Content for TS 23.279 Word version: 17.0.0
8 Information flows
8.1 Exchange of capability information at CS call setup
8.2 Exchange of UE capability information
...
...
8 Information flows p. 15
8.1 Exchange of capability information at CS call setup p. 15
It shall be possible for the UE to perform end-to-end information exchange about the current radio environment during CS call setup. The current radio environment information exchange procedure shall include the information as outlined in clause 7.2.1.
The sequence diagram in Figure 8-1 outlines the exchange of information about the current radio environment, at CS call setup. The diagram the messages that should be used to transport the information of the current radio environment: the full message sequences for UUS-1 are specified in TS 23.087. For this procedure to be successful, the network must handle the radio capability information transparently.
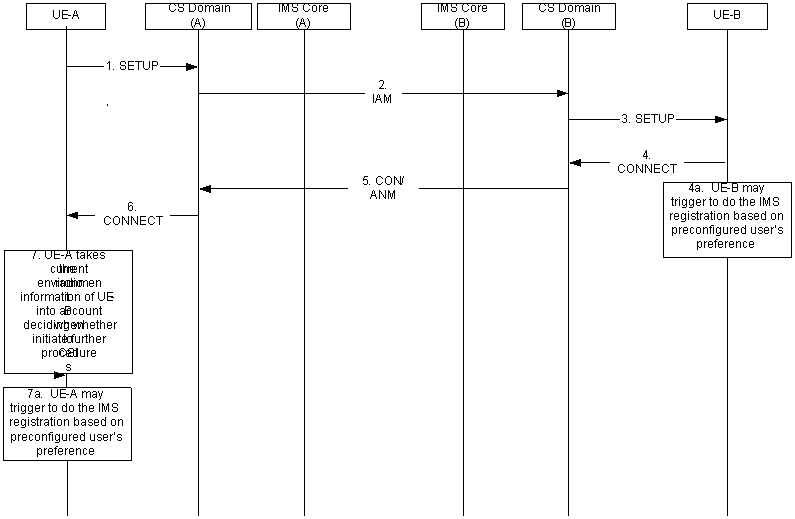
Figure 8-1: Exchange of current radio environment information "at" CS call setup
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
The UE-A initiates a CS call by sending a SETUP message towards UE-B, including the current radio environment information encoded in the User-User Signalling IE.
Step 2.
The CS domain of the originating network sends an IAM message including the current radio environment information of UE-A to the CS domain of the terminating network. Whether the MSC performs the procedures for UUS-1 (refer to TS 23.087), or, whether the MSC merely copies the User-User Signalling IE from the SETUP message into the IAM is implementation dependent. Additional MSC based policing of the UUS information content is also implementation dependent.
Step 3.
The CS domain of the terminating network sends a SETUP message IAM including the current radio environment information of UE-A to the UE-B. Whether the GMSC and/or the VMSC performs the procedures for UUS-1, or, whether they merely copy the information into the User-User Signalling IE of the SETUP message from the IAM is implementation dependent.
Step 4.
The UE-B stores the current radio environment information of UE-A and sends the current radio environment information of UE-B in the final response to the SETUP message, i.e. the CONNECT message. UE-B takes the current radio environment information of UE-A into account when deciding what service options to present to the user and/or whether to initiate a UE capability information exchange, see clause 8.2.
If UE-B find that UE-A and UE-A's current radio environment supports simultaneous CS and PS services and the IM Status indicates that an IMS communication is likely to be successful, then UE B should attempt an IMS registration (in case IMS registration had not previously been performed) based on preconfigured user's preference.
Step 5.
The CS domain of the terminating network sends an ANM or CON message including the current radio environment information of UE-B to the CS domain of the originating network.
Step 6.
The CS domain of the originating network sends a CONNECT message including the current radio environment information of UE-B to the UE-A.
Step 7.
The UE-A takes the current radio environment information of UE-B received into account when deciding what service options to present to the user and/or whether to initiate a UE capability information exchange, see clause 8.2.
If UE-A find that UE-B and UE-B's current radio environment supports simultaneous CS and PS services and the IM Status indicates that an IMS communication is likely to be successful, then UE A should attempt an IMS registration (in case IMS registration had not previously been performed) based on preconfigured user's preference.
8.2 Exchange of UE capability information p. 16
This clause outlines the exchange of UE related capability information using the SIP OPTIONS procedure to minimize the amount of network signalling and resource usage as well as the number of failed SIP INVITE requests. It also allows an up-to-date indication to the user which capabilities he could add to the ongoing call. Note that UE capability information exchange at IMS session initiation is specified in clause 8.4.
It shall be possible for a UE to request the SIP OPTIONS request to be sent to any other registered UE. In case of existing IMS session between UE-A and UE-B, to guarantee that SIP OPTIONS request is routed to UE-B, the SIP OPTIONS request should be sent as part of the existing IMS session. In case there is an ongoing CS call between UE-A and UE-B, it should be possible to provide a higher probability that the UE capability exchange is routed to the UE-B.
As the SIP OPTIONS request include both the IMS Public User Identity in the form of an SIP URI and the MSISDN the procedure enables both UE-A and UE-B to correlate the IMS session with the CS call and within one context inform the user what capabilities the user is able to use.
The execution of this SIP OPTIONS request procedure is recommended when UE-A has not stored capability information for UE B, or when UE-A has become aware that UE-B has changed its capabilities by comparing the stored and received UE capability version.
A SIP OPTIONS may also be sent by UE-A to UE-B in case UE-A's capabilities have been updated. This request triggers UE B to initiate SIP OPTIONS request towards UE-A to retrieve the updated capabilities.
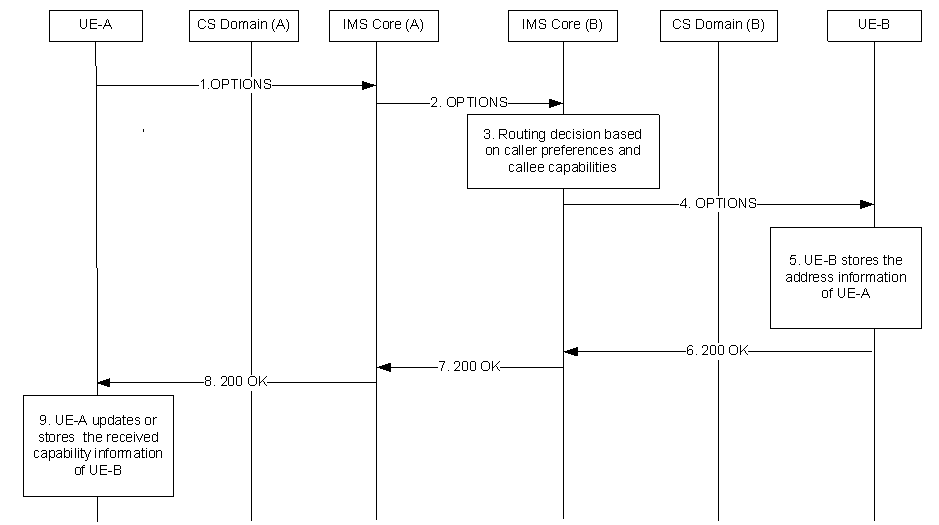
Step 1.
For the capability exchange procedure to work properly UE-B should send an SIP OPTIONS request towards UE-A, in the following situations, provided that the associated conditions are met:
UE-A sends an SIP OPTIONS request towards UE-B preferably using a SIP URI of UE-B, or a TEL URI, if no valid SIP URI is available. In case of an existing IMS session, the OPTIONS request should be sent as part of the existing session. Subject to privacy controls, in UE-A the SIP OPTIONS request shall contain MSISDN of UE-A, if available.
Step 2.
The IMS Core (A) performs the normal security procedures and forwards the SIP OPTIONS request towards IMS Core (B). If the destination address is in the format of a TEL URI, IMS Core (A) performs MSISDN to SIP URI translation as per clause 4.3.5 in TS 23.228, before forwarding the SIP OPTIONS request to IMS Core (B).
The IMS Core (A) should add the MSISDN of UE-A to the SIP OPTIONS request, if not included by UE-A.
Step 3.
If the SIP OPTIONS request is not sent as part of an existing dialog, the IMS Core (B) makes a routing decision based on information in the caller preferences, as defined in RFC 3841 [19], in the SIP OPTIONS request and any registered caller capabilities, as defined in RFC 3840 [18], (e.g. CS-Voice or CS-Video).
Step 4.
The IMS Core (B) then forwards the SIP OPTIONS request to UE-B. If privacy is requested, IMS Core (B) shall remove the MSISDN of UE-A.
Step 5.
The UE-B stores the address information of UE-A.
Step 6.
The UE-B sends a 200 OK that, subject to UE-B's privacy settings contain the information outlined in clause 7.2.2.
Step 7.
The IMS Core (B) forwards the 200 OK to IMS Core (A).
The IMS Core (B) should add the MSISDN of UE-B to the 200 OK, if not included by UE-B.
Step 8.
The IMS Core (A) forwards the 200 OK to UEA-A. If privacy is requested, IMS Core (A) shall remove the MSISDN of UE-B.
Step 9.
The UE-A stores or updates the UE capability information received and if not already available stores the address information of UE-B.
-
An SIP INVITE request is received from UE-A, and
- The SIP INVITE request received from UE-A did not include any UE's capabilities capability information, and
- UE-B has not stored capability information for UE A's capabilities, or UE-B's capabilities have been updated e.g. UE-B has been upgraded with video capability or supports a new service, or;
- The UE capability version included in the SIP INVITE request received from UE-A is different from the previously stored UE-A's capability version.
-
UE-B is in a CS call with UE-A, and
- UE-B has not stored capability information for UE A or has received a UE capability version different from previously stored UE-A's capability version from UE-A during CS call setup, and
- If received, the current radio environment information indicates that UE-A is capable of supporting CS and PS simultaneously.
-
A SIP OPTIONS request is received from UE-A, and
- There is no ongoing (or recently finished) UE-B initiated capability exchange with UE-A.