Content for TS 33.102 Word version: 18.0.0
6.8.8 PS handover from Iu to Gb mode
6.8.9 PS handover from Gb to Iu mode
6.8.10 SRVCC - between HSPA and UTRAN/GERAN
6.8.11 Handling of the START value in intersystem mobility cases
...
...
6.8.8 PS handover from Iu to Gb mode |R6| p. 53
PS Handover is described in TS 43.129
6.8.8.1 UMTS security context |R7| p. 53
A UMTS security context is only established for UMTS subscribers. At the network side, two cases are distinguished:
- In case of a PS intra SGSN Handover, the SGSN derives the 64-bit GSM cipher key Kc from the UMTS cipher/integrity keys CK and IK agreed during the latest UMTS AKA procedure (using the conversion function c3) and applies it if the selected GEA ciphering algorithm requires a 64-bit key. If the selected GEA ciphering algorithm requires a 128-bit key, the SGSN shall apply the 128-bit GSM cipher key Kc 128 derived from the CK and IK agreed during the latest UMTS AKA.
- In case of a PS inter SGSN handover, the initial SGSN sends the UMTS cipher/integrity keys CK and IK agreed during the latest UMTS AKA procedure to the new SGSN. The new SGSN stores the keys, derives the 64-bit GSM cipher key Kc and applies the latter if the selected GEA ciphering algorithm requires a 64-bit key. If the selected GEA ciphering algorithm requires a 128-bit key, the SGSN shall apply the 128-bit GSM cipher key Kc 128 derived from the CK and IK agreed during the latest UMTS AKA. The new SGSN becomes the new anchor point for the service.
6.8.8.2 GSM security context p. 53
A GSM security context is only established for GSM subscribers. At the network side, two cases are distinguished:
- In case of a PS intra SGSN Handover, the SGSN starts to apply the 64-bit GSM cipher key Kc agreed during the latest GSM AKA procedure.
- In case of a PS inter SGSN Handover, the initial SGSN sends the 64-bit GSM cipher key Kc agreed during the latest GSM AKA procedure to the (new) SGSN. The new SGSN stores the key and applies it. The new SGSN becomes the new anchor point for the service.
6.8.9 PS handover from Gb to Iu mode |R6| p. 54
PS Handover is described in TS 43.129
6.8.9.1 UMTS security context p. 54
A UMTS security context is only established for UMTS subscribers. At the network side, two cases are distinguished:
- In case of a PS intra SGSN Handover, the UMTS cipher/integrity keys CK and IK agreed during the latest UMTS AKA procedure are sent to the target RNC or BSC.
- In case of a PS inter SGSN Handover, the initial SGSN sends the UMTS cipher/integrity keys CK and IK agreed during the latest UMTS AKA procedure to the new SGSN controlling the target RNC or BSC. The new SGSN becomes the new anchor point for the service. The new SGSN then stores the UMTS cipher/integrity keys CK and IK and sends them to the target RNC or BSC.
6.8.9.2 GSM security context p. 54
A GSM security context is only established for GSM subscribers. At the network side, two cases are distinguished:
- In case of a PS intra SGSN handover the SGSN derives UMTS cipher/integrity keys CK and IK from the 64-bit GSM cipher key Kc (using the conversion functions c4 and c5) agreed during the latest GSM AKA procedure and sends them to the target RNC or BSC.
- In case of a PS Inter SGSN handover the initial SGSN sends the 64-bit GSM cipher key Kc agreed during the latest GSM AKA procedure to the new SGSN controlling the target RNC or BSC. The new SGSN becomes the new anchor point for the service. The new SGSN stores the 64-bit GSM cipher key Kc and derives the UMTS cipher/integrity keys CK and IK which are then forwarded to the target RNC or BSC.
6.8.10 SRVCC - between HSPA and UTRAN/GERAN |R8| p. 54
6.8.10.1 SRVCC from HSPA to circuit switched UTRAN/GERAN |R11| p. 54
HSPA SRVCC to UTRAN/GERAN is described in TS 23.216.
Case 1: UMTS subscribers
Case 1.1: HO to UTRAN
When the SRNC decides to start a SRVCC from HSPA to UTRAN, it shall initiate the SRVCC Preparation procedure described in TS 25.413. The source SGSN shall generate a NONCE and derive CK' CS||IK' CS from the NONCE and the CK PS||IK PS generated during the latest UMTS AKA procedure.
In case the current UMTS security context is mapped from an EPS security context and there has been no UMTS AKA run since the current UMTS security context was mapped, the CK PS, IK PS and GPRS Kc belonging to the mapped UMTS security context shall be considered to be the keys from the latest UMTS AKA.
The source SGSN shall transfer CK' CS, IK' CS, KSI'CS (=KSIPS) and the NONCE to the SRNC and transfer CK' CS, IK' CS and KSI'CS (=KSIPS) to the MSC server enhanced for SRVCC. The SRNC shall transfer the NONCE to the target RNC. The target RNC shall include the NONCE in the handover command to be sent to the UE. The SRNC shall also transfer the security context, including CK' CS, IK' CS, KSI'CS and START CS (which is received by the SRNC during RRC connection establishment), to the target RNC.
Upon reception of the handover command, the ME shall derive CK' CS||IK' CS from CK PS||IK PS and the NONCE, and set KSI'CS to KSIPS. The ME shall convert GSM ciphering key Kc' from CK' CS||IK' CS, and set GSM CKSN' CS equal to KSI'CS.
For the definition of the Key Derivation Function and its inputs see Annex B.3.
Case 1.2: HO to GERAN
When the SRVCC is from HSPA to GERAN, the source SGSN shall generate a NONCE and derive CK' CS, and IK' CS from the NONCE and the CK PS||IK PS generated during the latest UMTS AKA procedure.
In case the current UMTS security context is mapped from an EPS security context and there has been no UMTS AKA run since the current UMTS security context was mapped, the CK PS, IK PS and GPRS Kc belonging to the mapped UMTS security context shall be considered to be the keys from the latest UMTS AKA.
The source SGSN shall append the NONCE to the GSM HO command, received from the target BSS, when forwarding the command to the SRNC. The SRNC shall forward the NONCE together with the GSM HO command to the UE.
The source SGSN shall transfer the security context, including CK' CS, IK' CS and KSI'CS (=KSIPS) to the MSC server enhanced for SRVCC. The MSC server enhanced for SRVCC and the ME shall convert CK' CS||IK' CS to GSM ciphering key Kc', and set GSM CKSN' CS to KSI'CS.
Upon reception of the handover command, the ME shall derive CK' CS, and IK' CS from CK PS||IK PS and the NONCE, convert GSM ciphering key Kc' from CK' CS||IK' CS, and set GSM CKSN' CS to KSI'CS.
For the definition of the Key Derivation Function and its inputs see Annex B.3.
If a 128-bit GSM ciphering algorithm is taken into use, the target MSC server enhanced for SRVCC and UE shall derive the GSM ciphering key Kc 128 key derived from CK' CS||IK' CS as described in Annex B.5.
For both cases 1.1 and 1.2:
The MSC server enhanced for SRVCC shall overwrite the stored parameters CK CS, IK CS and KSICS if any, with the parameters CK' CS, IK' CS and KSI'CS received from the source SGSN when the SRVCC handover has been completed successfully. The ME shall overwrite the stored parameters CK CS, IK CS , KSICS , GSM ciphering key Kc and GSM CKSN CS if any, with the derived parameters CK' CS, IK' CS, KSI'CS, GSM ciphering key Kc' and GSM CKSN' CS in both ME and USIM when the SRVCC handover has been completed successfully. If the SRVCC handover isn't completed successfully, the MSC server enhanced for SRVCC and the UE shall discard CK' CS, IK' CS and KSI'CS.
The MSC server enhanced for SRVCC shall delete the stored parameters CK CS and IK CS if the SRVCC handover is not completed successfully.
Case 2: GSM subscribers
Case 2.1: HO to UTRAN
When the SRNC decides to start a SRVCC from HSPA to UTRAN, it shall initiate the SRVCC Preparation procedure (see TS 25.413). The source SGSN shall generate a NONCE and derive GSM ciphering key Kc' from the NONCE and the GPRS Kc generated in the latest successful GSM AKA.
The source SGSN shall set GSM CKSN'CS and KSI'CS to GPRS CKSNPS. . The source SGSN shall compute CK' CS, IK' CS from GSM ciphering key Kc', using the conversion functions c4 and c5, and transfer CK' CS, IK' CS and KSI'CS to the SRNC. The SRNC shall transfer the NONCE to the target RNC. The target RNC shall include the NONCE in the handover command to be sent to the UE. The SRNC shall transfer the security context, including CK' CS, IK' CS, KSI'CS and START CS (which is received by the SRNC during RRC connection establishment), to the target RNC.
The source SGSN shall also transfer GSM ciphering key Kc' and GSM CKSN' CS to the MSC server enhanced for SRVCC.
Upon reception of the handover command, the UE shall derive GSM ciphering key Kc' from the GPRS Kc generated in the latest successful GSM AKA and the NONCE. The UE shall set GSM CKSN'CS and KSI'CS to GPRS CKSNPS. The UE shall compute CK' CS, IK' CS from GSM ciphering key Kc', using the conversion functions c4 and c5.
For the definition of the Key Derivation Functions see Annex B.4.
Case 2.2: HO to GERAN
When the SRVCC is from HSPA to GERAN, the source SGSN shall generate a NONCE and derive GSM ciphering key Kc' from the NONCE and the 64-bit GPRS Kc generated in the latest successful GSM AKA.
The source SGSN shall append the NONCE to the GSM HO command, received from the target BSS, when forwarding the command to the SRNC. The SRNC shall forward the NONCE together with the GSM HO command to the UE.
The source SGSN shall set GSM CKSN'CS to GPRS CKSNPS and transfer GSM ciphering key Kc' and GSM CKSN'CS to the MSC server enhanced for SRVCC.
Upon reception of the handover command, the UE shall derive GSM ciphering key Kc' from the GPRS Kc generated in the latest successful GSM AKA and the NONCE, and set GSM CKSN'CS to GPRS CKSNPS.
For the definition of the Key Derivation Functions see Annex B.4.
For both cases 2.1 and 2.2:
The MSC server enhanced for SRVCC shall overwrite the stored parameters 64-bit GSM ciphering key Kc and GSM CKSNCS, if any, with the parameters GSM ciphering key Kc' and GSM CKSN'CS received from the source SGSN when the SRVCC handover has been completed successfully. The UE shall overwrite the stored parameters 64-bit GSM ciphering key Kc and GSM CKSNCS, if any, with the derived parameters GSM ciphering key Kc' and GSM CKSN'CS in both ME and SIM when the SRVCC handover has been completed successfully. If the SRVCC handover isn't completed successfully, the MSC server enhanced for SRVCC and the UE shall discard GSM ciphering key Kc' and GSM CKSN'CS.
If the SRVCC is for an emergency call and the session in HSPA complies with clause 6.4.9.1, the security procedure in this subclause shall be applied.
If the SRVCC is for an emergency call and the session in HSPA complies with clause 6.4.9.2, the security procedure in this subclause shall not be applied, i.e., no key derivation is needed.
The MSC server enhanced for SRVCC shall delete the stored parameters CK CS and IK CS if the SRVCC handover isn't completed successfully, so for any subsequent CS connection a new CS key-set is generated.
6.8.10.2 SRVCC from circuit switched GERAN to HSPA |R11| p. 56
SRVCC handover from circuit switched GERAN to HSPA is defined in TS 23.216.
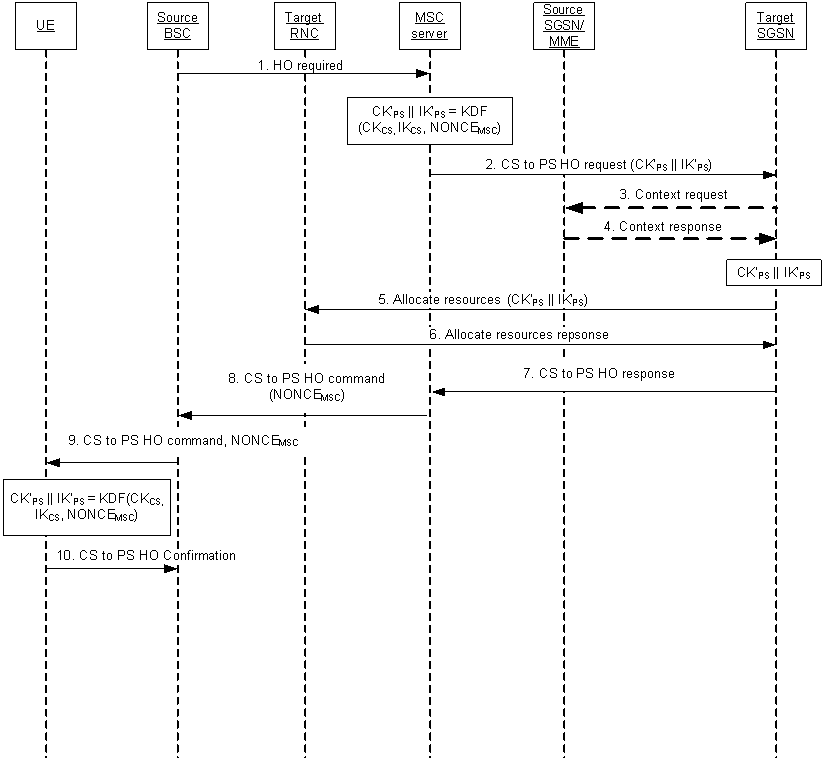
The numbering in the following clauses refers to the signalling numbering in Figure 20.
In the following, the term "latest" keys refer to the keys from the latest UMTS AKA or GSM AKA run respectively. If the current UMTS or GSM security context is mapped from an EPS security context and no AKA has been run in the current CS access, the term "latest" keys refer to the keys from the currently active UMTS or GSM security context
Step 2.
For UMTS subscribers, the source MSC server enhanced for SRVCC shall generate a NONCE MSC and derive CK' PS and IK' PS from this NONCE MSC and the latest CK CS and IK CS. The derivation shall be according to Annex B.6. For The source MSC server enhanced for SRVCC shall further set the KSI'PS equal to the KSICS associated with the latest key set for UMTS subscribers,
For GSM susbscribers, the source MSC server enhanced for SRVCC shall derive GPRS Kc' from the generated NONCE MSC and the latest GSM Kc. The derivation shall be according to Annex B.7. The MSC server enhanced for SRVCC shall further set the CKSN'PS equal to CKSNCS associated with the latest key set for GSM subscribers.
For UMTS subscribers, the MSC server enhanced for SRVCC shall transfer the CK' PS/IK' PS and the KSI'PS, to the target SGSN in the CS to PS handover request.
For GSM subscribers, the MSC server enhanced for SRVCC shall transfer the GPRS Kc' and the CKSN'PS, to the target SGSN in the CS to PS handover request.
Step 3 and 4.
The target SGSN can request context information for the UE from an old SGSN. The target SGSN shall discard any CK PS, IK PS, GPRS Kc, CKSNPS and KSIPS received from an old SGSN. If the target SGSN received any authentication vectors from the old SGSN, the target SGSN shall process these authentication vectors according to clause 6.3.4 of the present document.
Step 5.
If the target SGSN received a GPRS Kc' and a CKSN'PS from the MSC server enchanced for SRVCC, then the target SGSN shall compute CK' PS and IK' PS from the GPRS Kc' using functions c4 and c5 of the present document. The target SGSN shall associate the CK' PS and IK' PS with KSI'PS, which shall be set equal to CKSN'PS received from the source MSC server enhanced for SRVCC.
SGSN shall send the CK' PS, IK' PS to the target RNC.
Step 6a.
The target RNC shall include the transparent container (RRCConnectionReconfiguration message) sent to the source BSC via the core network.
Step 7.
The target SGSN shall include the transparent container received from the target RNC in the CS to PS HO Response message sent to source MSC server enhanced for SRVCC.
Step 8.
Source MSC server enhanced for SRVCC shall include the transparent container and the NONCE MSC in the CS to PS HO command sent to the source BSC.
Step 9.
The source BSC shall include the transparent container and the NONCE MSC in the CS to PS HO command sent to the ME.
For UMTS subscribers, the ME shall derive CK' PS and IK' PS. The derivation shall be done according to Annex B.6, using the NONCE MSC received in the CS to PS HO command, the latest CK CS and IK CS. The ME shall set KSI'PS equal to KSICS and associate the newly derived keys with KSI'PS. If the USIM supports storage of GPRS Kc, the ME shall derive GPRS Kc' from CK' PS and IK' PS using the function c3 of the present specification. The ME shall associate the GPRS Kc' with CKSN'PS which shall be set equal to KSI'PS. The ME shall overwrite the stored parameters CK PS, IK PS , KSIPS , GPRS ciphering key Kc and GPRS CKSN PS if any, with the derived parameters CK' PS, IK' PS, KSI'PS, GPRS ciphering key Kc' and GPRS CKSN' PS in both ME and USIM when the SRVCC handover has been completed successfully..
For GSM subscribers, the ME shall derive GPRS Kc' according to Annex B.7, using the NONCE MSC received in the CS to PS HO command and the latest GSM Kc. The ME shall set CKSN'PS equal to CKSNCS associated with the latest GSM security context and associate it with the GPRS Kc'. The ME shall in this case also derive CK' PS and IK' PS from the GPRS Kc' using the c4 and c5 functions of the present specification. The ME shall associate the CK' PS and IK' PS with KSI'PS which shall be set equal to CKSN'PS. The ME shall overwrite the stored parameters 64-bit GPRS ciphering key Kc and GPRS CKSNPS, if any, with the derived parameters GPRS ciphering key Kc' and GPRS CKSN'PS in both ME and SIM when the SRVCC handover has been completed successfully.
Step 10.
The ME sends the CS to PS handover confirmation message to the target RNC and the CK' PS and IK' PS shall become the active key set both in the ME and in the RNC.
If the SRVCC handover fails, the ME and the network shall discard all changes of state as specified above.
6.8.11 Handling of the START value in intersystem mobility cases |R11| p. 58
The START values (see clause 6.4.8) shall be kept in the volatile memory of the ME in the following cases:
- Intersystem idle mobility for CS Services - from UTRAN to GSM BSS;
- Intersystem handover for CS Services - from UTRAN to GSM BSS;
- Intersystem change for PS Services - from UTRAN to GSM BSS;
- PS handover from Iu to Gb mode;
- SRVCC - from HSPA to UTRAN/GERAN;