Content for TS 23.548 Word version: 18.6.0
1…
4…
4.3
5…
6…
6.2.2.3…
6.2.3…
6.2.3.2.3…
6.2.3.2.5…
6.2.3.3…
6.3…
6.4…
6.5…
6.6
6.7…
6.7.2.4…
6.7.2.6…
6.7.3…
6.8…
7…
A
B…
F…
6.5 Support of 3GPP Application Layer Architecture for Enabling Edge Computing
6.5.1 General
6.5.2 ECS Address Provisioning
6.5.2.1 ECS Address Configuration Information
6.5.2.2 ECS Address Configuration Information Provisioning to the UE
6.5.2.3 ECS Address Provisioning by a 3rd Party AF
6.5.2.4 ECS Address Provisioning by MNO
6.5.2.5 Interworking with EPC
6.5.2.6 ECS Address Provisioning in Roaming
6.5.2.6.1 General
6.5.2.6.2 ECS Address Configuration Information Provision from AF via NEF in VPLMN
6.5.2.6.3 ECS Address Configuration Information Provision to the SMF in VPLMN
...
...
6.5 Support of 3GPP Application Layer Architecture for Enabling Edge Computing p. 47
6.5.1 General p. 47
The 3GPP application layer architecture for Enabling Edge Computing that is specified in TS 23.558 includes the following functional entities:
- Edge Enabler Client (EEC).
- Edge Configuration Server (ECS).
- Edge Enabler Server (EES).
6.5.2 ECS Address Provisioning p. 48
6.5.2.1 ECS Address Configuration Information p. 48
The ECS Address Configuration Information consists of one or more ECS Configuration Information as defined in clause 8.3.2.1 of TS 23.558. The ECS Configuration Information may contain Spatial Validity Conditions, which includes one of the following alternatives:
- a Geographical Service Area (see TS 23.558);
- a list of TA(s); or
- a list of countries (list of MCC);
- a list of PLMN IDs (see Table 4.15.6.3d-1 of TS 23.502).
6.5.2.2 ECS Address Configuration Information Provisioning to the UE p. 48
If the UE hosts an EEC and supports transferring the ECS address received from the 5GC to the EEC, the UE indicates in the PCO at PDU Session establishment that it supports the ability to receive ECS address(es) via NAS and to transfer the ECS Address(es) to the EEC(s) (see TS 23.502). As described in TS 23.502, if the UE supports the ability to receive ECS Address Configuration Information via NAS and to transfer the ECS address(es) to the EEC(s), the UE may receive ECS Address Configuration Information from the SMF via PCO during PDU Session Establishment and/or during PDU Session Modification procedures. If Spatial Validity Condition of ECS is provided, the UE uses the appropriate ECS as defined in TS 23.558.
The SMF may receive ECS Address Configuration Information and associated spatial validity conditions from the UDM together with SM subscription information. The UDM in the HPLMN may provide the SMF (in HPLMN in HR case, in VPLMN in LBO case) with ECS address configuration information that depends on the serving PLMN of the UE.
The SMF determines the ECS Address Configuration Information to be sent to the UE based on UE subscription information received from UDM (as described in Table 4.15.6.3d-2 of TS 23.502).
The SMF may decide to send updated ECS Address Configuration Information to the UE based on locally configured policy or updated UE subscription information. The PDU Session Modification procedure is used to send updated ECS Address Configuration Information to the UE as described in clause 4.3.3 of TS 23.502.
6.5.2.3 ECS Address Provisioning by a 3rd Party AF p. 49
As described in TS 23.558, the Edge Configuration Server can be deployed in a 3rd party domain by a service provider. An AF in the MNO domain or, if the Edge Configuration Server is deployed in a 3rd party domain by a service provider, a 3rd party AF can use Nnef_ParameterProvision to provide, update, or delete AF provided ECS Address Configuration Information applying on a DNN and/or S-NSSAI for a group of UE, or any UE (See clause 4.15.6.2 of TS 23.502).
When the AF uses Nnef_ParameterProvision to send a new AF provided ECS Address Configuration Information to the UDM (e.g. because on Application layer activity, etc.), the UDM may notify the impacted SMF(s) of the updated Subscription provided ECS Address Configuration Information and the new ECS Address Configuration Information will be sent to the UE(s) in a PDU Session Modification procedure.
6.5.2.4 ECS Address Provisioning by MNO p. 49
The ECS Address Configuration Information can be provisioned by the MNO subscription provisioning in UDM.
6.5.2.5 Interworking with EPC p. 49
In interworking scenarios, if the UE hosts an EEC and supports transferring the ECS address received from the 5GC to the EEC, the UE indicates in the PCO at PDN Connection establishment that it supports the ability to receive ECS address(es) via NAS and to transfer the ECS Address(es) to the EEC(s) (see TS 23.502) and the bearer modification procedure without bearer QoS update procedure is used to send updated ECS Address Configuration Information to the UE as described in clause 4.11.0a.5 of TS 23.502.
6.5.2.6 ECS Address Provisioning in Roaming |R18| p. 49
6.5.2.6.1 General p. 49
For both LBO and HR case, the subscription data of the ECS Address Configuration Information in UDM or UDR is stored per PLMN ID.
For the LBO case, an AF in the visited PLMN may provide the EACI via External Parameter Provisioning procedure as described in clause 4.15.6.3d of TS 23.502 to UDM via H-NEF. This ECS Address Configuration Information is further provided to SMF as part of subscription information.
For the HR case when access to EHE in VPLMN is allowed:
- The HPLMN has the knowledge of EACI in the VPLMN: For this scenario, the AF is able to interact with NEF in HPLMN. The AF may provide the VPLMN EACI to H-NEF via External Parameter Provisioning procedure as described in clause 4.15.6.3d in TS 23.502, and further to the UDM. During the HR PDU session establishment procedure, the H-SMF sends the VPLMN EACI to V-SMF and then to UE. The V-SMF does not modify, but just delivers the EACI provided by the H-SMF.
- HPLMN does not have the knowledge of EACI in VPLMN: For this scenario, the AF can't interact with NEF in HPLMN. As defined in clauses 6.5.2.6.2 and 6.5.2.6.3, V-NEF stores the VPLMN EACI received from AF deployed in the VPLMN in V-UDR, and V-SMF subscribes from V-NEF to retrieve the VPLMN EACI. During the HR PDU Session establishment, the V-SMF sends the VPLMN EACI obtained from V-NEF to the H-SMF, and H-SMF decides the VPLMN ECS Address Configuration Information sent to V-SMF and then to UE according to the PLMN ID additionally.
6.5.2.6.2 ECS Address Configuration Information Provision from AF via NEF in VPLMN p. 50
The AF provides non-PDU Session specific ECS Address Configuration Information via NEF in VPLMN to 5GC is defined in this clause.
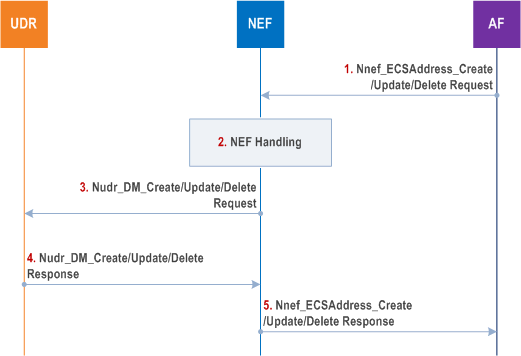
Step 1.
The AF invokes the Nnef_ECSAddress_Create /Update/Delete service operation to provide ECS Address Configuration Information to the NEF in VPLMN.
Step 2.
NEF checks whether the AF is authorized to perform the request based on the operator policies.
Step 3.
The NEF invokes the Nudr_DM_Create /Update/Delete to the UDR in VPLMN if it is authorized.
Step 4.
The UDR stores/updates/removes the corresponding information (and responds a Nudr_DM_Create /Update/Delete Response to the NEF).
Step 5.
The NEF sends Nnef_ECSAddress_Create /Update/Delete Response to the AF.
6.5.2.6.3 ECS Address Configuration Information Provision to the SMF in VPLMN p. 50
V-SMF supporting HR-SBO may receive the ECS Address Configuration Information from NEF in VPLMN via Subscribe/Notify procedure is defined in this clause.
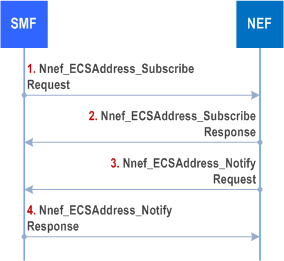
Step 1-2.
As pre-requisite condition, the SMF subscribes to ECS Address Configuration Information Change Notification from the NEF by sending Nnef_ECSAddress_Subscribe message. The SMF may indicate that the current status of ECS Address Configuration Information shall be notified immediately (if available). The SMF may indicate for which (list of) DNN and/or S-NSSAI it subscribes. NEF may further subscribe to ECS Address Configuration Information Change Notification from the UDR using Nudr_DM_Subscribe .
Step 3-4.
The NEF invokes Nnef_ECSAddress_Notify (ECS Address Configuration Information) to the SMF if the ECS Address Configuration Information is updated. If there is ECS Address Configuration Information available and immediate report is required, the NEF notifies the SMF(s) with such information immediately. NEF may retrieve the ECS Address Configuration Information from UDR using Nudr_DM_Query /Notify.