Content for TS 23.682 Word version: 18.0.0
1…
4.2
4.3…
4.4…
4.5…
4.5.7…
4.5.14…
4.6…
5…
5.3…
5.5…
5.6…
5.6.2…
5.6.6…
5.7…
5.8…
5.9…
5.13…
5.14…
5.15
5.16
5.17…
5.18
5.19…
A…
C…
5.6 Monitoring Procedures
5.6.0 Common Parameters
5.6.1 Monitoring Event configuration and deletion via HSS
...
...
5.6 Monitoring Procedures |R13| p. 57
5.6.0 Common Parameters |R15| p. 57
This clause describes the common parameters required for Monitoring Event procedures.
SCEF Reference ID is a parameter created by the SCEF to associate a Monitoring Event report or a deletion of a Monitoring Event to a specific Monitoring Request and the associated context information within the SCEF. SCEF Reference ID is stored by HSS, MME, SGSN, and IWK-SCEF.
SCEF ID indicates the SCEF to which the Monitoring Indication message has to be sent to by the HSS, MME, SGSN, or IWK-SCEF. SCEF ID is stored by the HSS, MME, SGSN, and IWK-SCEF.
SCEF Reference ID for Deletion identifies the monitoring event configuration that shall be deleted before applying the requested monitoring event configuration.
Monitoring Type identifies the specific Monitoring Event being requested.
If the Monitoring Event Configuration requested from the SCEF is for a group of UEs, the HSS includes User Identity in the monitoring event configuration.
Maximum Number of Reports is an optional parameter that indicates the maximum number of event reports to be generated by the HSS, MME, or SGSN until the associated monitoring event is considered to expire. This parameter can be used when configuring a monitoring event for an individual UE or a group. When the parameter is configured for a group, the configured value is applied to each individual UE's monitoring event configuration. A value of one implies a single event report is to be generated which makes it equivalent to a One-time Monitoring Request.
Monitoring Duration is an optional parameter that indicates the absolute time at which the related monitoring event request is considered to expire. For Monitoring Requests for a group, this parameter applies to every group member UE.
Inclusion of either Maximum Number of Reports (with a value higher than one) or Monitoring Duration makes the Monitoring Request a Continuous Monitoring Request. For a Continuous Monitoring Request, a single Monitoring Request may generate more than one Monitoring Indication message. Support of continuous monitoring is optional.
Absence of both Maximum Number of Reports and Monitoring Duration makes the Monitoring Request a One-time Monitoring Request. For One-time Monitoring Requests, a single Monitoring Request generates only one Monitoring Report for an individual UE and for an individual group member UE.
If for a given Monitoring Event both Maximum Number of Reports and Monitoring Duration are included then the monitoring request is considered to expire as soon as one of the conditions is met.
Chargeable Party Identifier is an optional parameter included by the SCEF. It identifies the entity towards which accounting/charging functionality is performed by the involved 3GPP network elements.
MTC Provider Information is an optional parameter included by the SCEF. It identifies the MTC Service Provider and/or MTC Application. Optionally the MTC Provider Information may also be provided by the SCS/AS.
Group Reporting Guard Time is an optional parameter for group-based monitoring configuration to indicate the time for which the Monitoring Event Reporting(s) detected by the UEs in a group can be aggregated before sending them to the SCEF/SCS/AS. The value of the Group Reporting Guard time should be set less than the Monitoring Duration. For the continuous monitoring reporting, unless the Monitoring Duration has been reached, the Group Reporting Guard timer is restarted when it expires. If the time left until Monitoring Duration is less than the Group Reporting Guard Time, then the Group Reporting Guard timer shall be set to expire when the Monitoring Duration expires. If the Monitoring Duration is expired, the Group Reporting Guard Time, if running, shall be considered to expire and aggregated Monitoring Event Reporting(s) is sent to destination immediately.
Number of UEs is a parameter that is provided to the SCEF during group-based monitoring configuration to indicate the number of UEs within the group identified by the External Group Identifier. The SCEF uses this value to determine whether the monitoring event has been reported for all group member UEs.
5.6.1 Monitoring Event configuration and deletion via HSS p. 58
5.6.1.1 Configuration Procedure p. 58
Figure 5.6.1.1-1 illustrates the procedure of configuring monitoring at the HSS or the MME/SGSN. The procedure is common for various Monitoring Event types. Common parameters for this procedure are detailed in clause 5.6.0. The steps and parameters specific to different Monitoring Event types are detailed in clauses 5.6.1.3 to 5.6.1.9.
The procedure is also used for deleting a previously configured Monitoring Event either as a standalone procedure or together with configuring a new Monitoring Event between the same SCEF and the same SCS/AS, or replacing a previously configured Monitoring Event with a new Monitoring Event of the same type between the same SCEF and the same SCS/AS, or for one-time reporting if the Configured Monitoring Event is available at the configured node or cancelling the event monitoring for certain UEs (i.e. one individual UE or a sub-set of UEs) in a group of UEs for which there is a configured Monitoring Event or adding the event monitoring for certain new UEs (i.e. one individual UE or a sub-set of UEs) in a group of UEs for which there is a configured Monitoring Event.
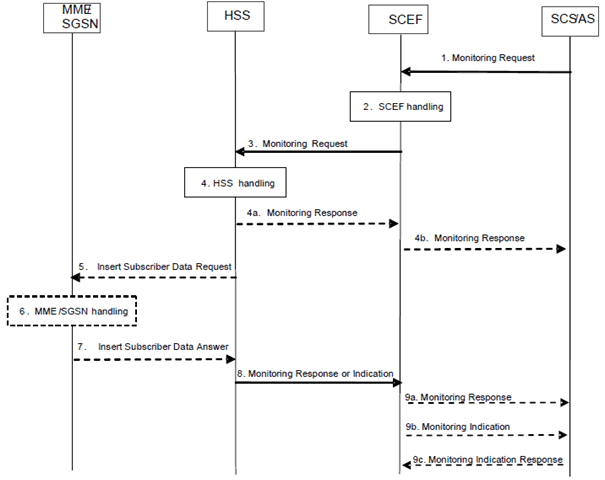
Figure 5.6.1.1-1: Monitoring event configuration and deletion via HSS procedure
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
If the HSS detects that the current serving MME/SGSN cannot support a requested Monitoring Event or the group-basis monitoring event feature (e.g. after a UE mobility event), the HSS performs the procedures given below.
The SCS/AS sends a Monitoring Request (External Identifier or MSISDN or External Group ID, SCS/AS Identifier, Monitoring Type, Maximum Number of Reports, Monitoring Duration, T8 Destination Address, TLTRI for Deletion, TLTRI for Update, the External Identifier(s) or MSISDN(s) of the individual member UE(s) to be cancelled or added for an existing group event, operation indication (cancellation or addition), Group Reporting Guard Time, MTC Provider Information) message to the SCEF. The SCEF assigns a TLTRI that identifies the Monitoring Request, if a new monitoring event is being configured. The SCS/AS may perform deletion of a previously configured Monitoring Event together with configuring a new Monitoring Event. If the SCS/AS wants to perform deletion of a previously configured Monitoring Event, then it shall include TLTRI for Deletion.
If the SCS/AS wants to configure Monitoring Event for the group of UEs, the SCS/AS can send Monitoring Request message including External Group Identifier and Group Reporting Guard Time. If the SCS/AS includes External Group Identifier in the Monitoring Request message, External Identifier or MSISDN shall be ignored. A Group Reporting Guard Time is an optional parameter to indicate that aggregated Monitoring Event Reporting(s) which have been detected for the UEs in a group needs to be sent to the SCS/AS once the Group Reporting Guard Time is expired.
If the SCS/AS decides to cancel or add the monitoring event for certain UEs (i.e. one individual UE or a sub-set of UEs) in a group of UEs for which there is a configured Monitoring Event, the SCS/AS can send Monitoring Request message including the TLTRI for Update corresponding to the existing monitoring event configuration and the External Identifier(s) or MSISDN(s) of the individual member UE(s) to be cancelled or added with the operation indication which is either cancellation or addition.
Step 2.
The SCEF stores SCS/AS Identifier, T8 Destination Address, Monitoring Duration, Maximum Number of Reports and Group Reporting Guard Time, if provided. If the SCEF assigned a TLTRI, the SCEF stores the TLTRI, and also assigns it to an SCEF Reference ID. Based on operator policies, if either the SCS/AS is not authorized to perform this request (e.g. if the SLA does not allow for it) or the Monitoring Request is malformed or the SCS/AS has exceeded its quota or rate of submitting monitoring requests, the SCEF performs step 9 and provides a Cause value appropriately indicating the error. If the SCEF received a TLTRI for Update, the SCEF looks up the SCEF context pointed to by the TLTRI for Update to derive the related SCEF Reference ID. If the SCEF received a TLTRI for Deletion, the SCEF looks up the SCEF context pointed to by the TLTRI for Deletion to derive the related SCEF Reference ID for Deletion.
If the SCEF received a request to cancel the monitoring event for indicated UEs (i.e. one individual UE or a sub-set of UEs) in a group of UEs for which there is a configured Monitoring Event and if the Maximum Number of Reports applies to the monitoring event configuration, the SCEF sets the stored number of reports of the indicated UE(s) to Maximum Number of Reports.
The SCEF uses the Group Reporting Guard Time for a Monitoring Event Reporting for the group of UEs when the Monitoring Indication message is sent from the MME/SGSN to the SCEF. The SCEF sets the Group Reporting Guard Time for HSS less than the value for the SCEF received from SCS/AS in order to ensure to receive accumulated Monitoring Indication from HSS before the Group Reporting Guard Timer for SCEF is expired.
Step 3.
The SCEF sends a Monitoring Request (External Identifier or MSISDN or External Group Identifier, SCEF ID, SCEF Reference ID, Monitoring Type, Maximum Number of Reports, Monitoring Duration, SCEF Reference ID for Deletion, the External Identifier(s) or MSISDN(s) of the individual member UE(s) to be cancelled or added, operation indication (cancellation or addition), Chargeable Party Identifier, Group Reporting Guard Time, MTC Provider Information) message to the HSS to configure the given Monitoring Event on the HSS and on the MME/SGSN, if required. If the External Group Identifier is included, External Identifier or MSISDN shall be ignored. For one-time Monitoring Request of Roaming Status, the SCEF does not indicate the Group Reporting Guard Time.
Step 4.
The HSS examines the Monitoring Request message, e.g. with regard to the existence of External Identifier or MSISDN or External Group Identifier, whether any included parameters are in the range acceptable for the operator, whether the monitoring event(s) is supported by the serving MME/SGSN, whether the group-basis monitoring event feature is supported by the serving MME/SGSN, or whether the monitoring event that shall be deleted or updated is valid. The HSS optionally authorizes the chargeable party identified by Chargeable Party Identifier. If this check fails the HSS follows step 8 and provides a Cause value indicating the reason for the failure condition to the SCEF.
The HSS stores the SCEF Reference ID, the SCEF ID, Maximum Number of Reports, Monitoring Duration and the SCEF Reference ID for Deletion as provided by the SCEF. For a Monitoring Request for a group, such parameters are stored for every group member UE. For a Monitoring Request with the External Identifier(s) or MSISDN(s) of the individual member UE(s) to be cancelled or added as in step 3, such parameters together with the operation indication as provided by the SCEF are stored for every indicated UE.
The HSS uses the Group Reporting Guard Time for a Monitoring Event Reporting for the group of UEs when the Monitoring Indication message is sent from the HSS to the SCEF.
Step 4a.
For group based processing, if the HSS receives the Monitoring Request with an External Group Identifier, the HSS sends a Monitoring Response (SCEF Reference ID, Number of UEs, Cause) message to the SCEF to acknowledge acceptance of the Monitoring Request immediately before beginning the processing of individual UEs indicating that Group processing is in progress. The HSS deletes the monitoring event configuration identified by the SCEF Reference ID, if it was requested.
If the HSS receives the Monitoring Request with the External Identifier(s) or MSISDN(s) of the individual member UE(s) to be cancelled or added as in step 3 and the event was monitored by the HSS, the HSS cancels or adds the event monitoring for the indicated UE(s).
Step 4b.
The SCEF sends a Monitoring Response (TLTRI, Cause) message to the SCS/AS. The Cause value indicates progress of Group processing request.
Step 5.
If required by the specific Monitoring Type and when Monitoring Event(s) is supported by the serving MME/SGSN, the HSS sends an Insert Subscriber Data Request (Monitoring Type, SCEF ID, SCEF Reference ID, Maximum Number of Reports, Monitoring Duration, SCEF Reference ID for Deletion, Chargeable Party Identifier) message to the MME/SGSN for each individual UE and for each individual group member UE. If the Monitoring Request message is for a group of UEs, for each UE group member, the HSS includes the selected External ID or the MSISDN in the monitoring event configuration and sends an Insert Subscriber Data Request message per UE to all the MME/SGSN(s) serving the members of the group. If the HSS has received in step 3 Monitoring Request with the External Identifier(s) or MSISDN(s) of the individual member UE(s) to be added, for each indicated UE group member, the HSS includes the corresponding External ID or the MSISDN in the monitoring event configuration and sends an Insert Subscriber Data Request message to the MME/SGSN(s) serving such indicated UE group member. If the HSS has received in step 3 Monitoring Request with the External Identifier(s) or MSISDN(s) of the individual member UE(s) to be cancelled and the event is monitored by MME/SGSN, the HSS includes the received value of the SCEF Reference ID within the SCEF Reference ID for Deletion towards to the MME/SGSN. Optionally, the HSS allocates a Provider-Group-ID based on the MTC Provider Information (different from the IMSI-Group-Id) and sends it to the MME/SGSN to assist the serving node(s) when selecting and differentiating configurations for a given MTC Service Provider (e.g. to delete the configurations for a specific MTC Service Provider at the MME/SGSN).
Step 6.
If the MME/SGSN is configured to use an IWK-SCEF for the PLMN of the SCEF then clause 5.6.6 applies. Otherwise, the MME/SGSN verifies the request, e.g. if the Monitoring Type is covered by a roaming agreement when the request is from another PLMN or whether it serves the SCEF Reference ID for Deletion and can delete it. If this check fails, the MME/SGSN follows step 7 and provides a Cause value indicating the reason for the failure condition to the HSS. Based on operator policies, the MME/SGSN may also reject the request due to other reasons (e.g. overload or HSS has exceeded its quota or rate of submitting monitoring requests defined by an SLA).
The MME/SGSN stores the received parameters and starts to watch for the indicated Monitoring Event unless it is a One-time request and the Monitoring Event is available to the MME/SGSN at the time of sending Insert Subscriber Data Answer. The MME/SGSN deletes the monitoring configuration identified by the SCEF Reference ID for Deletion, if provided.
Step 7.
If the monitoring configuration is successful, the MME/SGSN sends an Insert Subscriber Data Answer (Cause) message to the HSS. If the requested Monitoring Event is available to the MME/SGSN at the time of sending Insert Subscriber Data Answer, then the MME/SGSN includes the Monitoring Event Report in the Insert Subscriber Data Answer message.
Step 8.
For single UE processing, the HSS sends a Monitoring Response (SCEF Reference ID, Cause, Monitoring Event Report) message to the SCEF to acknowledge acceptance of the Monitoring Request and the deletion of the identified monitoring event configuration, if it was requested. The HSS deletes the monitoring event configuration identified by the SCEF Reference ID, if it was requested. If the requested Monitoring Event is available to the HSS at the time of sending Monitoring Response message or was received from the MME/SGSN in step 7, then the HSS includes a Monitoring Event Report in the Monitoring Response message.
If it is a One-time request and the Insert Subscriber Data Answer includes a Monitoring Event Report, the HSS deletes the associated Monitoring Event configuration for the individual UE or for the individual group member UE.
For group-based processing, if the HSS sent the Monitoring Response in step 4a, i.e. due to having received a Monitoring Request with an External Group Identifier and if the Group Reporting Guard Time was provided in the Monitoring Request, the HSS accumulates multiple responses for the UEs of the group within the Group Reporting Guard Time. After the Group Reporting Guard Time expiration, the HSS sends a Monitoring Indication with the accumulated responses. The HSS includes UE identity(ies) and a Cause value indicating the reason for the failure in the message if the monitoring configuration of the group member failed.
In the case of UE mobility, the HSS determines whether the new MME/SGSN supports requested Monitoring Event(s).
Step 9a.
For single UE processing, the SCEF sends a Monitoring Response (Cause, Monitoring Event Report) message to the SCS/AS to acknowledge acceptance of the Monitoring Request and the deletion of the identified monitoring event configuration, if it was requested. If the SCEF received a Monitoring Event Report then it includes the Monitoring Event Report in the Monitoring Response message. If it is a One-time request for an individual UE and the Monitoring Response includes a Monitoring Event Report for the UE, the SCEF deletes the associated Monitoring Event configuration.
Step 9b.
For group-based processing, if no Group Reporting Guard Time was set, then the SCEF sends the Monitor Indication (TLTRI, Cause, Monitoring Event Report) message to the SCS/AS as it receives them from the HSS. Otherwise, it accumulates Monitoring Event for the UEs of the group until the expiration of Group Reporting Guard Time. Upon expiration, the SCEF sends a Monitoring Indication (TLTRI, Cause, list of (External Identifier or MSISDN, Monitoring Event Report)) message to the SCS/AS. A list of accumulated Monitoring Event Report for each UE identified by either External Identifier or MSISDN is also included.
If the Monitoring Request is a one-time request for a group of UEs or if Maximum Number of Reports is included for continuous monitoring of group of UEs, the SCEF uses the list of UE Identities that were received in step 8 and the Number of UEs parameter that was received in step 4a to check if the reports for all the individual group member UEs have been received. If the SCEF determines that all reports for all individual group member UEs have been received, the SCEF sends a request to the HSS to delete the associated Monitoring Event configuration for the group.
Step 9c.
For each Monitoring Indication message received in step 9b, the SCS/AS sends a Monitoring Indication Response (Cause) message to the SCEF. Cause value reflects successful or unsuccessful acknowledgement of Monitoring Indication message.
-
Notify the SCEF that the configured Monitoring Event for the UE is considered to be suspended. The SCEF interprets this to mean that the network will temporarily be unable to serve the configured Monitoring Event. In this case:
- When the MME/SGSN for the UE changes (e.g. due to UE mobility), and the new MME/SGSN supports the suspended Monitoring Event, the HSS shall configure the new MME/SGSN with the Monitoring Event and notify the SCEF of resumption of the suspended Monitoring Event;
- If the criteria for Continuous Reporting expire while the Monitoring Event is suspended, the HSS and the SCEF shall independently delete the Monitoring Event.
5.6.1.2 Void
5.6.1.3 Specific Parameters for Monitoring Event: Loss of connectivity p. 62
Loss of connectivity indicates when the 3GPP network detects that the UE is no longer reachable for either signalling or user plane communication. Such condition is identified when the mobile reachability timer expires in the MME or SGSN (see TS 23.401, TS 23.060, when the UE detaches and when an active UE is purged (see TS 29.272)). The SCS/AS may provide a Maximum Detection Time, which indicates the maximum period of time without any communication with the UE after which the SCS/AS is to be informed that the UE is considered to be unreachable.
- The SCS/AS sets Monitoring Type to "Loss of Connectivity", and optionally adds Maximum Detection Time prior to sending Monitoring Request to the SCEF as in step 1 of clause 5.6.1.1.
- The SCEF executes step 2 of clause 5.6.1.1.
- The SCEF executes step 3 of clause 5.6.1.1.
- The HSS executes step 4 of clause 5.6.1.1. In addition, it checks whether the Maximum Detection Time is within the range defined by operator policies, and, if acceptable then the HSS sets the subscribed periodic RAU/TAU timer using the value of Maximum Detection Time, if it is provided. If the Maximum Detection Time is not acceptable, the HSS rejects the request by executing step 8, and provides a Cause value indicating the reason for the failure condition to the SCEF. If the Enhanced Multiple Event Monitoring feature is not supported and if the subscribed periodic RAU/TAU Timer was previously set by a different Monitoring Request identified by a different SCEF Reference ID for the same UE then, depending on operator configuration, the HSS either performs step 8 to reject the Monitoring Request with an appropriate Cause or accepts the request. If the HSS accepts this request, then it cancels the previously accepted Monitoring Request by including the SCEF Reference ID of that Monitoring Request in step 8. For group based processing, if the previously accepted Monitoring Request is associated with a group of UEs and the HSS is not cancelling the previously accepted Monitoring Request for all UEs in the group, then the HSS provides the list of affected UEs (identified by External Identifier or MSISDN) as well as operation indication (cancellation or addition) to the SCEF in step 8. If the Enhanced Multiple Event Monitoring feature is supported, and if the subscribed periodic RAU/TAU Timer was previously set by a different Monitoring Request or Network Parameter Configuration identified by a different SCEF Reference ID for the same UE, as long as the Maximum Detection Time is within the range defined by operator policies, the HSS shall accept the request. If the newly received Maximum Detection Time is lower than the provided subscribed periodic RAU/TAU timer, the HSS shall set the subscribed periodic RAU/TAU timer using the newly received Maximum Detection Time as described in clause 4.5.6.2. The HSS may notify the SCEF (which then notifies the SCS/AS) of the actual value that is being applied in the 3GPP network.
-
The HSS executes step 5 of clause 5.6.1.1. In addition:
- if the Enhanced Multiple Event Monitoring feature is not supported and the HSS accepts new monitoring event configuration and cancel the existing monitoring event configuration, the HSS includes the new monitoring event configuration information, the SCEF Reference ID for Deletion of the cancelled monitoring event configuration with an appropriate Cause, and the subscribed periodic RAU/TAU Timer (if modified). When HSS accepts new configured Monitoring Event for UEs in step 4 above, the HSS includes the new monitoring event configuration information and the subscribed periodic RAU/TAU Timer (if modified). When HSS removes a previously configured Monitoring Event for UEs in step 4 above, the HSS also deletes the previously configured Monitoring Event in the MME/SGSN, if applicable.
- If the Enhanced Multiple Event Monitoring feature is supported, the HSS includes the new monitoring event configuration information and the subscribed periodic RAU/TAU Timer (if modified). When HSS modifies a previously configured Monitoring Event for UE(s) in step 4 above, the HSS also updates the previously configured Monitoring Event in the MME/SGSN, if applicable.
- The MME/SGSN executes step 6 of clause 5.6.1.1. If the MME/SGSN receives a subscribed periodic RAU/TAU timer value from the HSS, it allocates the subscribed value to the UE as the periodic TAU/RAU timer. The MME/SGSN starts watching for the expiration of the mobile reachable timer.
- Step 7 of clause 5.6.1.1 is executed.
- Step 8 of clause 5.6.1.1 is executed. The HSS may include the SCEF Reference ID of previously accepted Monitoring Request which needs to be cancelled and the cancellation cause. If the HSS, in step 4 above, decides to cancel Monitoring Event for indicated UEs (i.e. one individual UE or a sub-set of UEs) in the group of UEs for which there was a previously configured Monitoring Event, the HSS also includes the External Identifier or MSISDN of these indicated UEs towards the SCEF. If the HSS, in step 4 above, decides to add Monitoring Event for indicated UEs (i.e. one individual UE or a sub-set of UEs) in the group of UEs for which there was a previously configured Monitoring Event, the HSS includes the External Identifier or MSISDN of these indicated UEs towards the SCEF.
- Step 9 of clause 5.6.1.1 is executed. If SCEF Reference ID of previously configured Monitoring Event for cancellation is included in step 8, then the SCEF executes steps 2-5 of clause 5.6.9 using the associated TLTRI towards the associated SCS/AS.
5.6.1.4 Specific Parameters for Monitoring Event: UE reachability p. 64
For UE that is not reachable at the time of monitoring event configuration, UE reachability indicates when the UE becomes reachable for sending either SMS or downlink data to the UE, which is detected when the UE transitions to ECM-CONNECTED mode (for a UE using Power Saving Mode or extended idle mode DRX) or when the UE will become reachable for paging (for a UE using extended idle mode DRX). If the UE is reachable at monitoring event configuration, the MME shall immediately send UE reachability event report. This monitoring event supports Reachabilty for SMS and Reachability for Data. Only a One-time Monitoring Request for Reachability for SMS is supported. The SCS/AS may include the following parameters in the Monitoring Event configuration request to the SCEF:
- Reachability Type indicating whether the request is for "Reachability for SMS", or "Reachability for Data", or both.
- Optionally, Maximum Latency indicating maximum delay acceptable for downlink data transfers. Maximum Latency is used for setting the periodic TAU/RAU timer for the UE as it sets the maximum period after which a UE has to connect to the network again and thereby becomes reachable. Determined by the operator, low values for Maximum Latency may deactivate PSM.
- Optionally, Maximum Response Time indicating the time for which the UE stays reachable to allow the SCS/AS to reliably deliver the required downlink data. Maximum Response Time is used for setting the Active Time for the UE. When the UE uses extended idle mode DRX, the Maximum Response Time is used to determine how early this monitoring event should be reported to the SCS/AS before the next Paging Occasion occurs.
- Optionally, Suggested number of downlink packets indicating the number of packets that the Serving Gateway shall buffer if the UE is not reachable.
- The SCS/AS sets Monitoring Type to "UE Reachability", and includes Reachability Type, and any combination of the following optional parameters: Maximum Latency, Maximum Response Time, Suggested number of downlink packets, and Idle Status Indication prior to sending the Monitoring Request to the SCEF as in step 1 of clause 5.6.1.1.
- The SCEF executes step 2 of clause 5.6.1.1. In addition, it checks whether the Maximum Latency (if included), the Maximum Response Time (if included), and the Suggested number of downlink packets (if included) are within the range defined by operator policies. If not, or if the network does not support Idle Status Indication, then depending on operator policies, the SCEF rejects the request by performing step 9 of 5.6.1.1 with an appropriate cause value.
- When "Reachability for SMS" is requested, the SCEF subscribes with the HSS by executing step 3 of 5.6.1.1 to get notified when the HSS is notified that the UE is reachable. The HSS performs the UE Reachability Notification Request procedure for getting a UE Activity Notification as described in TS 23.401 and/or uses the UE Reachability function as described in TS 23.060. The Mobile-Station-Not-Reachable-Flag (MNRF) handling is described in TS 23.040. When "Reachability for Data" is requested, the SCEF executes step 3 of 5.6.1.1. In addition, if provided, it includes Maximum Latency, Maximum Response Time, and Idle Status Indication.
-
The HSS executes step 4 of clause 5.6.1.1. In addition, it checks whether the Maximum Latency, if provided, is within the range defined by operator policies, and if acceptable, the HSS sets the subscribed periodic RAU/TAU timer using the value of Maximum Latency, if it is provided. If the requested timer value is not acceptable, the HSS rejects the request by executing step 8, and provides a Cause value indicating the reason for the failure condition to the SCEF. In addition, the HSS checks whether the Suggested number of downlink packets is within the range defined by operator policies. If it is not, then the HSS rejects the request by executing step 8, and provides a Cause value indicating the reason for failure condition to the SCEF.
If the Enhanced Multiple Event Monitoring feature is not supported and if the subscribed periodic RAU/TAU timer was previously set by a different Monitoring Request identified by a different SCEF Reference ID for the same UE then, depending on operator configuration, the HSS either performs step 8 to reject the Monitoring Request with an appropriate Cause or accepts the request. In the case that the HSS accepts this request, then it cancels the previously accepted Monitoring Request by including the SCEF Reference ID of that Monitoring Request in step 8. If the HSS supports Idle Status Indication, then it includes it in step 5.
For group based processing, if the previously accepted Monitoring Request is associated with a group of UEs and the HSS is not cancelling the previously accepted Monitoring Request for all UEs in the group, then the HSS provides the indicated UEs (External Identifier or MSISDN) as well as operation indication (cancellation or addition) to the SCEF in step 8.
If the Enhanced Multiple Event Monitoring feature is supported, and if the subscribed periodic RAU/TAU Timer, or Active Time, or Suggested number of downlink packets, or any combination were previously set by a different Monitoring Request or Network Parameter Configuration identified by a different SCEF Reference ID for the same UE, as long as the Maximum Latency (if received), and Maximum Response Time (if received) and Suggested number of downlink packets (if received) are within the range defined by operator policies, the HSS shall accept the request as follows:
- If the newly received Maximum Latency is lower than the provided subscribed periodic RAU/TAU timer, the HSS shall set the subscribed periodic RAU/TAU timer using the newly received Maximum Latency.
- If the newly received Maximum Response Time is higher than the provided subscribed Active Time (i.e. previously provided Maximum Response Time), the HSS shall set the subscribed Active Time using the newly received Maximum Response Time.
- If Suggested number of downlink packets is newly received, the HSS shall add the newly received value to the currently used value of Suggested number of downlink packets if the aggregated value is within the operator defined range. If the aggregated value is not within the operator defined range, the HSS shall set the subscribed Suggested number of downlink packets according to operator defined range.
-
The HSS executes step 5 of clause 5.6.1.1. In addition:
- if the Enhanced Multiple Event Monitoring feature is not supported and the HSS accepts new monitoring event configuration and cancel the existing monitoring event configuration, the HSS includes the subscribed periodic RAU/TAU timer (if modified), new received Maximum Response Time (if provided), new received Suggested number of downlink packets (if configured or provided), Idle Status Indication (if provided) and the SCEF Reference ID for Deletion of the cancelled monitoring event configuration and appropriate Cause. When HSS accepts new configured Monitoring Event for UEs in step 4 above, the HSS includes the subscribed periodic RAU/TAU timer (if modified), Maximum Response Time (if provided), Suggested number of downlink packets (if configured or provided) and Idle Status Indication (if provided). When HSS removes a previously configured Monitoring Event for UEs in step 4 above, the HSS also deletes the previously configured Monitoring Event in the MME/SGSN, if applicable.
- If the Enhanced Multiple Event Monitoring feature is supported, the HSS includes the subscribed periodic RAU/TAU timer (if modified), Maximum Response Time (if modified), Suggested number of downlink packets (if modified) and Idle Status Indication. the previously configured Monitoring Event in the MME/SGSN, if applicable.
- The MME/SGSN executes step 6 of clause 5.6.1.1 and starts watching for the UE entering connected mode. At every subsequent TAU/RAU procedure, the MME/SGSN applies the subscribed periodic RAU/TAU timer.
- Step 7 of clause 5.6.1.1 is executed.
- Step 8 of clause 5.6.1.1 is executed. The HSS may include the SCEF Reference ID of previously accepted Monitoring Request which needs to be cancelled and the cancellation cause. If the HSS, in step 4 above, decides to cancel Monitoring Event for indicated UEs (i.e. one individual UE or a sub-set of UEs) in the group of UEs for which there was a previously configured Monitoring Event, the HSS also includes the External Identifier or MSISDN of these indicated UEs towards the SCEF. If the HSS, in step 4 above, decides to add Monitoring Event for indicated UEs (i.e. one individual UE or a sub-set of UEs) in the group of UEs for which there was a previously configured Monitoring Event, the HSS includes the External Identifier or MSISDN of these indicated UEs towards the SCEF.
- Step 9 of clause 5.6.1.1 is executed. If SCEF Reference ID of previously configured Monitoring Event for cancellation is included in step 8, then the SCEF executes steps 2-5 of clause 5.6.9 using the associated TLTRI towards the associated SCS/AS.
5.6.1.5 Specific Parameters for Monitoring Event: Location Reporting p. 66
This monitoring event allows the SCS/AS to request either the Current Location or the Last Known Location of a UE. The supported Accuracy in the network may be at different levels, which are described in clause 4.9.2. Only One-time Reporting is supported for the Last Known Location. One-time and Continuous Location Reporting are supported for the Current Location. For Continuous Location Reporting, unless a Minimum Reporting Interval was provided, the serving node(s) sends a notification every time it becomes aware of a location change. The granularity depends on the accepted Accuracy.
Minimum Reporting Interval is an optional parameter that indicates a minimum time interval between Location Reporting notifications. If this parameter was provided to the MME/SGSN, when sending each Location Reporting notification, the MME/SGSN starts a timer which runs for the duration of Minimum Reporting Interval. While the timer is running the MME/SGSN suppresses sending Location Reporting notification(s). If at least one Location Reporting notification was suppressed while the timer was running, on expiry of the timer the MME/SGSN sends location information that was contained in the latest suppressed Location Reporting notification and restarts the timer. If the MME/SGSN is relocated, the source MME/SGSN shall transfer the current value of the timer to the target MME/SGSN. The target MME/SGSN shall start the timer with the transferred value, i.e. with the time remaining from the Minimum Reporting Interval.
Step 1.
The SCS/AS sets Monitoring Type to "Location Reporting", and adds Location Type, optionally Accuracy and optionally Minimum Reporting Interval prior to sending Monitoring Request to the SCEF as in step 1 of clause 5.6.1.1.
Location Type indicates whether the request is for Current Location or Last Known Location.
Step 2.
The SCEF executes step 2 of clause 5.6.1.1.
Step 3.
If Accuracy is included in step 1 then based on operator configuration the SCEF maps it to permissible granularity. If Accuracy is not included in step 1, the SCEF sets the granularity based on operator configuration. The SCEF adds Location Type, Accuracy and Minimum Reporting Interval (if included in step 1) prior to sending the Monitoring Request to the HSS as in step 3 of clause 5.6.1.1.
Step 4.
The HSS executes step 4 of clause 5.6.1.1.
Step 5.
Depending on the Location Type the HSS sets the "Current Location Request" (see TS 29.272), adds Accuracy and Minimum Reporting Interval (if included in step 3) prior to sending the Insert Subscriber Data Request to the MME/SGSN as in step 5 of clause 5.6.1.1.
Step 6.
The MME/SGSN executes step 6 of clause 5.6.1.1 and depending on the requested Accuracy invokes the appropriate procedures as defined in TS 23.401 or TS 23.060 for determining the location as requested. Unless it is a One-time request, the MME/SGSN starts watching for cell/RA/TA/eNodeB changes, depending on requested Accuracy.
If Minimum Reporting Interval is included in step 5, the MME/SGSN sends Location Reporting notifications with Minimum Reporting Interval option.
Step 7-9.
Steps 7-9 of clause 5.6.1.1 are executed and include the report of the current or last known location, depending on what was requested. Depending on operator configuration, the SCEF either maps the reported 3GPP system specific location information to the accepted Accuracy format or sends it as-is to the SCS/AS.
5.6.1.6 Specific Parameters for Monitoring Event: Change of IMSI-IMEI(SV) Association p. 67
Change of IMSI-IMEI(SV) indicates a change of the ME (IMEI(SV)) that uses a specific subscription (IMSI). It is based on the HSS being informed by the MME about the UE's IMEI(SV) according to the procedures defined in TS 23.401. The support of this Monitoring Event by the SGSN requires the support of the Automatic Device Detection (ADD) function/feature defined in TS 23.060.
Step 1.
The SCS/AS sets Monitoring Type to "Change of IMSI-IMEI(SV) Association", and adds Association Type prior to sending Monitoring Request to the SCEF as in step 1 of clause 5.6.1.1.
Association Type indicates whether change of IMEI or IMEISV to IMSI association shall be detected.
Step 2.
The SCEF executes step 2 of clause 5.6.1.1.
Step 3.
The SCEF adds Association Type prior to sending the Monitoring Request to the HSS as in step 3 of clause 5.6.1.1.
Step 4.
The HSS executes step 4 of clause 5.6.1.1.
Step 5-7.
Steps 5-7 of clause 5.6.1.1 shall not be executed for this Monitoring Event.
Step 8-9.
Steps 8-9 of clause 5.6.1.1 are executed.
5.6.1.7 Specific Parameters for Monitoring Event: Roaming Status p. 67
This monitoring event allows the SCS/AS to query the UE's current roaming status (the serving PLMN and/or whether the UE is in its HPLMN) and to get notified when that status changes. It is based on the HSS being informed of the UE's serving PLMN by the MME according to TS 23.401 and by the SGSN according to TS 23.060.
Step 1.
The SCS/AS sets Monitoring Type to "Roaming Status" prior to sending the Monitoring Request to the SCEF as in step 1 of clause 5.6.1.1. Optionally, it includes the "PLMN Information" parameter to request inclusion of the UE's Serving PLMN ID in the Monitoring Event Report.
Step 2.
The SCEF executes step 2 of clause 5.6.1.1.
Step 3.
The SCEF includes "PLMN Information", if sent in step 1, prior to sending Monitoring Request to the HSS as in step 3 of clause 5.6.1.1.
Step 4.
The HSS executes step 4 of clause 5.6.1.1.
Step 5-7.
Steps 5-7 of clause 5.6.1.1 shall not be executed for this Monitoring Event.
Step 8-9.
Steps 8-9 of clause 5.6.1.1 are executed. The Monitoring Event Report for this event is sent in the Monitoring Response message. The Monitoring Event Report indicates whether the UE is presently roaming or not as specified in clause 5.6.3.6. If PLMN Information was requested in step 1, and the operator policies allow, then the HSS includes for each Roaming Status in the Monitoring Event Report:
- the HPLMN PLMN-Id if the UE is in the HPLMN; or
- the Visited PLMN-Id (see TS 29.272) if the UE is in the VPLMN.
5.6.1.8 Specific Parameters for Monitoring Event: Communication failure p. 68
This monitoring event allows the SCS/AS to be notified of communication failure events, identified by RAN/NAS Release Cause codes per TS 23.401.
Step 1.
The SCS/AS sets Monitoring Type to "Communication Failure" prior to sending Monitoring Request to the SCEF as in step 1 of clause 5.6.1.1.
Step 2.
The SCEF executes step 2 of clause 5.6.1.1.
Step 3.
The SCEF executes step 3 of clause 5.6.1.1.
Step 4.
The HSS executes step 4 of clause 5.6.1.1.
Step 5.
The HSS executes step 5 of clause 5.6.1.1.
Step 6.
The MME/SGSN executes step 6 of clause 5.6.1.1 and starts watching for communication failure events.
Step 7-9.
Steps 7-9 of clause 5.6.1.1 are executed.
5.6.1.9 Specific Parameters for Monitoring Event: Availability after DDN Failure p. 68
This monitoring event allows the SCS/AS to be notified of availability of the UE after a DDN failure has occurred (see clause 5.7.1 Availability Notification after DDN Failure).
Step 1.
The SCS/AS sets Monitoring Type to "Availability after DDN Failure", and optionally Idle Status Indication prior to sending the Monitoring Request to the SCEF as in step 1 of clause 5.6.1.1.
Step 2.
The SCEF executes step 2 of clause 5.6.1.1.
Step 3.
The SCEF executes step 3 of clause 5.6.1.1 without adding Max Number of Reports, since the "Availability after DDN Failure" is an ongoing event that needs explicit deletion (see clause 5.6.1 for a description of Monitoring Event Deletion procedures) to cancel further reports.
Step 4-5.
Steps 4-5 of clause 5.6.1.1 are executed.
Step 6.
The MME/SGSN executes step 6 of clause 5.6.1.1 and starts watching for UE availability after DDN failure events.
Step 7-9.
Steps 7-9 of clause 5.6.1.1 are executed.
5.6.1.10 Specific Parameters for Monitoring Event: PDN Connectivity Status |R16| p. 68
This monitoring event allows the SCS/AS to be notified of the PDN Connectivity status when PDN Connections are created or deleted for the UE, and the existing PDN Connectivity status at the monitoring event configuration. The PDN Connectivity Status monitoring events report includes for each PDN Connection (that matches the requested APN if an APN has been specified) the IP address(es) allocated for the UE PDN connection(s), the PDN Types and optionally the APNs. This may be used by the SCS/AS to initiate communication with the UE, or to know when communication is no longer possible. Reporting is also done for PDN Connections using T6a/T6b connection towards the SCEF.
Step 1.
The SCS/AS sets Monitoring Type to "PDN Connectivity Status" and sends the Monitoring Request to the SCEF as in step 1 of clause 5.6.1.1.
Step 2.
The SCEF executes step 2 of clause 5.6.1.1.
Step 3.
The SCEF executes step 3 of clause 5.6.1.1. SCEF includes the APN for which the PDN Connectivity Status is to be monitored in the Monitoring Request to HSS. SCEF may also request PDN Connectivity Status for all PDN Connections regardless of APN (e.g. if APN is unknown in SCEF).
Step 4-5.
Steps 4-5 of clause 5.6.1.1 are executed. The HSS shall check if the SCS/AS is authorized to use the PDN Connectivity Status Monitoring Event and/or if operator policies allow the PDN Connectivity Status Monitoring Event usage for this subscriber (e.g. the subscription/UE is for CIoT). If an External Identifier was included in the authorization request, the HSS maps the external identifier to IMSI and/or MSISDN and updates the SCEF ID field of the PDN subscription context for the provided APN with the requesting SCEF's ID. Otherwise, if an External Group Identifier was included in the authorization request, the HSS authorizes the monitoring event configuration request for the received External Group Identifier, maps the External Group Identifier to a list of External Identifiers and maps the external identifiers to IMSIs and/or MSISDNs and updates the SCEF ID fields of the PDN subscription contexts for the provided APN with the requesting SCEF's ID. If the authorization check fails, then the HSS rejects the request by executing step 8, and provides a Cause value indicating the reason for failure condition to the SCEF.
Step 6.
The MME/SGSN executes step 6 of clause 5.6.1.1 and if PDN Connection(s) already exists (that matches the requested APN if an APN has been specified), the MME shall immediately send a PDN Connectivity Status event report for the existing PDN Connections. The MME/SGSN then starts watching for any further PDN Connectivity Status events.
Step 7-9.
Steps 7-9 of clause 5.6.1.1 are executed.