS Internal Handover with MSC Support" as described in detail in subclause 6.3.
In the case of Inter-3G_MSC relocation, 3G_MSC-A links out the transcoder.
In the Inter-3G_MSC relocation case, 3G_MSC-A is the 3G_MSC that controls the call and the mobility management of the UE during the call, before, during and after a basic or subsequent relocation. When RANAP procedures related to dedicated resources have to be performed towards the UE, they are initiated and driven by 3G_MSC-A. The 3G_MSC-A - 3G_MSC-B interface works as a 3G_MSC - RNS interface for the RANAP procedures. The Direct Transfer signalling is relayed transparently by 3G_MSC-B between 3G_MSC-A and the UE.
During a successful relocation the order to perform location reporting at change of Service Area is not transferred to the target RNS. In the Intra-3G_MSC-A relocation case, the 3G_MSC-A re-issues the Location Reporting Control towards the target RNS. In the Inter-3G_MSC relocation case, 3G_MSC-A keeps the control of the Location Report Control procedure. However, re-issuing the Iu-LOCATION-REPORTING-CONTROL messages due to subsequent Intra-3G_MSC-B relocations is the responsibility of 3G_MSC-B.
During a basic relocation, 3G_MSC-A initiates and controls all the relocation procedure, from its initiation (reception of Relocation Required from RNS-A on Iu-interface) until its completion (reception of Relocation Complete from 3G_MSC-B on E-interface).
During a subsequent relocation back to 3G_MSC-A, 3G_MSC-A acts as an RNS towards 3G_MSC-B, which controls the relocation procedure until the termination in 3G_MSC-A of the handover radio resources allocation (sending of the Relocation Request Acknowledge to 3G_MSC-B from 3G_MSC-A). Then all relocation related messages shall terminate at 3G_MSC-A (e.g. Relocation Detect/Complete from RNS-B, Relocation Cancel from RNS-A).
During a subsequent relocation to a third 3G_MSC-B', 3G_MSC-A works towards 3G_MSC-B' as described above in the basic relocation paragraph and towards 3G_MSC-B as described above in subsequent relocation paragraph.
In the Inter-System, inter-3G_MSC handover case, 3G_MSC-A is the 3G_MSC which controls the call and the mobility management of the UE/MS during the call, before, during and after a basic or subsequent inter-system handover. When BSSAP procedures related to dedicated resources have to be performed towards the UE/MS, they are initiated and driven by 3G_MSC-A. The 3G_MSC-A - MSC-B interface works as a 3G_MSC - BSS interface for a subset of BSSMAP procedures. These BSSMAP procedures described in TS 49.008 are those related to dedicated resources. The DTAP signalling is relayed transparently by MSC-B between 3G_MSC-A and the UE/MS.
During a basic inter-system UMTS to GSM handover, 3G_MSC-A initiates and controls all the handover procedure, from its initiation (reception of Relocation Required from RNS-A on Iu-interface) until its completion (reception of Handover Complete from MSC-B on E-interface).
During a subsequent inter-system UMTS to GSM handover back to 3G_MSC-A, 3G_MSC-A acts as a BSS towards 3G_MSC-B, which controls the handover procedure until the termination in 3G_MSC-A of the handover radio resources allocation (sending of the Handover Request Acknowledge to 3G_MSC-B from 3G_MSC-A). Then all handover related messages shall terminate at 3G_MSC-A (e.g. Handover Detect/Complete from BSS-B, Relocation Cancel from RNS-A).
During a subsequent inter-system UMTS to GSM handover to a third 3G_MSC, 3G_MSC-A works towards MSC-B' as described above in the basic inter-system handover paragraph and towards 3G_MSC-B as described above in subsequent inter-system handover paragraph.
During a basic inter-system GSM to UMTS handover, 3G_MSC-A initiates and controls all the handover procedure, from its initiation (reception of Handover Required from BSS-A on A-interface) until its completion (reception of Handover Complete from 3G_MSC-B on E-interface).
During a subsequent inter-system GSM to UMTS handover back to 3G_MSC-A, 3G_MSC-A acts as an RNS towards MSC-B, which controls the handover procedure until the termination in 3G_MSC-A of the handover radio resources allocation (sending of the Handover Request Acknowledge to MSC-B from 3G_MSC-A). Then all handover related messages shall terminate at 3G_MSC-A (e.g. Relocation Detect/Complete from RNS-B, Handover Failure from BSS A).
During a subsequent inter-system GSM to UMTS handover to a third 3G_MSC, 3G_MSC-A works towards 3G_MSC-B' as described above in the basic inter-system handover paragraph and towards MSC-B as described above in subsequent inter-system handover paragraph.
3G_MSC-A may assign a priority level defined as RAB parameter in TS 25.413 for each bearer. In case of relocation of a multicall configuration the 3G_MSC-B or the target RNC shall select the bearers to be handed over according to the priority level, if the target cell is not able to accommodate all bearers. If a selection has to be made between bearers of the same priority level, then the selection criteria are implementation dependent.
For network sharing (see subclause 7.2.3 of TS 25.401) 3G MSC-A shall send the SNA information to 3G_MSC-B except for emergency calls.
If 3G_MSC-A supports the optional supplementary service Multicall (See TS 23.135) and UE is engaged with multiple bearers the following description applies:
- In the Intra-3G_MSC relocation case, the 3G-MSC-A tries to relocate all bearers to a new RNS.
- In the basic relocation case, the 3G-MSC-A tries to relocate all bearers to 3G_MSC-B. If 3G_MSC-A receives an indication that the 3G_MSC-B does not support multiple bearers, then 3G_MSC-A shall be able to select one bearer to be handed over according to TS 22.129 and tries again to relocate the selected bearer.
- In the subsequent relocation to a third 3G_MSC-B' case, the 3G-MSC-A tries to relocate all bearers to 3G_MSC-B'. If 3G_MSC-A receives an indication that the 3G_MSC-B' does not support multiple bearers, then 3G_MSC-A shall be able to select one bearer to be handed over according to TS 22.129 and tries again to relocate the selected bearer.
- In the Intra-3G_MSC inter-system UMTS to GSM handover case and the basic inter-system UMTS to GSM handover case, the 3G_MSC-A shall be able to select one bearer to be handed over according to TS 22.129 and tries to handover the selected bearer.
- In all cases described above, 3G_MSC-A shall release some calls which has been carried by the bearers failed to set up in new RNS or the bearers not to be handed over.
4.3.2 Functional composition of 3G_MSC-A and its interfaces for handover/relocation p. 21
In order to simplify the description of the handover/relocation procedures the controlling 3G_MSC (3G_MSC-A) can be considered to be composed of five functional units, as shown in Figure 4.
Signalling functions:
- RNC/BSC/3G_MSC (UE/MS/RNC/BSC) Procedures 3G_MSC-A. This unit is used to control the signalling between the 3G_MSC, RNC or BSC and UE/MS. Interface Iu' is the connection to the old RNC and interface Iu'' is the connection to the new RNC, when an Intra-3G_MSC relocation takes place. Interface Iu' is the connection to the old RNC and interface A'' is the connection to the new BSC, when an Intra-3G_MSC UMTS to GSM handover takes place. Interface A' is the connection to the old BSC and interface Iu'' is the connection to the new RNC, when an Intra-3G_MSC GSM to UMTS handover takes place. Interface x represents the interworking connection to the Handover/Relocation Control Procedures 3G_MSC-A.
- Call Control Procedures 3G_MSC-A. This unit is used to control the call. Interface B' is used for normal call control procedures. When a Basic relocation from 3G_MSC-A to 3G_MSC-B is to be performed then interface B'' is employed to provide a signalling and call control connection to 3G_MSC-B. If a Subsequent handover/relocation to 3G_MSC-B' is to be performed then interface B''' is used. Similarly, when a Basic inter-system handover from 3G_MSC-A to 3G_MSC-B is to be performed, then interface B'' is employed to provide a signalling and call control connection to 3G_MSC-B. If a Subsequent inter-system handover to 3G_MSC-B' is to be performed then interface B''' is used.
- Handover/Relocation Control Procedures 3G_MSC-A. This unit provides both the overall control of the handover/relocation procedure and interworking between the internal interfaces (x, y and z).
- MAP Procedures 3G_MSC-A. This unit is responsible for controlling the exchange of MAP messages between 3G_MSCs during an Inter-3G_MSC handover/relocation, or between 3G_MSC-A and MSC-B during an Inter-system Inter-3G_MSC handover. This unit communicates with the Handover/Relocation Control Procedures 3G_MSC-A via interface z.
- Switch and Handover/Relocation Device 3G_MSC-A. For all calls this unit is responsible for connecting the new path into the network via interface B'. In specific cases it may be unnecessary to take any explicit action in the 3G_MSC concerning the handover/relocation device. The handover/relocation device interconnections are illustrated in Figure 5.
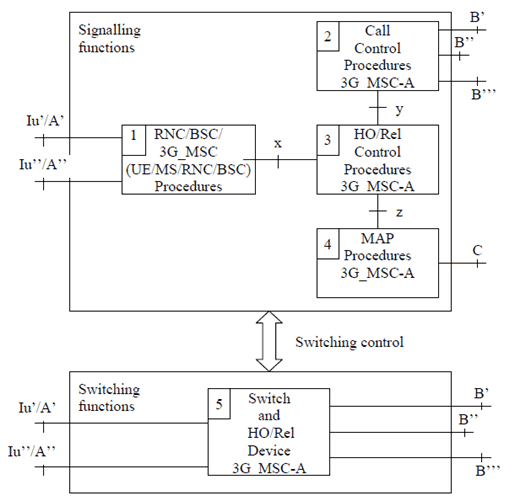
Figure 4: Functional composition of the controlling 3G_MSC (3G_MSC-A) for supporting handover/relocation
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
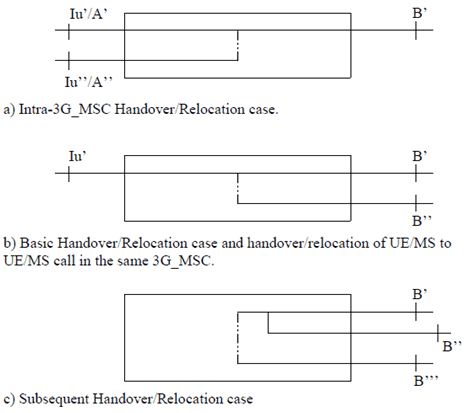
For UE/MS to UE/MS calls in the same 3G_MSC the configuration in Figure 5 b applies. In this case interface B'' is internal to 3G_MSC-A and does not connect to another 3G_MSC.
The handover/relocation device can be either a three-party bridge or a switching facility without three-party connection capabilities. For a three-party bridge configuration the states of the handover/relocation device are as shown in Table 2. The three-party configuration exists in the intermediate state. This type of handover/relocation device may reduce the interruption time. However, this may require noise reduction if one of the radio channels is unterminated at some time in the intermediate state.
For a handover/relocation device consisting of a simple switch there will be no intermediate state.
| Case | Initial Connection | Intermediate Connection | Resulting Connection | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Successful Procedure | Unsuccessful Procedure | |||
| Figure 5 a) | B' to Iu' | B' to Iu' and Iu'' | B' to Iu'' | B' to Iu' |
| B' to Iu' | B' to Iu' and A'' | B' to A'' | B' to Iu' | |
| B' to A' | B' to A' and Iu'' | B' to Iu'' | B' to A' | |
| Figure 5 b) | B' to Iu' | B' to Iu' and B'' | B' to B'' | B' to Iu' |
| Figure 5 c) | B' to B'' | B' to B''and B''' | B' to B''' | B' to B'' |
4.4 3G_MSC-B p. 23
For roles and functional composition of the 3G_MSC-B working as pure GSM MSC, please see previous clause ("MSC-B").
4.4.1 Role of 3G_MSC-B p. 23
In the Intra-3G_MSC-B handover/relocation case, the 3G_MSC-B keeps the control of the whole Intra-3G_MSC-B handover/relocation procedure. 3G_MSC-B notifies MSC-A or 3G_MSC-A of intra-3G_MSC-B InterSystem handover and intra GSM handovers (including "BSS Internal Handover with MSC Support"), by using the A-HANDOVER-PERFORMED message.
- If the security algorithms have been changed during an intra-3G_MSC-B SRNS relocation; or
- if the codec type or codec modes of the Iu Selected codec have been changed during this relocation and the Iu Supported Codecs List was received by 3G_MSC-B before,
- an A-HANDOVER-PERFORMED message, when encapsulated BSSAP is used on the E interface; or
- an Iu-LOCATION-REPORT message, when encapsulated RANAP is used on the E interface.
- In the basic relocation case, the 3G_MSC-B shall be able to allocate a Handover Number for each bearer. The 3G_MSC-B shall also be able to select some bearers to be handed over according to the priority level defined as RAB parameters in TS 25.413 so that the number of bearers will fulfill the maximum number of bearers supported by the 3G_MSC-B. If a selection has to be made between bearers of the same priority level, then the selection criteria are implementation dependent.
- In the Intra-3G_MSC relocation case, the 3G_MSC-B tries to relocate all bearers to a new RNS.
- In the subsequent relocation back to the 3G_MSC-A or to a third 3G_MSC-B' case, the 3G_MSC-B tries to request to the 3G_MSC-A to relocate all bearers to the 3G_MSC-A or to the 3G_MSC-B'.
- In the Intra-3G_MSC inter-system UMTS to GSM handover case and the subsequent inter-system UMTS to GSM handover back to the 3G_MSC-A or to a third MSC-B' case, the 3G_MSC-B shall be able to select one bearer to be handed over according to TS 22.129 and tries to handover the selected bearer.
4.4.2 Functional composition of 3G_MSC-B and its interfaces for handover/relocation p. 26
The functional composition of a 3G_MSC acting as 3G_MSC-B is essentially the same as that of 3G_MSC-A. However, there are some differences. The functional units are as follows (see Figure 6).
Signalling functions:
- RNC/BSC/3G_MSC (UE/MS/RNC/BSC) Procedures 3G_MSC-B. This unit is used to control the signalling between the 3G_MSC, RNC, BSC and UE/MS. Interface Iu' is the connection to the old RNC and interface Iu'' is the connection to the new RNC, when an Intra-3G_MSC relocation takes place. Interface Iu' is the connection to the old RNC and interface A'' is the connection to the new BSC, when an Intra-3G_MSC UMTS to GSM handover takes place. Interface A' is the connection to the old BSC and interface Iu'' is the connection to the new RNC, when an Intra-3G_MSC GSM to UMTS handover takes place. Interface x represents the interworking connection to the Handover/Relocation Control Procedures 3G_MSC-B.
- Call Control Procedures 3G_MSC-B. This unit is used for normal call control and signalling to 3G_MSC-A or MSC-A in the case of inter-system inter-3G_MSC handover.
- Handover/Relocation Control Procedures 3G_MSC-B. This unit provides both the overall control of the handover/relocation procedure and interworking between the internal interfaces (x, y and z) in 3G_MSC-B.
- MAP Procedures 3G_MSC-B. This unit is responsible for controlling the exchange of MAP messages between 3G_MSC-A, or MSC-A, and 3G_MSC-B and for signalling to the VLR in 3G_MSC-B.
- Switch 3G_MSC-B. For all calls this unit is responsible, with RNS-B, for connecting the circuit from 3G_MSC-A, or MSC-A, to RNS-B. This unit may also need to act as a handover/relocation device for Intra-3G_MSC handovers/relocation controlled by 3G_MSC-B. In specific cases it may be unnecessary to take any explicit action in the 3G_MSC concerning the handover/relocation device.
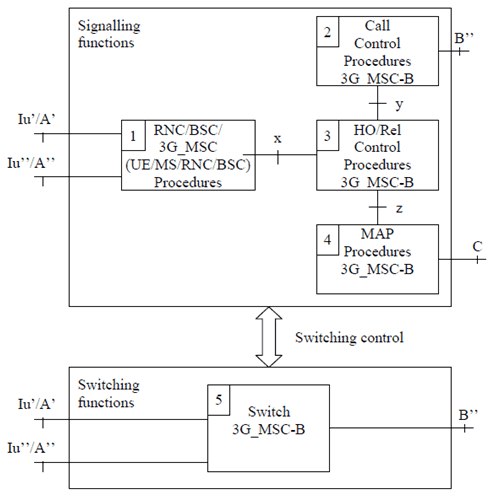
Figure 6: Functional composition of 3G_MSC-B for supporting handover/relocation
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
4.5 MSC server enhanced for SRVCC features |R8| p. 27
4.5.1 Role of SRVCC MSC p. 27
SRVCC MSC takes the roles of 3G_MSC-A as defined in subclause 4.3.1 with the following modification for an SRVCC handover:
- During a SRVCC handover, SRVCC MSC initiates and controls all the Circuit Switch handover procedure, from its initiation (i.e., reception of SRVCC PS to CS Request via the Sv-interface as defined in TS 29.280 from MME) until its completion (i.e., reception of Relocation/Handover Complete from 3G_MSC-B or MSC-B on E-interface or from RANAP or BSSMAP procedure if the target access network is connected via the same SRVCC MSC);
- Call flows on the interaction between Sv signalling and the handover signalling with the target network by SRVCC MSC is defined in TS 23.216;
- SRVCC MSC initiates a normal call setup procedure to SCC AS with STN-SR for session continuity procedure as defined in TS 23.216; and
- After SRVCC handover is completed, the UE is connected to SCC AS via target CS domain access. The subsequent handover to another BSS/RAN or inter-MSC HO follows the procedures defined for 3G_MSC-A. There is no handover back to E-UTRAN via the Sv interface.
4.5.2 Functional composition of SRVCC MSC-And its interfaces for handover/relocation p. 28
Functional composition of SRVCC MSC and its interfaces for handover/relocation follows the 3G_MSC-A as defined in subclause 4.3.2 with the following modification for an SRVCC handover:
- Interface Iu'/A' is not used. This is replaced by Sv interface;
- Interface B' is used for normal call control procedure to SCC AS for SRVCC session continuity procedures as defined in TS 23.216; and
- During SRVCC procedure, B' is a one-way connection with SCC AS and is not connected to Sv interface. After SRVCC procedure is completed, B' is connected to A''/Iu''.
4.5.3 Role of vSRVCC MSC |R11| p. 28
vSRVCC MSC takes the role of an SRVCC MSC as described in subclause 4.5.1 with the following modifications for a vSRVCC handover:
- During a vSRVCC handover, vSRVCC MSC initiates and controls all the Circuit Switch handover procedure, from its initiation (i.e., reception of SRVCC PS to CS Request via the Sv-interface as defined in TS 29.280 from MME) until its completion (i.e., reception of Relocation/Handover Complete from 3G_MSC-B on E-interface or from RANAP procedure if the target access network is connected via the same vSRVCC MSC);
- Call flows on the interaction between Sv signalling and the handover signalling with the target network by vSRVCC MSC are defined in TS 23.216;
- vSRVCC MSC performs query to SCC AS to determine whether to perform the SRVCC or vSRVCC procedure, as defined in TS 23.216 and TS 24.237;
- vSRVCC MSC initiates a normal call setup procedure to SCC AS with STN-SR for session continuity procedure as defined in TS 23.216; and
- After vSRVCC handover is completed, the UE is connected to SCC AS via target CS domain access. The subsequent handover to another RAN or inter-MSC HO follows the procedures defined for 3G_MSC-A. There is no handover back to E-UTRAN via the Sv interface.
4.5.4 Functional composition of vSRVCC MSC-And its interfaces for handover/relocation |R11| p. 28
Functional composition of vSRVCC MSC and its interfaces for handover/relocation follows an SRVCC MSC for an SRVCC handover as specified in subclause 4.5.2. In addition, the following modifications to subclause 4.5.2 are required for a vSRVCC handover:
- Interface B' is used for performing query to SCC AS to determine whether to perform the SRVCC or vSRVCC procedure, as defined in TS 23.216 and TS 24.237;
- Interface B' is used for normal call control procedure to SCC AS for vSRVCC session continuity procedures as defined in TS 23.216; and
- During vSRVCC procedure, B' is a one-way connection with SCC AS and is not connected to Sv interface. After vSRVCC procedure is completed, B' is connected to Iu''.
5 Handover initiation conditions p. 28
Handover may be initiated by the network based on RF criteria as measured by the MS or the Network (signal level, Connection quality, power level propagation delay) as well as traffic criteria (e.g. current traffic loading per cell, interference levels, maintenance requests, etc.).
In order to determine if a handover is required, due to RF criteria, it is typically the MS that shall take radio measurements from neighbouring cells. These measurements are reported to the serving cell on an event driven or regular basis. When a network determines a need for executing a handover the procedures given in TS 48.008, TS 25.303, TS 25.331 are followed.
The decision process used to determine when to perform soft handover or hard handover will typically differ. Depending on the support for soft or hard handover the Intra-MSC and Inter-MSC handover may differ.
In the case of an ongoing GSM voice group call (see TS 43.068) the criteria described above shall only apply to the mobile station currently assigned the uplink and other users with a dedicated connection, no actions shall be taken for the listening users.