Content for TS 24.502 Word version: 18.0.0
7.3A IKE SA establishment procedure for trusted non-3GPP access
7.3A.1 General
7.3A.2 EAP session over non-3GPP access
7.3A.3 IKE SA and signalling IPsec SA establishment procedure
7.3A.4 Procedure for devices without NAS support
...
...
7.3A IKE SA establishment procedure for trusted non-3GPP access |R16| p. 46
7.3A.1 General p. 46
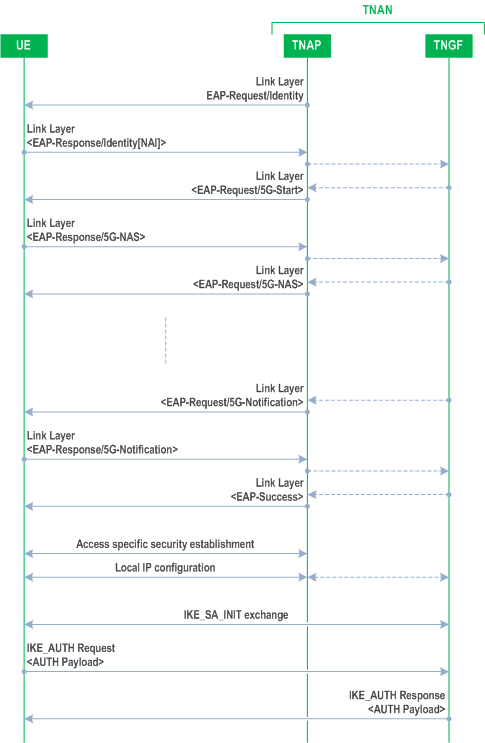
A trusted non-3GPP access network (TNAN) includes a trusted non-3GPP access point (TNAP) and a trusted non-3GPP gateway function (TNGF). The TNAN and a UE initiate an exchange of EAP-Request and EAP-Response messages including Identity as specified in RFC 3748 for link layer authentication of the UE by the TNAP. Upon completion of the EAP-Request/Response messages, an exchange of the EAP-5G messages are initiated once the UE receives an EAP-Request/5G-Start from the TNGF. The UE also at that time informs the upper layers that the access stratum connection is established.
An exchange of the NAS messages which are encapsulated in EAP-5G messages occur until the UE is authenticated by the 5GCN. Upon completion of the UE authentication and reception of the EAP-Success by the UE, the UE and the TNAP employs the TNAP key to establish access specific layer-2 security such as 4-way handshake in case IEEE 802.11 [19] is used between the TNAP and the UE.
Upon completion of successful establishment of access specific layer-2 security, the UE is configured with an IP address by TNAN by e.g. DHCP and the UE initiates an IKE_SA_INIT exchange as specified in RFC 7296.
The UE establishes the IP based secure connection by establishing an IKE SA and first child SA for NAS signalling traffic to the TNGF over NWt. Once the UE establishes the IKE SA and the signalling IPsec SA with the TNGF, the UE initiates establishment of a TCP connection for transport of NAS message with TNGF, secured using the signalling IPsec SA. The UE and the TNGF exchanges NAS messages over the TCP connection once it is established. Additional child SAs (user plane IPsec SAs) can be established to transfer user plane traffic (see clause 7.5).
An example of an IKE SA and first child SA establishment procedure is shown in Figure 7.3A.1-1. The Figure illustrates that EAP messages are employed for the communication between the UE and the TNAP while the TNAP is transparent to the communication between the UE and the TNGF when employing EAP-5G messages. Link layer protocol is used to exchange these messages between the UE and the TNAN. The internal protocol used for the communications between the TNAP and the TNGF, is illustrated as dashed lines in this Figure and is out of the scope of 3GPP.
7.3A.2 EAP session over non-3GPP access p. 48
7.3A.2.1 General p. 48
The UE and the TNAN establishes a connection depending on the access link between the UE and the TNAP. For instance if the TNAP is a trusted WLAN access point, IEEE 802.11 [19] describes the connection between the UE and the TNAP. If the access link between the UE and the TNAP is Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) as specified in RFC 1661, the Link Control Protocol (LCP) as specified in RFC 1570 describes the connection between the UE and the TNAP.
In the trusted non-3GPP access network:
- the TNAP and the UE exchange EAP-request/Identity message and EAP-response/Identity message; and
- the TNGF and the UE exchange EAP messages of EAP-5G method,
7.3A.2.2 Identity transaction p. 48
Upon reception of EAP-Request/Identity message (as described in RFC 3748), encapsulated in the link layer protocol packets from the TNAP, the UE shall:
- construct an EAP-Response/Identity message as described in IETF RFC 3748 containing an NAI as specified in clause 28.7.6 of TS 23.003 to request a PLMN or SNPN when the trusted connectivity is 5G connectivity using trusted non-3GPP access; and
- transmit the EAP-Response of identity type encapsulated in the link layer protocol packets towards the TNAP.
7.3A.2.3 EAP-5G session initiation p. 48
The UE and the TNGF shall exchange EAP-5G messages. The TNGF on reception of the NAI by TNAP and passed on to TNGF, shall initiate EAP-5G session by sending an EAP-Request/5G-Start message. Upon reception of an EAP-Request/5G-Start message, the UE shall send an EAP-Response/5G-NAS message encapsulated in link layer protocol packets. In the EAP-Response/5G-NAS message, the UE:
- shall include a NAS-PDU field containing a NAS message, for example, a REGISTRATION REQUEST message;
- shall include an AN-parameters field containing access network parameters, such as UE identity, selected PLMN ID or SNPN, requested NSSAI and establishment cause, selected NID if the UE is accessing SNPN services via trusted non-3GPP access network, and onboarding indication if the UE is accessing SNPN for onboarding services in SNPN via trusted non-3GPP access network, see TS 23.502, each of which is up to 255 (decimal) octets long; and
- if at least one access network parameter is longer than 255 (decimal) octets, shall include an extended-AN-parameters field containing one or more access network parameters, such as UE identity, see TS 23.502, each of which is longer than 255 (decimal) octets.
7.3A.2.4 EAP-5G session completion initiated by the network p. 49
Upon completion of successful authentication and on reception of the acknowledgement from the UE that it had received the access network parameters, the TNAN shall send an EAP-Success message encapsulated in the link layer protocol packets towards the UE via the TNAP.
7.3A.2.5 EAP-5G session completion initiated by the UE p. 49
For trusted non-3GPP access, the procedure for when the EAP-5G session completion initiated by the UE, is the same as that of untrusted non-3GPP access as described in clause 7.3.3.3 with the difference that the N3IWF shall be replaced by the TNGF.
7.3A.3 IKE SA and signalling IPsec SA establishment procedure p. 49
7.3A.3.1 IKE SA and signalling IPsec SA establishment initiation p. 49
In a trusted non-3GPP access network, once the EAP- 5G authentication is successfully complete and the UE is configured with a local IP address, the UE shall use the TNGF IP address received in the EAP-Request/5G-Notification message (see clause 7.3A.2.3) to establish a secure connection between the UE and the TNGF over NWt to exchange NAS signalling messages with the AMF. The UE shall establish the secure connection by establishing an IKE SA and signalling IPsec SA (first child SA) by initiating the IKE_SA_INIT exchange and then IKE_AUTH exchange for mutual authentication with the TNGF and NULL encryption as specified in RFC 2410. The UE shall set the IDi payload of the IKE_AUTH request message in the IKE_AUTH exchange (see RFC 7296) to the NAI format of 5G-GUTI or the NAI format of SUCI as specified in TS 23.003, depending on the employed UE identity in the EAP-Response/5G-NAS message at the time of EAP-5G session initiation according to clause 7.3A.2.3.
7.3A.3.2 IKE SA and signalling IPsec SA establishment accepted by the network p. 49
The UE shall establish the IKE SA and signalling IPsec SA (first child SA) according to clause 7.3.2.2 with the difference that the N3IWF is replaced by the TNGF.
Upon completion of the IKE SA and signalling IPsec SA (first child SA) establishment between the UE and the TNGF, the UE and the TNGF shall send further NAS messages over the TCP connection within the signalling IPsec SA (first child SA).
7.3A.3.3 IKE SA and signalling IPsec SA establishment not accepted by the network p. 49
For trusted non-3GPP access, the procedure for when the IKE SA and signalling IPsec SA establishment are not accepted by the network, is the same as that of the untrusted non-3GPP access as described in clause 7.3.2.3 with the difference that the N3IWF shall be replaced by the TNGF.
7.3A.4 Procedure for devices without NAS support p. 50
7.3A.4.1 General p. 50
A trusted non-3GPP access network (TNAN) may be implemented as a trusted WLAN access network (TWAN) which supports a WLAN access technology such as the one described in IEEE 802.11 [19]. A non 5G capable over WLAN (N5CW) device does not support NAS signalling with the 5GCN over WLAN, but may access 5GCN via a TWAN supporting a trusted WLAN interworking function (TWIF). An N5CW device may be a UE with capability for NAS signalling with the 5GCN using the N1 reference point as specified in TS 24.501 over 3GPP access although it lacks capability of NAS signalling over WLAN.
7.3A.4.2 N5CW device registration over trusted WLAN access network p. 50
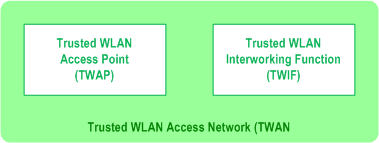
A trusted WLAN access network (TWAN) includes a trusted WLAN access point (TWAP) and a trusted WLAN interworking function (TWIF) as illustrated in Figure 7.3A.4.2-1.
The EAP-AKA' authentication procedure is executed for connecting the N5CW device to a TWAN according to clause 7A.2.4 of TS 33.501.
The TWAN and an N5CW device initiate an exchange of EAP-Request/Identity message and EAP-Response/Identity message as specified in RFC 3748 for link layer authentication of the UE by the TWAP. In the trusted WLAN access network, the TWAP and the N5CW device exchange EAP-Request/Identity message and EAP-Response/Identity message, encapsulated in the link layer protocol packets i.e. IEEE 802.11/802.1x packets.
Upon reception of EAP-Request/Identity message encapsulated in the IEEE 802.11/802.1x packets from the TWAP, the N5CW device shall:
- construct an EAP-Response/Identity message as described in IETF RFC 3748 containing an NAI as specified in clause 28.7.7 of TS 23.003 to request a PLMN or SNPN when the trusted connectivity is 5G connectivity without NAS using trusted non-3GPP access; and
- transmit the EAP-Response of identity type encapsulated in the link layer protocol packets towards the TWAP.