Content for TS 23.279 Word version: 17.0.0
A.3.4 Call flows for adding IMS sessions to existing voice calls for CSI origination with CSI interworking
$ Change history
A.3.4 Call flows for adding IMS sessions to existing voice calls for CSI origination with CSI interworking p. 33
In addition to the call flows described above, the following call flows describe some of the cases where CSI interworking can occur within the network on the terminating side.
Figure A.5 below shows a call flow for adding an IMS session (e.g. MSRP session) to an existing voice call. In this case the voice call was established with IMS origination, and the interworking is performed in the network. The addition of the IMS session is from the terminal that performed the IMS origination.
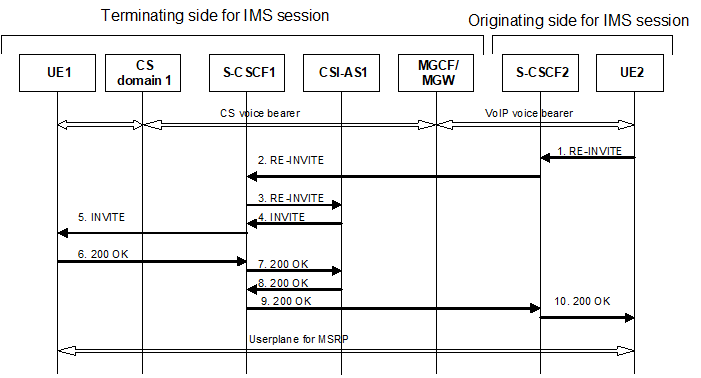
Figure A.5: Call flow for adding IMS session to existing voice call using a the existing dialog
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
Figure A.6 shows a call flow for adding an IMS session (e.g. MSRP session) to an existing voice call. In this case the voice call was established with CSI origination, and the interworking is performed in the network. The addition of the IMS session is from the terminal that performed the CSI origination.
The flow below assumes that the CSI interworking was performed in the originating network.
The UE 2 initiates a request for adding the MSRP by sending the RE INVITE message within the existing dialogue.
Step 2.
The S CSCF 2 of the originating network sends the RE INVITE message for the MSRP to the S CSCF 1 of the terminating network, in accordance with the already established sessions.
Step 3.
The S CSCF 1 sends the INVITE message for the MSRP to the CSI AS
Step 4.
The CSI AS generates an INVITE that is targeted towards the user of UE1 and sends this to S CSCF1
Step 5.
The S CSCF1 sends the INVITE towards UE1
Step 6.
The UE 1 responds to the INVITE message with the 200OK message.
Step 7.
The S CSCF1 sends the 200OK message to the CSI AS1.
Step 8.
The CSI AS1 generates a 200OK and sends it to S CSCF1.
Step 9.
S CSCF1 sends the 200OK message to S CSCF 2 of the originating network.
Step 10.
The S CSCF 2 of the originating network sends the 200OK message to the UE 2.
Step 11.
Finally, the user plane for the MSRP is created.
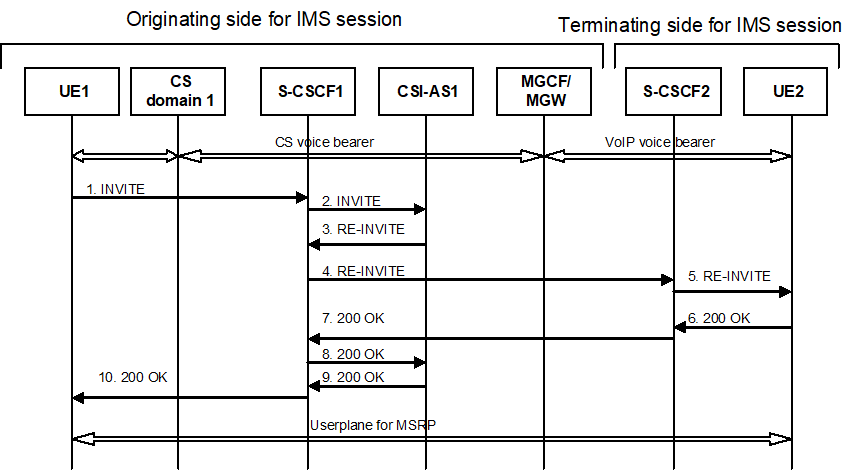
Figure A.6: Call flow for adding IMS session to existing voice call using a the existing dialog
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
Figure A.7 shows a call flow for adding a voice call to an existing IMS session (e.g. MSRP session). In this case the original IMS session was established with CSI origination, and the interworking is performed in the network. The addition of the IMS session is from the terminal that performed the CSI origination.
The flow below assumes that the CSI interworking is performed in the originating network.
The UE1 initiates a request for adding the MSRP by sending an INVITE message within the destination towards UE2.
Step 2.
The S CSCF 1 of the originating network sends the INVITE message for the MSRP to CSI AS1 based upon the filter criteria.
Step 3.
The CSI AS1 generates a RE INVITE message within the existing dialogue towards UE2. This is returned to the S CSCF1. The RE INVITE contains the SDP for the original media (e.g. the audio) and the added media (e.g. MSRP).
Step 4.
S CSCF1 forwards the RE INVITE message towards S CSCF2 within the existing dialogue.
Step 5.
S CSCF2 forwards the RE INVITE towards UE2.
Step 6.
The UE 2 responds to the INVITE message with the 200OK message.
Step 7.
The S CSCF12sends the 200OK message to S CSCF2.
Step 8.
S CSCF1 forwards the 200OK message CSI AS1.
Step 9.
CS AS1 generates a 200OK messages and forwards the message to S CSCF1.
Step 10.
S CSCF1 of the originating network sends the 200OK message to the UE1.
Step 11.
Finally, the user plane for the MSRP is created. Note that the MSRP media could go through the CSI AS.
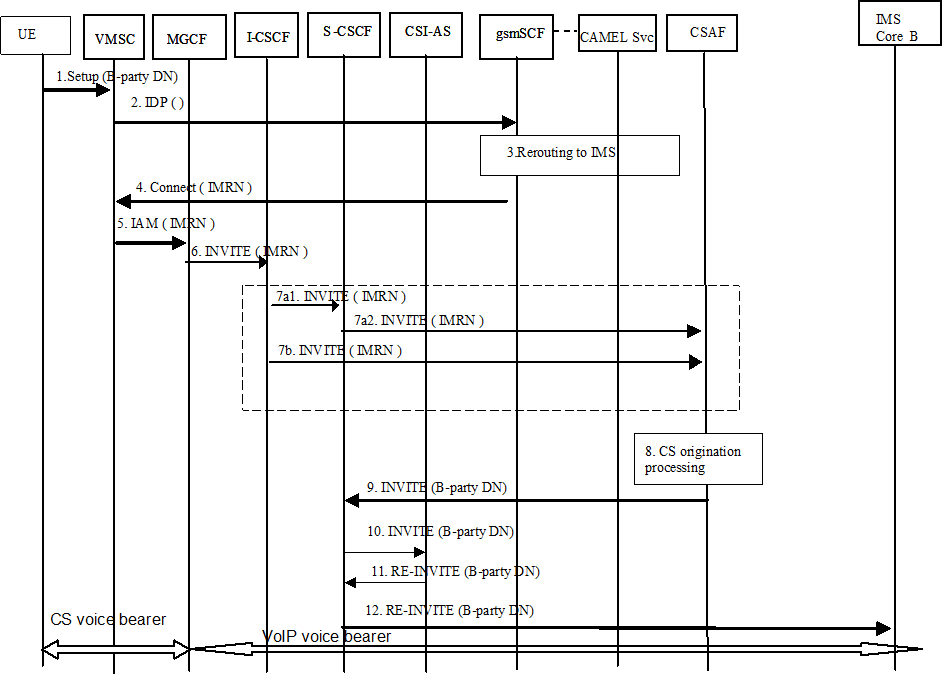
Figure A.7: Call flow for adding a voice call to an existing IMS session
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
The rest of the call is established as per normal SIP signalling with interworking towards the CS domain. The voice call is considered to be established.
The CSI user originates a voice call in the CS domain using a CSI UE to party B.
Step 2.
Origination triggers at the VMSC are detected; VMSC sends an Initial DP message towards the gsmSCF.
Step 3.
The gsmSCF invokes the CSI interworking Application's CAMEL Service that determines that the call needs to be interworked to IMS for CSI; thus, the CAMEL Service interworks the call to the IMS by allocating an IMRN and returning it to the gsmSCF; otherwise it responds with a CAP Continue.
Step 4.
The gsmSCF responds with a CAP Connect message containing the Original Called party ID and Destination Routing Address. Destination Routing Address contains the IMRN to route the call to the CSAF. Handling of Destination Routing Address and Original Called party ID is as defined in TS 23.078.
Step 5.
The VMSC routes the call towards the user's home IMS network using the IMRN via an MGCF in the home network.
Step 6.
The MGCF initiates an INVITE towards the I CSCF in the home IMS of the originating CSI user. The calling party number and/or original called number are included in the INVITE if they are received from the PSTN call setup signalling (e.g. ISUP).
Step 7.
The I CSCF routes the INVITE based on one of the following standard procedures specified in "PSI based Application Server termination direct" and "PSI based Application Server termination - indirect" procedures in TS 23.228.
Step 7a.
The I CSCF forwards the INVITE to the CSAF via the S CSCF that is assigned to the IMRN.
Step 7b.
The I CSCF forwards the INVITE directly to the CSAF.
Step 8.
If, when the INVITE arrives at the CSI Interworking Application, it is processed by the CSAF of the CSI Interworking Application that may use the IMRN to retrieve the original called party number and the calling party number from the CAMEL Service. The CSAF uses the original called number and the calling party number to setup the outgoing call leg to party B in accordance with the AS origination procedure defined in clause 5.6.5 of TS 23.228.
Step 9.
The CSAF sends the INVITE back to the S CSCF for completion of the call toward the remote end.
Step 10.
The S CSCF forwards the INVITE to the CSI AS.
Step 11.
The CSI AS forwards the RE INVITE to the S CSCF. The RE INVITE contains the SDP for the original media (e.g. MSRP) and the added media (e.g. audio).
Step 13.
The CSI AS forwards the RE INVITE to the IMS Core B. The CS part of the CSI session is now interworked to IMS Core B.