Content for TS 23.256 Word version: 18.3.0
1…
4…
4.2…
4.3…
4.4…
4.5…
5…
5.2.3…
5.2.4…
5.2.5…
5.2.5.3…
5.2.5.4…
5.2.7
5.2.8…
5.2.9…
5.3…
5.4…
5.5…
6…
6.2…
6.3…
6.3.4…
4.2 Architectural reference model
4.2.1 General
4.2.1.1 Support for general UAV features
4.2.2 Logical UAV Reference Architecture
4.2.3 5GS Non-roaming Reference Architecture
4.2.4 5GS Roaming Reference Architecture
4.2.5 Service-based interfaces
4.2.6 Reference points
...
...
4.2 Architectural reference model p. 13
4.2.1 General p. 13
4.2.1.1 Support for general UAV features |R18| p. 13
This specification covers UAV functionality provided by 5GC connected to NG-RAN and EPC connected to LTE.
The following functionality is defined for UAV support in the 3GPP system:
- An UAV is authenticated and authorized by USS via a USS UAV Authentication & Authorization (UUAA) with the support of the 3GPP system before connectivity for UAS services is enabled.
-
Depending on 3GPP network operator and/or regulatory requirements, the UUAA is performed:
- In 5GS: either as a separate procedure during the 5GS registration procedure (optional and based on specific PLMN policies, USS requirements, and geographic regulatory requirements), or when the UAV requests user plane resources for UAV operation (i.e. PDU session establishment). The UAV shall support UUAA during Registration and PDU session establishment procedure. The network shall support UUAA during PDU session establishment.
- In EPS: during the attach procedure and the corresponding PDN connection establishment. The network shall support UUAA during PDN connection establishment. The UAV shall support UUAA during PDN connection establishment procedure.
- A UAV that is provisioned with a CAA-Level UAV ID shall provide the CAA-Level UAV ID in 5GS in both Registration and in PDU Session establishment. In EPC, a UAV that is provisioned with a CAA-Level UAV ID provides the CAA-Level UAV ID in PDN Connection establishment in SM-PCO. The CN determine whether UUAA is executed at 5GS registration or at PDU session/PDN Connection establishment, based on local policies.
- The UUAA is performed at PDU session establishment when the UAV requests user plane resources for UAV operation and the UAV provides its CAA Level ID during PDU session (PDN connection) establishment.
- The UAV flight authorization and UAV-UAVC pairing authorization is performed at PDU session/PDN connection establishment/modification procedures.
- The 3GPP system supports USS authorization of pairing between a UAV and a networked UAVC or a UAVC that connects to the UAV via Internet connectivity during either the establishment of the PDN connection/PDU session for C2 communication or a modification of a PDN connection/PDU session either dedicated to C2 communication or common to USS communication and C2 communication. Modifications of the pairing or re-authorization take place via modification of the established PDN connection/PDU session. During such procedures, the USS provides to the 3GPP system information (e.g. QoS requirement, data flow descriptors, etc.) that enable traffic between the UAV and the UAVC.
- For EPC, the PDN connections used by UAV are served by SMF+PGW-C regardless of whether the UAV support 5G NAS or whether their subscription allows access to 5GC. The APN(s) used by the UAV for contacting USS or for C2 communication always resolves to a SMF+PWG-C.
- It is assumed that the UAV trying to access UAS services using 3GPP connectivity is already registered with a USS and has been assigned a CAA-Level-UAV ID. The procedure for UAV registration and assignment of CAA-Level-UAV ID is out of scope of 3GPP. The USS assigns to the UAV a CAA-Level UAV ID, or is made aware of the assigned CAA-Level UAV ID.
- A UAV is associated with an Aerial subscription in the UDM. The Aerial subscription contains aerial UE indication in the Access and Mobility Subscription data (to be used similarly to aerial UE indication defined in EPS), an aerial service indication in the Session Management Subscription data for each DNN dedicated for UAS services (C2 and UUAA-SM) which indicates that corresponding authentication/authorization has to be done using API based mechanism.
-
An UAV is identified by USS using a CAA-level UAV ID, and identified by the 3GPP System using a 3GPP UAV ID assigned by the MNO:
- It is assumed that an aerial subscription associated to a UAV includes at least one GPSI to be used as 3GPP UAV ID.
- A UAV is registered with the USS either before connecting with the 3GPP system or using plain internet connectivity via the 3GPP system. Before registering for UAS services with the 3GPP system, the UAV shall be provisioned with a CAA-Level UAV Identity.
- In roaming scenarios, it is assumed that access to USS is in the VPLMN, thus packet data connectivity for UAV-USS communication is in local breakout, and the UAS NF function is located in the VPLMN.
- In this Release, the UAV uses 3GPP access (i.e. LTE & NR) for 3GPP UAV related operations.
- Activation of RAN aerial features for UAV accessing via E-UTRA reuses the existing mechanism defined in TS 36.300.
- One or more USS(s) may be present in a specific region and may manage UAVs over one or more 3GPP networks.
- The 3GPP Network subscription for the UAV is not assumed to contain any information about the USS.
- The USS address, if known to the UAV, is configured in the UAV via mechanisms outside the scope of 3GPP.
- For PC5, Release 15 (and later) version of the specification is the baseline.
4.2.1.2 Void
4.2.2 Logical UAV Reference Architecture p. 15
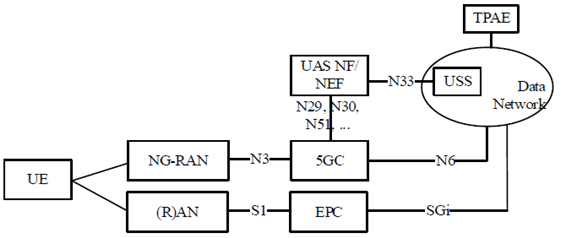
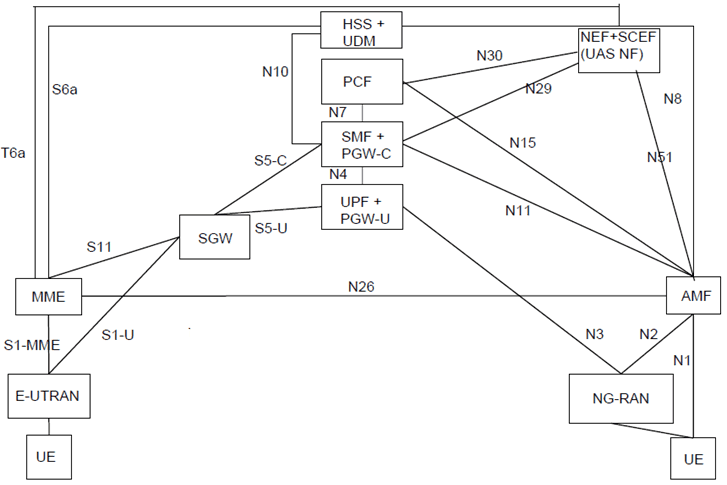
Figure 4.2.2-2: Non-roaming architecture for interworking between 5GS and EPC/E-UTRAN
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
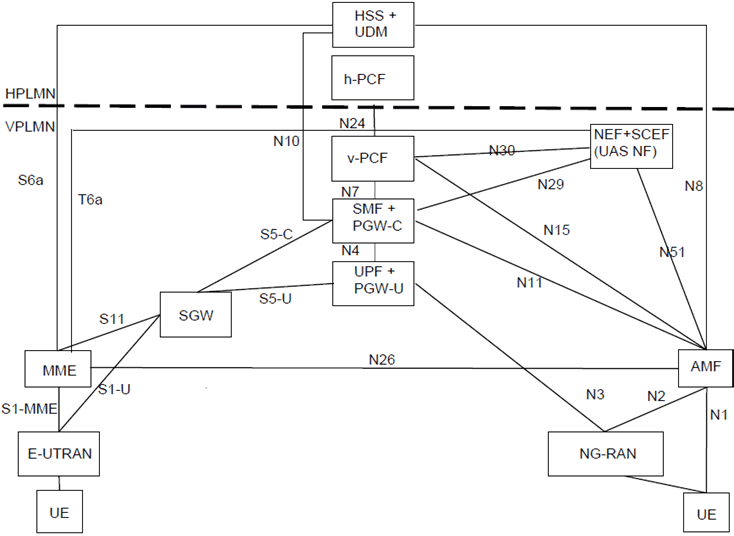
Figure 4.2.2-3: Local breakout roaming architecture for interworking between 5GS and EPC/E-UTRAN
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
4.2.3 5GS Non-roaming Reference Architecture p. 17
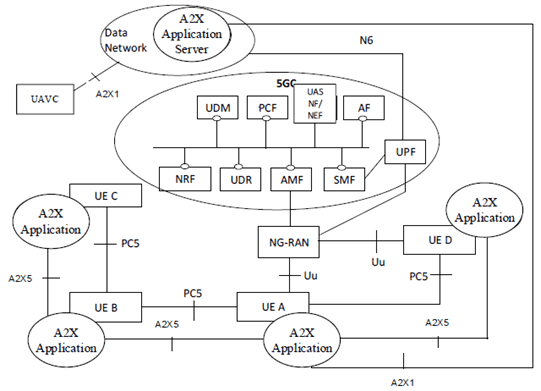
Figure 4.2.3-1: 5G System non-roaming architecture for UAVs and for A2X communication over PC5 and Uu reference points
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
4.2.4 5GS Roaming Reference Architecture p. 18
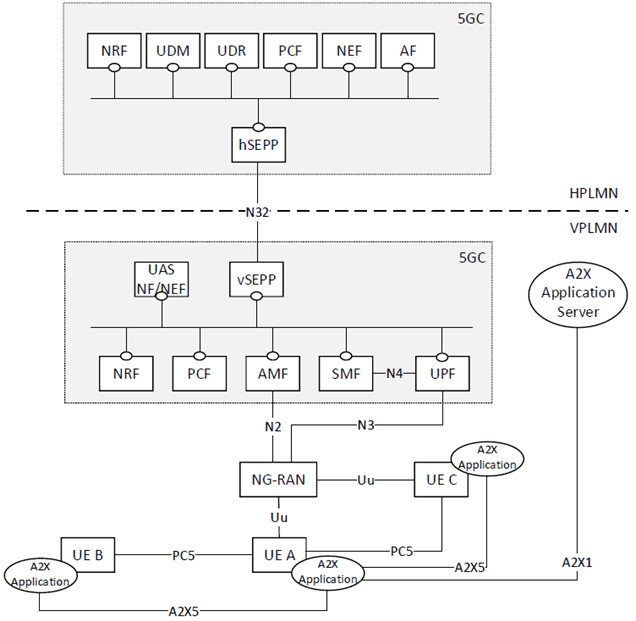
Figure 4.2.4-1: Roaming 5G System architecture for UAVs and for A2X communication over PC5 and Uu reference points - local breakout scenario in service-based interface representation
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
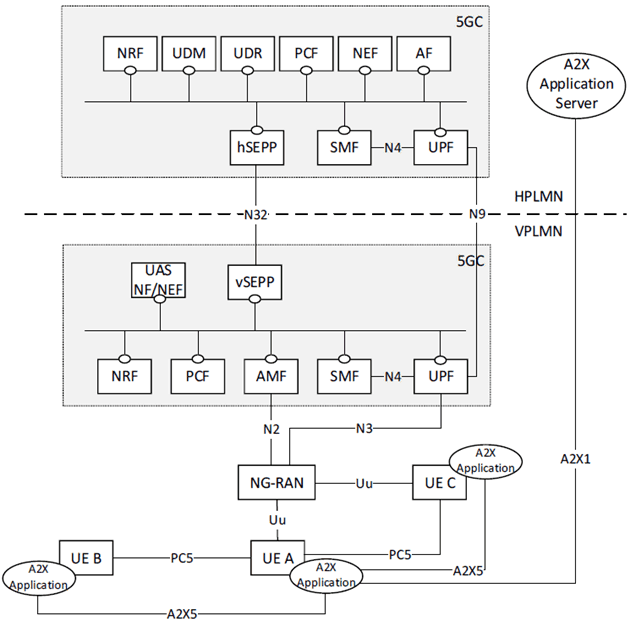
Figure 4.2.4-2: Roaming 5G System architecture for UAVs and for A2X communication over PC5 and Uu reference points - Home routed scenario
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
4.2.4A Void
4.2.5 Service-based interfaces p. 19
The 5G System Architecture for UAVs contains the service-based interfaces defined in TS 23.501, with the following differences:
Nudm:
In the case of A2X Service, services provided by UDM are used to get A2X Service related subscription information to AMF during Initial registration procedure or UE Configuration Update (UCU) procedure to inform AMF subscription information has changed.
Npcf:
In the case of A2X Service, services provided by H-PCF are used to provide A2X Service related parameters to V-PCF for UE and NG-RAN in the roaming case.
Nudr:
In the case of A2X Service, services provided by UDR are used to notify the PCF and the UDM of the update of the A2X Service related information.
Nnef:
In the case of A2X Service, services provided by NEF are used by the A2X Application Server to update A2X Service related information of 5GC.
Namf:
In the case of A2X Service, services provided by AMF are consumed by PCF to provide the A2X Service related parameters for the UE and the NG-RAN to AMF, and to enable the AMF create or update UE context related to A2X service.
Nnrf:
In the case of A2X Service, services provided by NRF are used to discover the PCF that supports A2X.
4.2.6 Reference points p. 20
The 5G System Architecture for UAV contains the reference points defined in TS 23.501. In addition, the reference points of TS 23.287 apply, with the following differences:
A2X1:
The reference point between the A2X applications in the UAV UE and in the UAV-C, and the A2X Application Server. This reference point is out of scope of this specification.
A2X5:
The reference point between the A2X applications in the UEs. This reference point is not specified in this release of the specification.
N1:
In addition to the relevant functions defined in TS 23.501 for N1, in the case of A2X Service it is also used to convey the A2X Policy and parameters (including service authorization) from AMF to UE and to convey the UE's A2X Capability and PC5 Capability for A2X information from UE to AMF.
N2:
In addition to the relevant functions defined in TS 23.501 for N2, in the case of A2X Service it is also used to convey the A2X Policy and parameters (including service authorization) from AMF to NG-RAN.